Blood
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
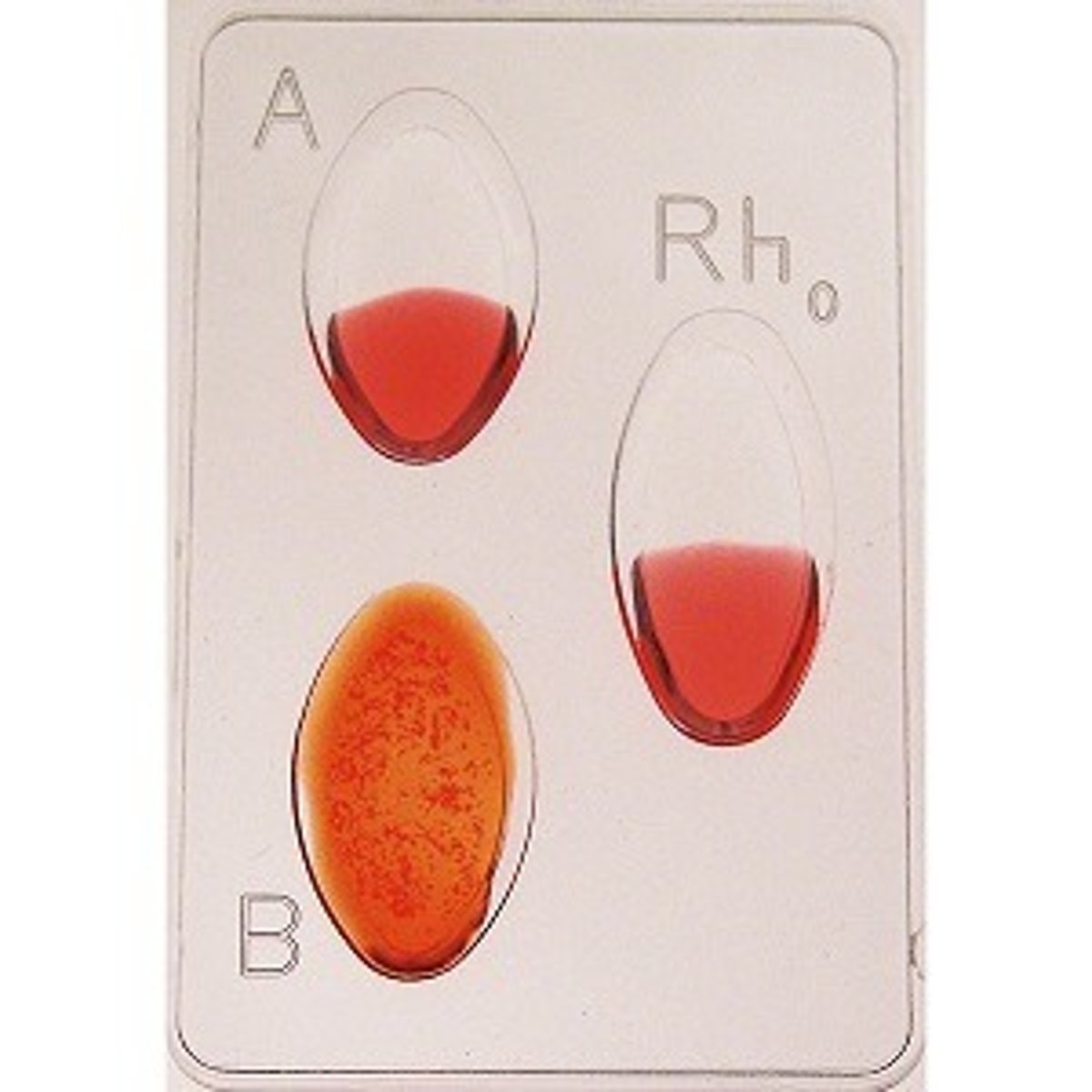
B negative
What is the blood type?

histamine and heparin
What do the granules of this cell release?
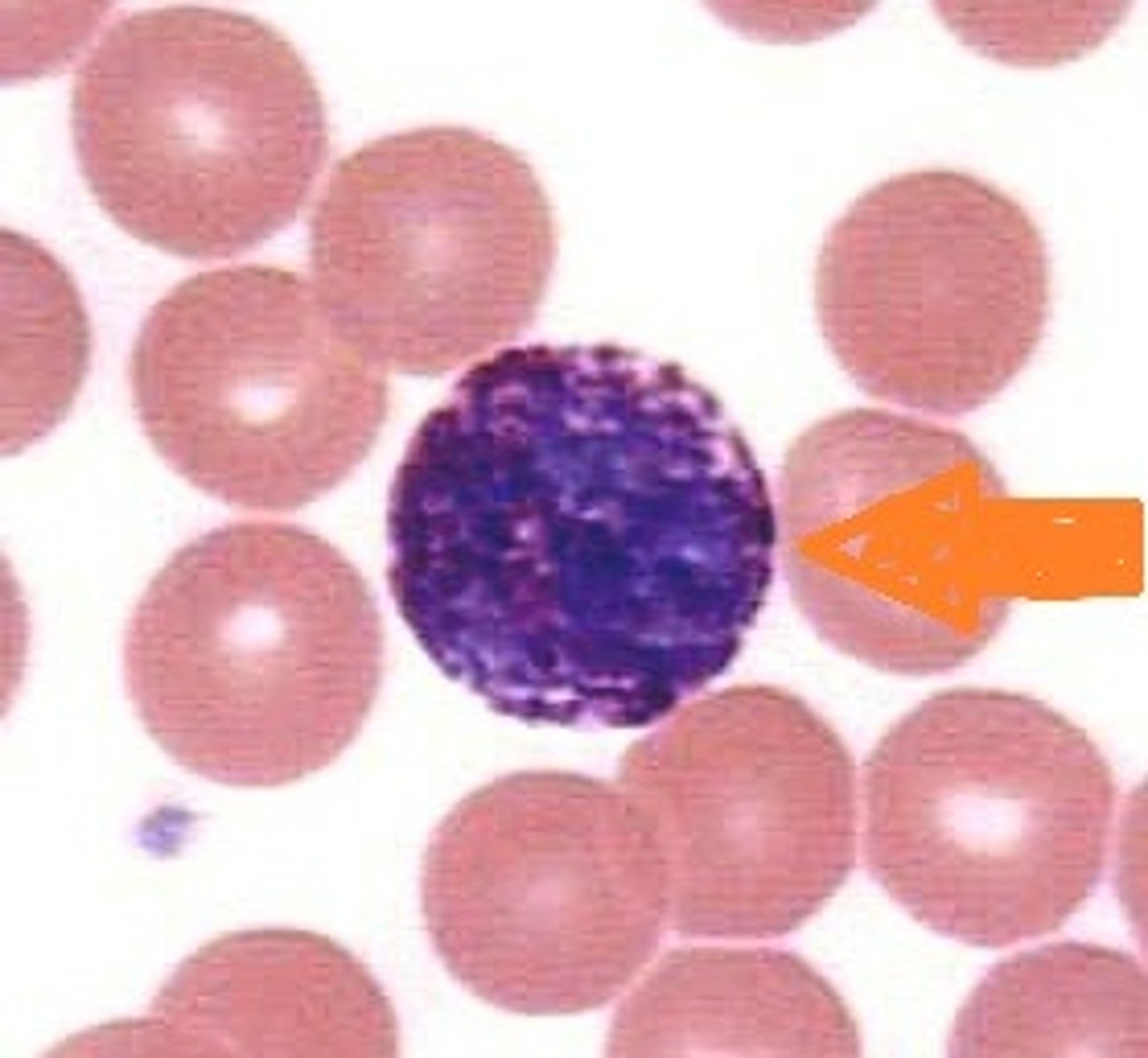
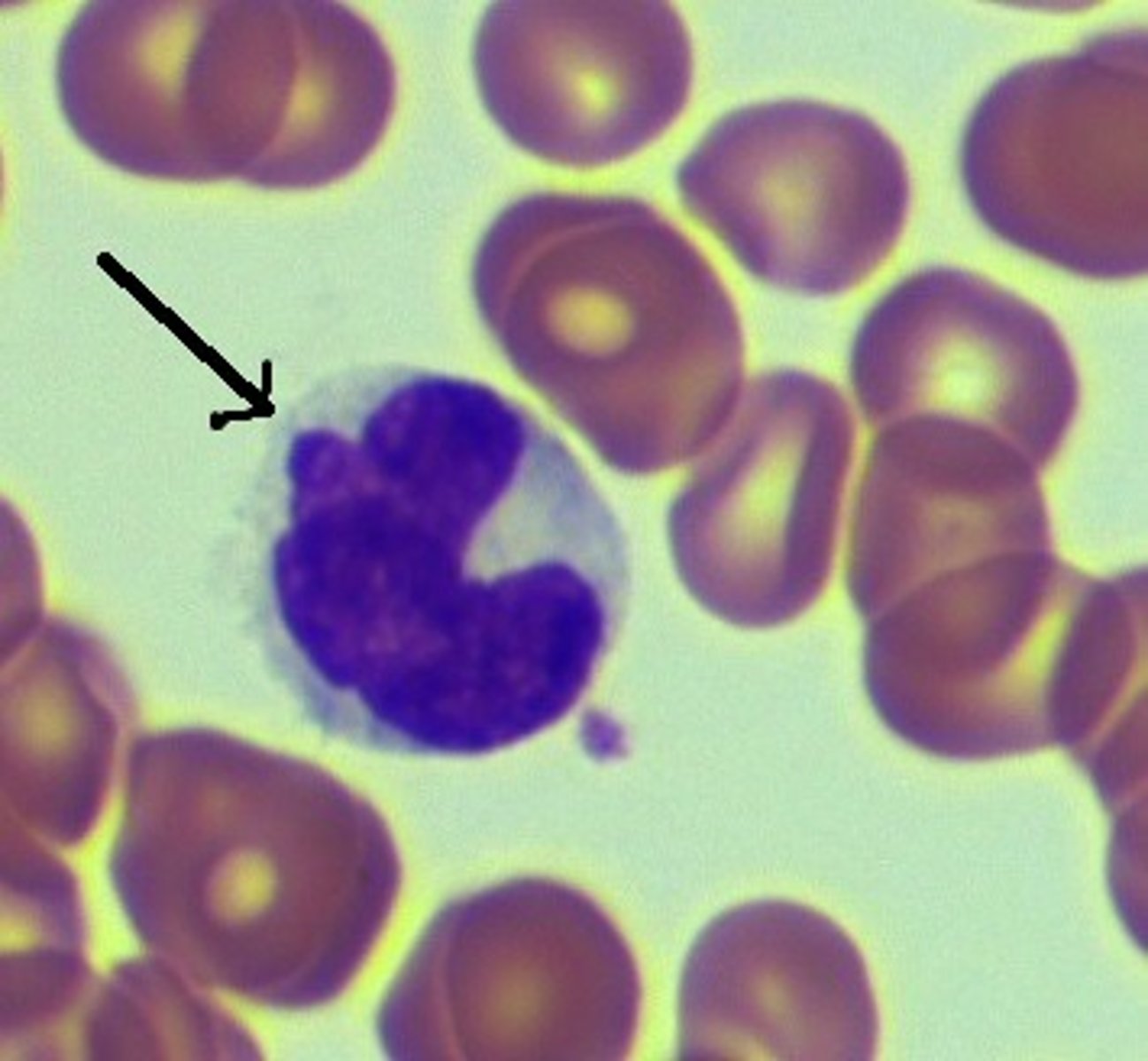
eosinophil
Name the leukocyte.
