Topic 1 - Key Concepts
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Name the different parts of a light microscope
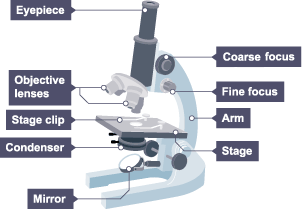
Microscope slide
a clear plastic/ glass piece on which you mount your specimen being investigated
Cover slip
a square clear plastic/ glass piece which goes on top of your specimen
Stage
where you clip your microscope slide into place
Eyepiece lens
part of the microscope you look through
Objective lens
these magnify the image and there are different types with different magnification levels
Lamp
this shines light to the specimen so it can be seen more clearly
Coarse/ Fine adjustment knobs
help focus the image so it is clearer
Differences between a light microscope and an electron microscope
Light microscope: used to study living cells, regular use when relatively low magnification and resolution is enough
Electron Microscope: provides higher magnification and higher resolution images, cannot be used to view living cells
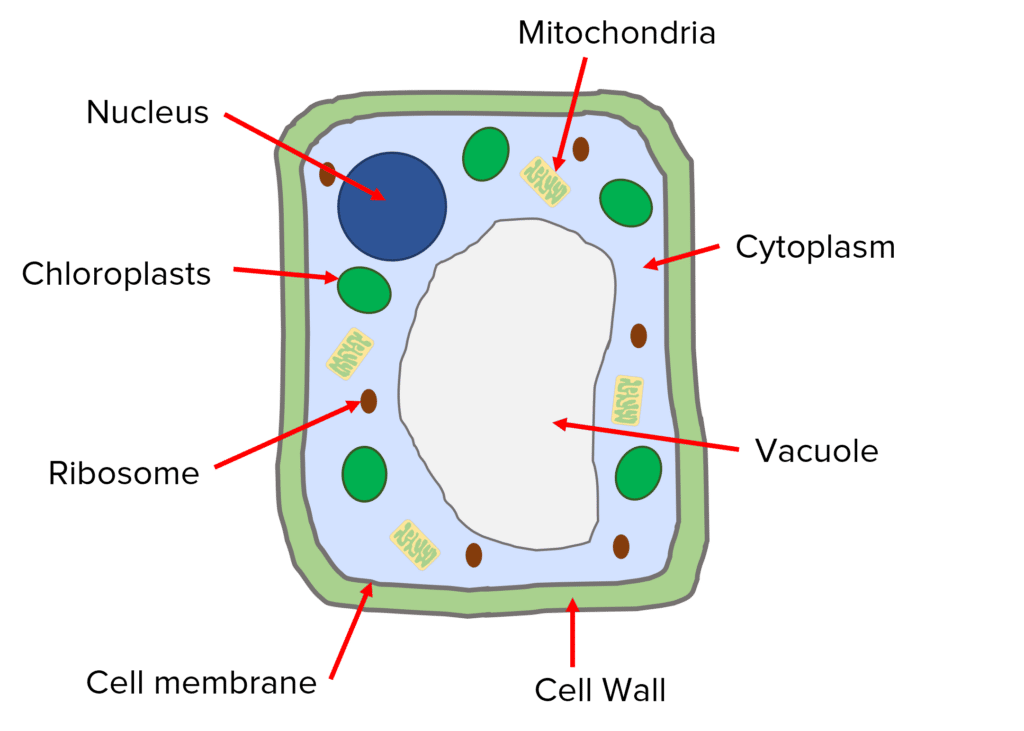
Draw a plant cell
Draw an animal cell
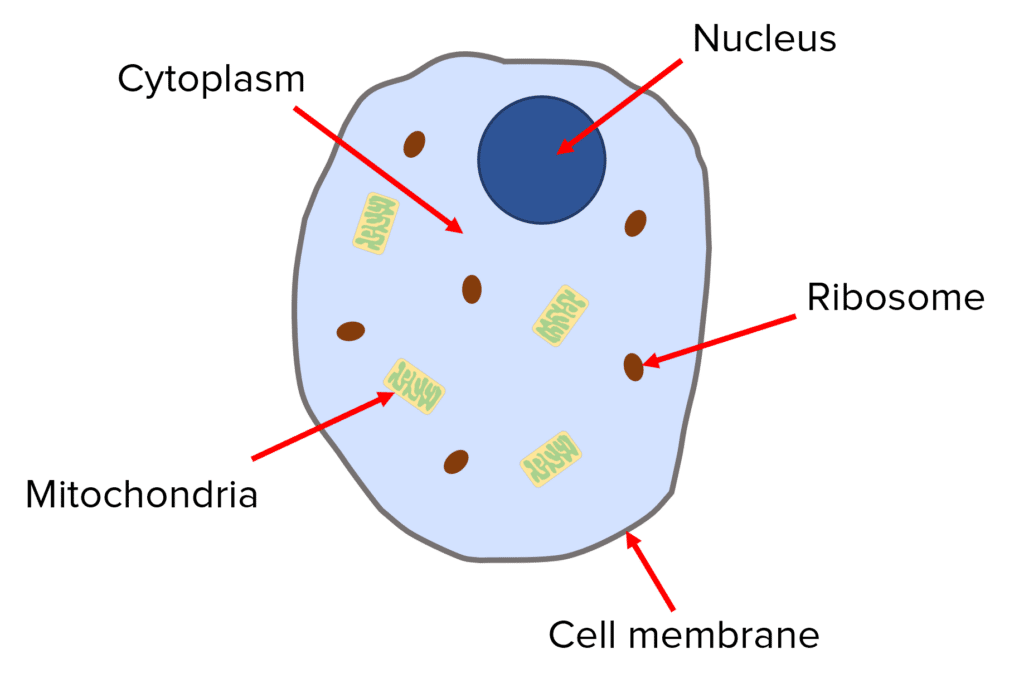
Nucleus
Contains dna , controls cell activities
Cell wall
Made of cellulose, keeps cell rigid
