Public Goods, Public Choice, and Income Distribution
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What are the two main characteristics of pure public goods?
Non-rival and non-excludable.
What does it mean for a good to be non-rival?
More than one person can consume the good or service at the same time, resulting in a marginal cost of an additional user being zero.
What does it mean for a good to be non-excludable?
It is impossible to keep others from deriving benefits from the public good or service.
What are impure public goods also known as?
Club goods.
What distinguishes club goods from pure public goods?
Club goods have public characteristics but can exclude customers to some degree due to crowding.
What is the efficient provision condition for private goods?
Marginal Benefit (MB) equals Marginal Cost (MC).
How do individuals value public goods differently?
Individuals consume the same amount of a public good but may value it differently, as seen in national defense.
What is the efficient provision condition for public goods?
Social Marginal Benefit (SMB) equals Marginal Cost (MC).
How does the government decide to produce a public good?
If the willingness to pay of all individuals in the community exceeds the marginal cost of producing the public good.
What is the free-rider problem?
Individuals may enjoy the benefits of a public good without contributing to its cost.
What is the median voter theorem in public choice?
Under certain conditions, the outcome of majority voting reflects the preferences of the median voter.
What are government bureaus?
U.S. agencies financed by appropriations from Congress, with taxpayers as the 'owners'.
What are the bureaucratic objectives of government bureaus?
To serve the public and maximize their budget.
What is the difference between direct democracy and representative democracy?
Direct democracy involves citizens voting on specific issues, while representative democracy involves citizens electing representatives to make decisions on their behalf.
What is the income distribution by quintiles in the U.S. as of 1970 for the poorest 20%?
4.1% of total income.
What percentage of income did the richest 20% of the population receive in 1970?
43.3% of total income.
What does the Lorenz curve represent?
It graphically represents the size of income distribution, showing the percentage of total income received by any given percentage of households.
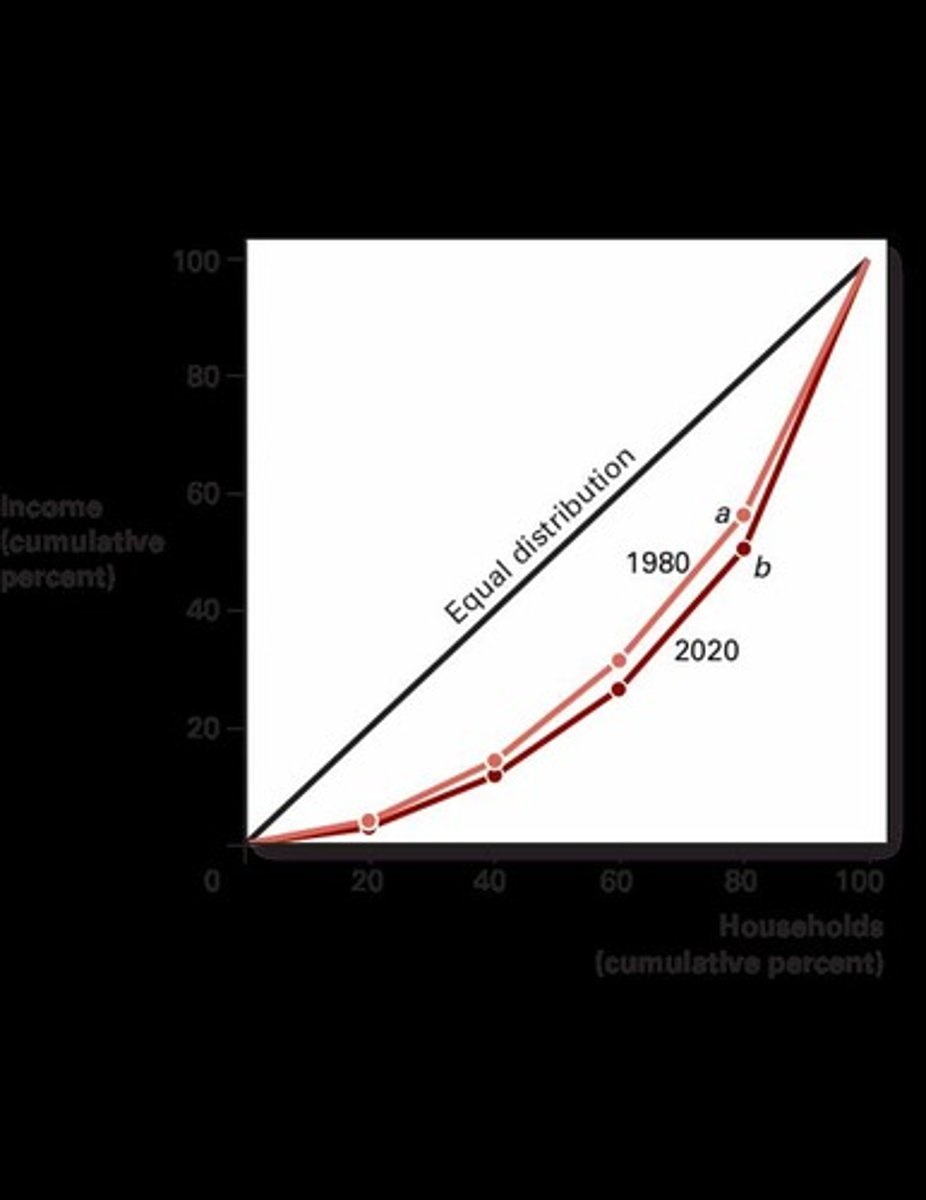
What does a straight line on the Lorenz curve indicate?