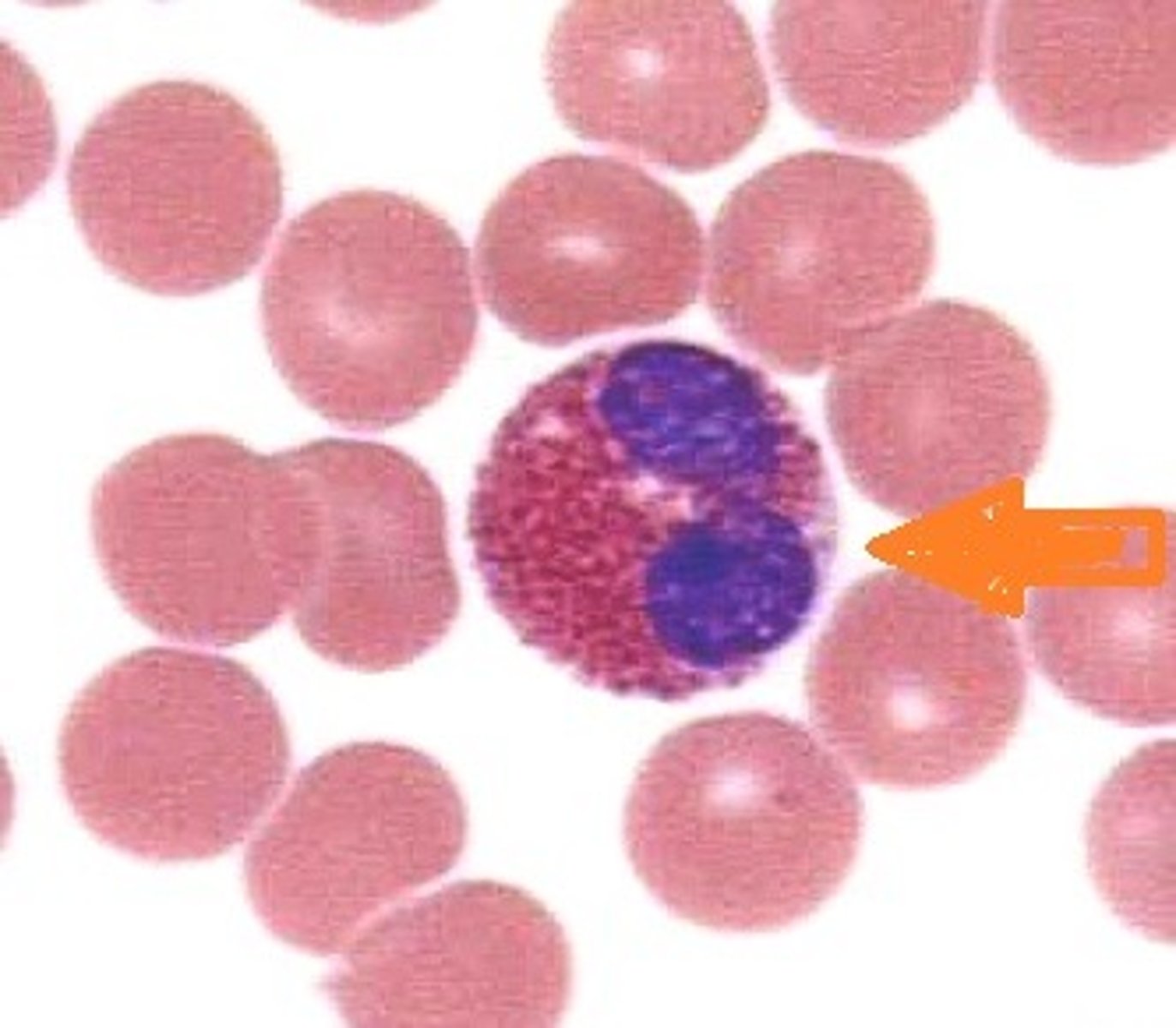
neutrophil
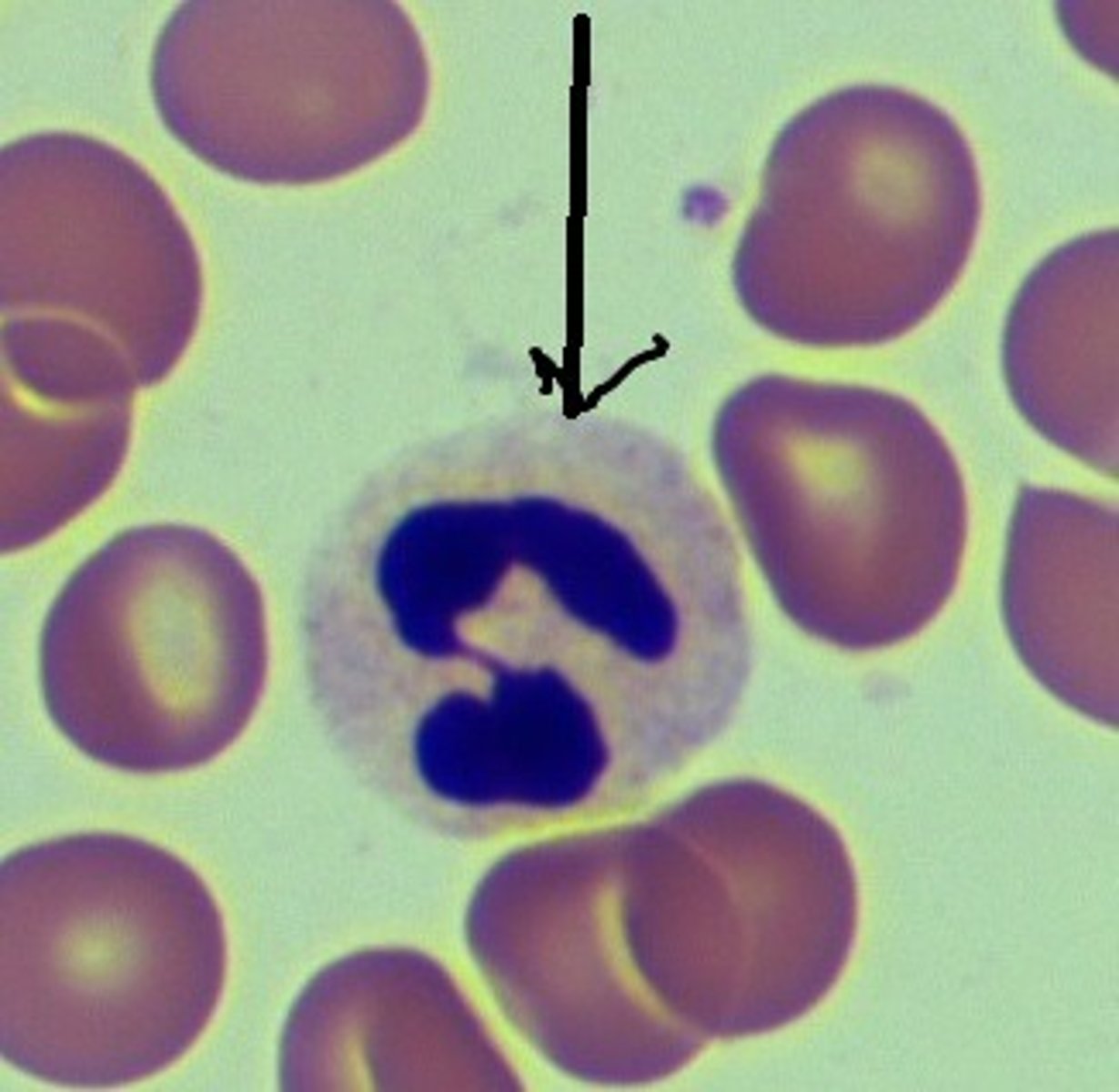
Name the leukocyte.
