BIN300 W2: Linkage mapping: mapping the SNPs
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
multipoint linkage analysis
2^(n-1) linkage phases for n loci
2,3,4,5, SNPs → 2,4,8,16
need map function
translates Ɵ to distance
can estimate interference/coincidence
gene order has to be found by ML
n!/2 gene orders
Gene orders for 3 SNPs, A, B, C
ABC, ACB, BAC
not CBA, because is ABC read from right to left
Example 2 loci: ABC
sire genotype
A1B1C1/A2B2C2
Allele inherited by progeny
probability
observed numbersS
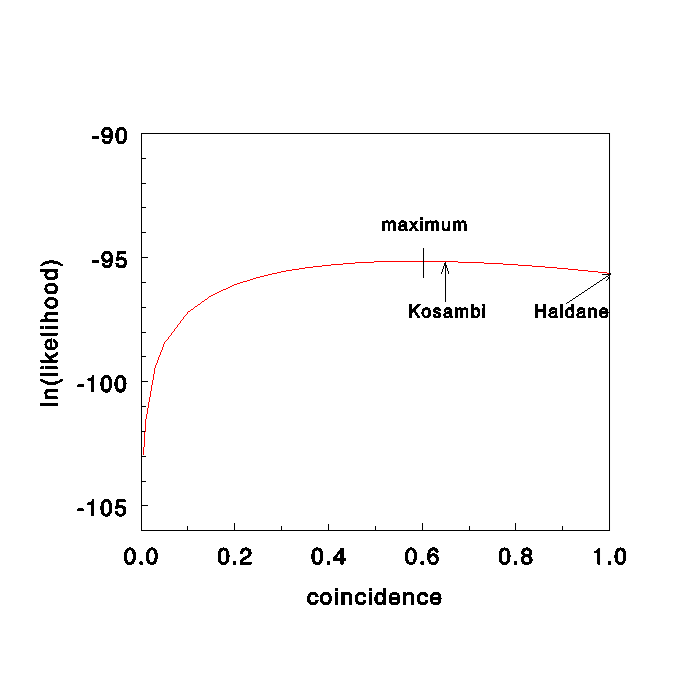
likelihood vs coincidence
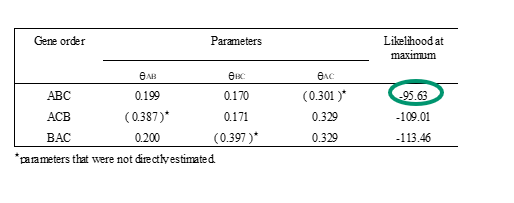
Alternative gene orders: 3 loci, ABC, ACB, CAB
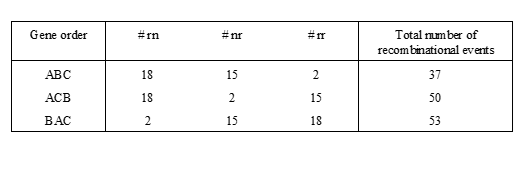
Alternative gene order: count number of recombinations
order many SNPs → marker map
complicated problem
n!/2 possible solutions (n=10 yields 2 mill)
computer cannot test all solutions
resemblance to travelling sales man problem
available computer algorithms: simulated annealling
closely linked SNPs
too little reocmbiantion to find (correct) order
need sequence data to order closely linked SNPs
asummes reference sequence is correct
linkage groups → chromosomes
marker mapping → linkage groups
linkage group = set of SNPs shown to be linked
within linkage group SNPs are ordered by mapping
linakge groups form into chromosomes
if suffiencient dense SNPs to connect all SNPs on chromosome
linkage mapping
detects SNPs in linkage gropu: ideally: map to chromosomes
determines order of SNPs: needs sequence data for fine-scale ordering
computationally difficult problem: many possible orders