Perfect income equality.
What systemic problems can contribute to income differences?
Unequal education opportunities and discrimination.
What is the official U.S. poverty level for a family of four in 2005?
$19,971.
What is considered 'deep poverty' according to the U.S. Census Bureau?
Living in a household with total cash income below 50% of the poverty threshold.
What are some examples of social insurance programs?
Social Security, Medicare, unemployment insurance, and workers' compensation.
What is the purpose of means-tested welfare programs?
To provide assistance only to individuals with incomes below a certain level.
What is the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) program?
A welfare program enacted in 1996 that replaced Aid to Families with Dependent Children (AFDC) and emphasizes work participation.
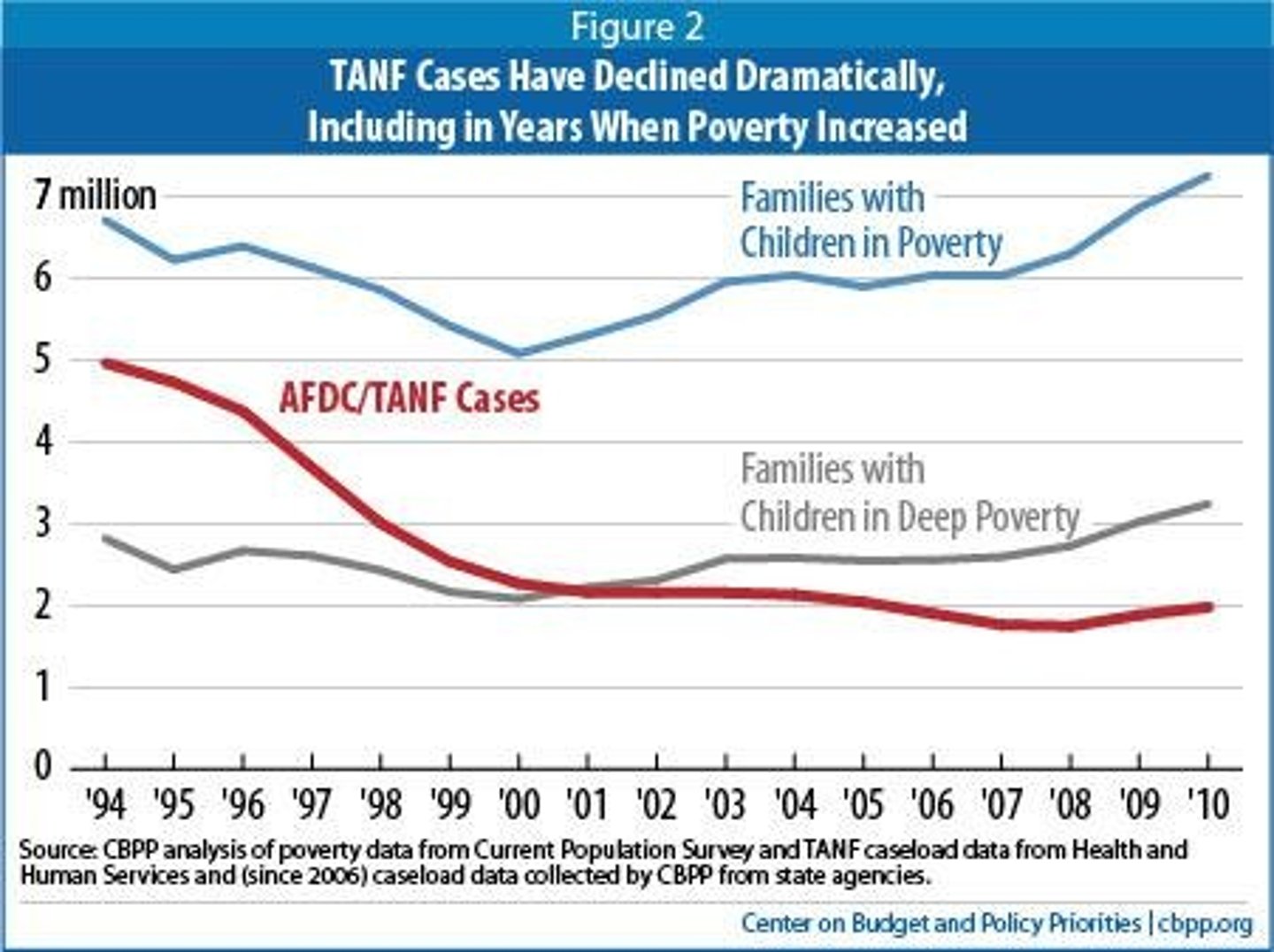
What is the 'feminization of poverty'?
The increasing proportion of the poor who are women, often due to factors like single-parent households.
What is the significance of the growth in spending for Social Security and Medicare?
It has contributed to a decline in poverty among the elderly.
What are some in-kind transfer programs?
Medicaid, SNAP benefits (food stamps), housing assistance, and support for daycare.