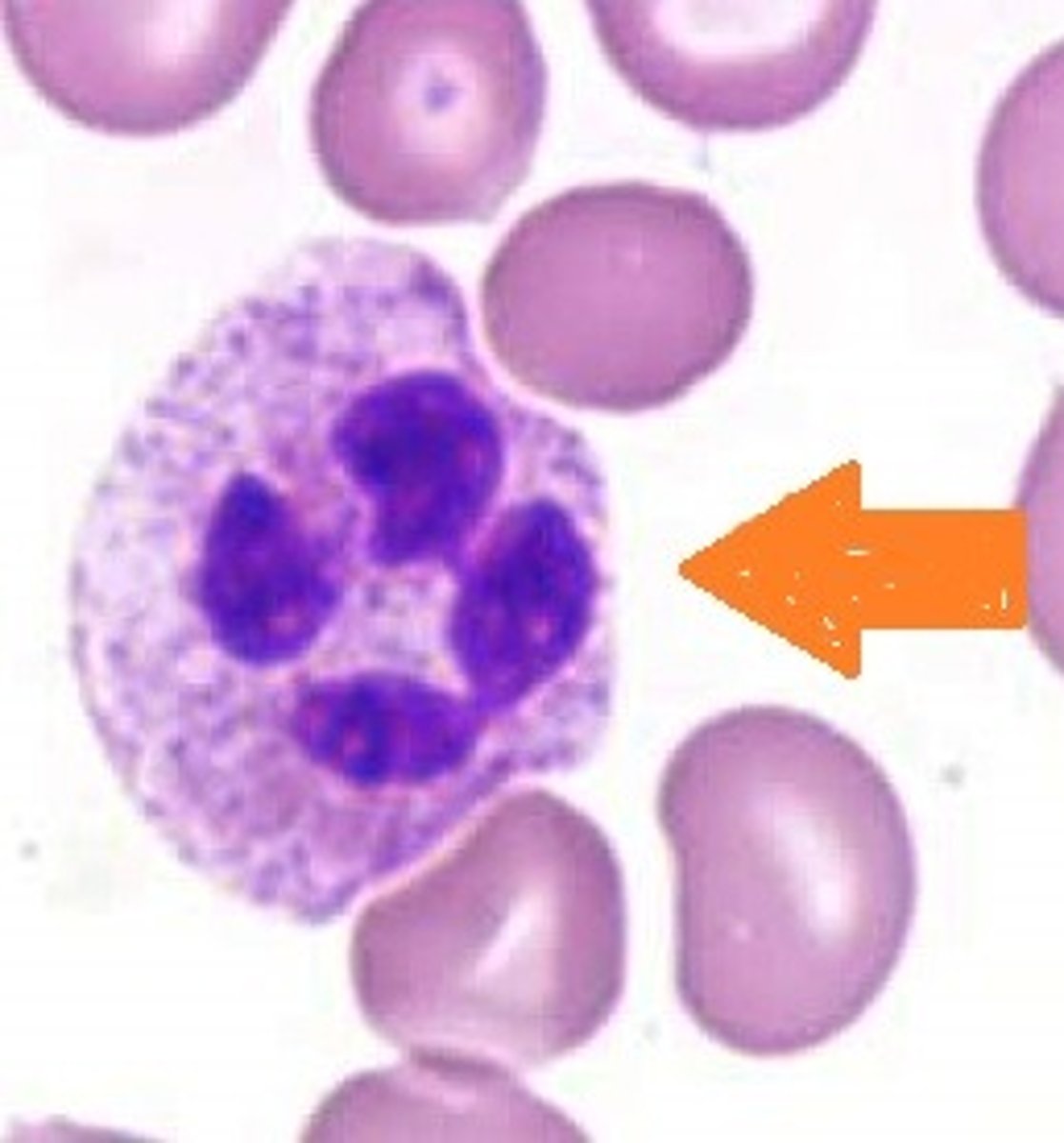
monocyte
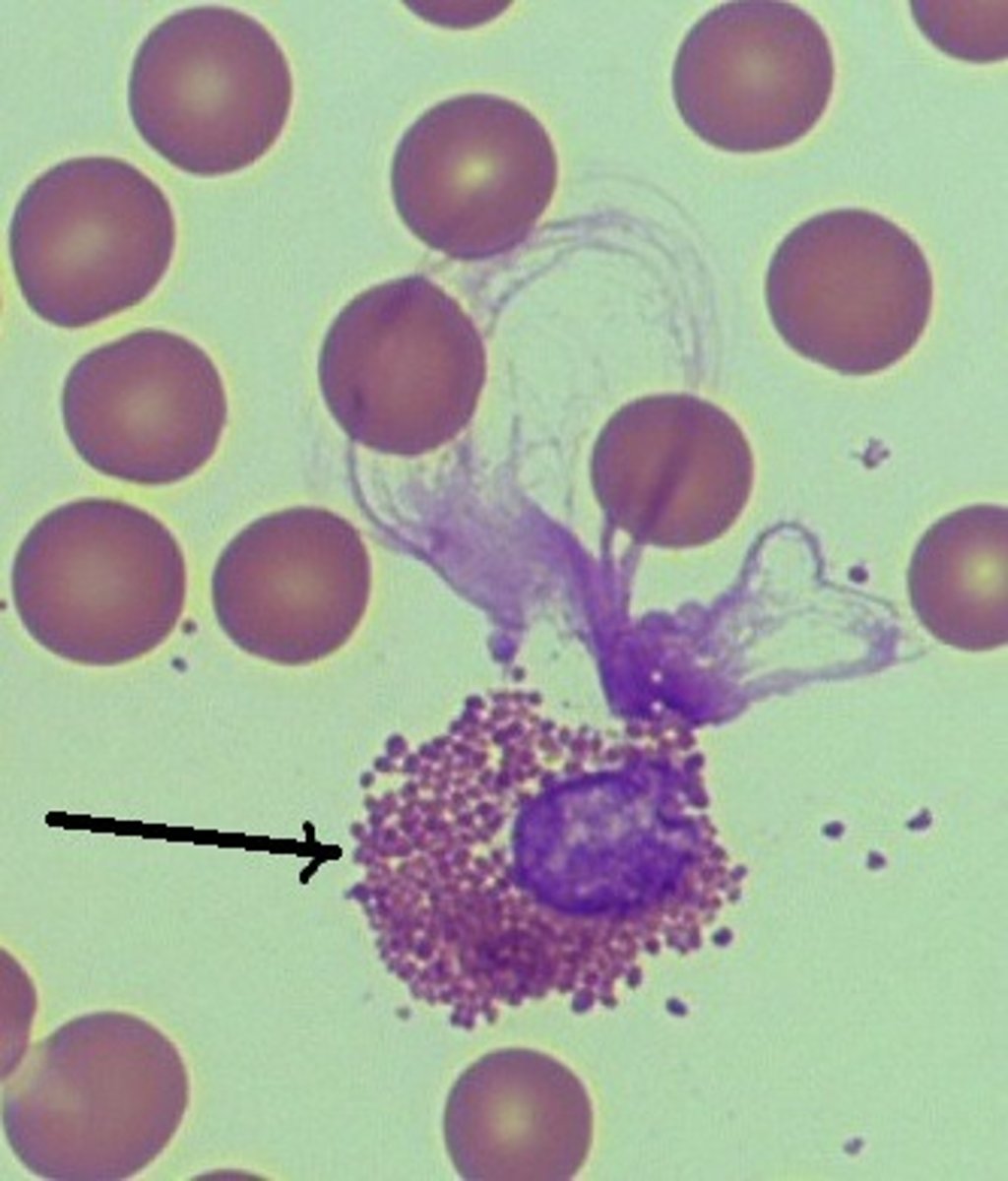
Name the leukocyte.
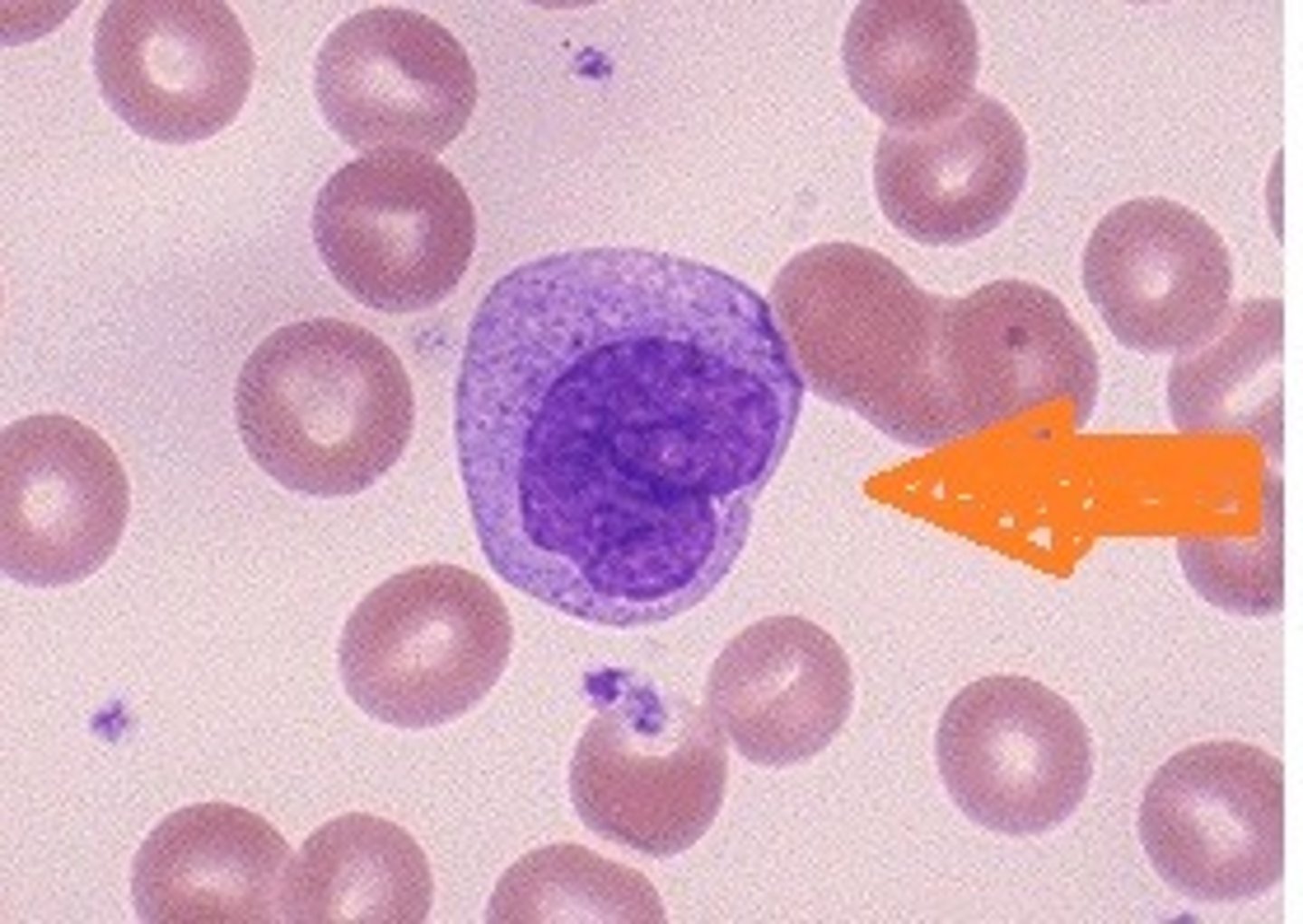
lymphocyte
Name the leukocyte.
