FNR 24150 Herps Exam 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
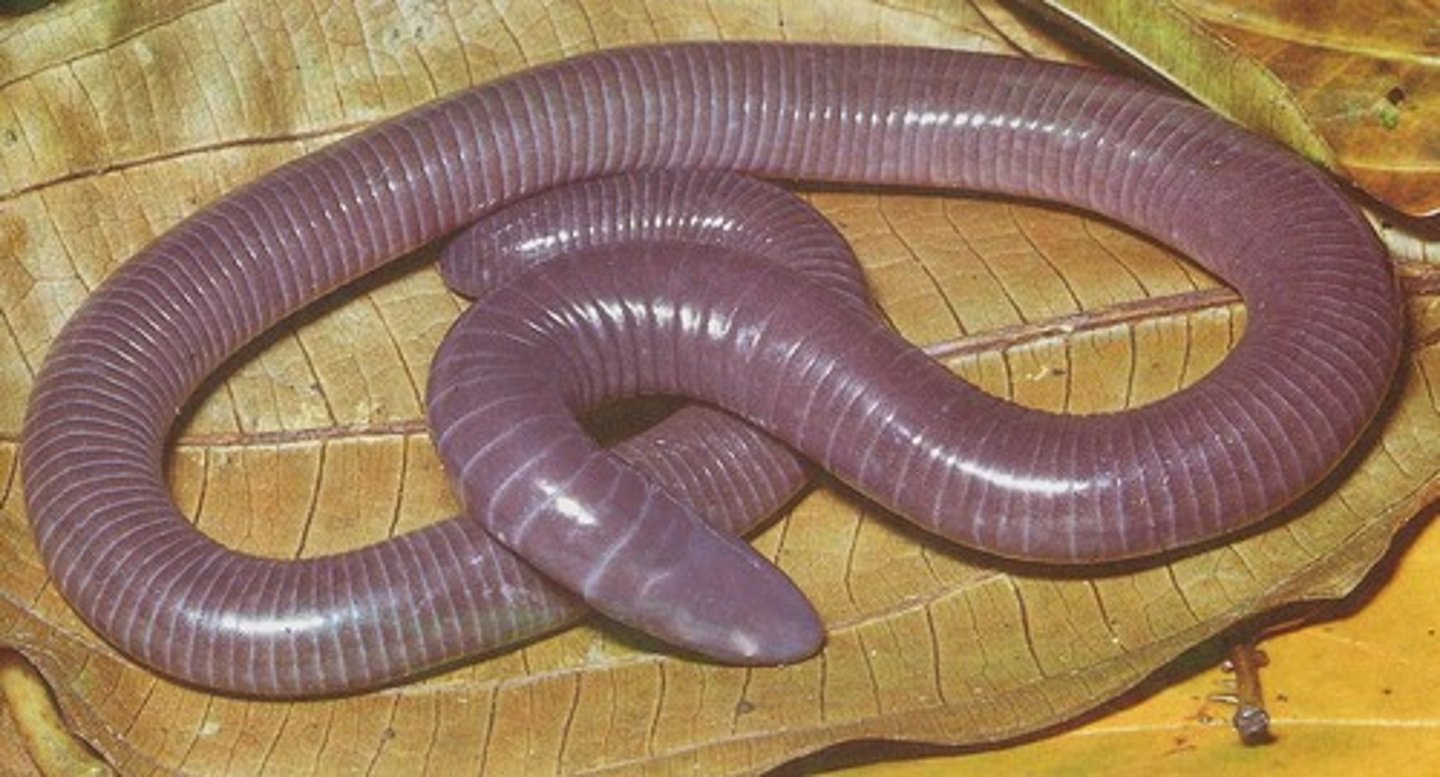
Gymnophiona
Caecilians
- Burrowing lifestyle, some fully aquatic
- Annulated and has wedge shaped skull
- Vestigial eyes, acute olfactory system
- Internal fertilization, all reproductive stages present
- Retractable sensory tentacles, special feeding mechanism

Caudata
Salamanders
- Mostly northern hemisphere (cooler habitats)
- 10 recognized families, 68 genera, ~800 species
- Smooth skin and long cylindrical bodies
- Short limbs, some no hind limbs
- Costal grooves
- Five toes on hind limbs, four toes on front limb
- Some aquatic, terrestrial, fossorial, or even arboreal
- Nocturnal/crepuscular
- Fossorial and secretive
- Mostly internal fertilization (except two families)
- Carnivorous

Sirenidae
Sirens
-External fertilization (predicted, but unconfirmed)
- Most primitive (No hind limbs, fully aquatic, paedomorphic)
- Lives in swamps, and even roadside ditches
- Aestivation: Mucous membrane to prevent drying out
Mostly nocturnal
- Hard to observe, Eastern North America

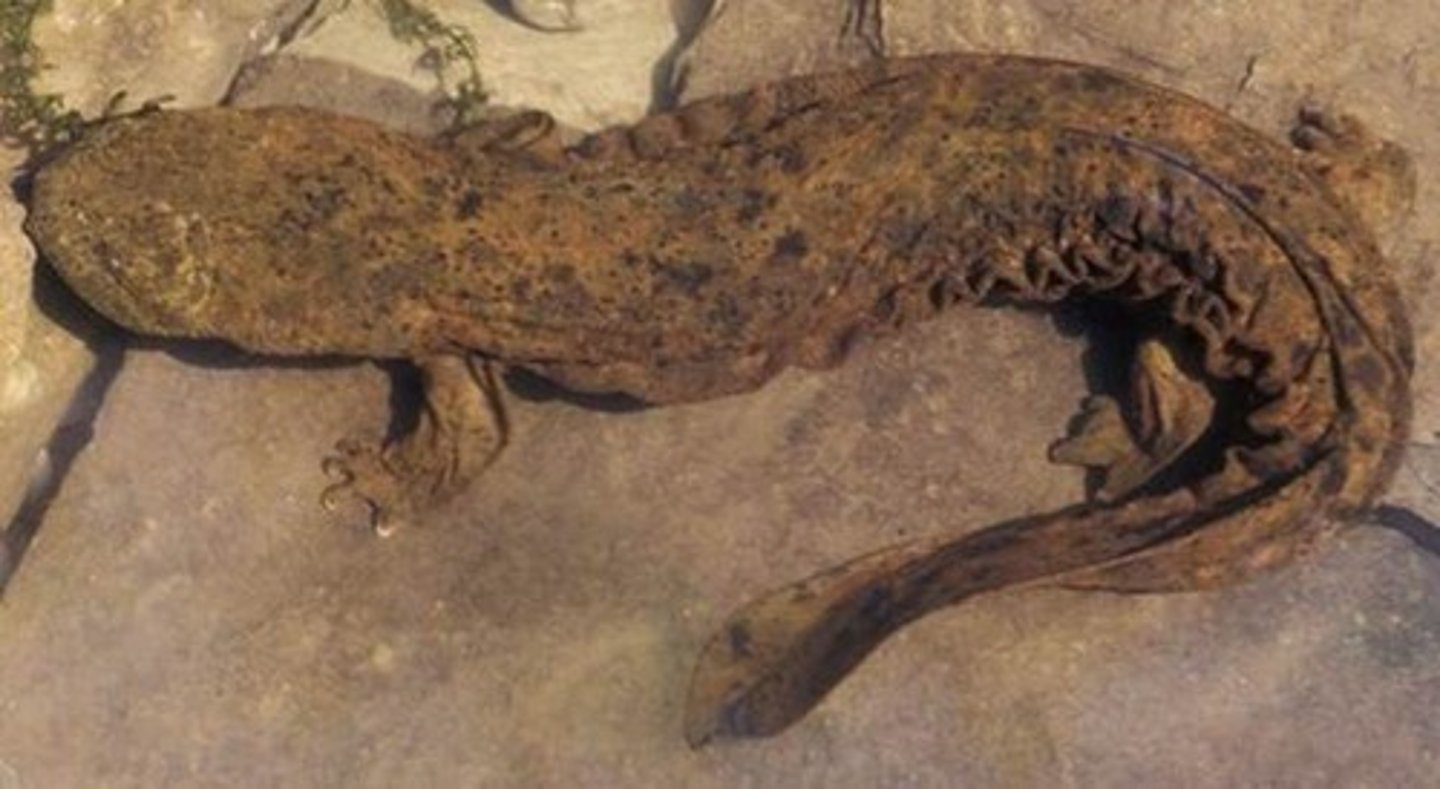
Cryptobranchidae
Hellbenders and Giant Salamanders
- External fertilization
- Long lives and older maturity age (7 years)
- Paedomorphic
- Lateral skin folds for cutaneous respiration
- Really small, mostly non-functional lungs
- Live in cold, fast flowing streams and hide under rocks
- Males super territorial of nests under rocks
- Females come to nest and lay eggs, males externally fertilize them

Plethodontidae
Lungless salamanders
- Largest group
- Nasolabial groove
-No lungs, just cutaneous respiration
-No gills, dependent on moist environments
- Prominent costal grooves
- Most are terrestrial, some fully aquatic or arboreal
- Diverse reproductive modes (aquatic larvae with metamorphosis, egg hatching into miniature adults with no external gills, etc.)
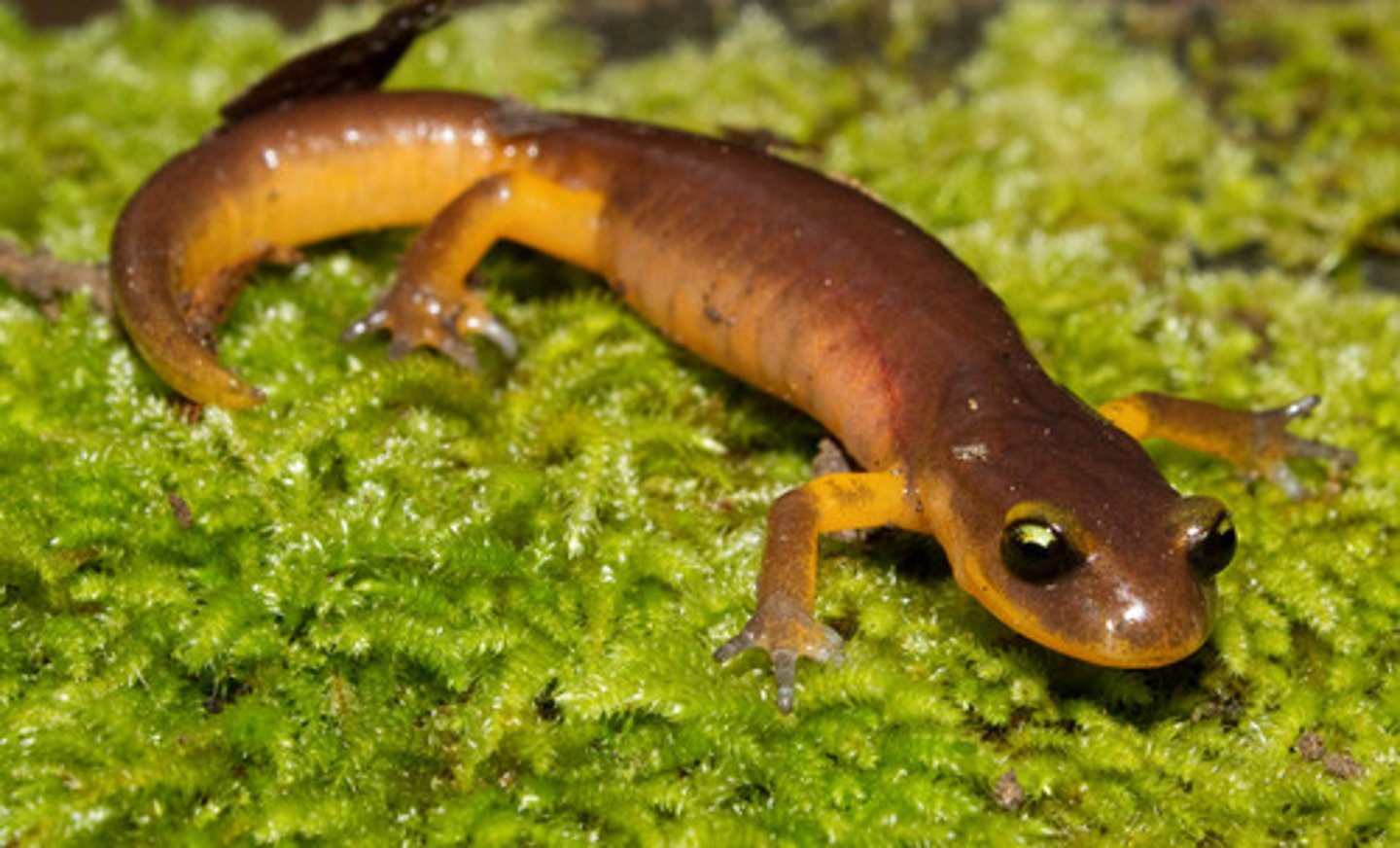

Proteidae
Mudpuppies
- Deep, clear lakes
- Have hindlimbs unlike sirens
- Paedomorphic, fully aquatic
- Internal fertilization, eggs attached to roof of burrow
- Unclear whether intentionally defended by female, but eggs protected by her presence
- Conservation concern because of water quality
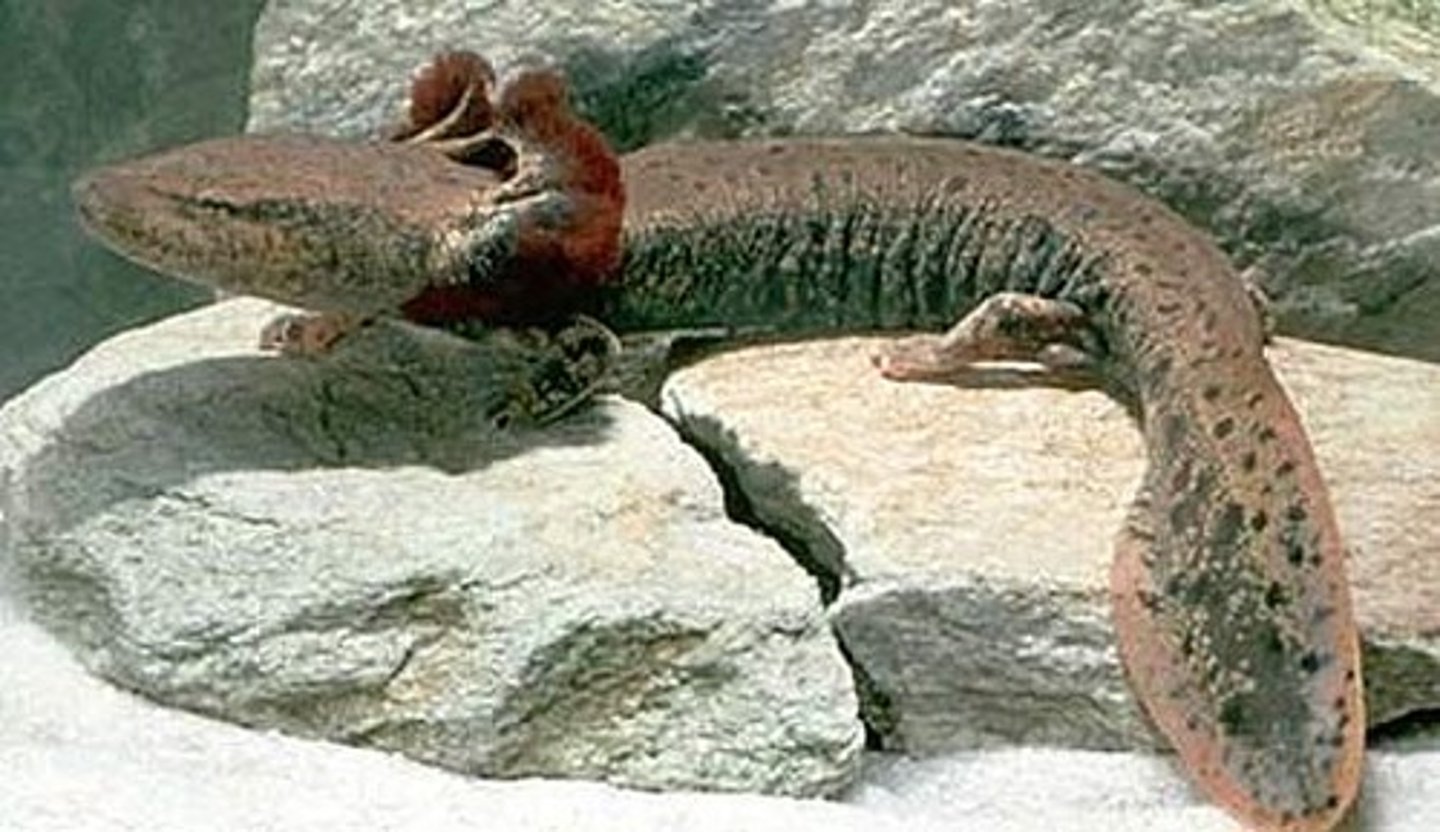

