Central Nervous System
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
The nervous system enables the body to respond to
continuous changes in its external and internal environment
CNS consists of
brain, spinal cord
Cerebellum
motor coordination
Brainstem
basic life functions (HR, breathing, etc)
Cerebrum
responsible for the integration of complex sensory and neural functions and the initiation and coordination of voluntary activity in the body
Gray Matter
outer covering or cortex
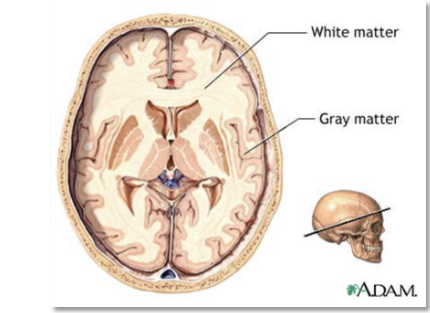
White Matter
inner core
contains only axons of nerve cells and the associated glial cells and blood vessels
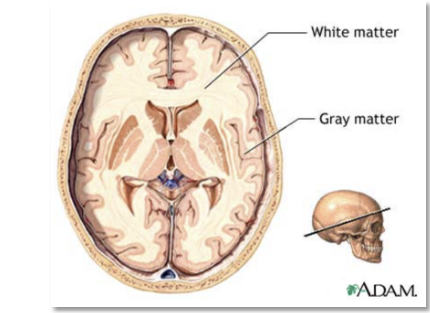
Cerebral cortex
outermost layer of the brain
contains nerve cell bodies, axons, dendrites
PNS consists of
peripheral nerves, ganglia
Planes of the Body
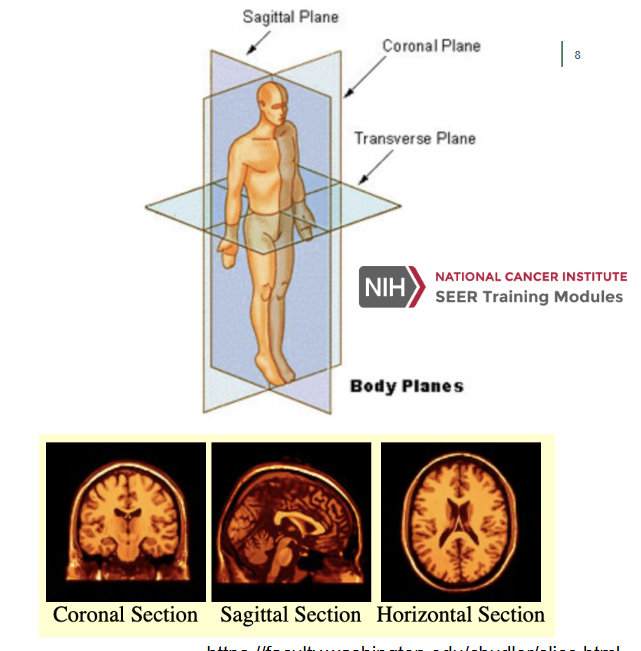
Coronal Plane (Frontal Plane)
A vertical plane running from side to side; divides the body or any of its parts into anterior and posterior portions
Sagittal Plane (Lateral Plane)
A vertical plane running from front to back; divides the body or any of its parts into right and left sides
Axial Plane (Transverse Plane)
A horizontal plane; divides the body or any of its parts into upper and lower parts
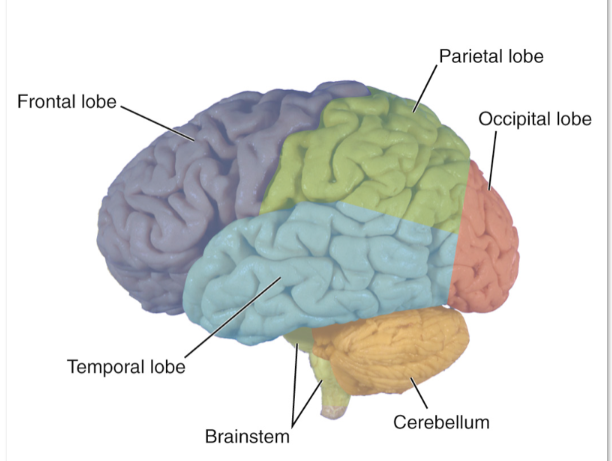
CNS Anatomy
Central sulcus divides
frontal and parietal lobes
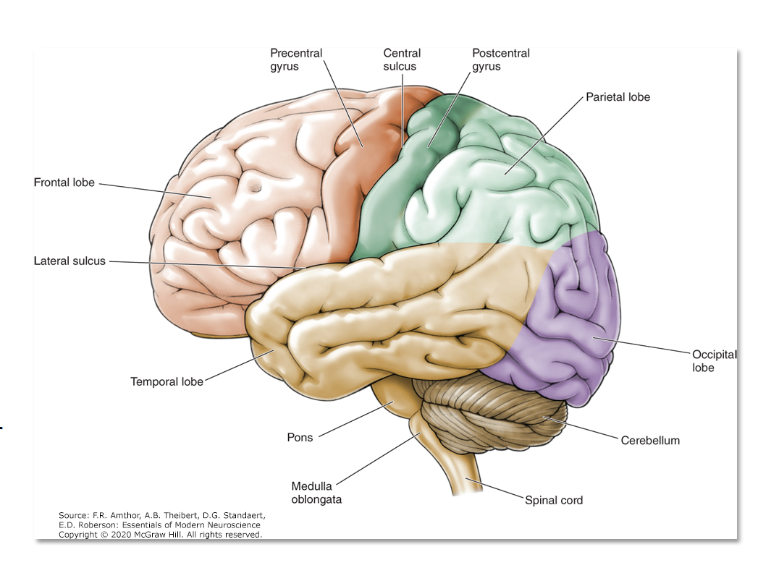