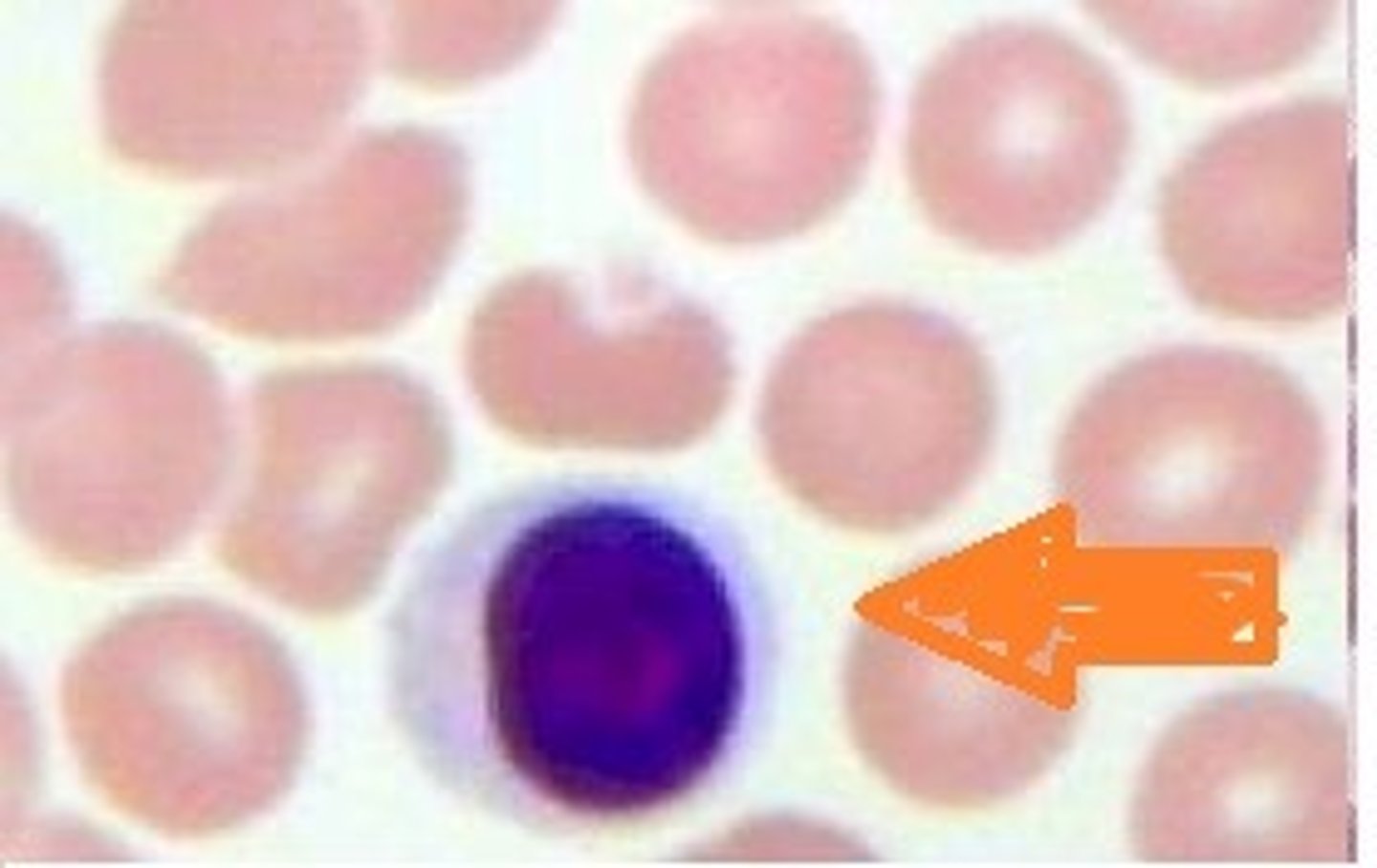
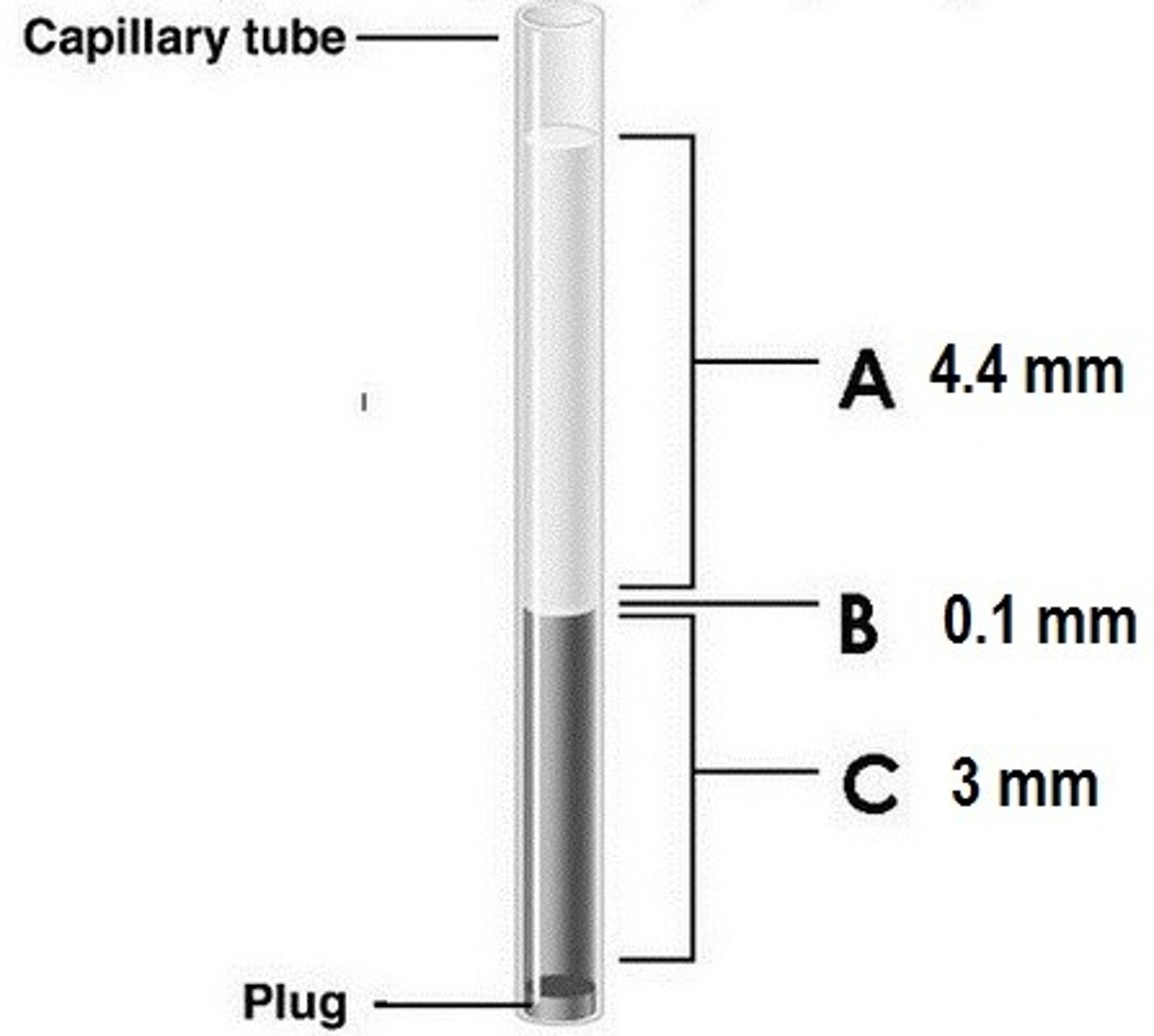
40%
Determine the hematocrit.