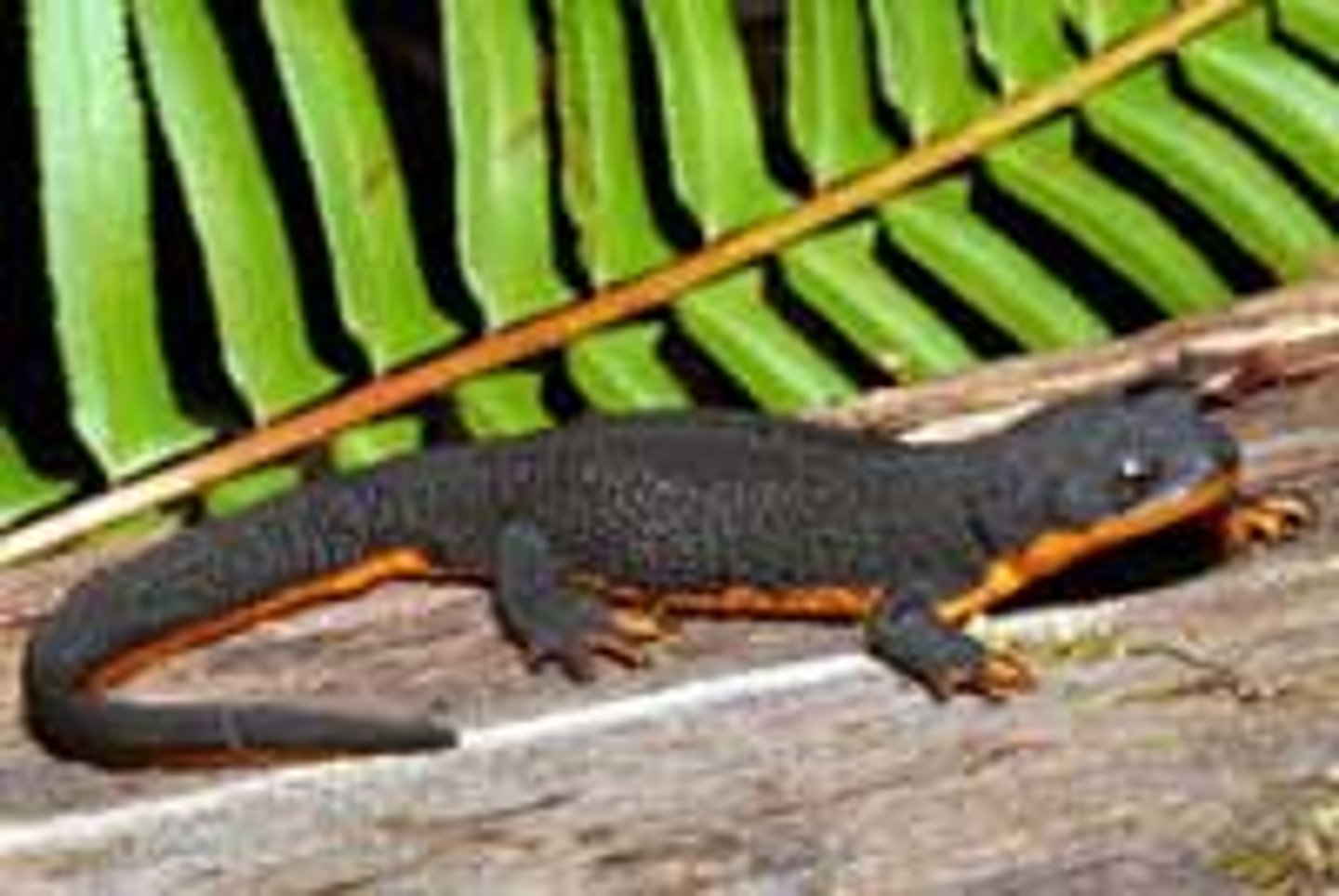
Salamandridae
True Salamanders and Newts
- Relatively small
- Lack gills and gill slits usually, present fuctional lungs
- Internal fertilization
Thick granular skin, numerous poison glandsm aposematic coloration
- Courtship displays, internal fertilization
- Carnivorous

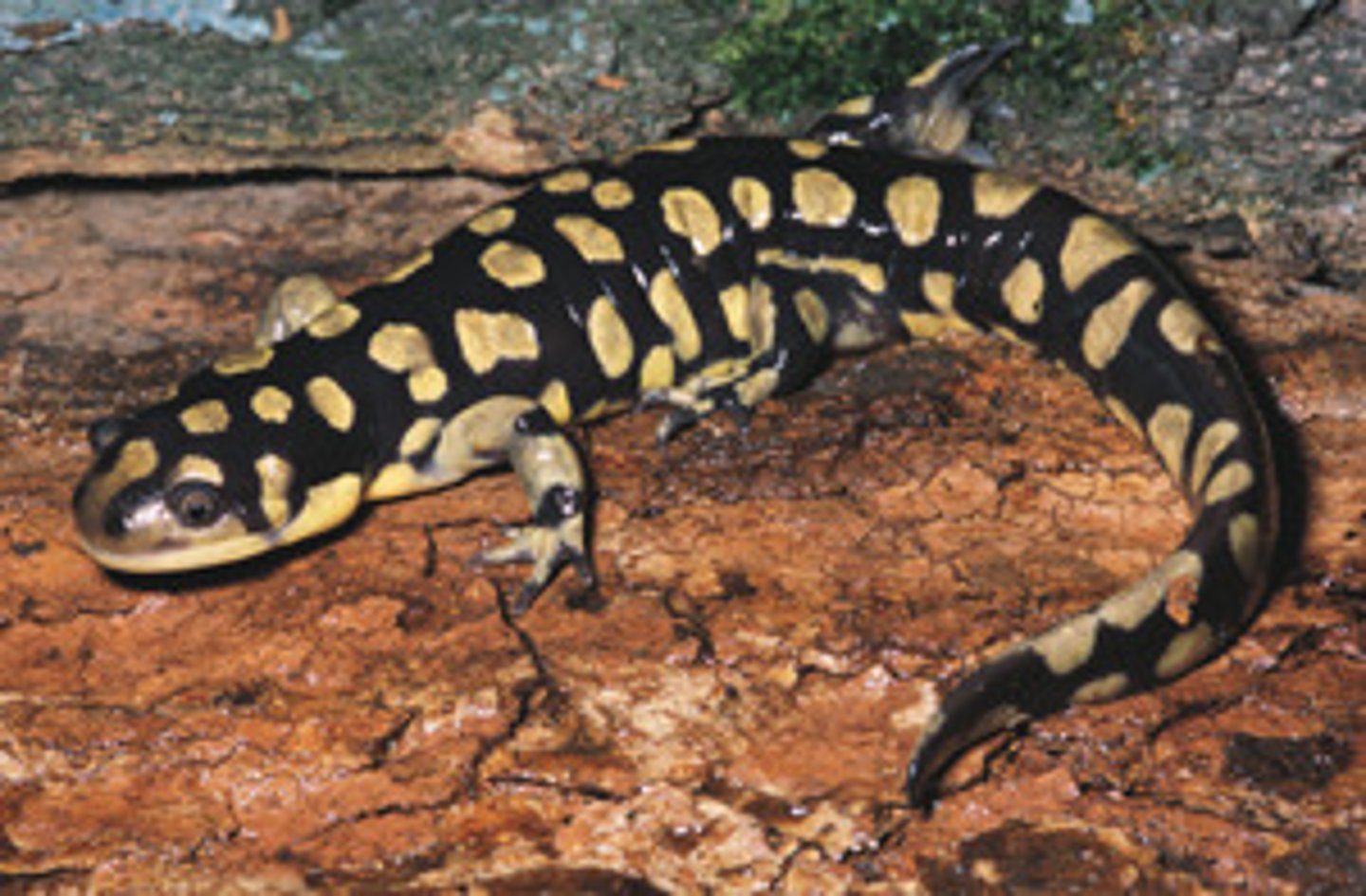
Ambystomatidae
Mole Salamanders
- Fossorial
- Stout bodies, thick limbs and tails, short blunt heads
- Costal grooves
- Adults terrestrial, lay eggs in water and they metamorphose
- Tiger salamanders can be neotenic (axolotl part of tiger salamanders)
- Some dont lay eggs in water (lay on land and wait for water inundation)
- Aggregate or explosive breeders (First warm, strong rain, males first then females, males lay spermatophores)

Anura
Frogs and toads
- Most diverse amphibians (57 families, 468 genera, ~7700 genera)
- Moist tropics mostly, large global distribution, cannot adapt to salt water
- Dorsolateral folds in some frogs
- Cranial crests and parotid glands in some toads
- Tympanum size
Size or presence of toad pads
- Movement strategy (jumping/hopping, walking, climbing, fully aquatic swimmers)
- Vocalizations (advertisement, aggresive, courtship, release, alarm or defense)
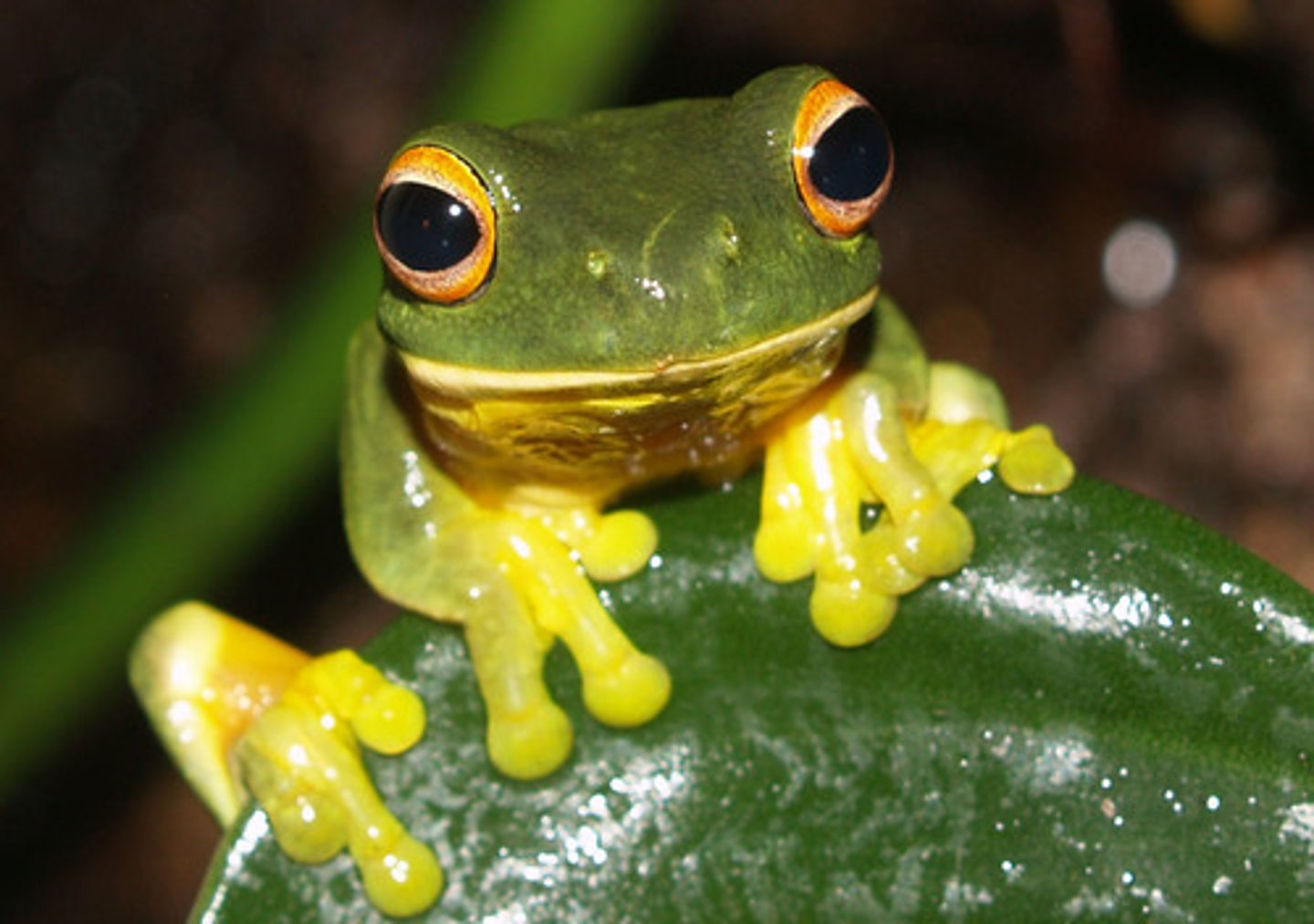

Leiopelmatidae
Tailed Frogs and New Zealand Frogs
- Five species of tailed frogs
- Tail-like structure for copulation ("tail" is actually highly vascularized extension of cloaca)