Precentral gyrus
motor cortex/ motor strip
Postcentral gyrus
sensory cortex/ sensory strip
Frontal Lobe
Planning, decision-making, problem-solving
Motor control: Voluntary movement via the motor cortex.
Speech production: Broca’s area (usually in the left hemisphere).
Personality and behavior: Emotional regulation, impulse control
Parietal Lobe
Sensory processing: Touch, temperature, pain, and proprioception.
Spatial awareness: Navigation and understanding spatial relationships.
Mathematical and analytical thinking
Temporal Lobe
Auditory processing: Hearing and interpreting sounds.
Language comprehension: Wernicke’s area (usually in the left hemisphere).
Memory formation: Especially in the hippocampus.
Emotional responses: Involvement of the amygdala
Occipital Lobe
Visual processing: Interpreting visual information like color, shape, and
motion
Telencephalon contains what?
Cerebral hemisphere and main lobes of cerebrum
• Limbic system
• Corpus striatum
• Olfactory Bulb
• Internal gray matter subcortical structures
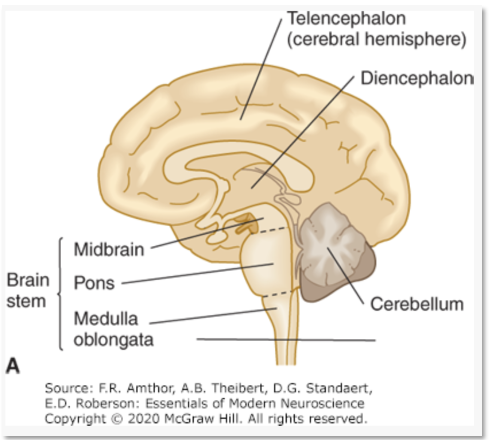
The Subcortical Structures contain…
Basal Ganglia
• Caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Dicephalon
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, pineal gland
Brain stem
midbrain, pons, medulla
Ventricles
cavities in the brain that produce and circulate CSF
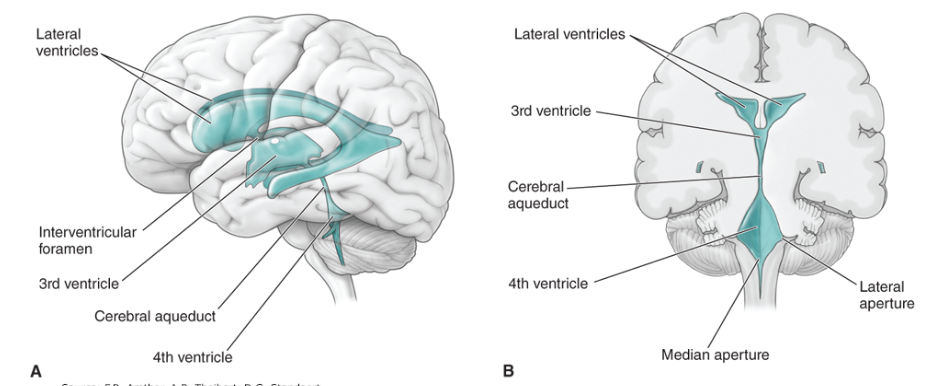
How many ventricles are there?
