Electrons, waves and photons
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is current
the rate of flow of charge (Amperes- measured using an ammeter)
What is charge
a physical quantitiy (+/-) Measured in coulombs, 1 coloumb is defined as the flow of charge in a time of 1 sec
How can charge be carried
The current in metals is carried by electrons (there is a lattice of +ve ions surrounded by free electrons, the +ve ions are fixed in place, when a side of the metal is made +ve and the other -ve, the electrons are attracted to the +ve side and move through the metal as electrical current)
Liquids can conduct charge. These liquids are called electrolytes and are mostly ionic solutions (they contain +ve and -ve ions)
describe the direction of conventional current and electron flow
conventional current (rate of flow of charge from the +ve to the -ve terminal)
the electron flow is in the opposite direction to the convectional current
What is kirchoffs 1st law
Sum of current entering a junction = sum of current leaving a junction
(conservation of charge)
Describe the current in a series circuit
the current in a series circuit is the same at each point
Describe how charge relates to current and time (equation)
Q=charge (coulombs), I=current (amps), t=time (seconds)
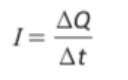
what does ‘e’ represent in electricity (& its units)
e is the elementary charge ( a proton has charge +e, an electron has charge -e)
units are coulombs
what is ‘mean drift velocity’
the average velocity of the charge carriers due to the applied electric field (it is an average as they are moving randomly in all directions, colliding frequently with positive metal ions)
What equation is used to calculate current, using mean drift velocity? (word & symbol equation with units)
I=nAve
I=current (amps), n=number density (n/a), A=cross sectional area (units²), v= mean drift velocity, e=elementary charge (coulombs)
Order conductors, semi conductors and insulators in order from highest number density to lowest (and give examples of each) :
highest- conductors (metal)
semi conductors (silicon and germanium)
lowest- insulators (plastic, wood, glass, rubber)
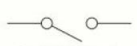
name this circuit symbol:
open switch

name this circuit symbol:
closed switch

name this circuit symbol:
cell
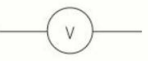
name this circuit symbol:
voltmeter
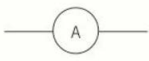
name this circuit symbol:
ammeter

name this circuit symbol:
thermistor
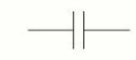
name this circuit symbol:
capacitor
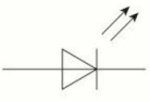
name this circuit symbol:
LED (light emitting diode)
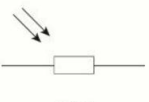
name this circuit symbol:
LDR (light dependent resistor)

name this circuit symbol:
resistor
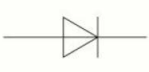
name this circuit symbol:
diode
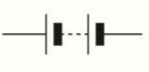
name this circuit symbol:
battery
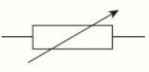
name this circuit symbol:
variable resistor
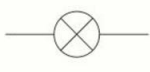
name this circuit symbol:
lamp

name this circuit symbol:
fuse
what is potential difference
the work done by each unit of charge; the difference in potential between two points in a circuit (measured in volts)
it describes when energy is transferred from electrical → another type
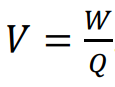
what is the electromotive force (e.m.f)
the work done to the charge carriers, when they gain energy as they pass through a cell or power supply.
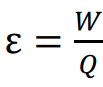
What is resistance?
how difficult it is for current to flow through an appliance
state ohms law, word and symbol equation
V=IxR
Ohm's law states the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided all physical conditions and temperatures remain constant.
what is meant by ‘an ohmic conductor’?
a conductor that obeys Ohm’s law
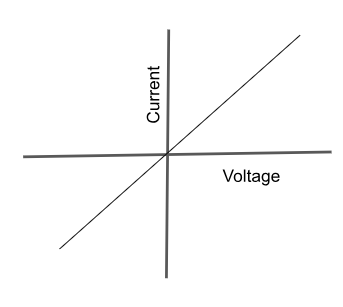
What does a current vs voltage graph look like for an ohmic conductor?
(the gradient passes throuhg the origin, it shows that voltage is directly proportional to current)
(gradient I/V=R)
What does a current vs voltage graph look like for filament lamp? & why does it look like this?
the flow of current causes collisions between the electrons and the metal lattice
these collisions increase temp, as temp increases, more collisions occur…
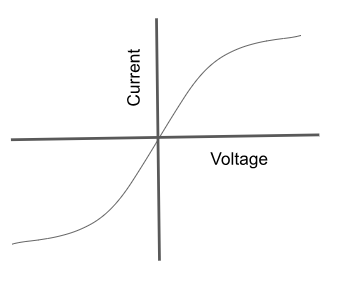
What does a current vs voltage graph look like for filament lamp? & why does it look like this?