Scaphiopodidae
Spadefoot toads

Hylidae
Tree frogs

Centrolenidae
Glass Frogs
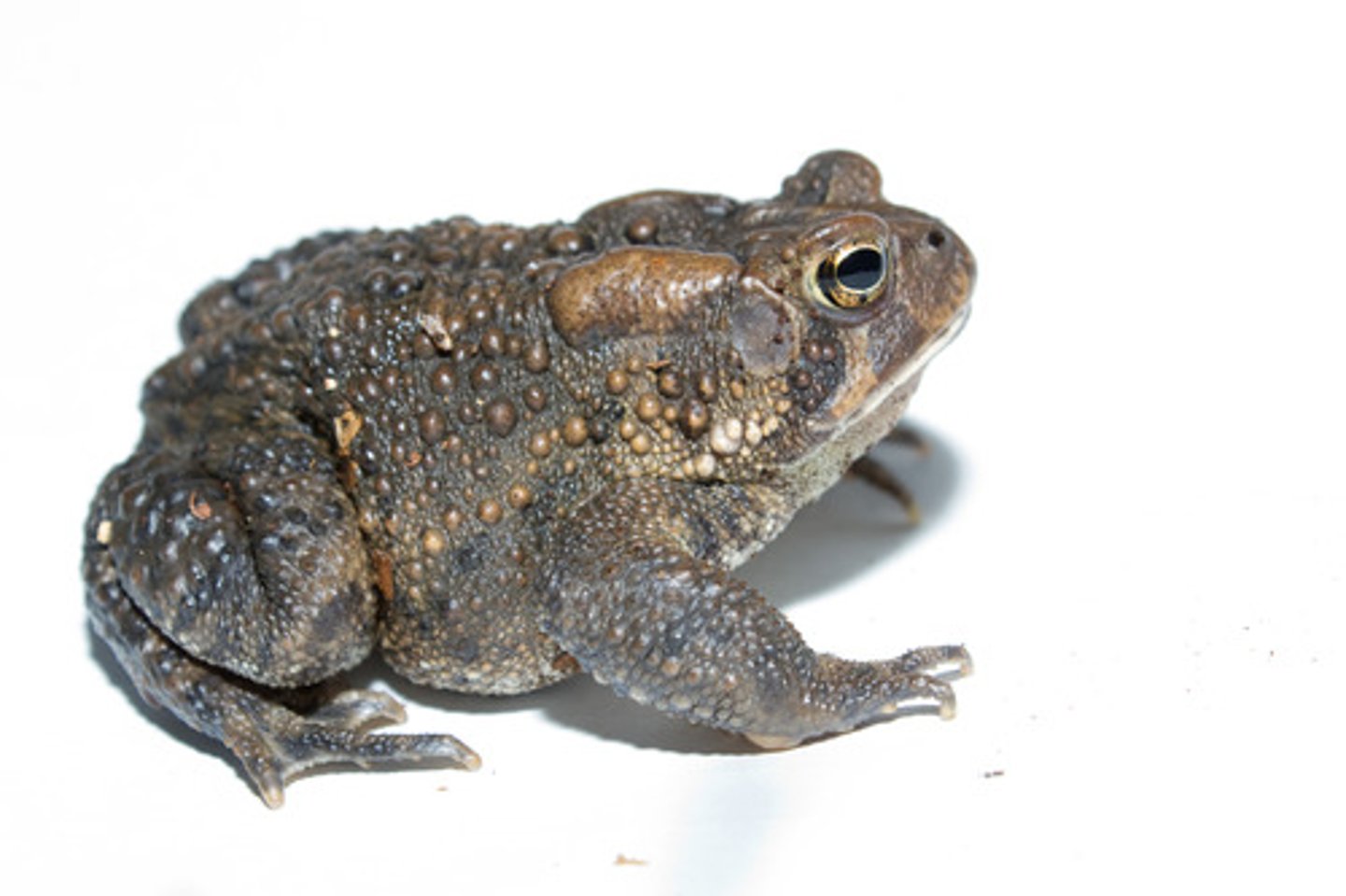
Bufonidae
True toads

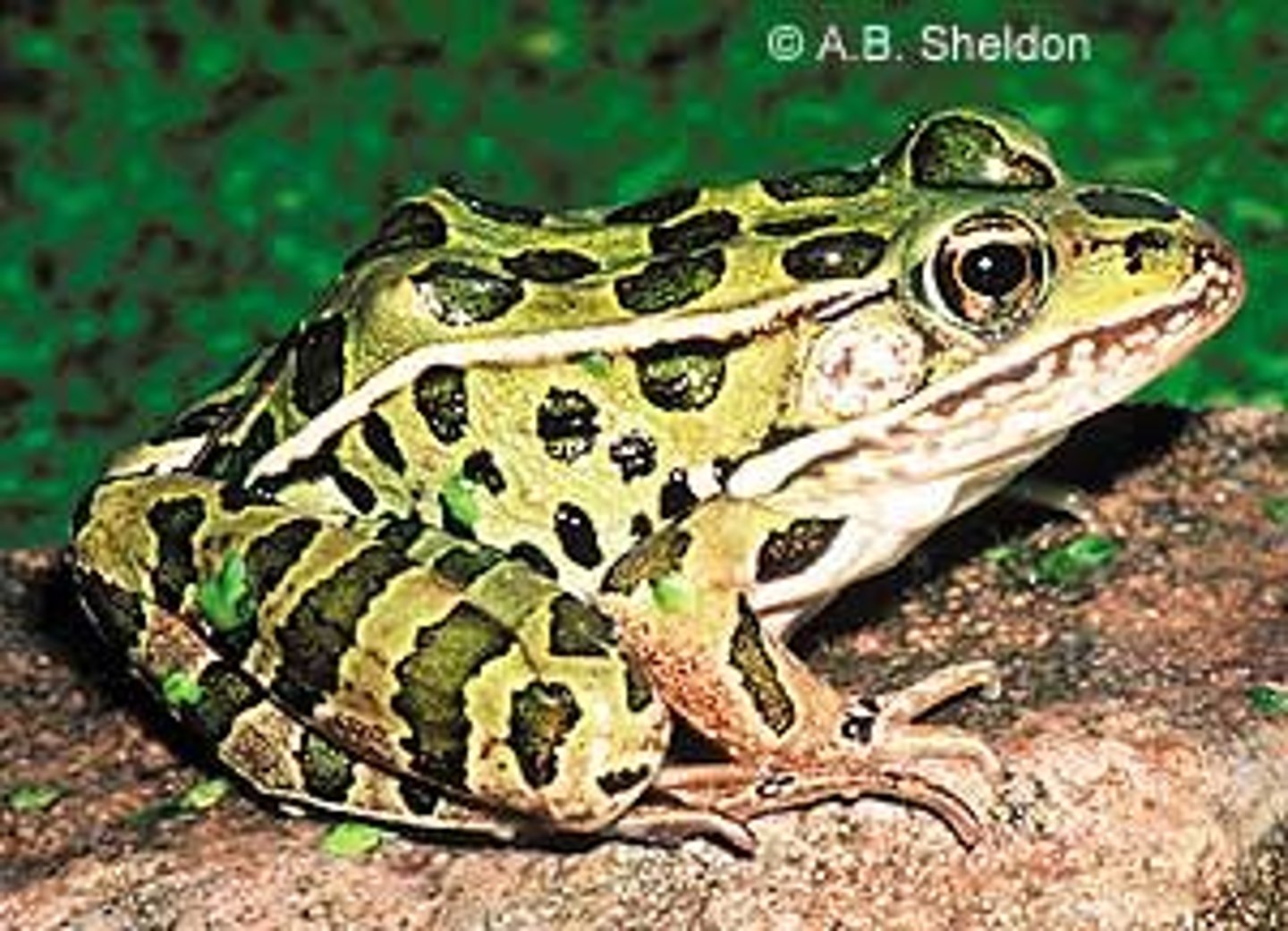
Ranidae
True Frogs

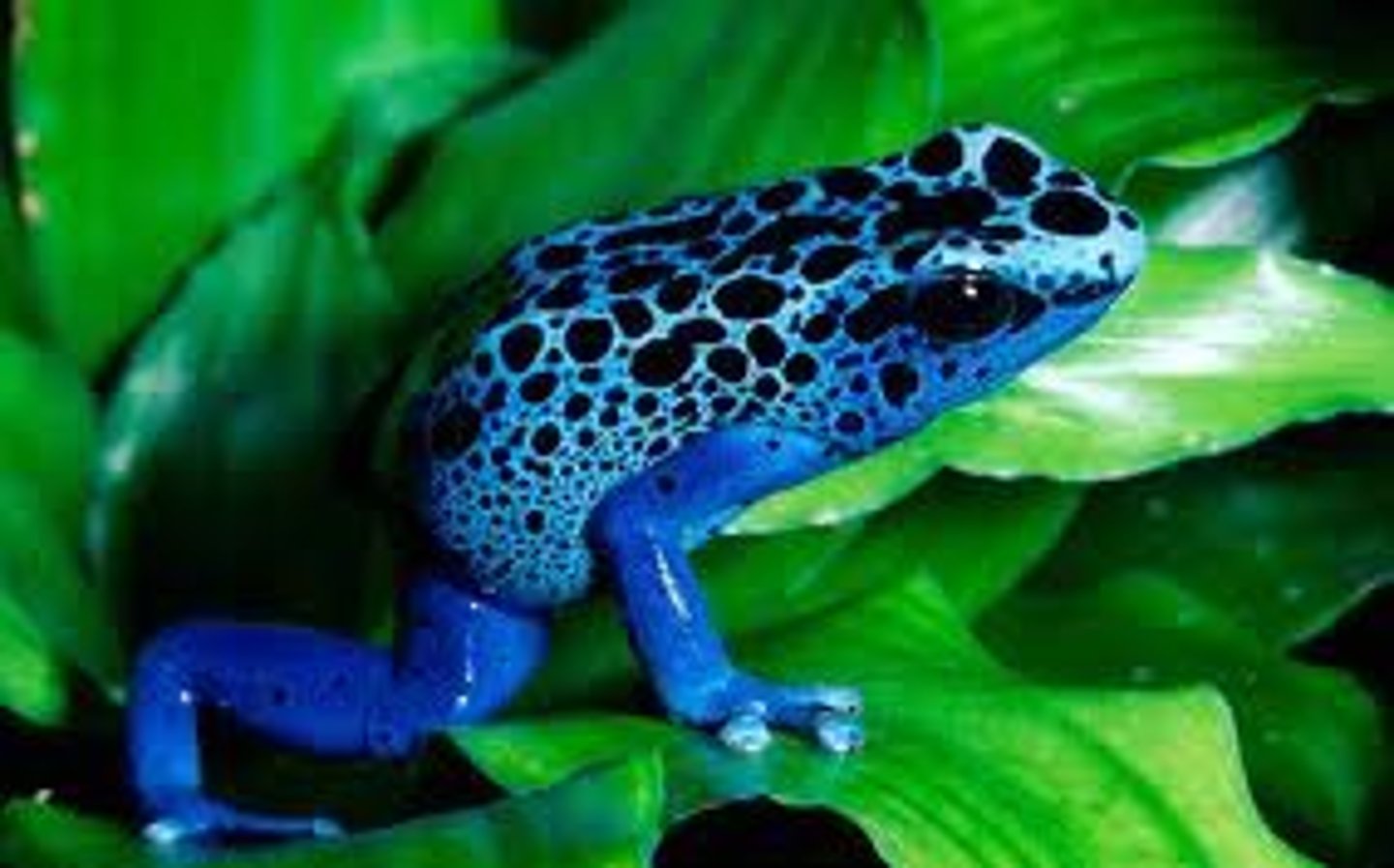
Dendrobatidae
Poison dart frogs

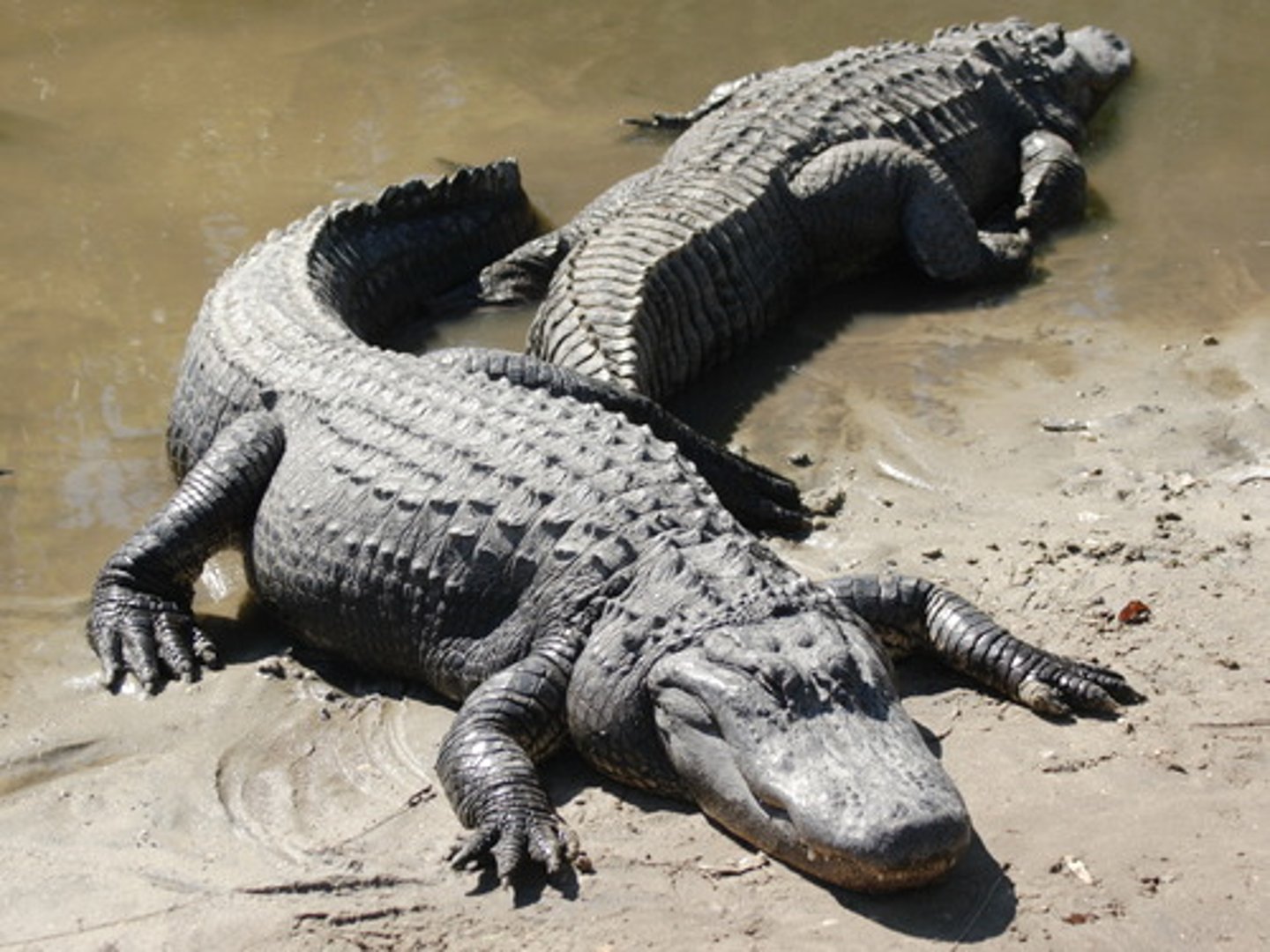
Crocodilia
Crocodiles and alligators
- Only remaining archosaurs
- 150 recognized species
- Armored, thick plated skin
- Largest living reptile
- Elongated head, string tooth jaws, short and strong limbs
- Nests on land (amniotic egg)
- Temperature-dependent sex characteristics