Cell membrane
Allows substances in and out of cell
Vacuole
fluid filled sac that stores water
Chloroplasts
Contains chlorophyll which is needed for photosynthesis
Ribosomes
Where proteins are made
mitochondria
Where respiration takes place
Draw a plant cell
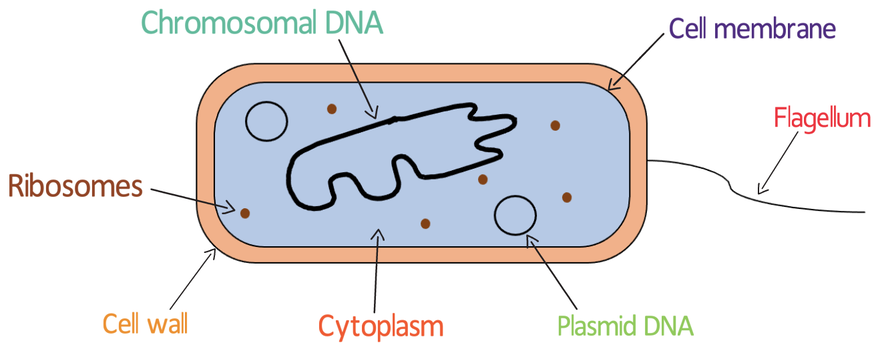
Flagellum
tail for moving
Flexible cell wall
Only found on bacteria cell, not made of cellulose
Chromosomal DNA
One long strand of DNA that controls the bacteria
Plasmid DNA
small loops of extra DNA
Sub cellular structure
compartments' where specific processes take place within the cell
Eukaryote
With nucleus
Prokaryote
Without nucleus
Differences between plant, animal and bacterial cell
Plant: eukaryotic (with nucleus), has cell wall, vacuole and chloroplasts
Animal: eukaryotic (with nucleus), has NO cell wall, vacuole and chloroplasts
Bacteria: prokaryotic (without nucleus) , has cell wall, no vacuole or chloroplasts , has flagellum, chromosomal DNA, plasmid DNA
Different between mm and um
1mm (millimeter) = 1000um (micrometer)
Formula for image, actual size and magnification
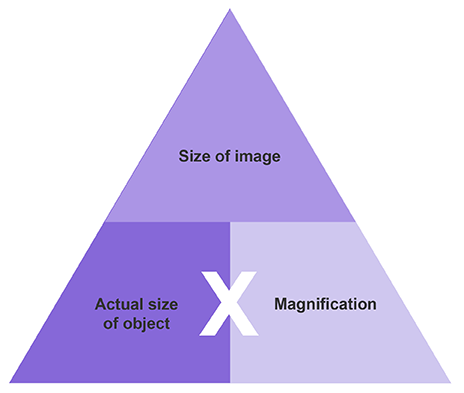
Total magnification formula
Total magnification = eyepiece lens X objective lens