4 total:
• 2 lateral ventricles
• 3rd ventricle
• 4th ventricle
Spinal Cord Anatomy
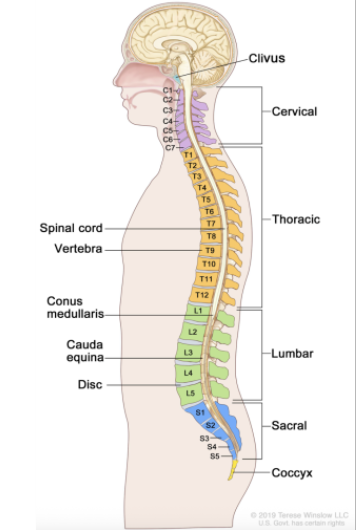
Spinal Cord Anatomy
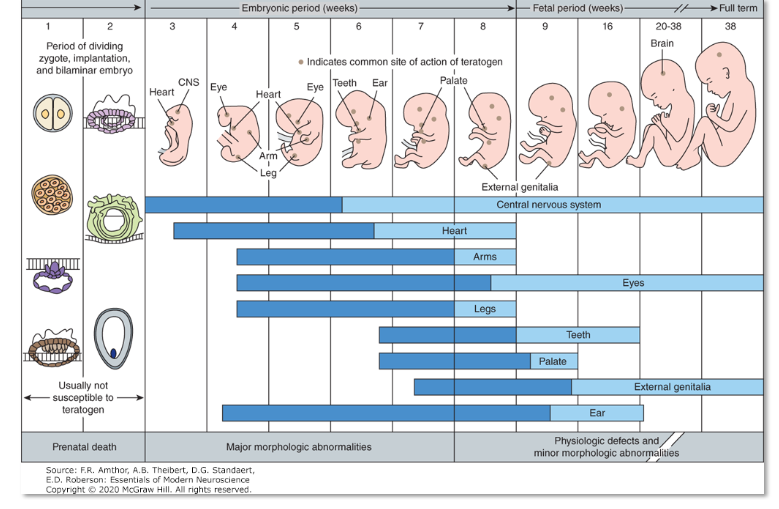
CNS Development
During the first 2 weeks of development, the embryo is typically
not susceptible to
teratogens
**Dark blue denote highly sensitive stages; light blue denote stages that
are less sensitive to teratogens
Teratogens
A substance either damages all or most of the cells of the embryo, resulting in its death, or it damages only a few cells, allowing the embryo to recover without developing defects
The neural plate folds during neurulation to form the
neural tube and neural crest
Four Stages of Development
A. Early in embryogenesis three germ cell layers—the
ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm—lie close
together.
B. The neural plate buckles at its midline to form the
neural groove and elevates the neural folds.
C. Closure of the dorsal neural folds forms the neural
tube, which gives rise to the CNS.
D. The neural tube lies over the notochord and is
flanked by somites, an ovoid group of mesodermal cells
that give rise to muscle and cartilage.