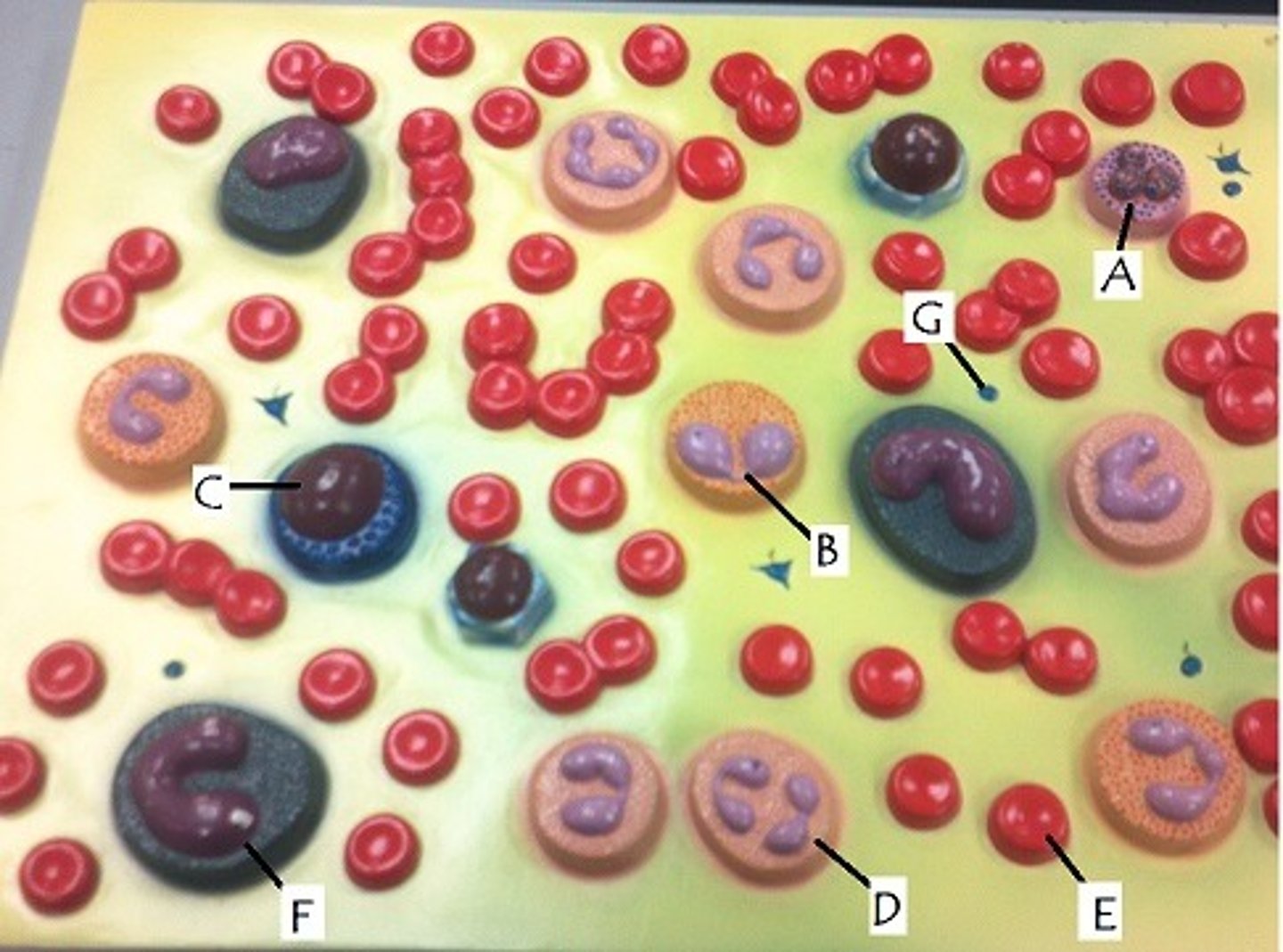
B, D, F
cells that are phagocytic
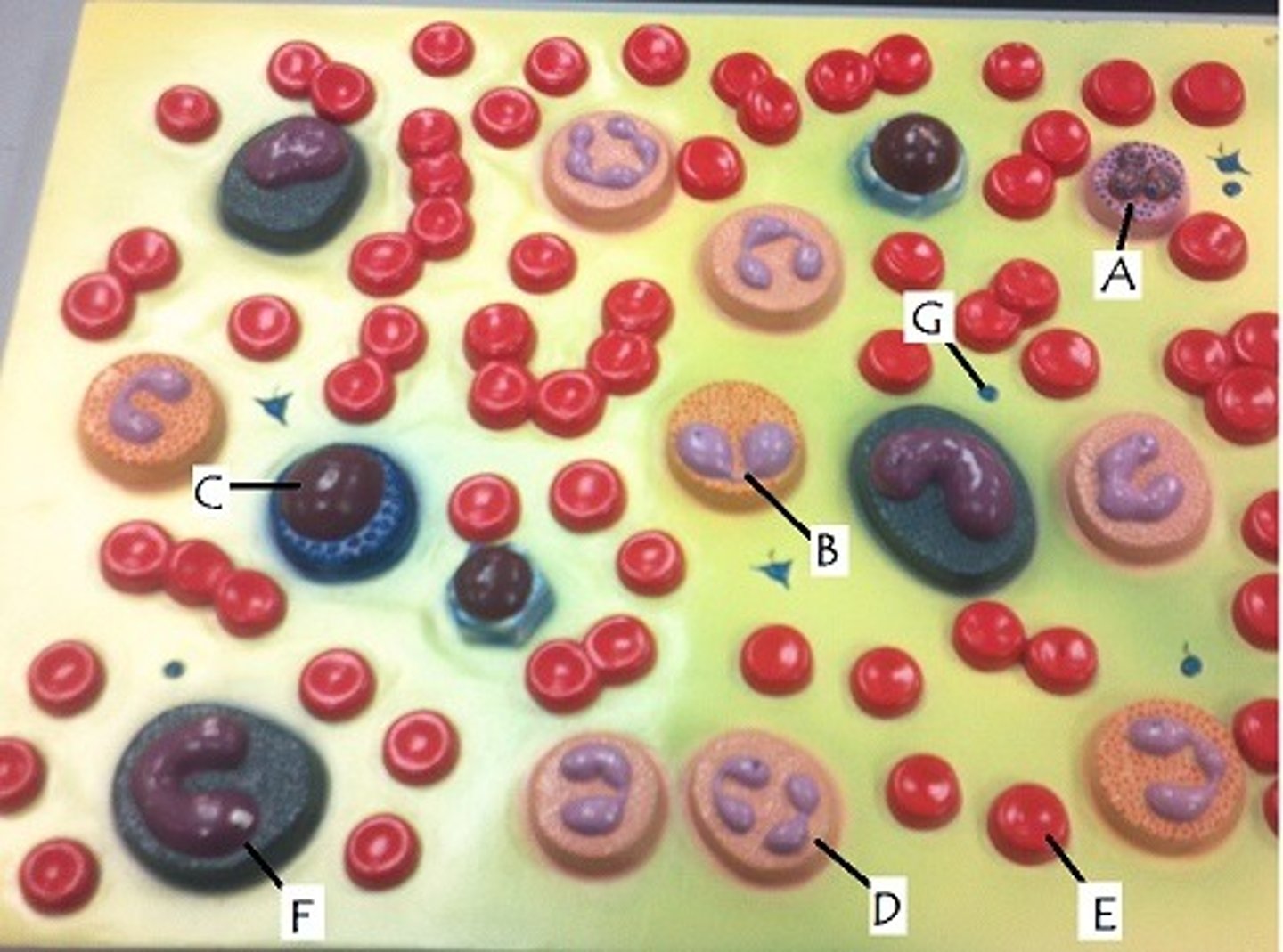
B
increased in parasitic infections
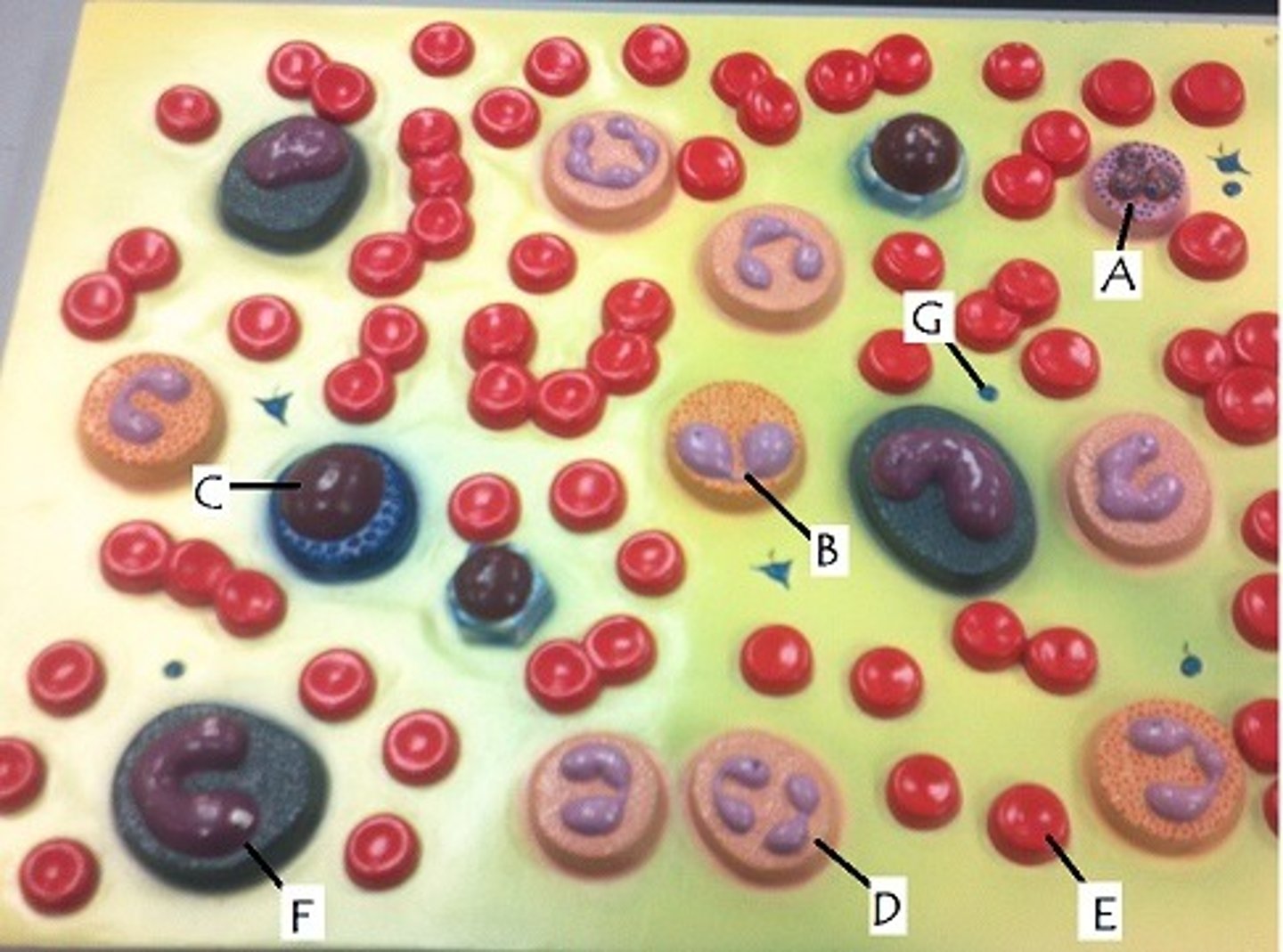
C
longest living of all leukocytes
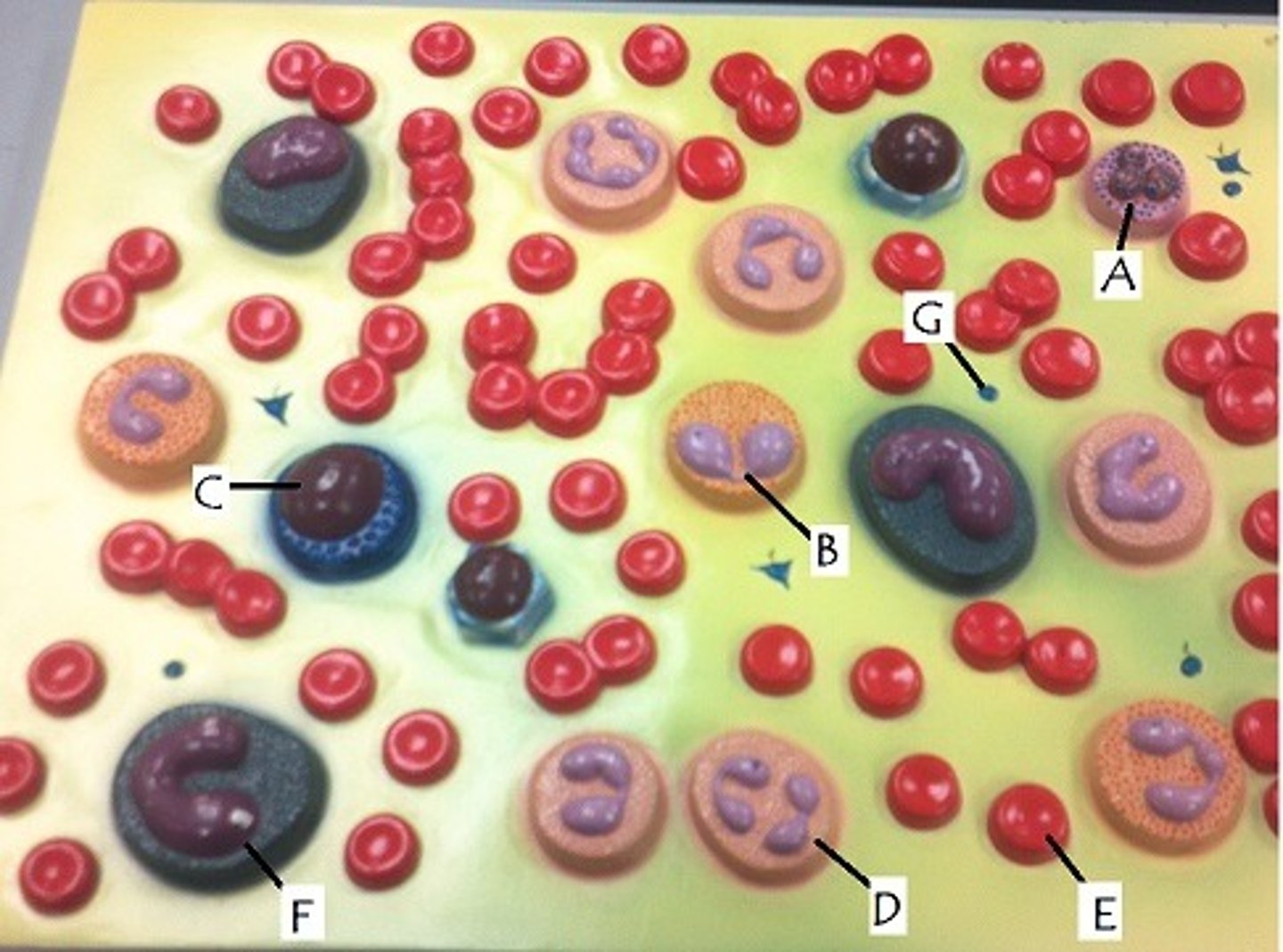
F
become macrophages; increased in mononucleosis, typhoid fever
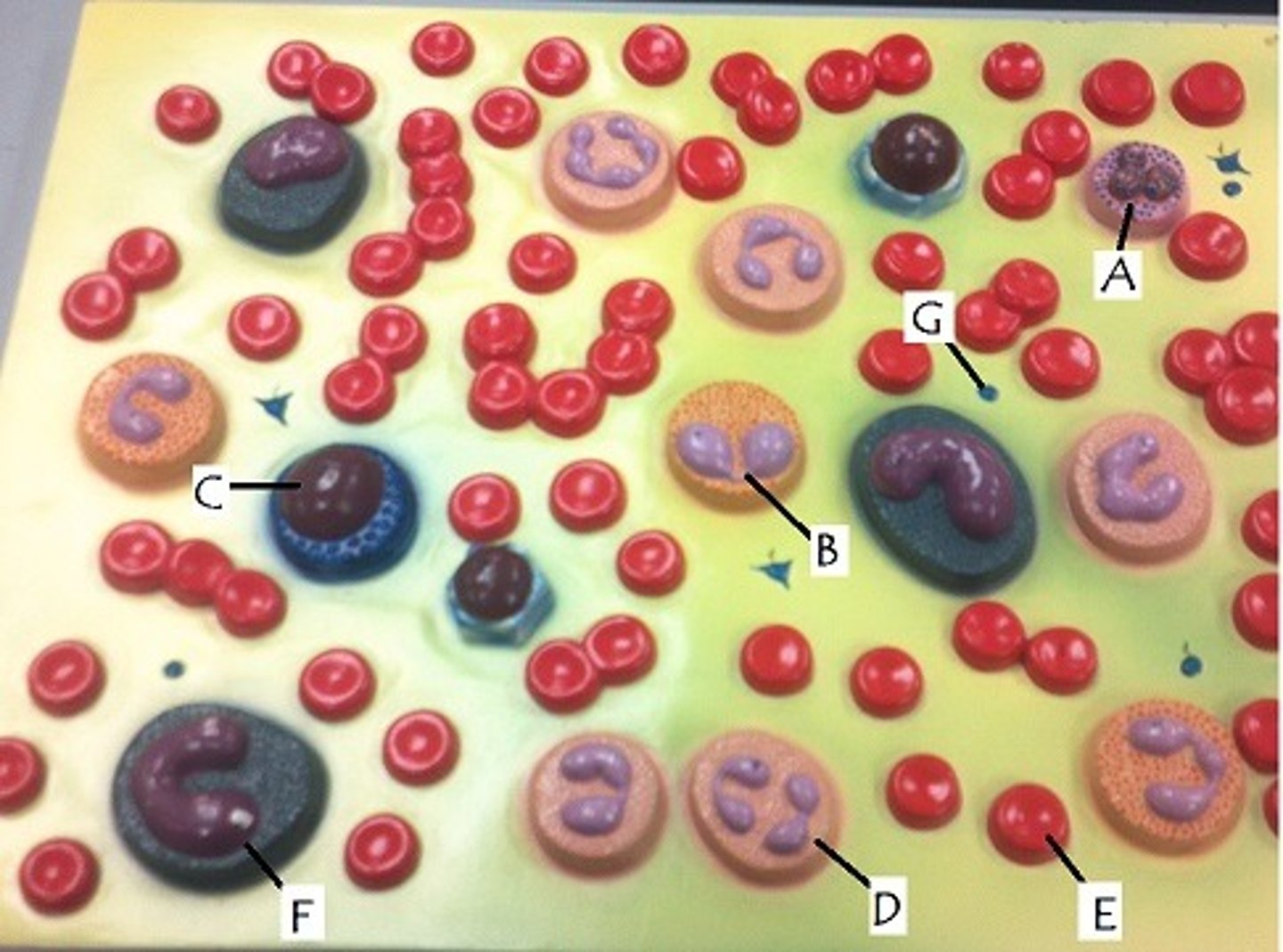
D
increased in acute infections
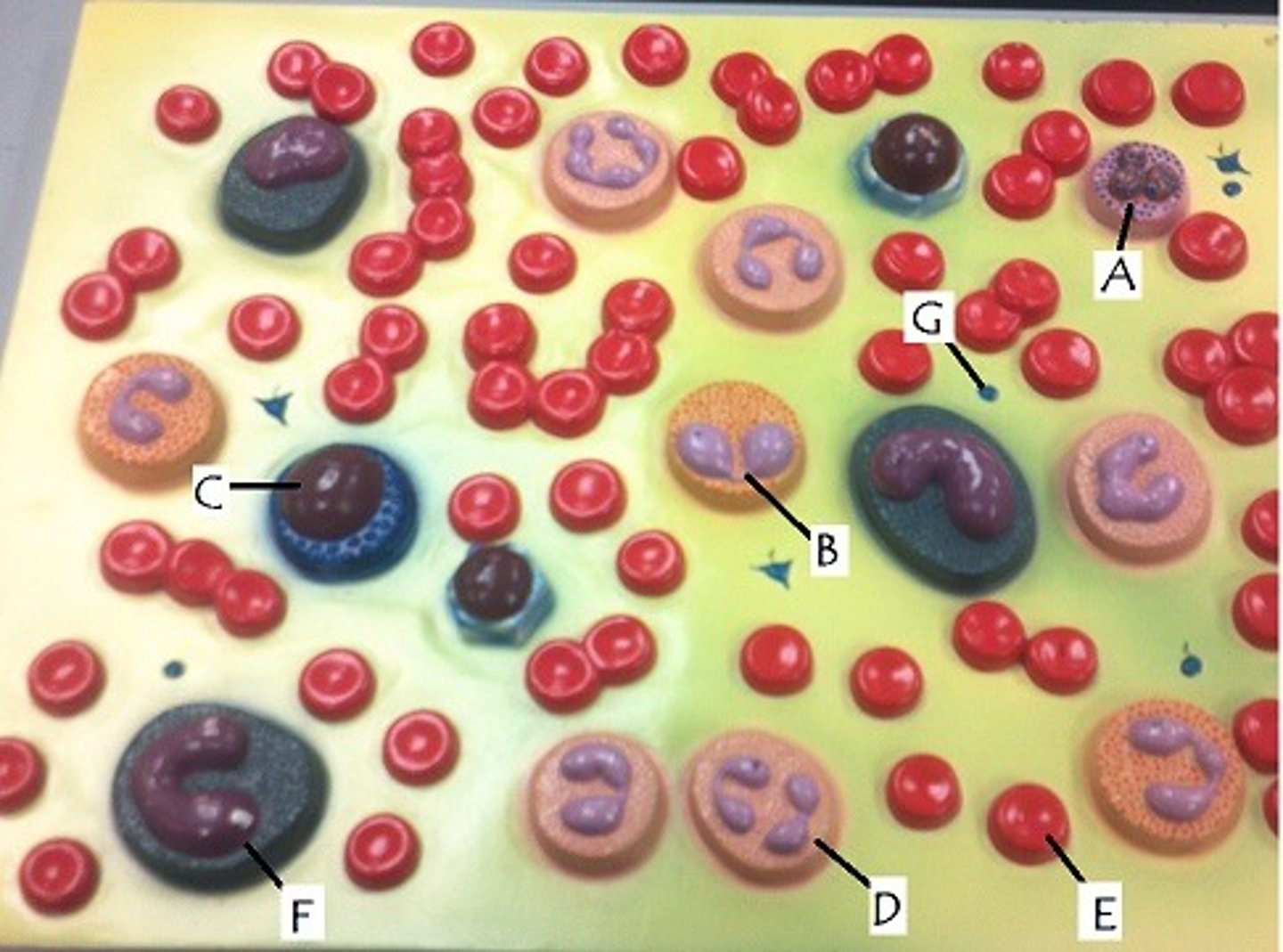
E
production stimulated by EPO
hematocrit
% of red blood cells in a sample of blood
agglutination
clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by cross-linking of antigen-antibody complexes.
hemoglobin
An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that reversibly binds oxygen.
hemostasis
stoppage of bleeding
iron
mineral in hemoglobin that binds oxygen
AB+
People with which blood type(s) could receive blood from people who are AB+?
O+, AB+, A+, B+
People with which blood type(s) could receive blood from people who are O+?