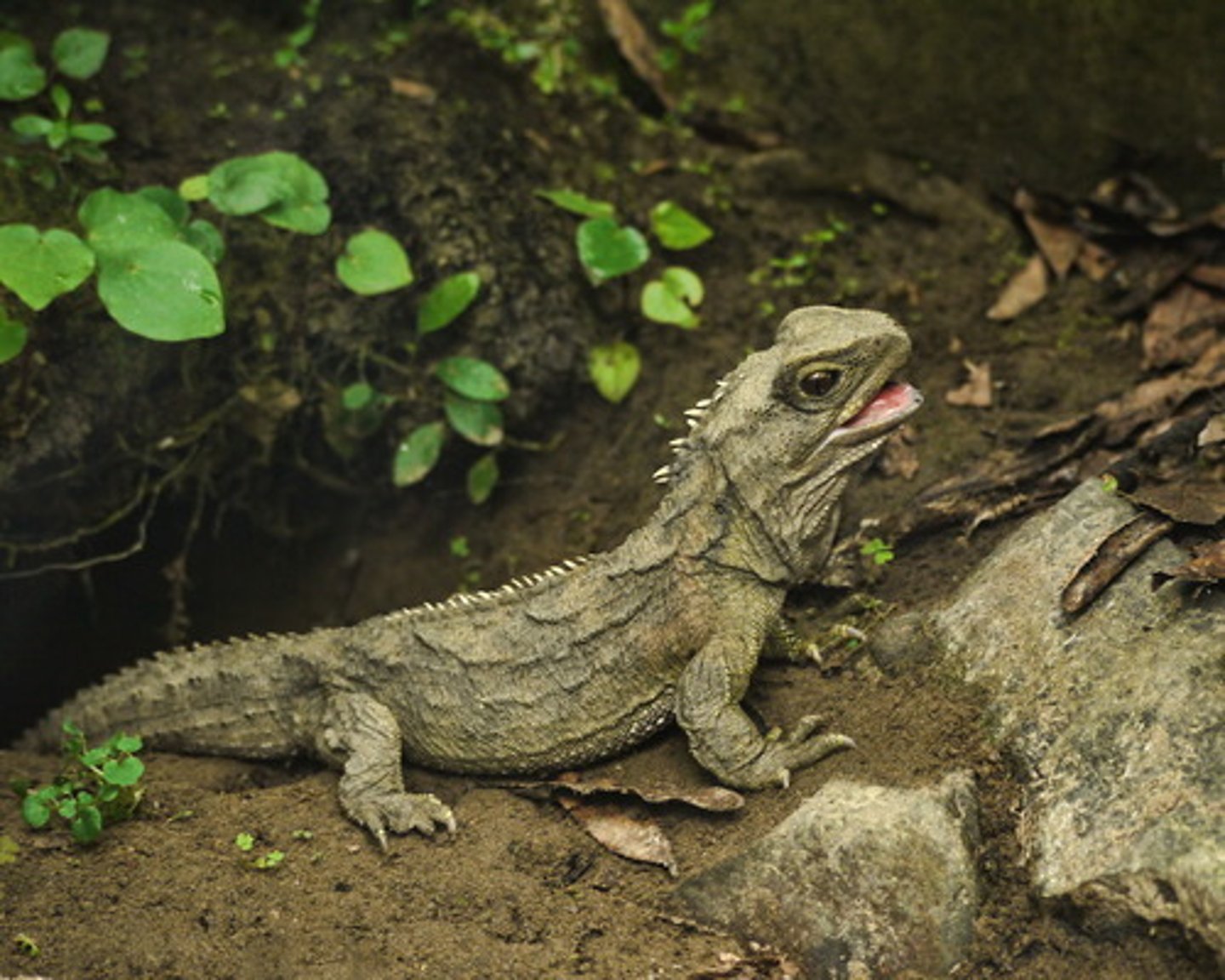
Rhynchocephalia/Sphenodontidae
Tuataras

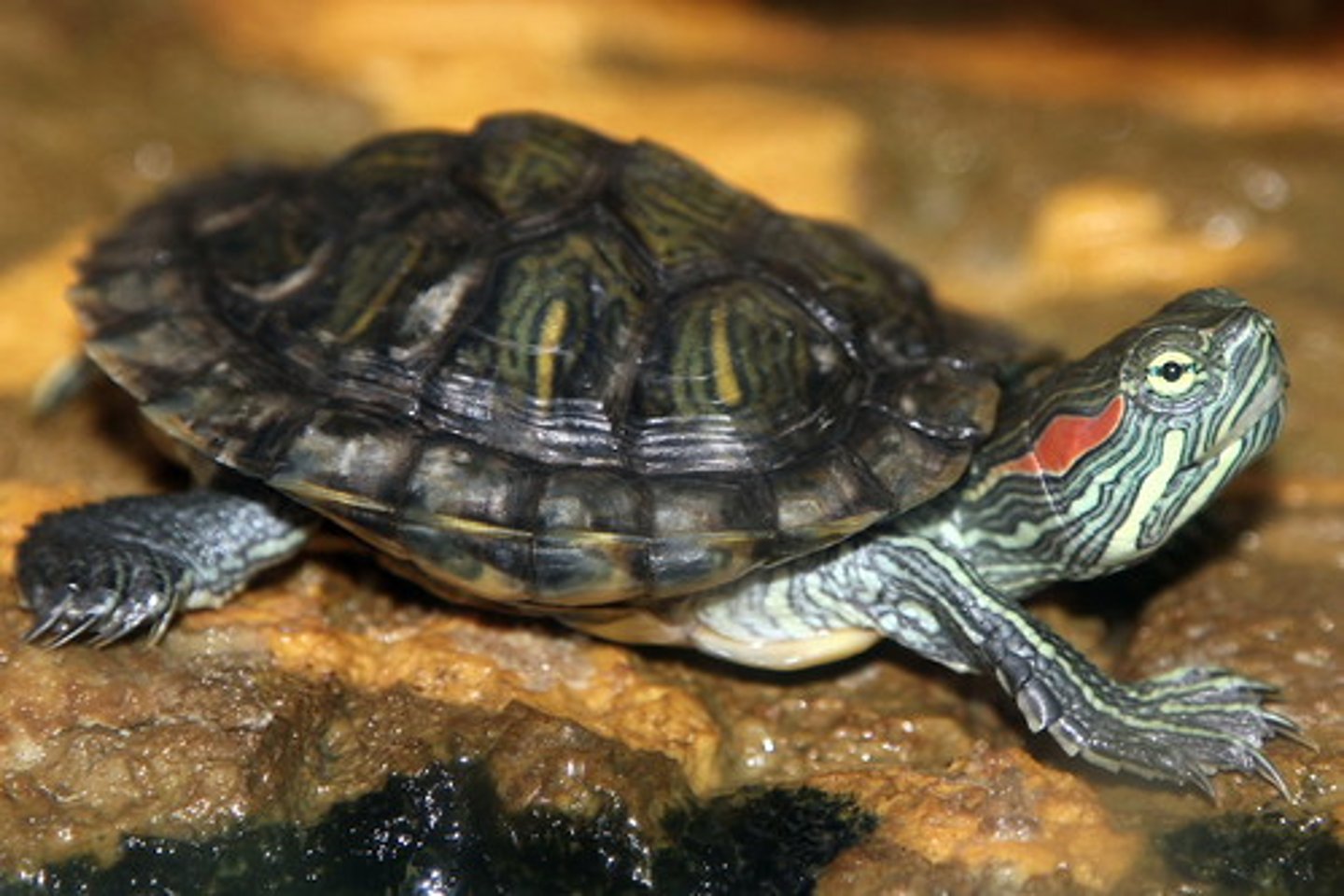
Testudines
Turtles and tortoises
- Shelled reptiles
- Ribs and vertebrae fused to form shell
- Upper is carapace, lower is plastron
- Diverse order and relatively species-rich
- Some fully aquatic, some fully terrestrial, some marine, some freshwater
- Highly diverse in size
- Flexible necks with 8 cervical vertebrae

