Pediatrics and Post-Menopausal Pelvis
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Pediatric Anatomy
Uterus is 3.5 cm long for the first 6-8 weeks after birth
Endometrium seen as a thin line or small amount of fluid
Uterine size decreases in size after postnatal period (hormone influences)
Cervix is prominent making up 2/3 of the uterus
Greatest increase at puberty
Fundus becomes larger than cervix
Ovaries are 15 × 2.5 × 3 mm (long and thin)
Transabdominal Exam - Pediatric Approach
Take time to explain the test
Allow one or both parents to stay
tailor explanation to pt’s age
Requires full bladder
Bottle of fluids 30 min prior → pt’s not potty trained
24 oz od not carbonated fluid 45-60 min prior → older children
Vagina, Uterus, and Fallopian Tube Pediatric pathology:
Primary tumors are rare in children
Malignant tumors are more common
Vagina more often than uterus
The most common reason for vaginal bleeding in a child is:
A foreign body
Pediatric Ovarian Pathology:
Cysts are fairly common
Malignant tumors are rare
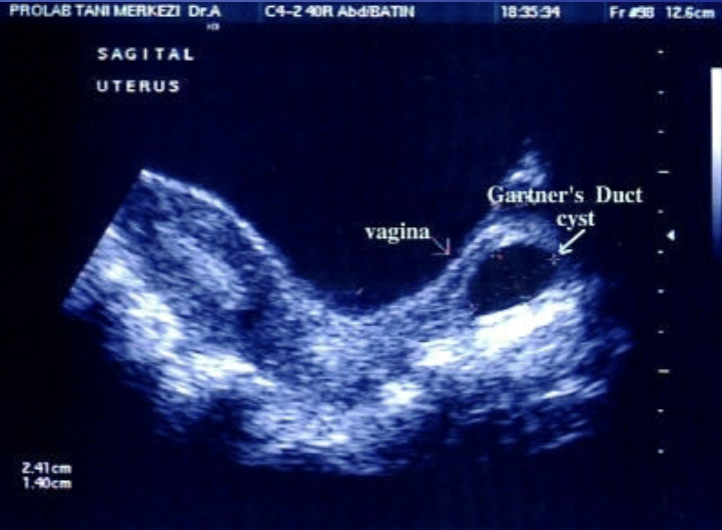
Gartner’s Duct Cyst
Benign cyst of the vagina
Most common cystic lesion of the vagina
Usually develop along the side walls of the vaginal canal
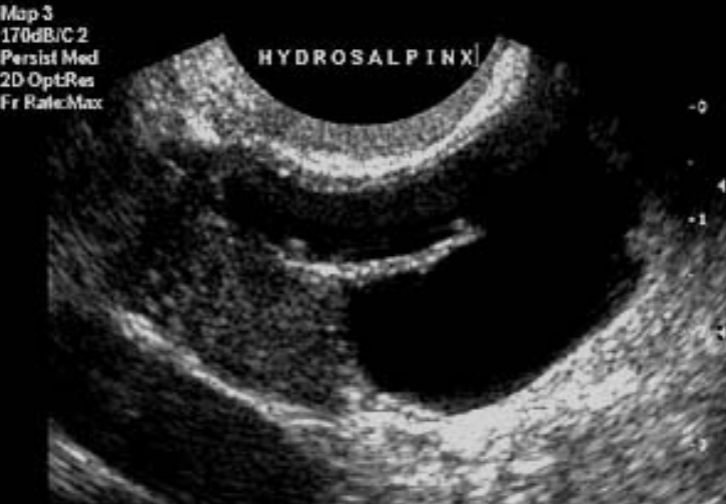
Hydrosalpinx or Pyosalpinx
Fluid or pus in the fallopian tubes
Associated with PID
Suspicious for sexual abuse
Sarcoma Botryoides
Most common vaginal and uterine lesion of young girls
See grape like structure coming out of vagina
Pt presents with bloody discharge
Usually originates in vagina and spreads to uterus
Primary Adenocarcinoma
Uterine or Cervical Tumor
Seen in daughters whose mothers took DES
Presents with vaginal bleeding and rapidly growing tumor
May occur in children younger than 1 y/o
Almost always occurs before age 11
Endodermal Sinus Tumor
Highly malignant vaginal and cervix tumor
Usually occurs by age 3
Similar sarcoma botryoides
Follicular cysts
Functional cysts
Hemorrhagic cysts
Bleeding within the cyst
Corpus Luteum Cyst
Mature Follicular cyst
Paraovarian cyst
Remnant of Wolffian Duct
“Floating” cyst
Polycystic Ovaries (PCOS)
May appear as enlarged ovaries
Follicles located in the periphery
“String of Peals” sign
Increased risk of ovarian torsion
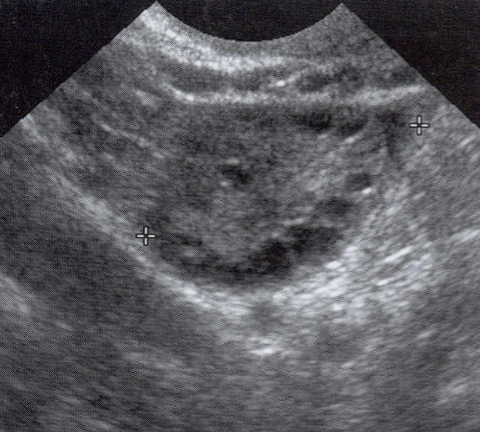
Benign Cystic Teratoma
Most common tumor during reproductive years
Uncommon before puberty
Risk of torsion
Contains hair, fat, teeth, bone, etc.