B-, B+, AB+, AB-
People who are B- could donate blood to people who are _____.
agglutinins
Specific antibodies formed in the blood.
agglutinogens
Antigens formed on the surface of red blood cells, whose presence and structure are genetically determined.
C
involved in specific immune defense
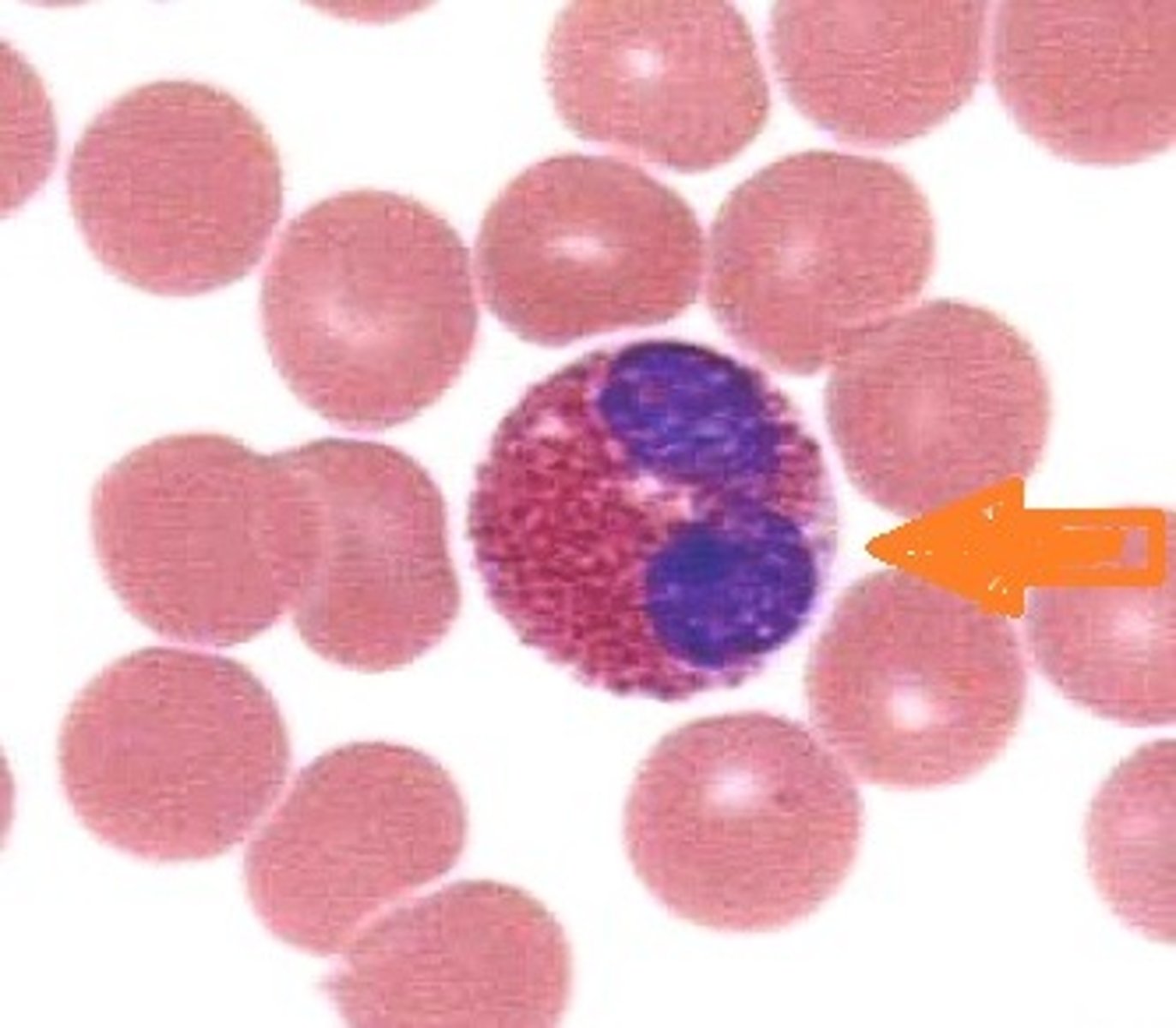
basophil
Which white blood cell is the most elevated in inflammatory reactions?
histamine
What is found in the granules of this cell?
anemia
A condition in which the blood is deficient in red blood cells, in hemoglobin, or in total volume. Oxygen carrying capacity is diminished.
plasma
Fluid portion of blood
platelet
Identify
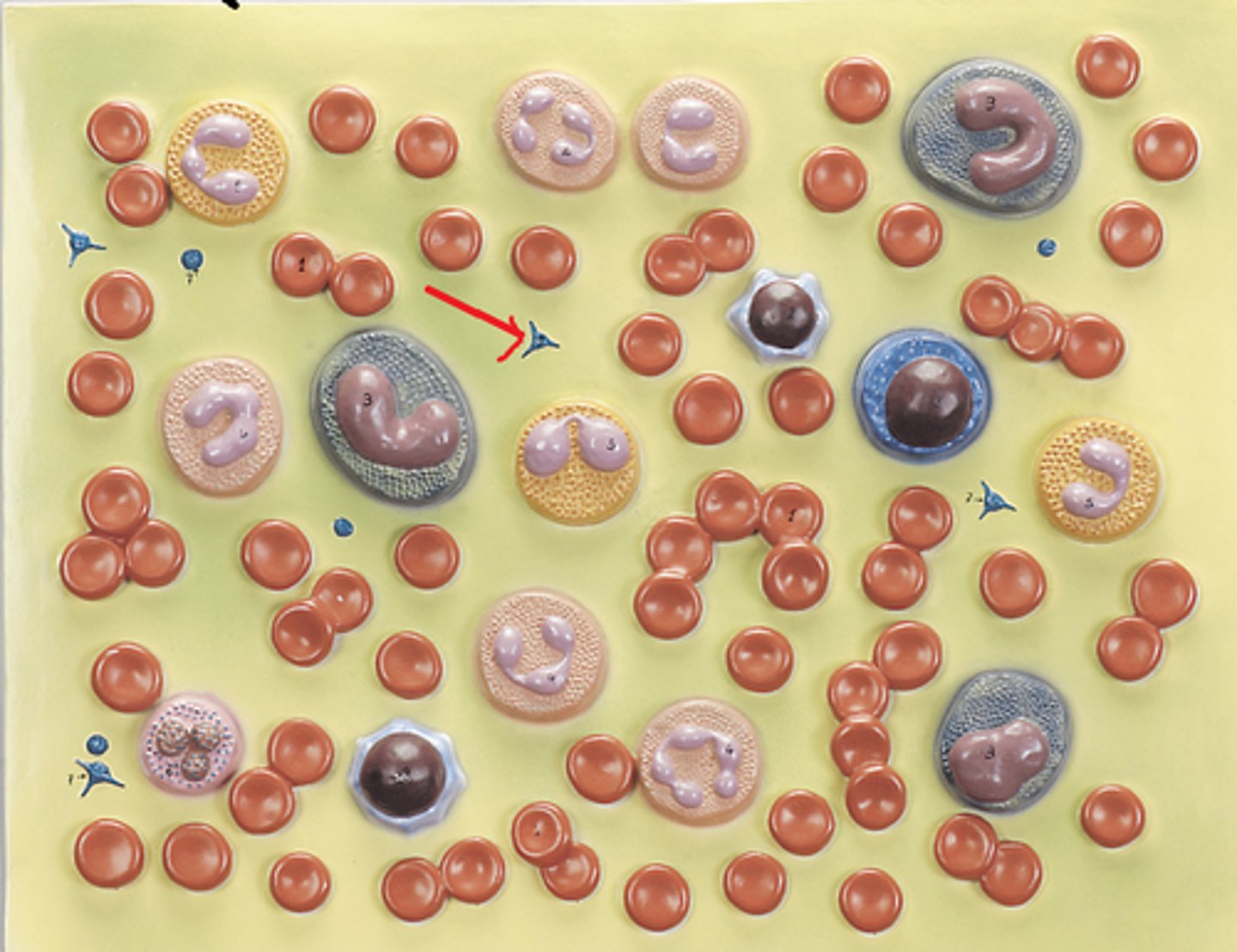
Platelets are fragments of what giant cells?
megakaryocytes
In bone marrow, _____ cells give rise to red blood cells, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and platelets.
myeloid stem
In bone marrow, _____ cells give rise to lymphocytes.
lymphoid stem
coagulation
function of platelets
serum
Clear fluid portion of blood that remains after coagulation
monocytes and lymphocytes
agranulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
granulocytes
O negative
universal donor
AB positive
universal recipient
A negative, B negative, AB negative, O negative
What are the possible blood types of the children of a couple whose blood types are A negative and B negative?