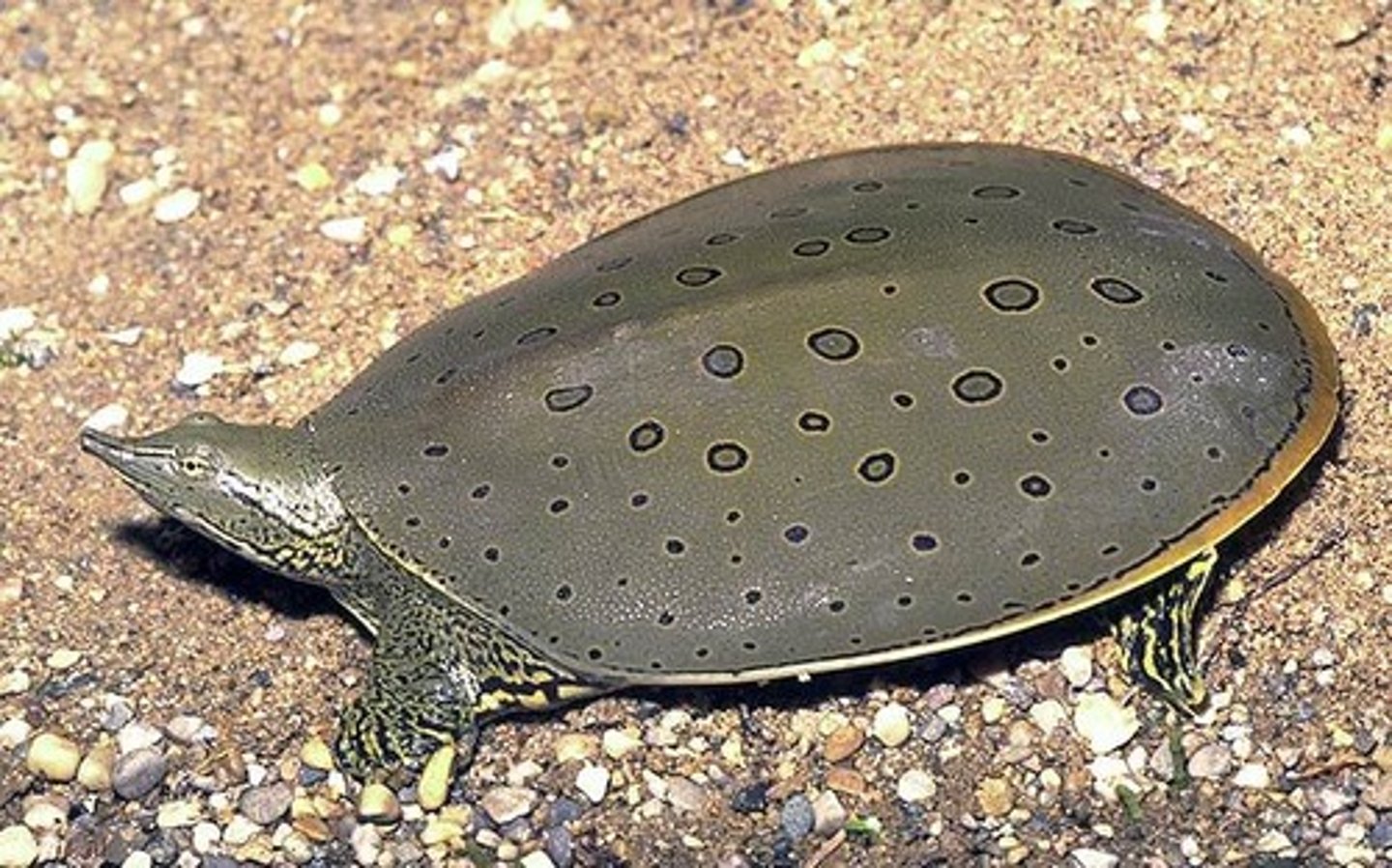
Trionychidae
Soft shelled turtles

Cheloniidae
Sea turtles
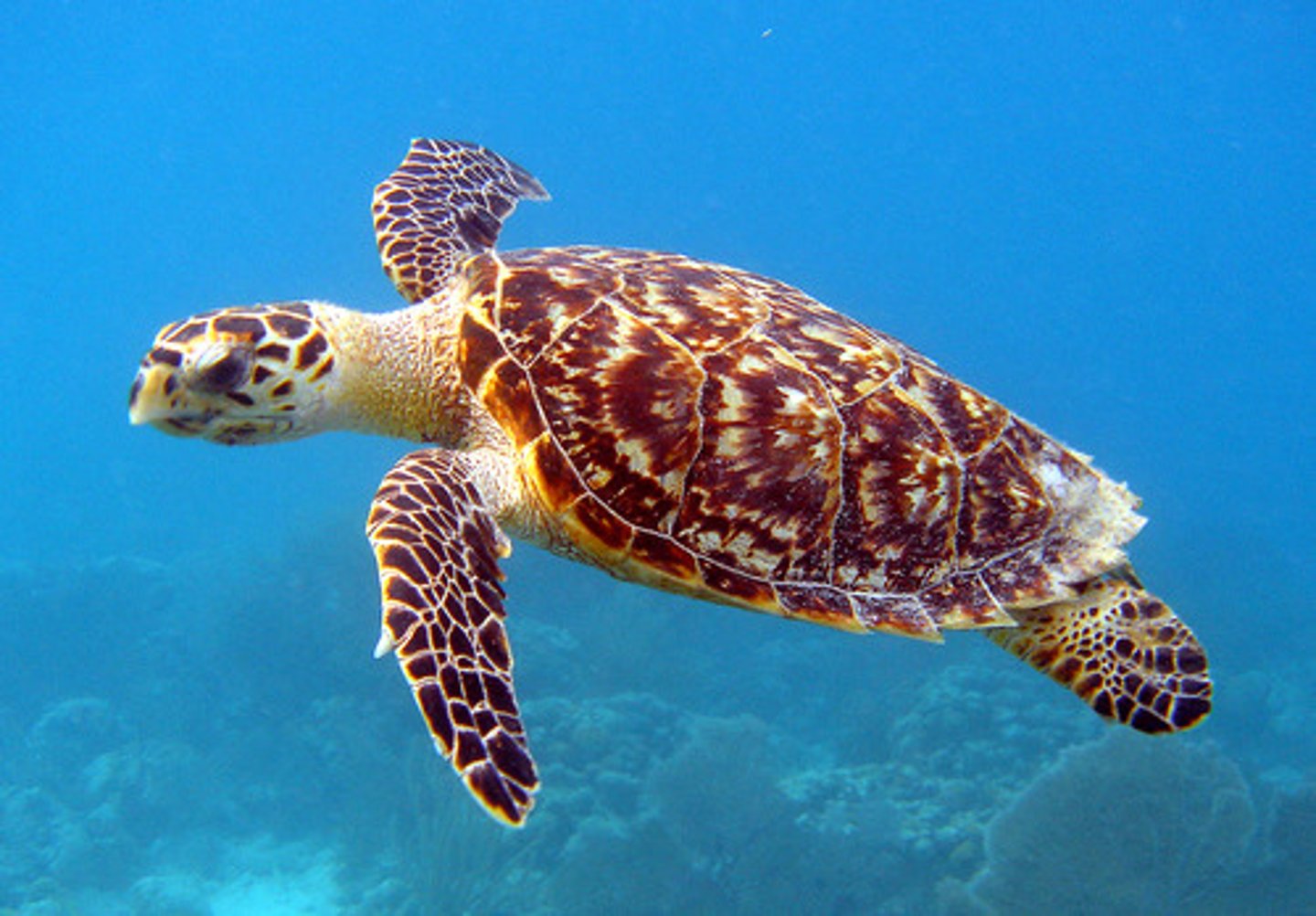

Chelydridae
Snapping turtles
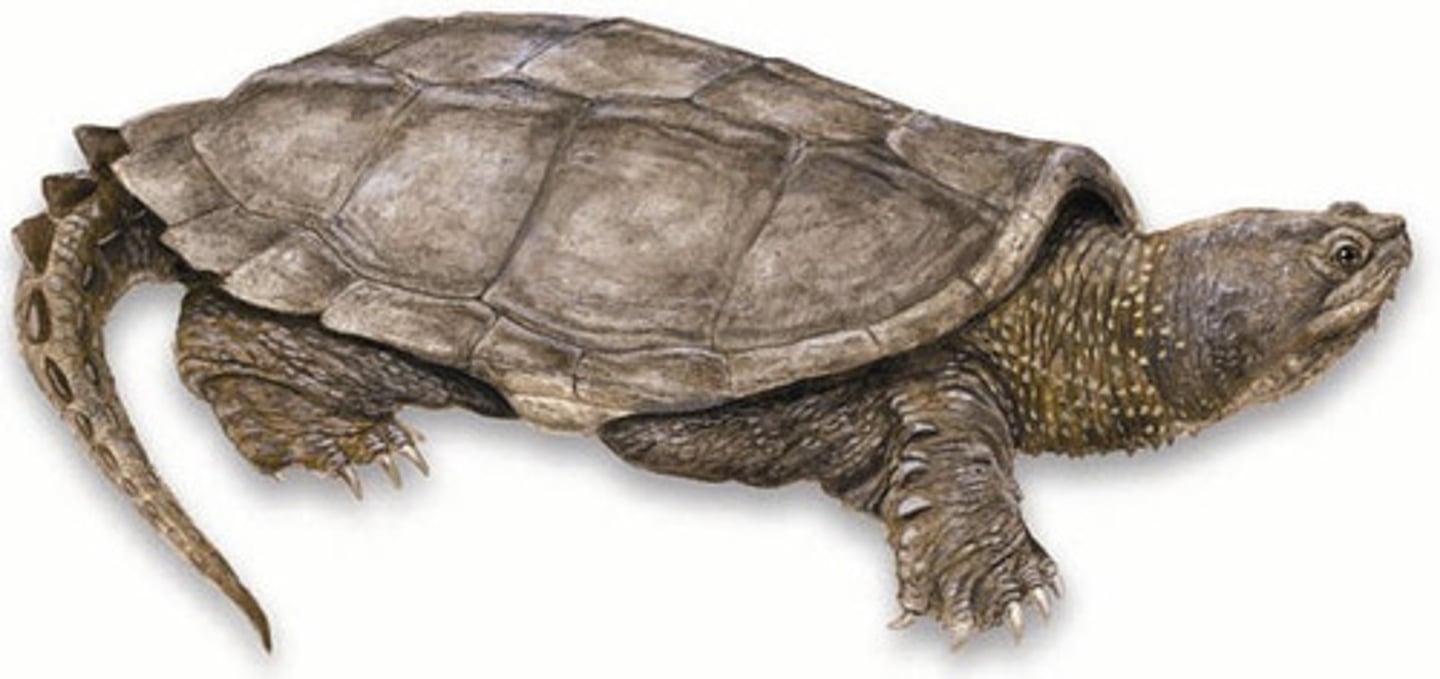

Kinosternidae
Mud and musk turtles
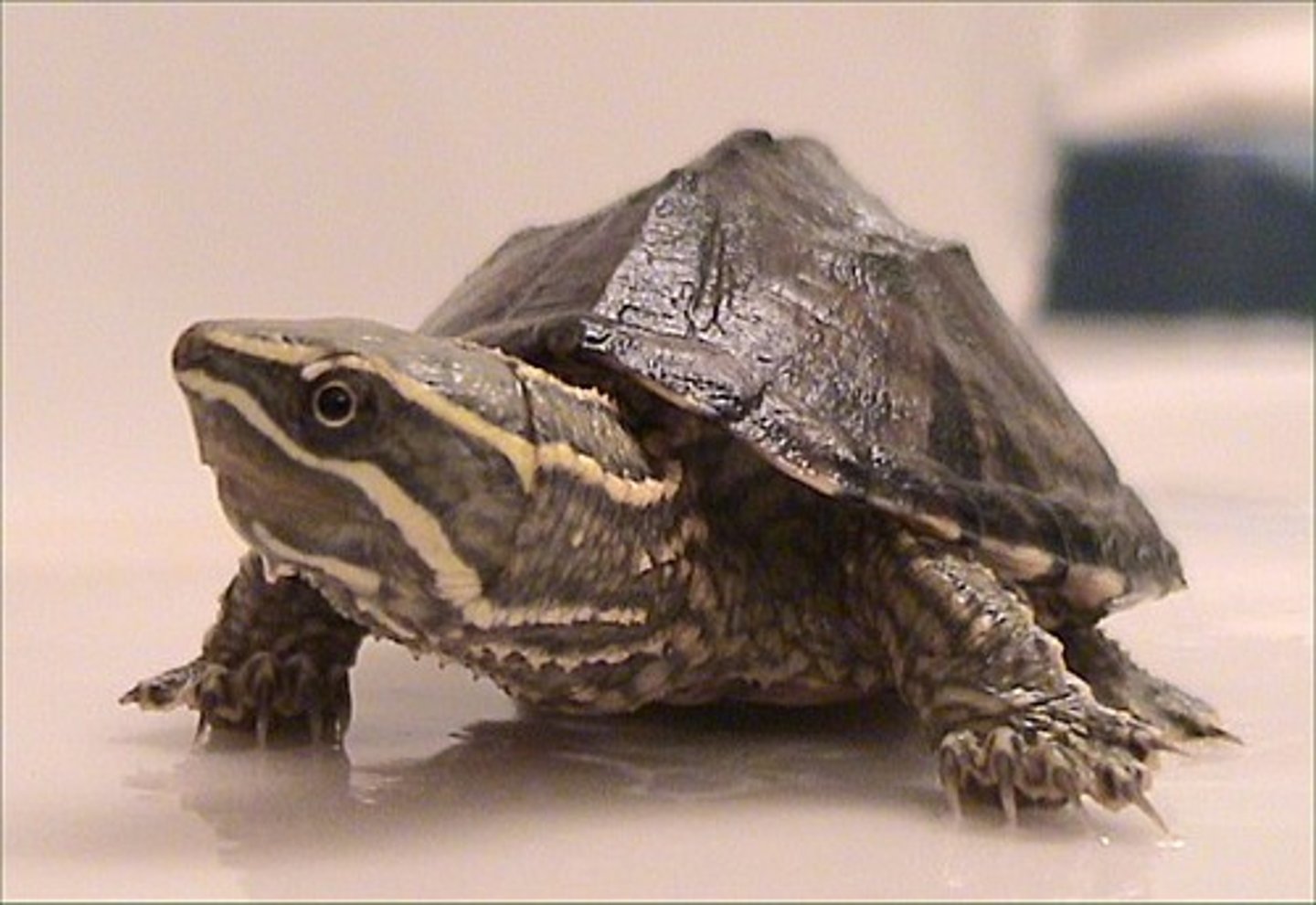

