7. Scaling LLM Training
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
What are FLOPs?
Measure for required compute for a model=> “Floating Point Operations”.
What are key differences between model Inference and Training?
Training takes 3x more compute than inference.
Training holds activations in memory for the backward pass.
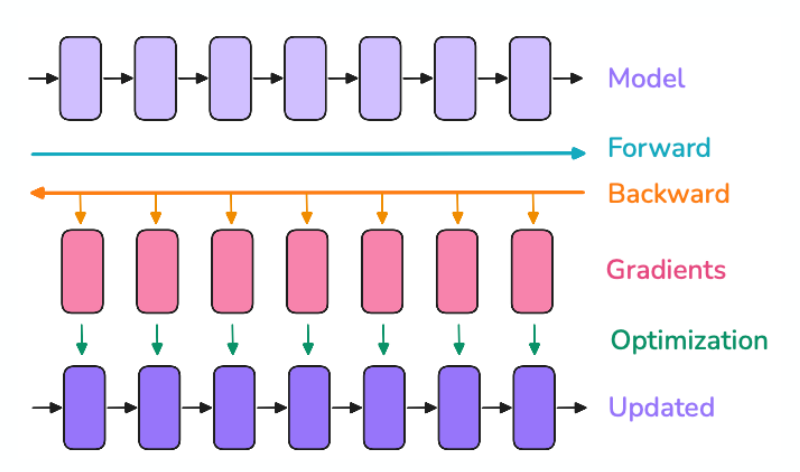
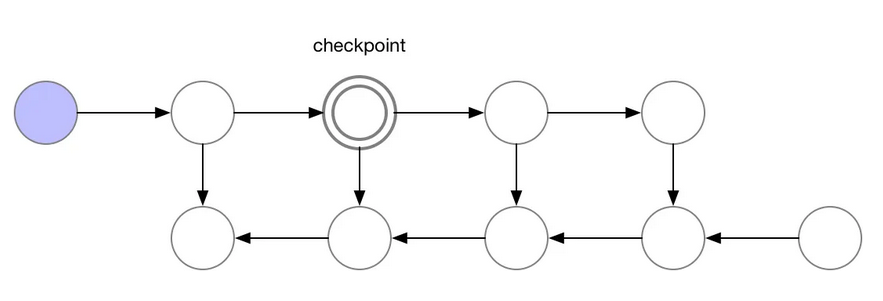
What is Activation Checkpointing?
Trade-off memory for compute in model training.
Drop activations from memory and re-compute when needed => keep some activations as “Checkpoints”.
=> Re-computing activations is slow when done from the beginning. Checkpoints throughout make average re-compute faster.
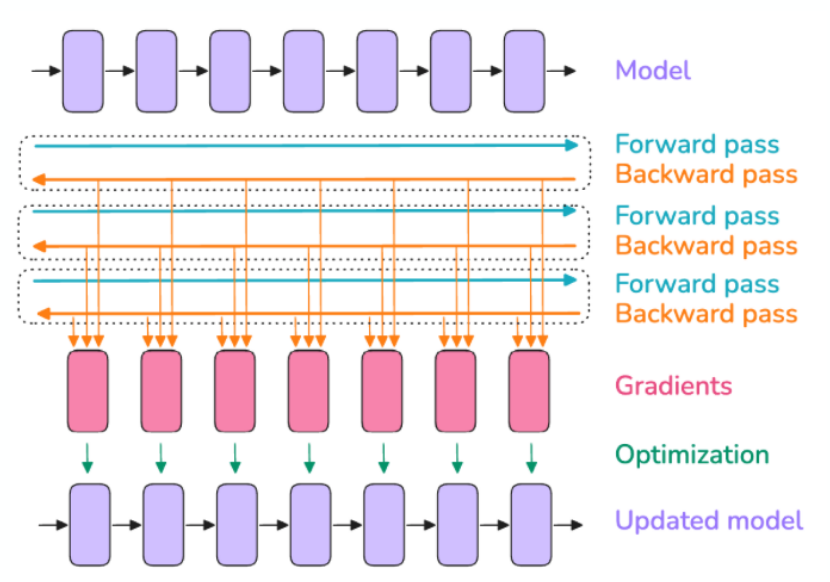
What is Gradient Accumulation?
Trade-off memory for compute in model training.
Problem: we want to run a large batch size, that does not fit in memory.
Solution: We run multiple forward-backward passes before doing an optimizer step, by keeping a running mean of the gradients.
