TOPIC #4: Action Potentials
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what is AP
transient all or none reversal of the memb pot produced by a regnerative [self reinforcing, utilzing + feedback, autocatalyzing] inward current in excitable membs
what are the 2 major functions of AP
*spikes or "impusles"
1. rapid transmission of info over long distances in nerve & muscle fibers
2. control of effector responses (muscle contraction or release of neurotransmitters)
what is spike transduction
translation of neural activity from a graded amplitude code to a spike freq code
what is a spike freq
1/interval btwn spikes ("interspike interval")
- as you further increase amount of depolarizing current --> fairly linear region where direct correlation of spike freq & amount of depolarization
what is an absolute refractory period
period after an action potential during which a stimulus can't elicit a 2nd AP
- length of absolute refractory period limits the max spike freq
What is the relative refractory period?
period after an AP during which the threshold for initiation of 2nd AP is increased
you can get a 2nd AP but requires depolarization
what is a propagated w/out amplitude decrement
amplitude of AP does not decline w/ distance, unlike an electronic (passive potential)
what is the venus fly trap mech & what does it result in
calcium mediated action potential very slow
what did bernstein suggest about ionic basis of the AP
all ionic "gates" open up during an AP ("breakdown" of memb resistance)
- if true, Em should go to 0 mV during an AP
what did the famous figure of cole & curtis show
showed that memb impedance decreased (conductance increased) during an AP in squid giant axon
consistent w/ bernsteins memb breakdown hypthesis
what did cole & curtis use for the experiment
used a 20 kHz oscillating current across axon memb w/ wheatstone bridge circuit to monitor memb impedence during an AP
what did cole & curtis widening of the trace indicate
indicates decreased memb impedance (resitance) or increased conductance
- memb became more electrically "leaky" during AP
what did hodgkin & huxley & cole & curtis showed
using same squid giant axon prepartion
- showed that membrane potential actually goes positve [reverse polarity] during AP, which is not consistent w/ Bernsteins memb "breakdown" hypothesis
1st intracellular recordings of AP's
what was the sodium hypothesis
Ap depends on the presence of extracellular Na+ ions
- Hodgkin showed that when extracellular Na+ ions were gradually replaced w/ choline, a + ion that can't cross memb, amplitude of Ap recorded in squid giant axon decreased proportionally
- provided evidence that during AP, there is selective & transitent increase in memb permeability to Na+ ions
what happened in the sodium hypothesis when they decreased external sodium
very dramatic reduction of amplitude of spike & little change of AP
what was richard D keynes able to produce
able to produce a # of ions per cm of axon that cross memb during Ap both influx & efflux
why does permeability changes occur
bc of opening of voltage gated Na+ channels in memb that allow Na+ to move down its [ ] gradient into cell
what happens in sodium hypothesis
- depolarization opens Na+ channels , causing rising phase [depolarization] of the AP
- falling phase (repolarization) of the AP is caused by inactivation of Na+ channels & opening of voltage gated K+ channels
how did they test the sodium hypothesis
- necessary to vary Em systematically & measure resulting changes in conductance through Na+ & K+ channels
- as soon as you depolarize the memb enough to open Na+ channels , that leads to further depolarization of memb & a full blow AP
what does the feedback amplifier generate
generates a current that is directly proportional to difference btwn measured memb pot & command pot
what happens when a cell is voltage clamped
voltaged gated ion channels are able to open or close in response to imposed change in Em, but voltgae clamp prevents resulting ionic currents from altering Em
what did the voltage clamp recordings from the squid giant axon reveal
2 d iff voltage gated ion currents
- an early inward current
- a late outward current
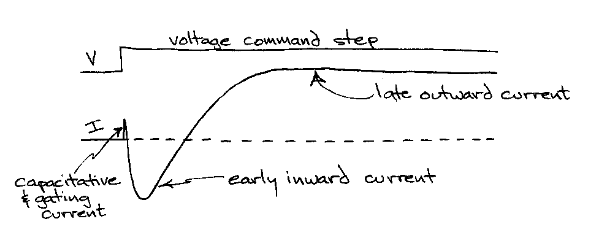
why does a constant voltage matter
- only part of any clamp current is going through ion channels , other part is charging the capacitor
- ion channels can change their conductance & current flow through them on millsec timescale
- if clamp pot rises slowly, then during changing voltage you can't sort out what is capactive current & what is ionic current