Emydidae
Pond and Box Turtles
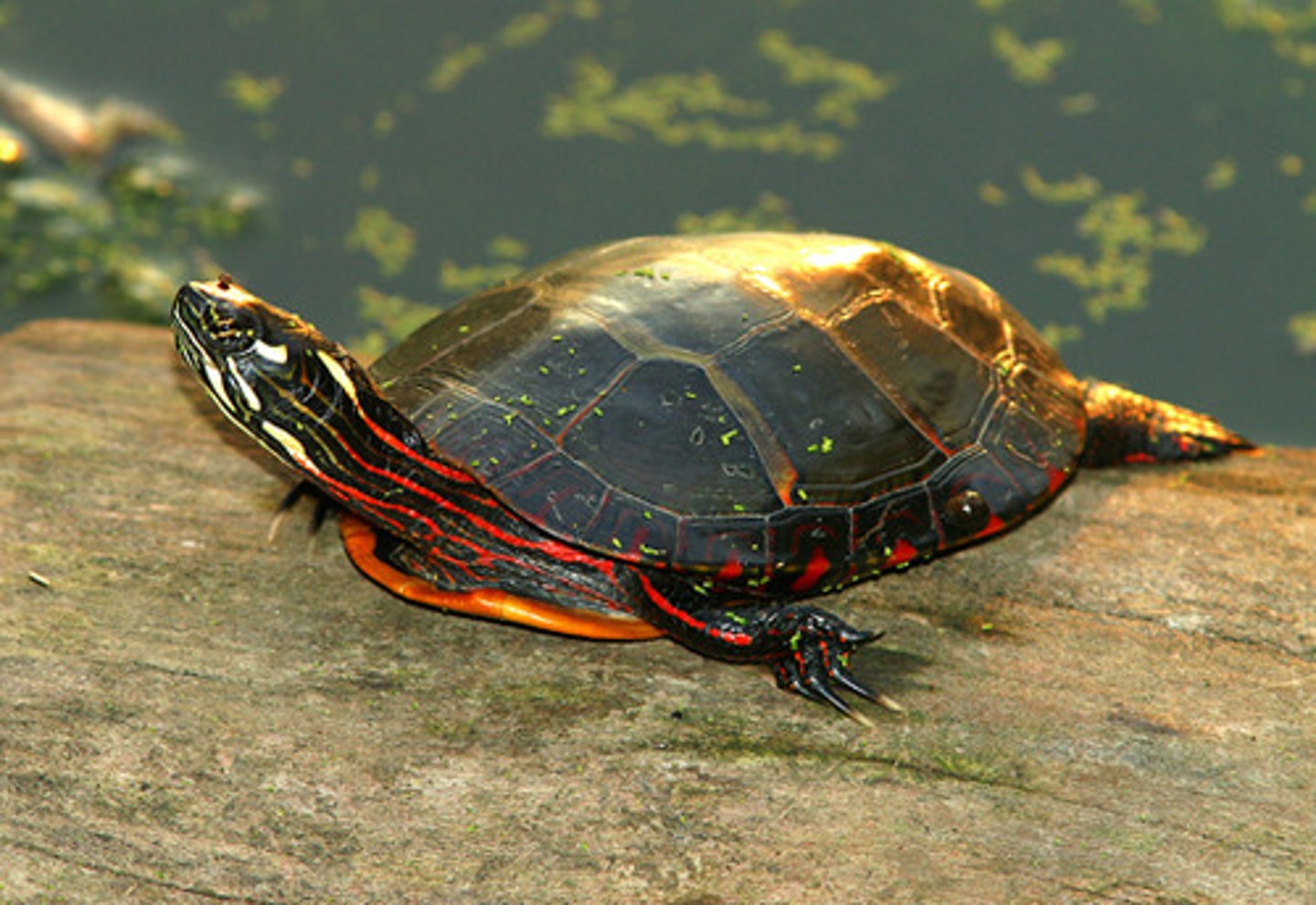

Testudinidae
Tortoises
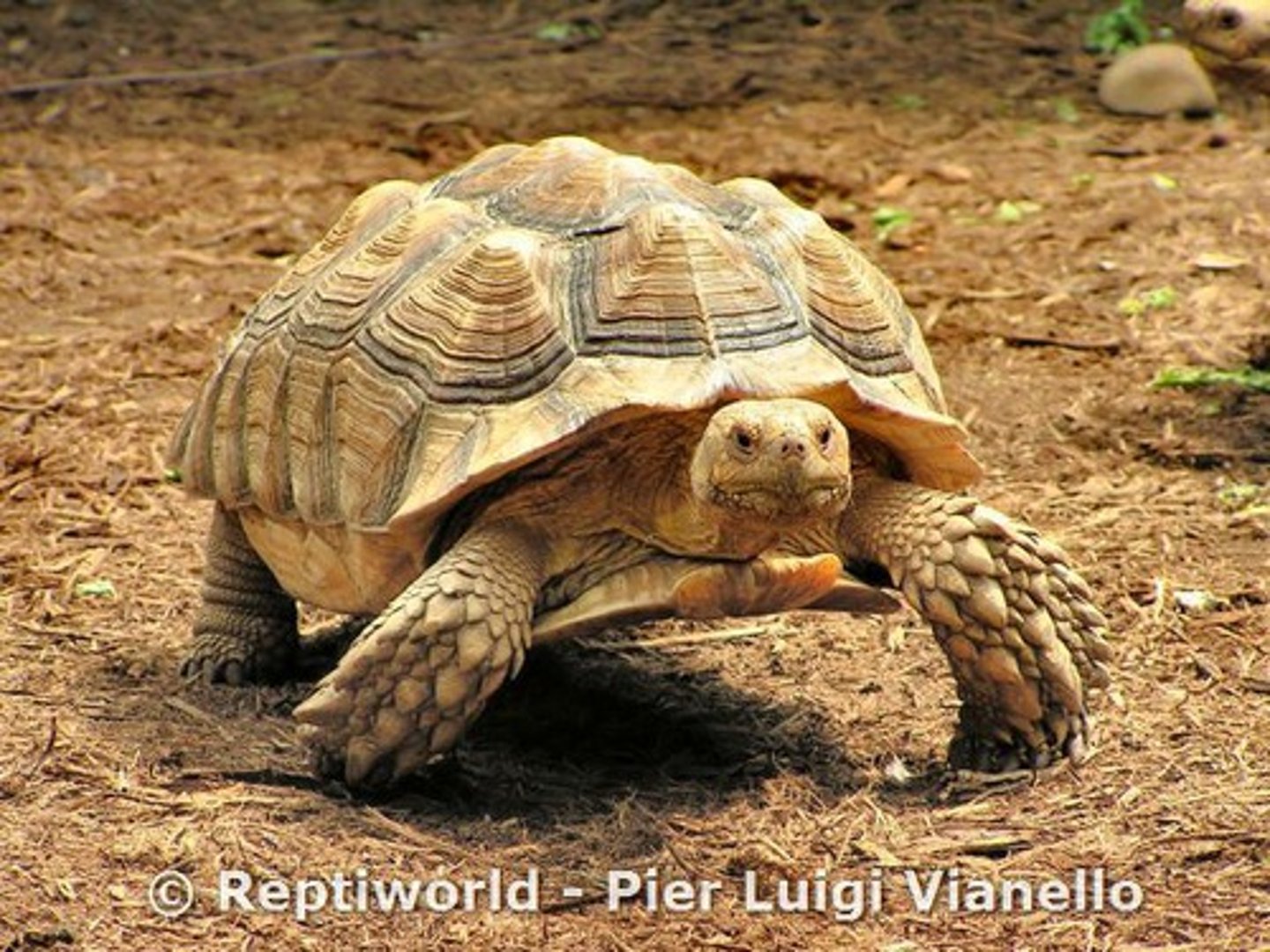

Squamata
Lizards and snakes
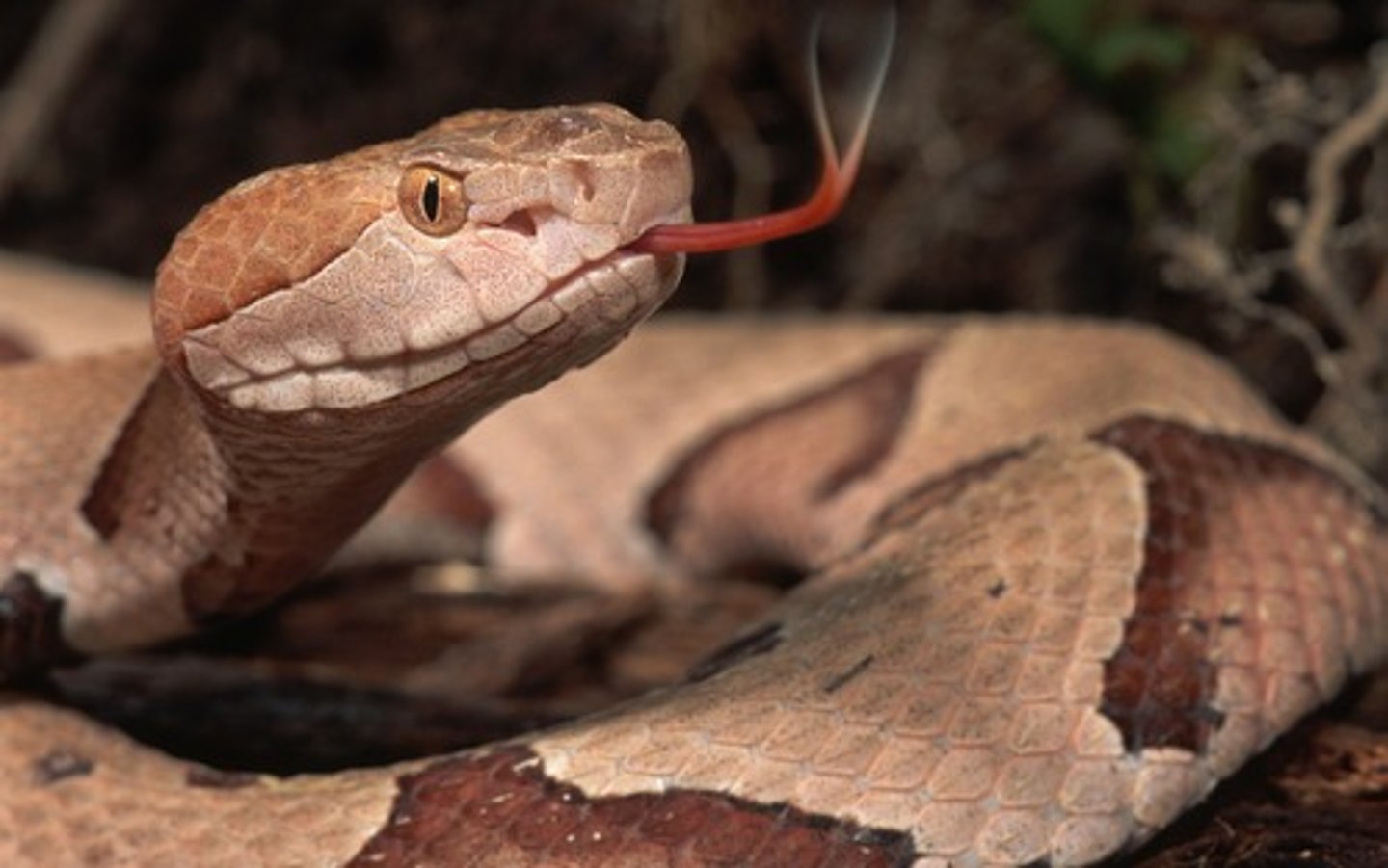

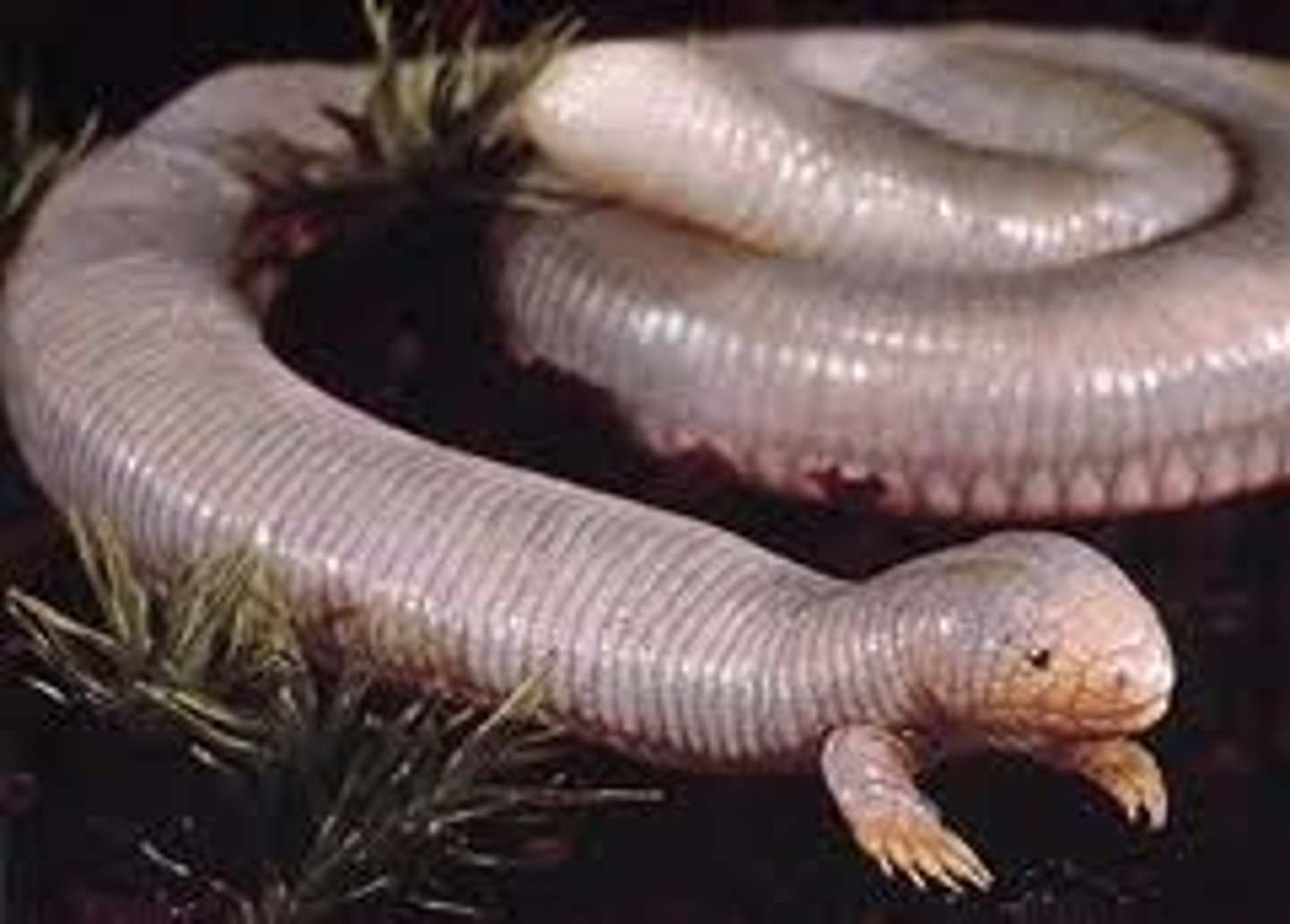
Amphisbaenia
worm lizards

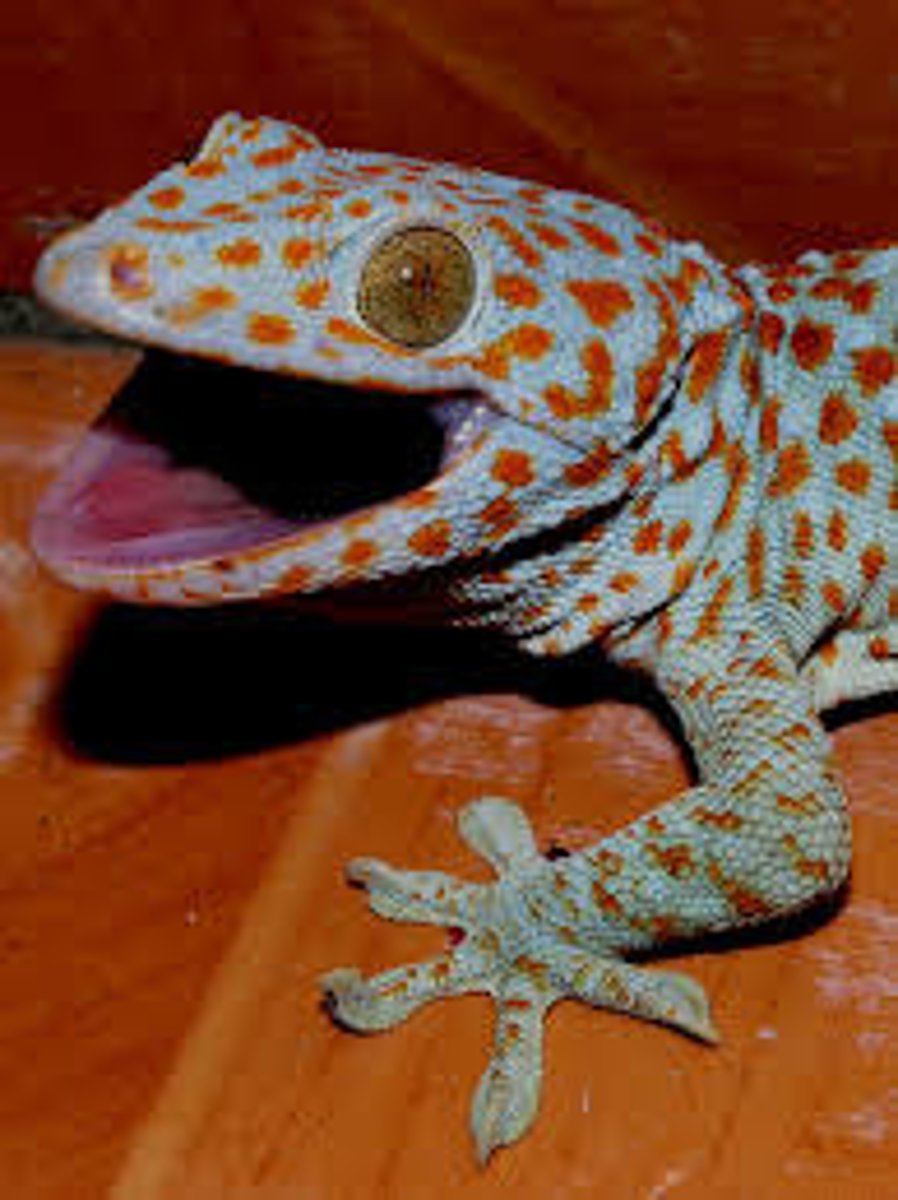