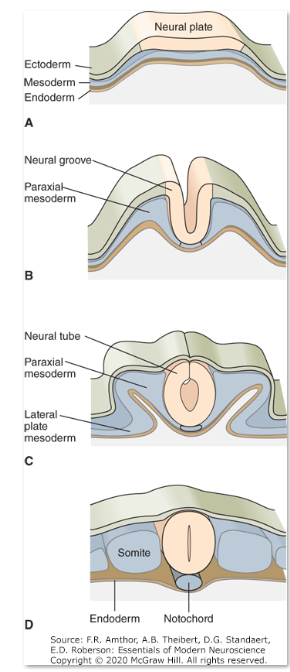
Ectoderm
nervous system, epidermis (skin)
Endoderm
internal organs (GI tract, lungs, other internal organs)
Mesoderm
muscles, bone, cartilage
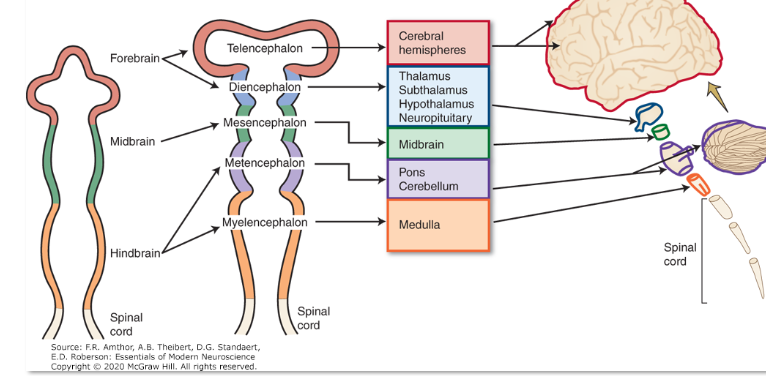
Early development of the neural tube produces the three primary vesicles called the
forebrain (prosencephalon), midbrain (metencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
Differentiation of each of the five vesicles produced the major
brain structures
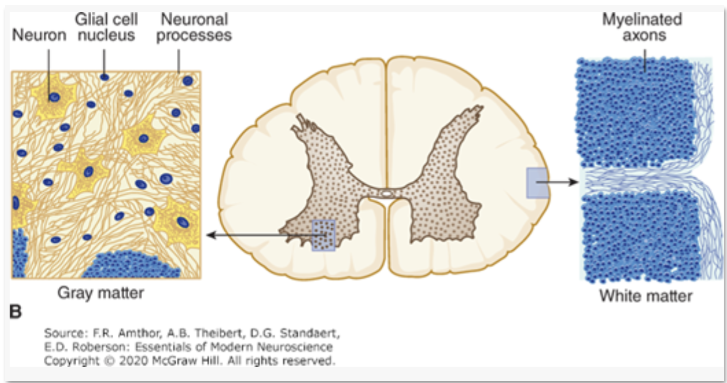
Nerve tissues consists of two types of cells
neurons and supporting cells (glial)
Supporting structures
meninges, blood-brain-barrier
Neuron is the ____ ___ of the nervous system
functional unit
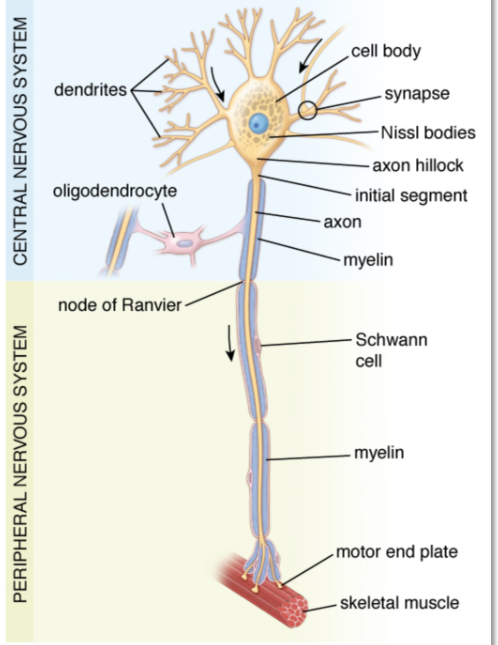
Cell body
contains the nucleus and several processes of varying length
Nerve cells are specialized to
receive stimuli from other cells and to conduct electrical impulses to other parts of the system via their processes
Specialized contacts exist between neurons to provide