Cystadenomas
Two types: Serous and Mucinous
RARE in children
Ovarian Fibroma
Rare solid CT tumor
Fibrous type of tumor
Sometimes seen in children
Associated with Meigs Syndrome
Subject to torsion
Dysgerminoma
Most common pediatric malignant ovarian mass
counterpart of testicular seminoma
low-grade malignancy
potentially curable
solid mass that may contain septa and calcifications
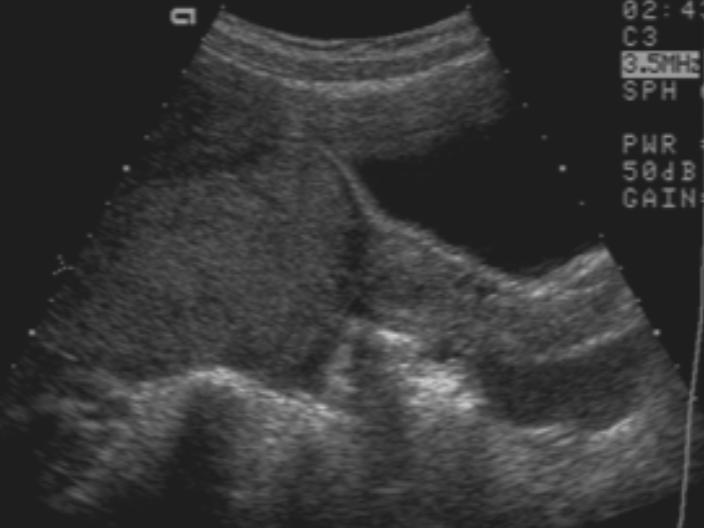
Malignant Ovarian Lesions U/S signs / labs:
Prominent arterial flow
Bilateral 10-15% of the time (usuallu unilateral)
Increased levels of HCG, LDH, AFP
Germ cell tumors are the most common malignant tumors in the pediatric genital tract
Endodermal Sinus Tumor of the Ovary
Germ cell tumor
Second most common of germ cell tumors
Grows rapidly
Unilateral
Malignant teratoma
Germ cell tumor
Usually contains more solid components
May not be able to tell difference of U/S
Primary Choriocarcinoma of the Ovary
Germ cell tumor
May lead to precocious puberty
Embryonal carcinoma
Germ cell tumor
Highly malignant
Unilateral
May lead to precocious puberty
U/S appearance of germ cell tumors:
purely cystic
solid
highly echogenic
cul-de-sac fluid
liver mets
nodal mets
abdominal ascites
Ambiguous Genetalia
1/5000 babies born with this
Early diagnosis is important
Ultrasound helps speed sexuality assignment
Vaginal atresia, fused labia, clitorimegaly, cryptorchidism
Hermaphrodite
has both ovarian and testicular tissue
Precocious Puberty
Puberty prior to age 8
Most causes are idiopathic
May be caused by pituitary or other endocrine abnormality
Pt’s experience breast development, pubic hair and menstruation
McCune-Albright Syndrome
Form of precocious puberty
Fibrous dysplasia of bone associated with café-au-lait skin pigmentation
Endocrine hyperfunction
Have large ovarian cysts
Large size discrepancy between the two ovaries
Menopause
Permanent cessation of menstrual activity
Cessation of ovulation, decreased estrogen and progesterone levels
Usually occurs between 35-58
Clinical post-menopausal problems are quite different from pre-menopausal women
Vaginal bleeding is concerning
Increased incidence of GYN cancer
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Replaces estrogen and progesterone in post-menopausal women
Relieves symptoms associated with menopause
Vaginal dryness, mood swings, hot flashes, bone & heart problems
Prevents severe osteoporosis
RIsk factors of Hormone Replacement Therapy:
MAY actually increase cardiovascular risks
Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB) can be a side effect
stimulating endometrium
If the patient IS on HRT, expect:
Cyclic bleeding
Thicker endometrium
Reduced risk of osteoporosis
Slightly increased risk of endometrial cancer
Increased breast cancer risk
Increased blood clot risk
Increased heart attack risk
If the patient is NOT on HRT, expect:
Atrophy of uterus, endometrium, and ovaries
vaginal drying
hot flashes
increased risk of osteoporosis
decreased fibroid size
no estrogen feeding them
Post-menopausal uterus
Nabothian Cysts of the cervix are commonly seen
Uterine atrophy
Vascular calcifications within the uterus
Normal post-menopausal endo NOT on HRT:
thin and hyperechoic
no bleeding
endometrium <8 mm
Abnormal post-menopausal endothelium NOT on HRT:
Thickened
Irregular
Heterogenous
Bleeding
Post-menopausal endo on HRT → Estrogen and Progesterone
Thin or <8 mm
Hyperechoic
Post-menopausal endo on HRT → Unopposed Estrogen (no Progesterone)
Will be thicker d/t estrogen
Should still be <8 mm
Post-Menopausal bleeding differential diagnosis:
HRT
Vaginitis
Endometrial Carcinoma, polyp, or hyperplasia
Cervical carcinoma or polyp
Ovarian tumor
Bleeding from the urinary tract
Post-menopausal ovaries U/S appearance:
Hypoechoic with absense of follicles
Size varies with hormonal status and number of years since menopause
Not always visualized
atrophy and migrate closer to pelvic walls
High resistance flow in ovarian artery
Post-menopausal Ovaries
Higher incidence of cancer
any cyst should be thoroughly evaluated
small ovarian cysts occur in 15%
CA 125 → screening for ovarian cancer
Usually measures 2 × 1.5 × 0.5 cm
If cysts seen on PM ovary:
<5 cm and simple
follow with ultrasound
>5 cm
surgery is recommended
Any septations or solid components warrant surgery regardless of size