Gekkonidae
Geckos

Phrynosomatidae
Spiny lizards
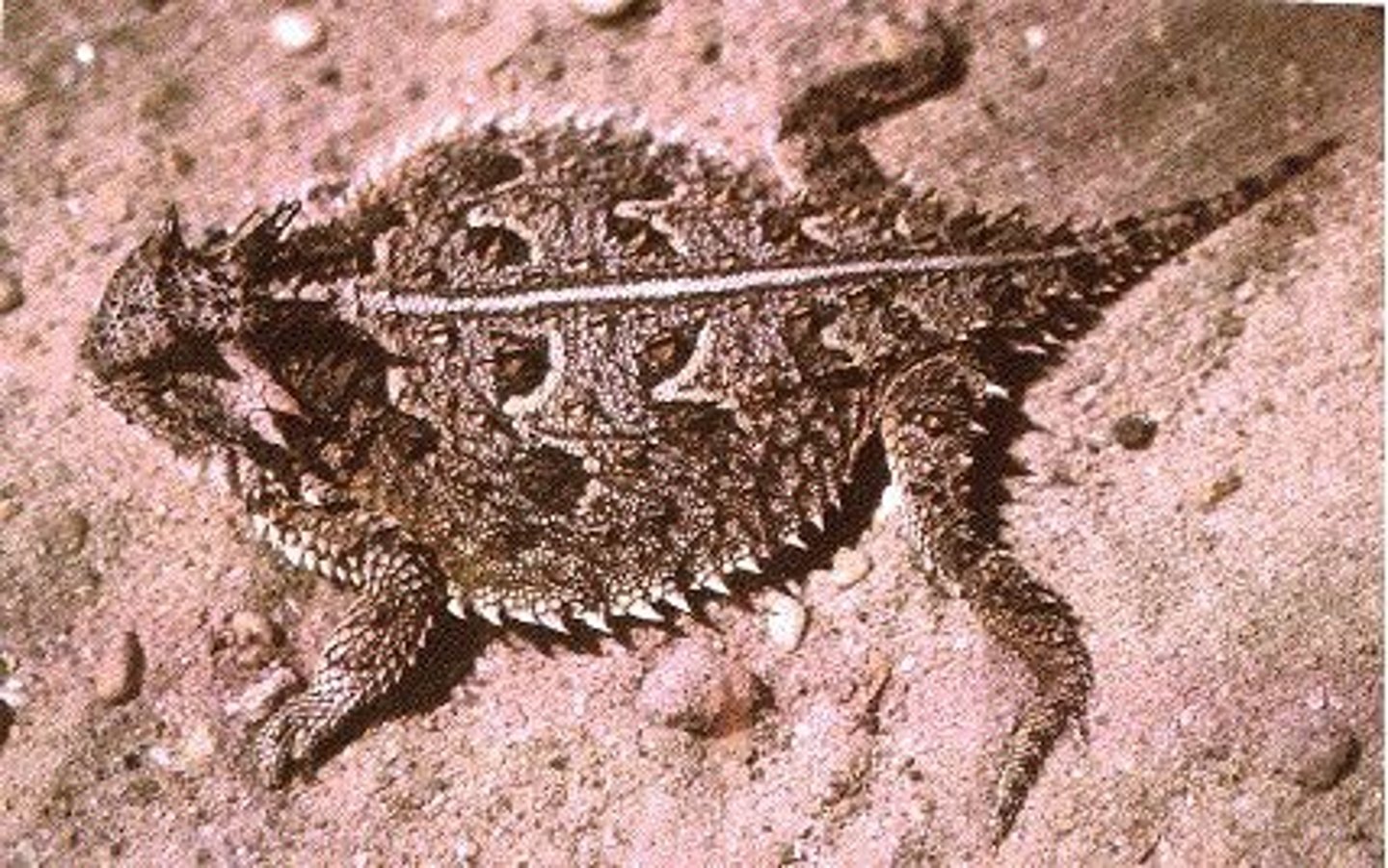

Anguidae
Glass lizards and alligator lizard
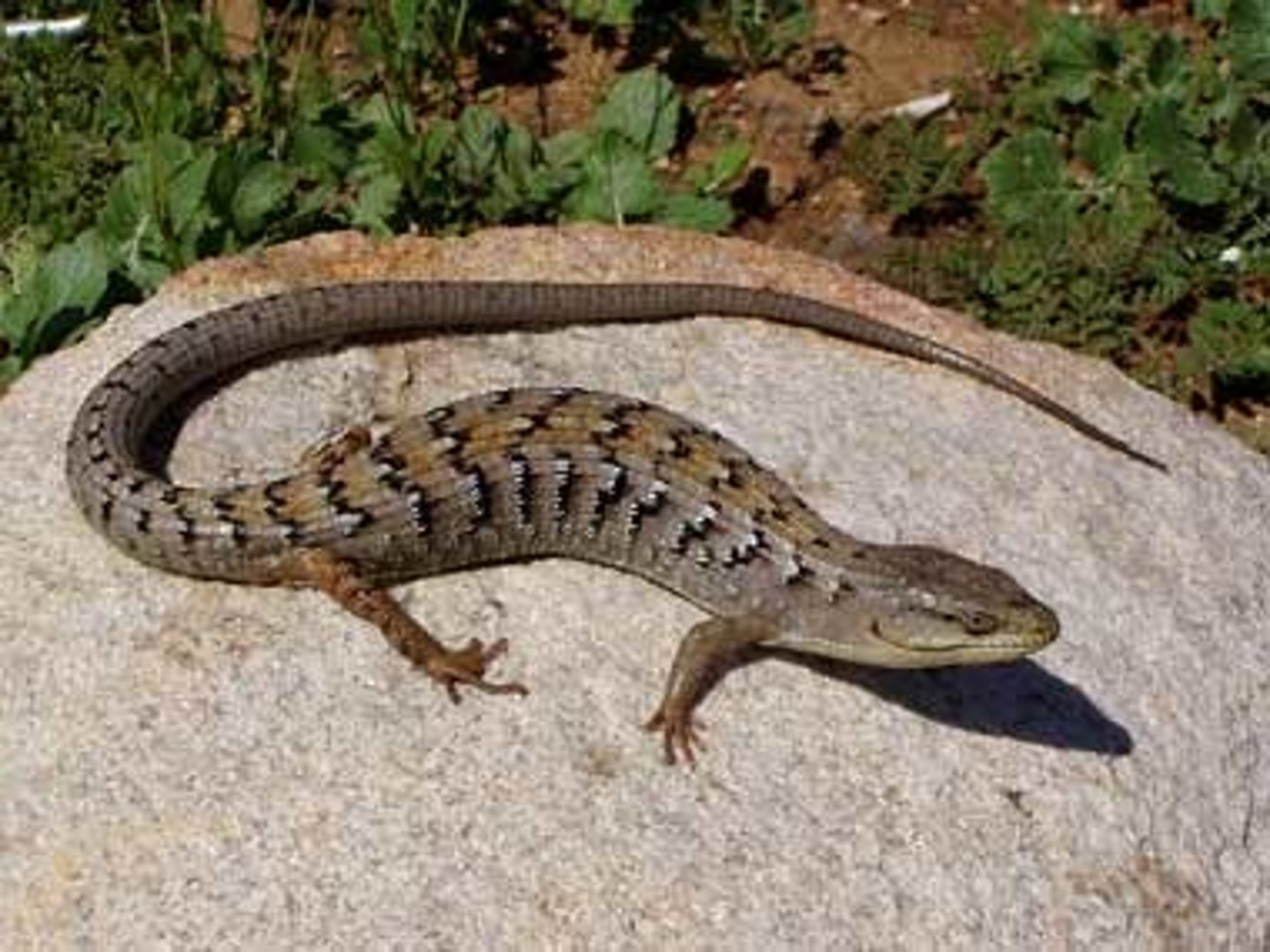

Helodermatidae
Gila monster and Mexican beaded lizard
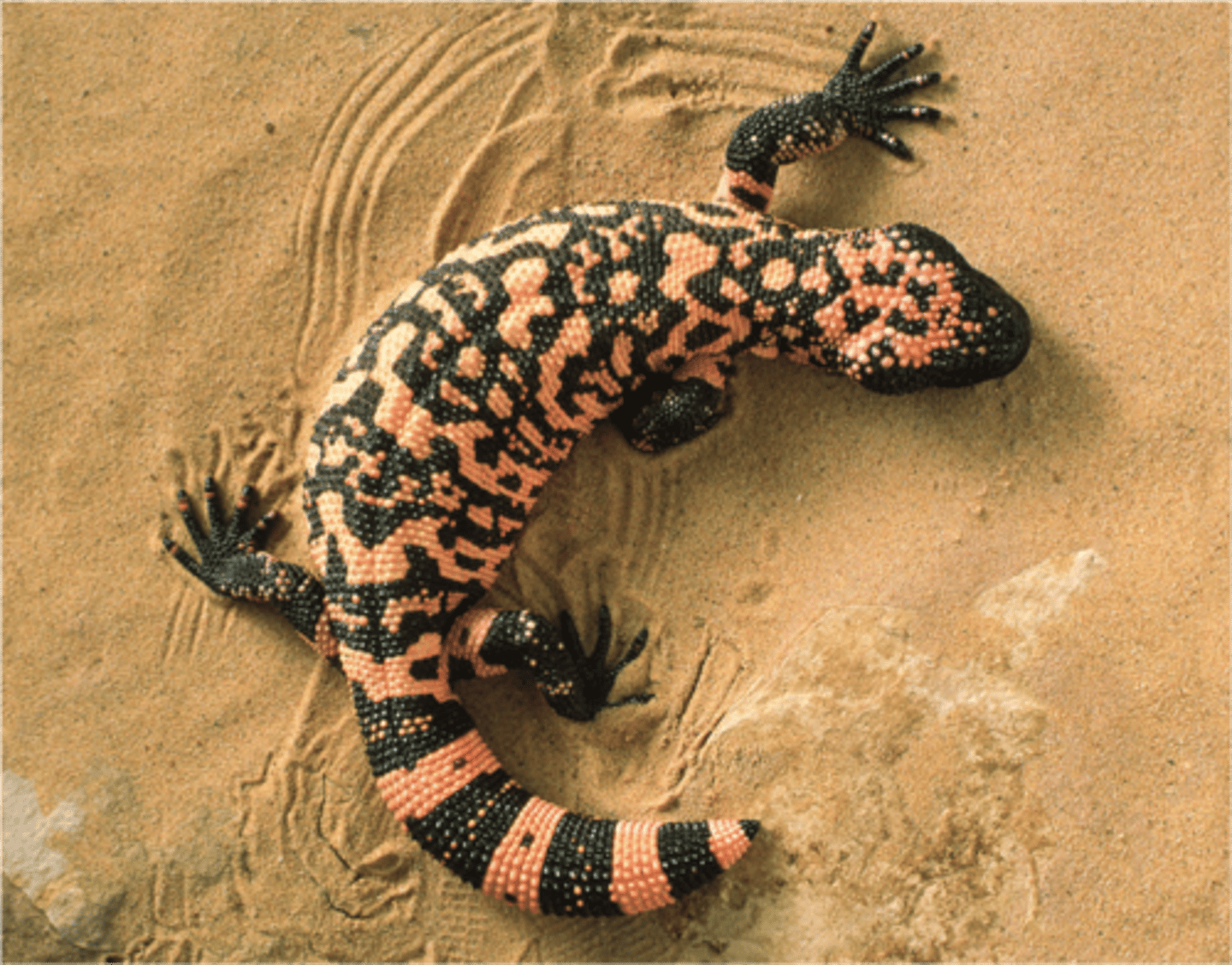