transmission of information from one neuron to the next are called synapses
Gray Matter Cells
Neuropil
meshwork of axonal, dendritic, and glial processes associated with the gray matter
The organization of the neuropil is not demonstrable in
H&E stained sections; cell type specific markers and immunostaining to visualize cell types
The inner core of the entire brain is called the
parenchyma
The parenchyma is the
function part of the brain and it does not include the outer coverings (meninges) of the brain
Brain Histology
Mostly the nuclei of glial cells are seen in routine histologic preparations of the CNS
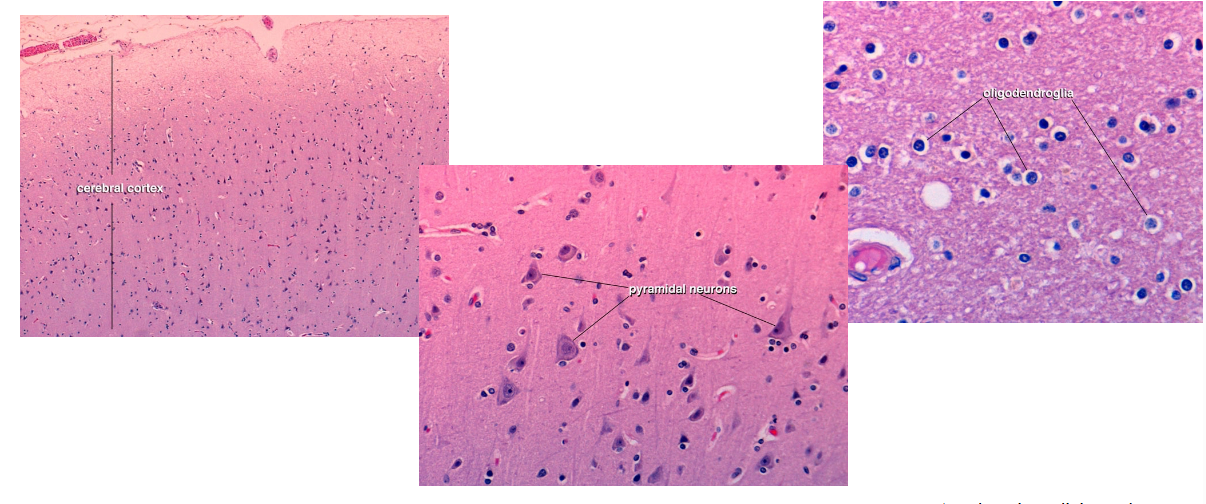
Glia Cells
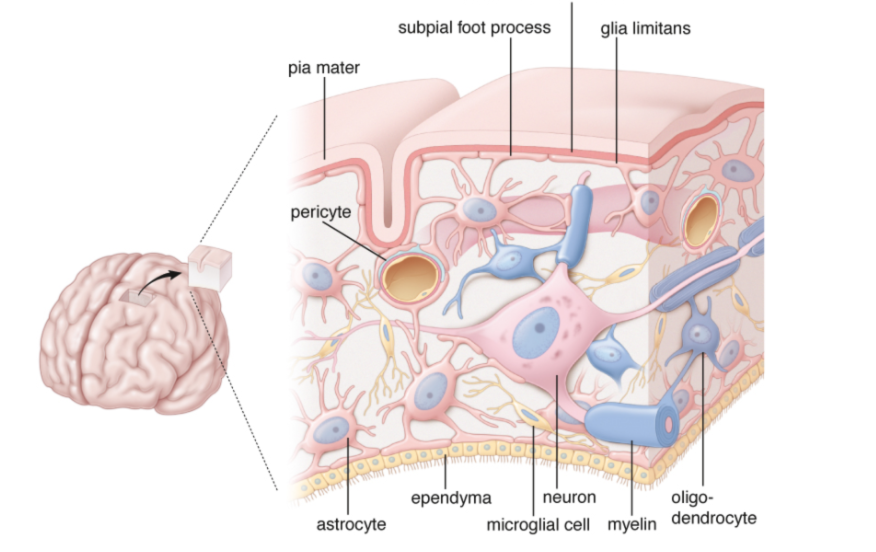
Astrocytes
morphologically heterogeneous cells that provide physical and
metabolic support for neurons of the CNS
Oligodendrocytes
are small cells that are active in the formation and
maintenance of myelin in the CNS
Microglia
are resident immune cells with small, dark, elongated nuclei that possess phagocytotic properties
Ependymal cells
are columnar cells that line the ventricles of the brain and the