anti-B
agglutinins of people who are A positive
anti-A
agglutinins of people who are B positive
none
agglutinins of people who are AB positive
anti-A and anti-B
agglutinins of people who are O positive
A and D
agglutinogens of people who are A positive
D
agglutinogens of people who are O positive
B and D
agglutinogens of people who are B positive
A, B, and D
agglutinogens of people who are AB positive
A and B
agglutinogens of people who are AB negative
A
agglutinogens of people who are A negative
B
agglutinogens of people who are B negative
none
agglutinogens of people who are O negative
anti-A, anti-B
agglutinins of people who are O negative
anti-B
agglutinins of people who are A negative
anti-A
agglutinins of people who are B negative
none
agglutinins of people who are AB negative
basophil
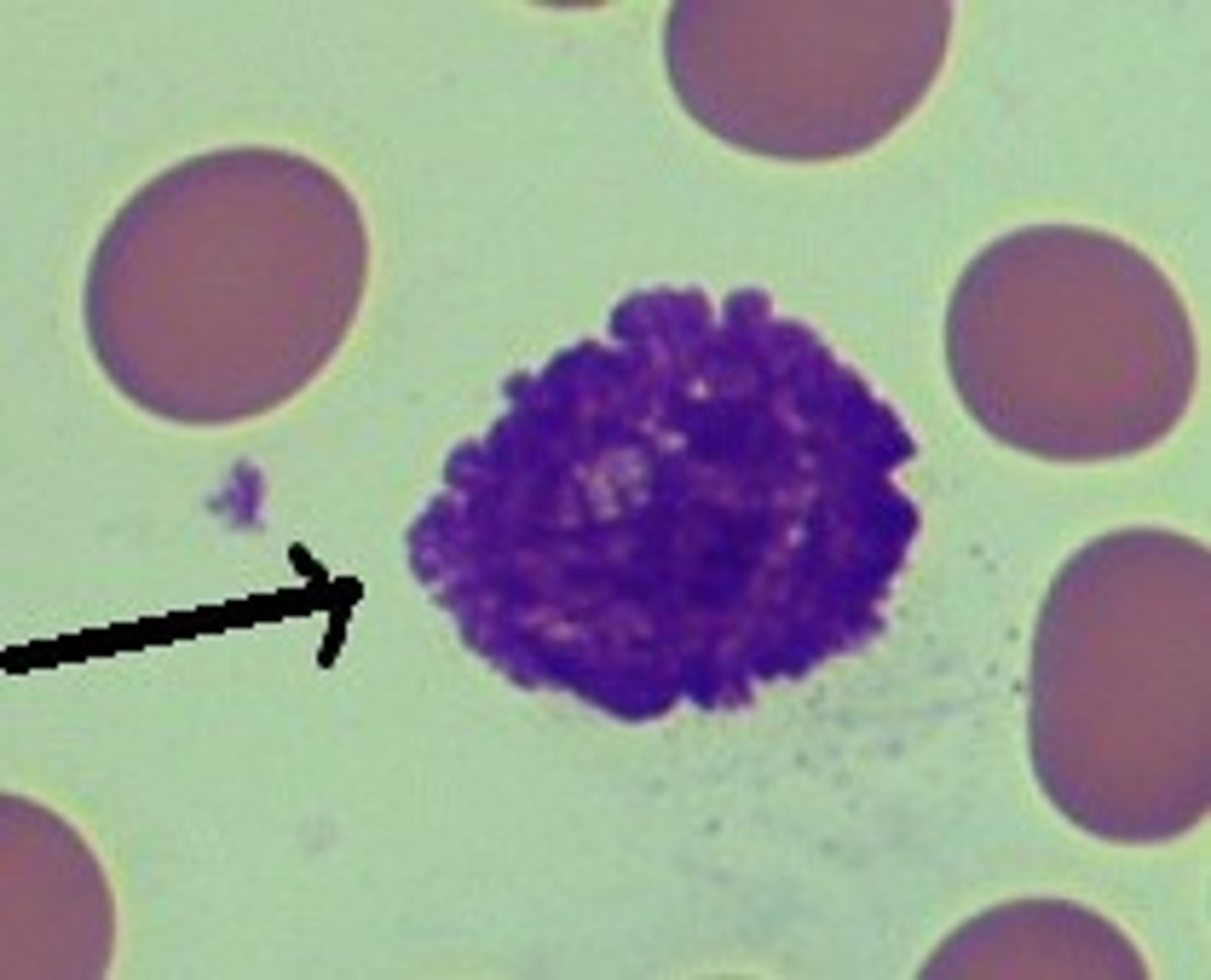
eosinophil
neutrophil
platelet
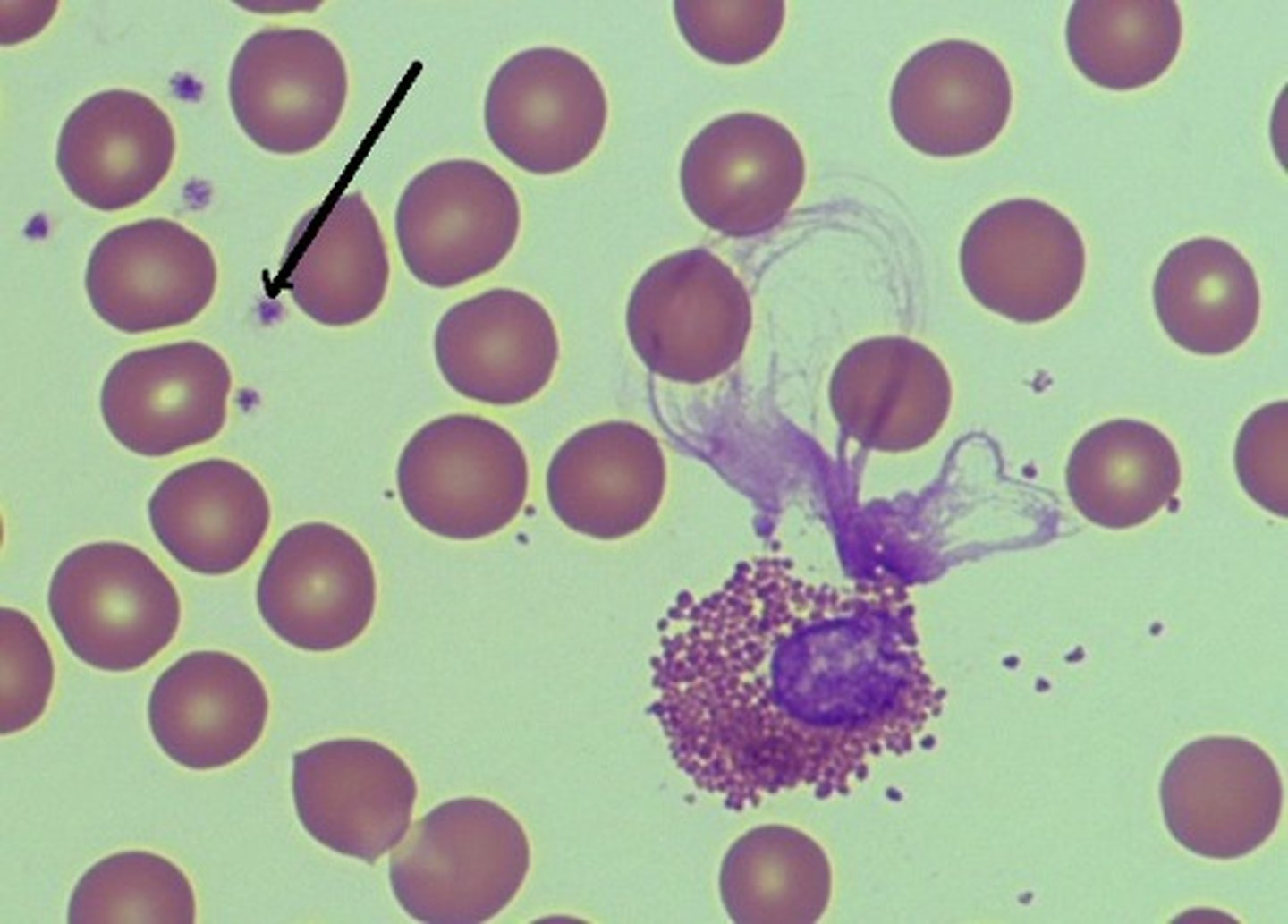
lymphocyte
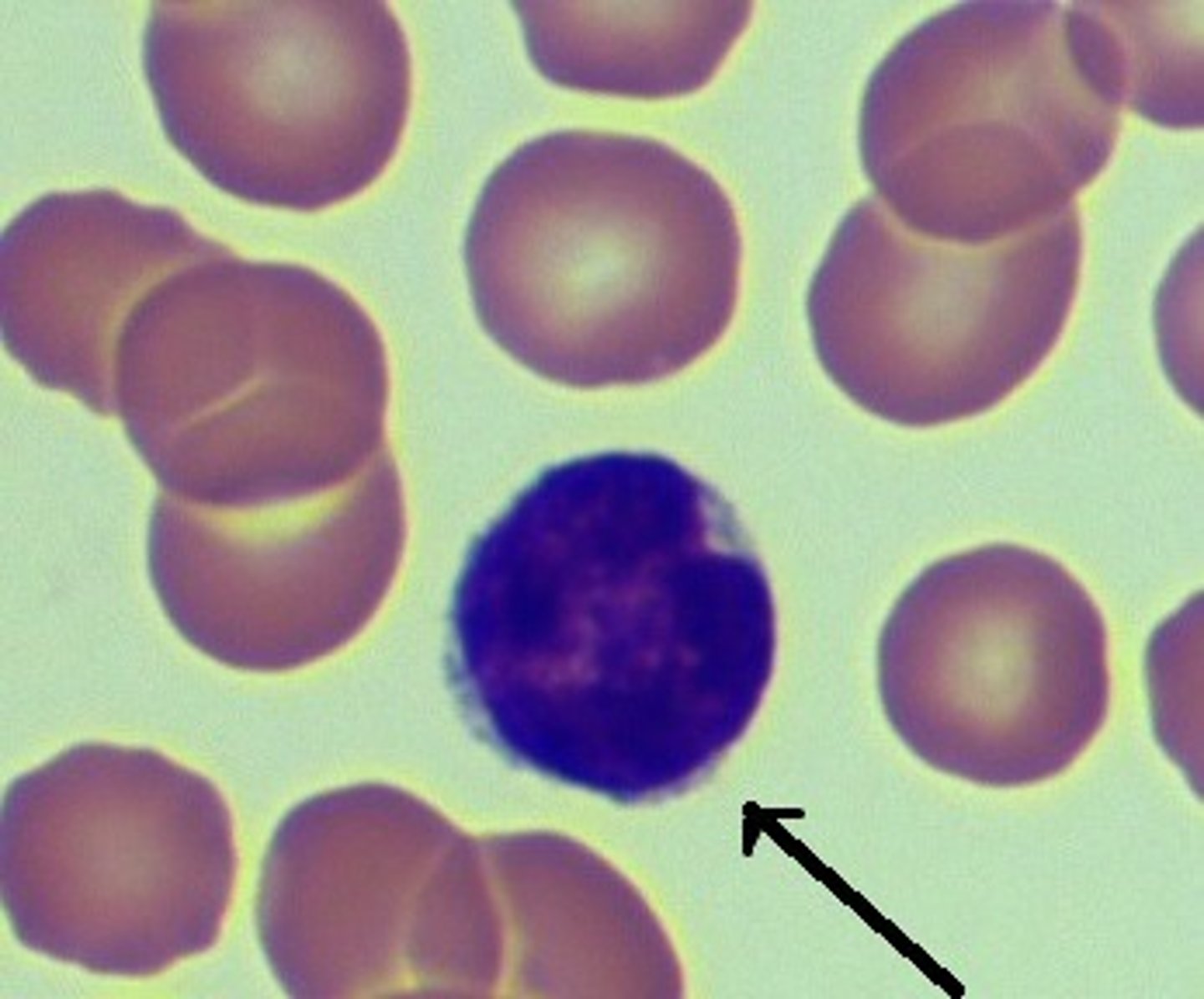
monocyte