Teiidae
whiptails
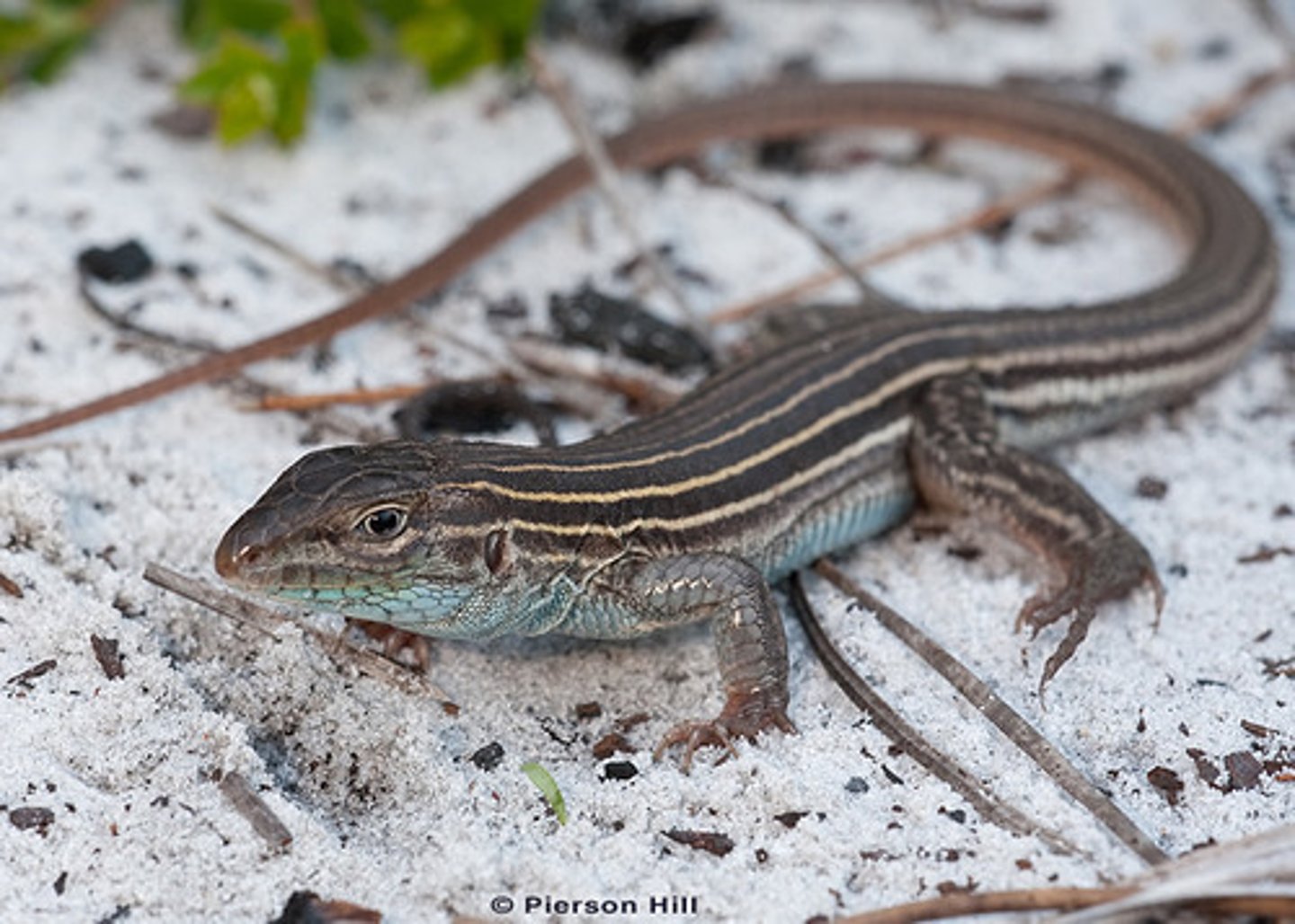

Scincidae
Skinks

Serpentes
snakes

Viperidae
vipers and pit vipers

Pythonidae
Pythons

Elapidae
coral snakes
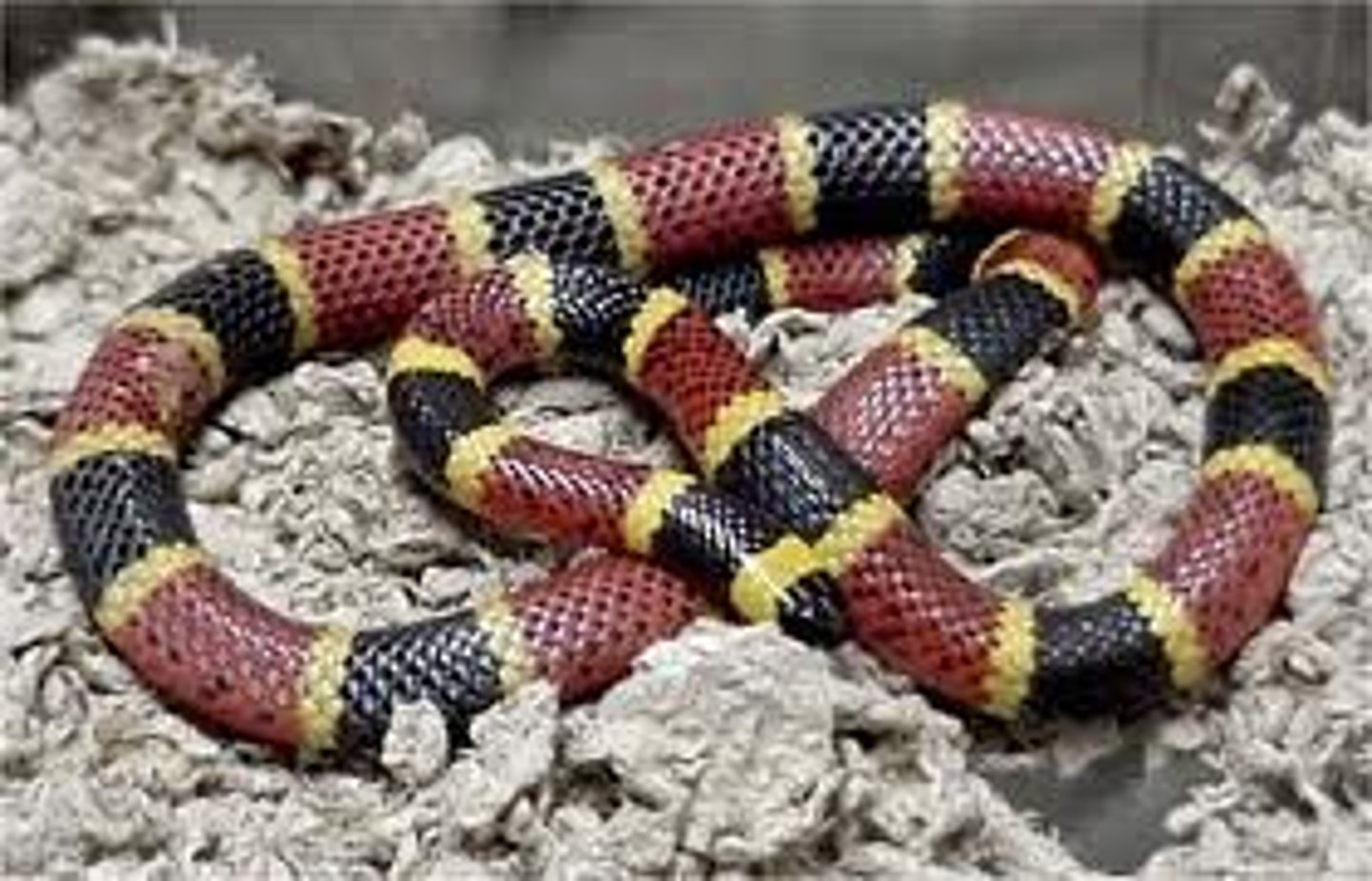

Colubridae
Colubrids
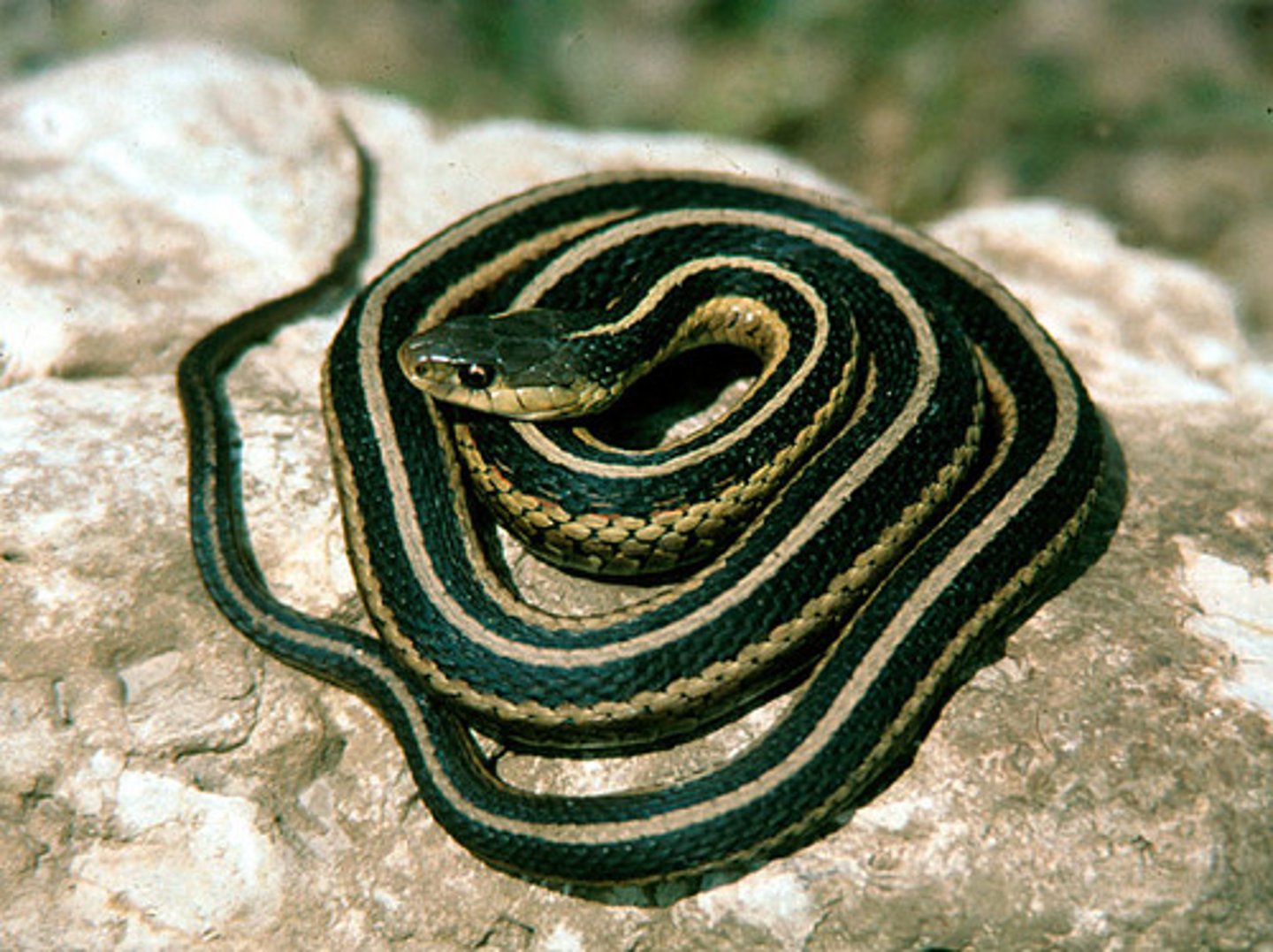

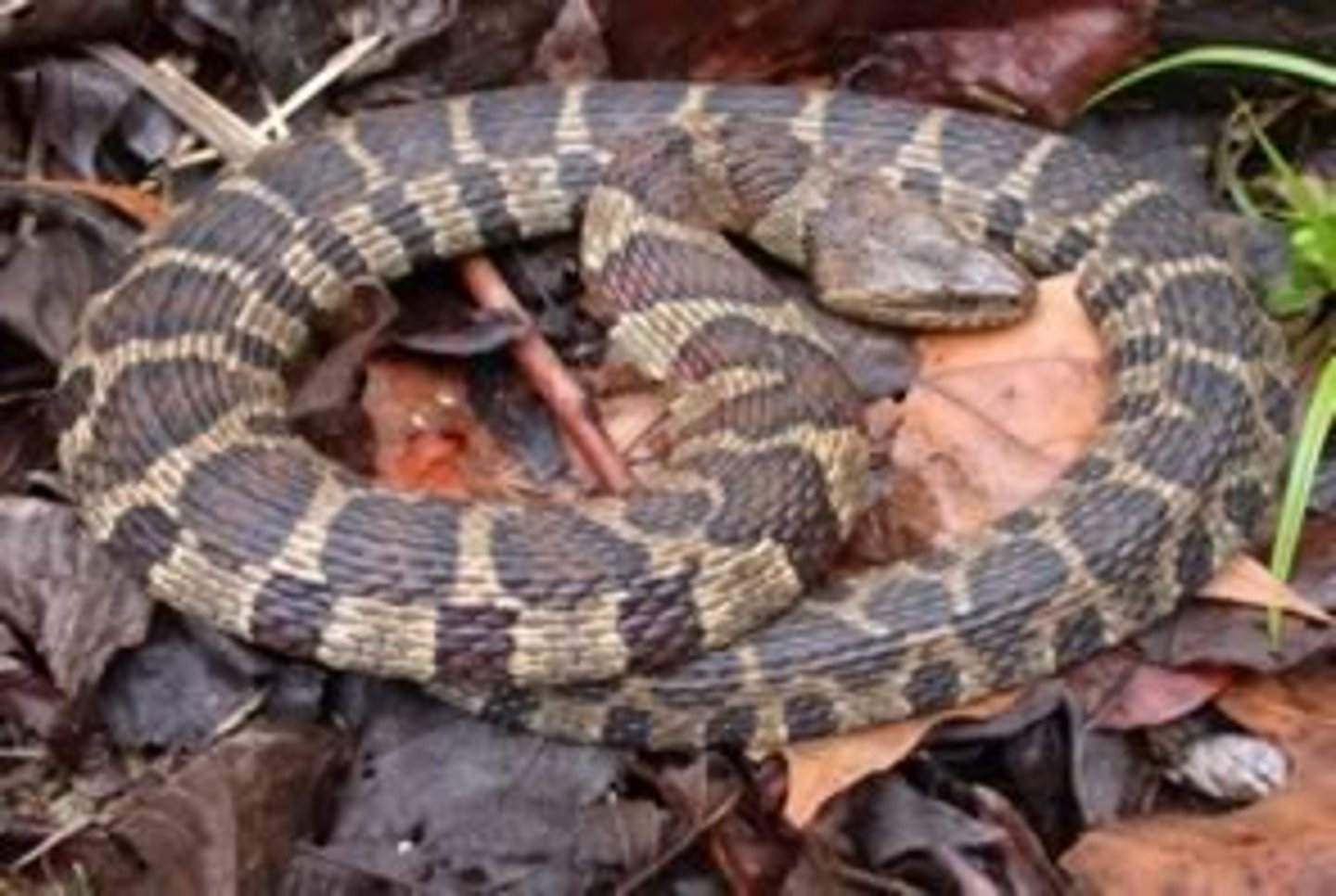
Natricidae
water snakes

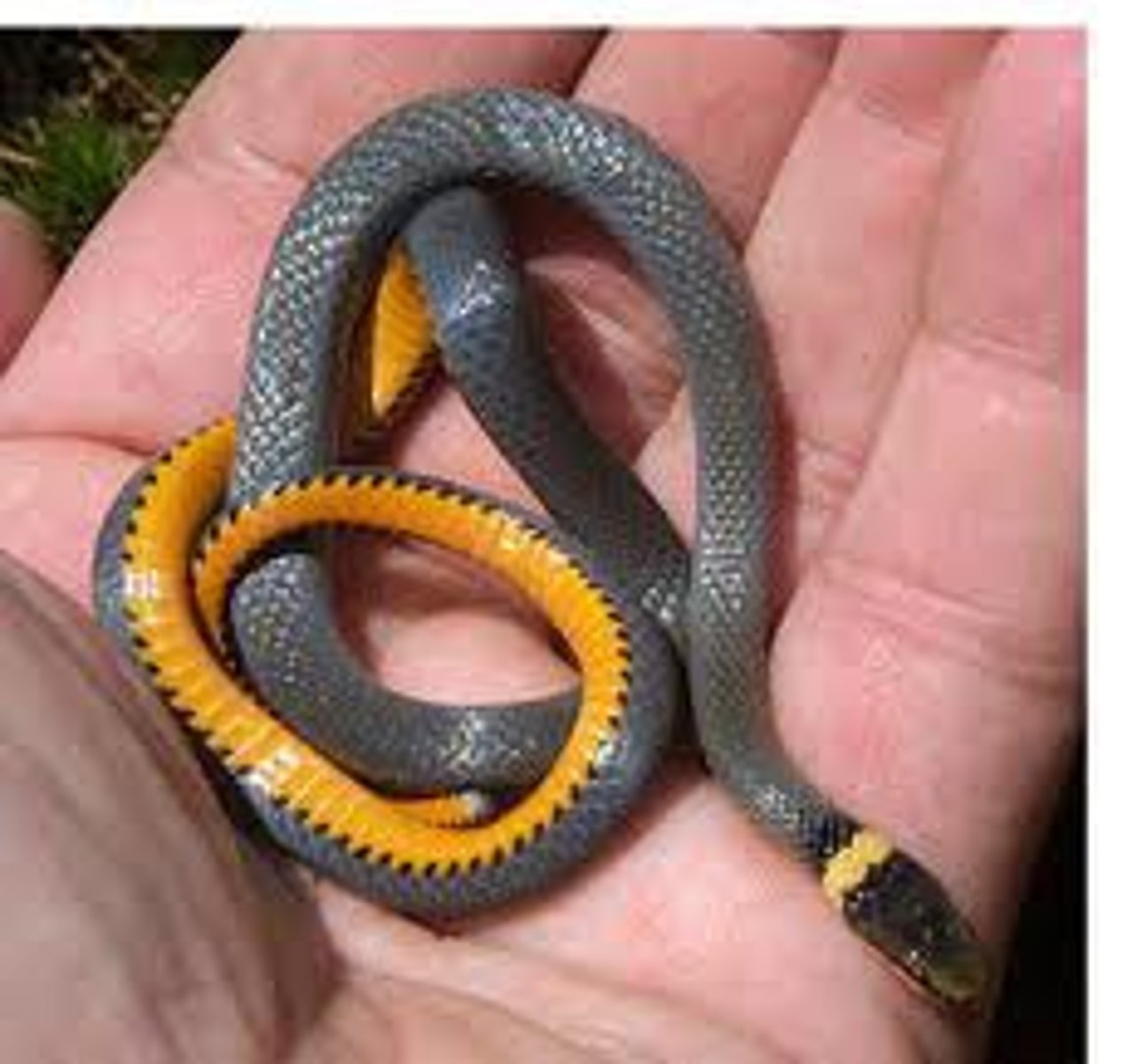
Dipsadidae
rear-fanged snakes

Eft stage
Stage in a salamander's life that allows them to stay in dry environments until sexual maturity, can be in this stage for 2-3 years
Unken Reflex
- Aposematic coloration
- Posturing behavior advertising toxicity to predators
- Used for chemical defense
- Used by many amphibians
Frogs vs toads
Toads have rough, warty skin and shorter hind-limbs for hopping. They are also more tied to land.
Frogs have smoother skin, longer legs for leaping, and are more tied to water
Which era is called the Age of Reptiles?
Mesozoic Era
Diapsids
Archosaurians and lepidosaurs
- Larger, stronger jaw muscles
Anapsids
Primitive group with no temporal fenestrae
Synapsids
Mammals and mammal-like reptiles
- Possess single large fenestrae
Amniotes
Small-lizard like animals
- Salamander-like and had the first amniotic egg
Hylonomus
Possibly the earliest known reptile
- Distinct scale marks, sharp teeth and insectivorous
- Anapsid morphology
Archosauromorphs
First major diapsid lineage
- Gave rise to crocodilians and birds (and potentially turtles)
Crocodilians
Surviving archosaurs
- Early ancestors lived in Jurassic to mid-Cretaceous
Lepidosauromorphs
2nd major diapsid lineage
- Lizards, snakes, tuataras
- Appeared in late Permian
Megachirella
Oldest lepidosaur fossil that lived in Triassic
Tuatara
Living fossils
- Descended from rhynchocephalia
- Late Triassic to Mesozoic
- One species exists today, endemic to New Zealand
Turtles: Anapsid vs Diapsid
- Often considered surviving anapsids, but modern study suggests they're diapsids
- Have no tmeporal fenestrae but some fossils have small ones
Odontochelys
- Toothed turtle in late triassic
- Toothy protrusions on shell
- Incomplete carapace
Proganochelys
- Contains few teeth in beak
- Shell more similar to modern turtles
Eileanchelys
Earliest pond turtle
- Contains characteristics of modern-day turtles
Archelon
- Largest turtle on record
- Leathery shell and large flipper-like limbs
- Leatherback is closest living relative
Alligators vs. Crocodiles
Alligators have no lingual salt glands, but crocodiles do