central canal of the spinal cord
Meninges
three sequential connective tissue membranes cover the brain and spinal cord
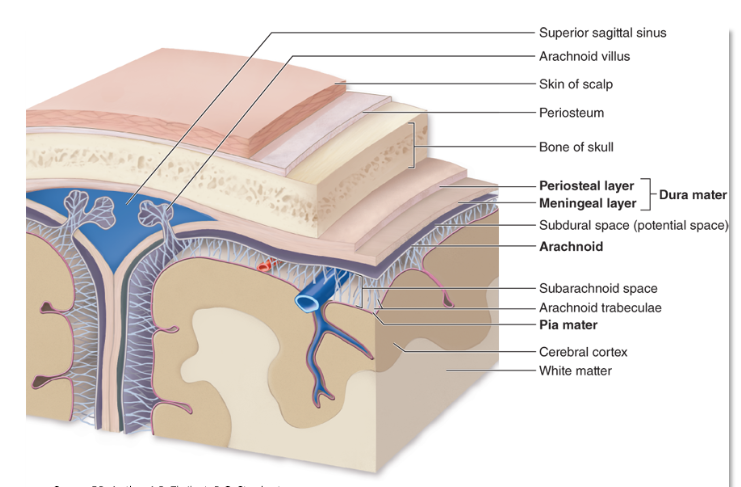
Dura Mater
the outermost thickest and toughest layer (“tough mother”)
Arachnoid layer
lies beneath the dura; Contains CSF cushion
Pia Mater
delicate layer resting directly on the surface of the brain and spinal cord (“tender mother”)
Blood Brain Barrier protects the CNS from
fluctuating levels of electrolytes, hormones, and tissue metabolites circulating in the blood vessels
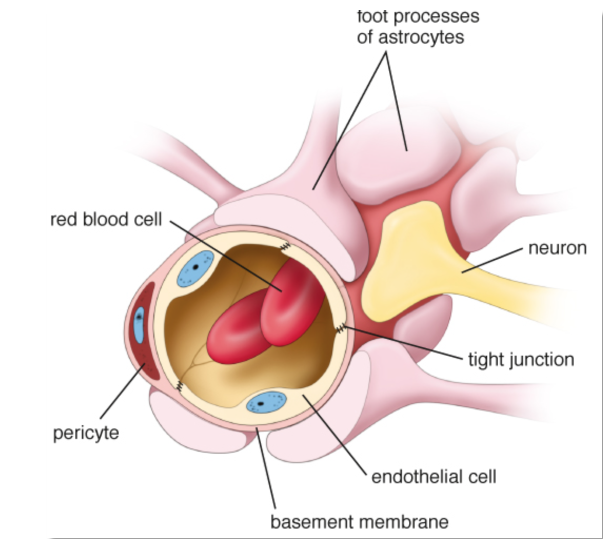
The barrier is created mostly by the ___ ___ between the ___ ___.
tight junctions between the endothelial cells
The tight junctions between the endothelial cells forms
continuous-type capillaries, pericyte (smooth muscle cell) and
association of astrocytes and their end foot processes
with the endothelial basal lamina
tight junctions eliminate gaps between
endothelial cells and prevent simple diffusion of solutes and fluid into the neural tissue