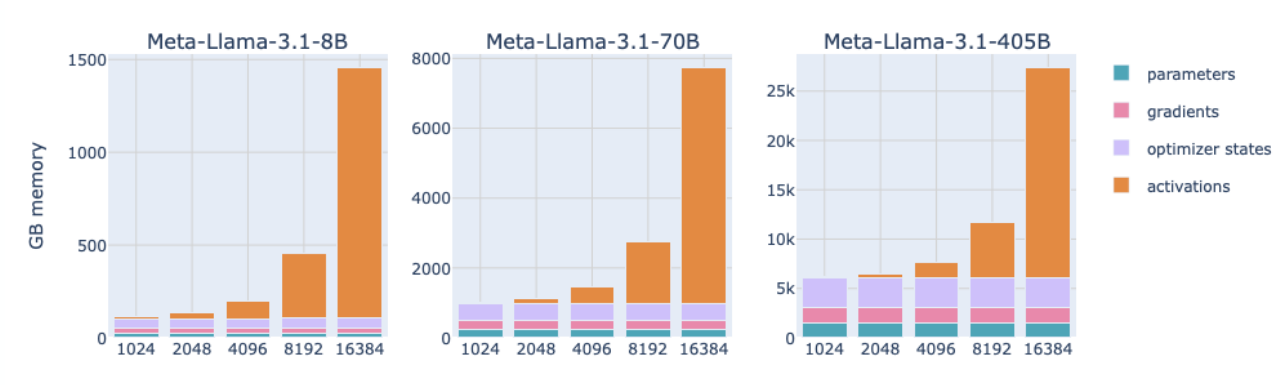
How does the memory footprint scale for Activations?
Small sequences => Memory for activations is negligible.
Large sequences => Memory footprint is way larger as params + grads + optimizer combined.
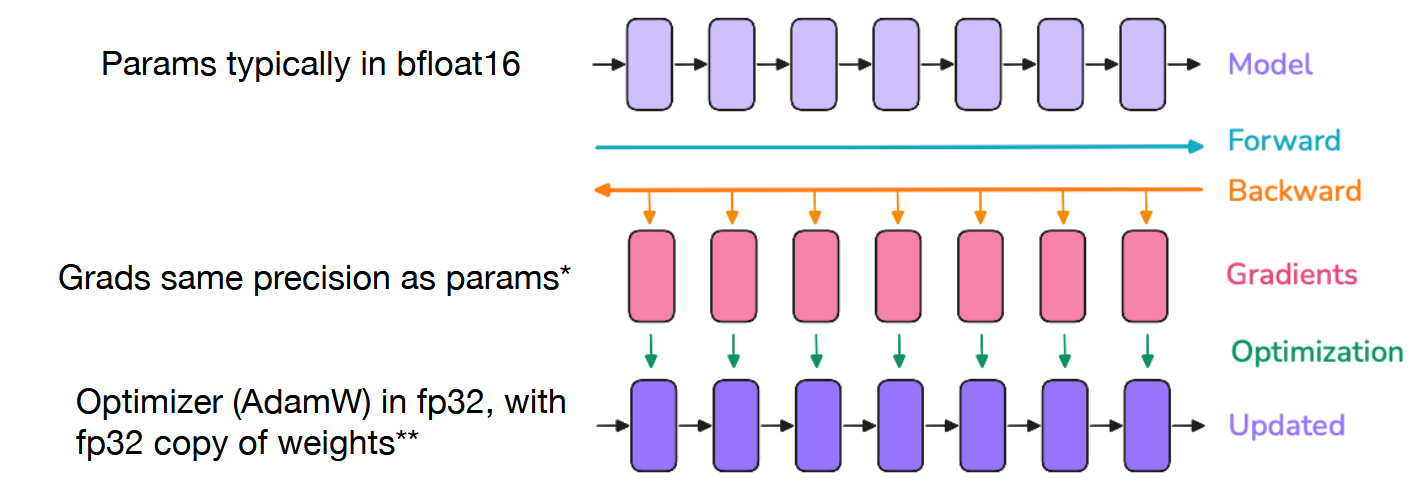
What needs to be in memory when training an LLM?
Parameters
Gradients
Optimizer
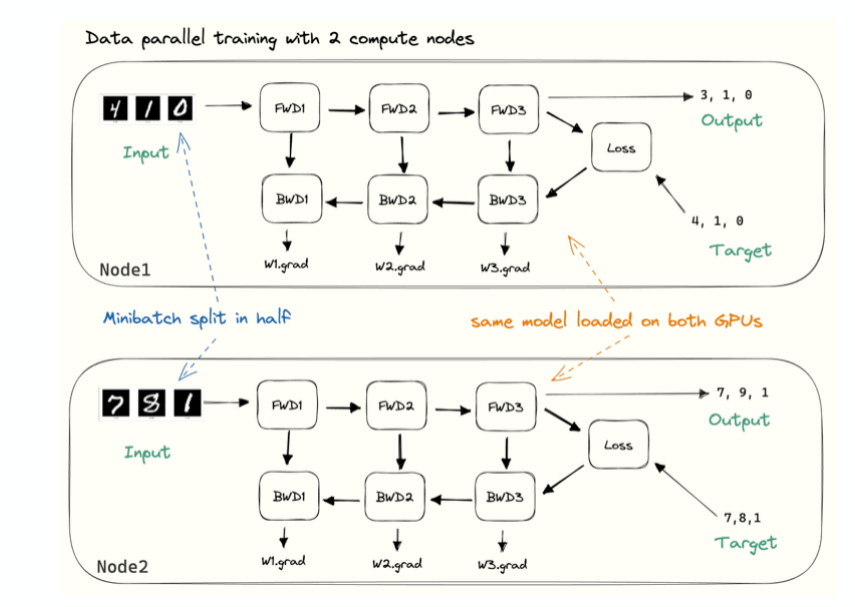
What is Data Parallelism in LLM Training?
Run different batches of data in parallel on different chips.
Model weights must be duplicated across chips.
After gradients are computed they must be communicated across different chips.