Neurophysiology: Graded Potentials
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 11.4-.5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Neurophysiology
Neurons are excitable and irritable
stimulus=capable of altering RMP
If stimulus is strong enough, action potential is initiated
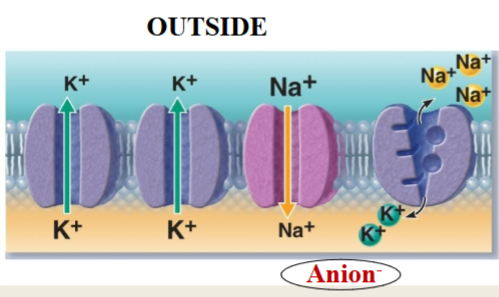
Resting Membrane Potential
Na+/K+ ATPase
More K+ leakage
Large anions inside
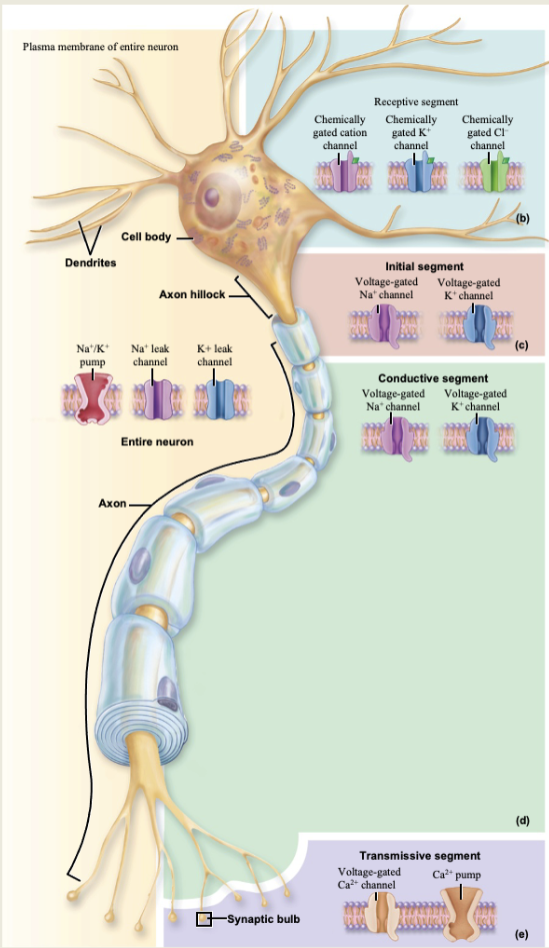
Membrane potential changes
Produced by changes in membrane permeability to ions
Membrane ion channels (leakage, chemically gated, voltage-gated, and mechanically-gated)
graded potentials and action potentials result
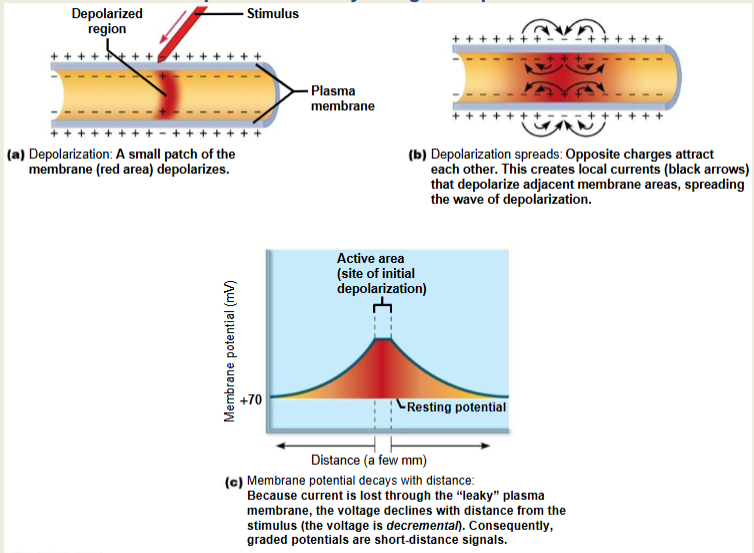
Graded Potentials
Short-lived, local changes in membrane potential due to a gated channel
dendrites, cell body locations
die out over distance
magnitude depends on strength of stimulus (how many ion channels are open/closed)
Graded potential types
Excitatory postsynaptic potential- EPSP
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential- IPSP
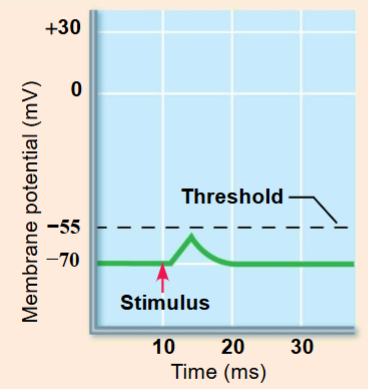
EPSP
Local depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
EPSPs bring the neuron closer to the AP threshold
Neurotransmitter binging opens chemically gated ion channels allowing Na+ and K+ to pass simultaneously (Na+ Influx > K+ efflux)
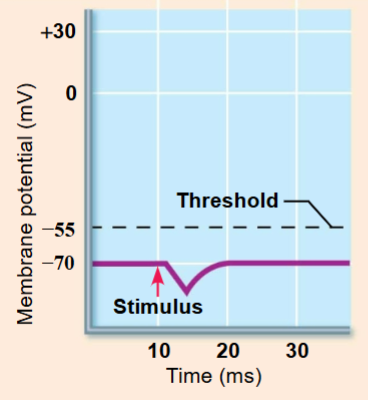
IPSP
Local hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
drive the neuron away from AP threshold
Neurotransmitter binding opens chemically gated ion channels permeable to either K+ OR Cl-
the spread and decay of graded potential
if at threshold value when it reaches axon hillock, an AP will be initiated and propagate down the length of the axon to the axon terminals (requires voltage-gated channels)
if too weak, the VG channels will not open