Pectoral Girdle and Shoulder Muscle Movements
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
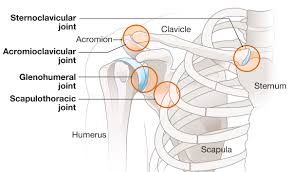
what makes up the sternoclavicular joint
sternal end of clavicle
articular disc
manubrium of sternum
movement of sternoclavicular joint
elevation and depression (lower angular range for depression)
protraction (forward movement) and retraction (backward movement)
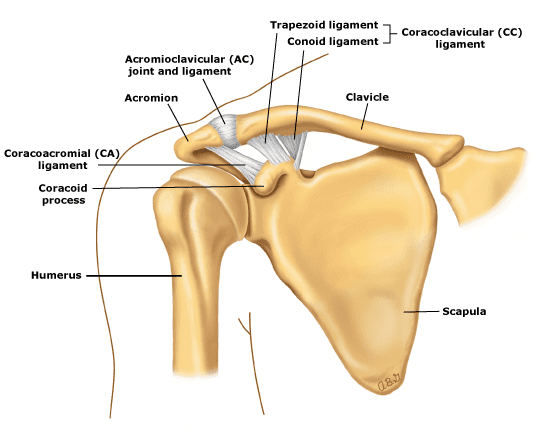
what makes up the acromioclavicular joint
clavicle
acromion and coracoid process of scapula
movement of acromioclavicular joint
gliding and rotation during scapular movement (overhead reaching and gliding)
what makes up the scapulothoracic joint
convex surface of posterior thoracic cage
concave surface of anterior scapula (attached to skeleton via acromioclavicular joint and sternoclavicular joint)
not true synovial joint (not surrounded by ligaments/capsule)
movement of scapulothoracic joint
elevation
depression
abduction (protraction)
adduction (retraction)
downward rotation (medial rotation)
upward rotation (lateral rotation)
what makes up the glenohumeral joint
head of humerus
glenoid cavity
glenoid labrum (connective tissue)
coracoid process of scapula
acromion of scapula
coracoacromial ligament (connects coracoid process to acromion)
enables widest range of movement bc shallow glenoid fossa can articular with enitre surface of humeral head - relatively unstable, frequently dislocated
movement of glenohumeral joint
flexion (arm towards face)
extension (arm away face)
abduction
adduction
medial rotation
lateral rotation
circumduction
how can we distinguish muscles of pectoral girdle
those that move the scapula, those that move the arm
scapula further divided according to location; anterior, posterior
anterior pectoral girdle muscles that move the scapula
pectoralis minor
serratus anterior
posterior pectoral girdle muscles that move the scapula
trapezius
levator scapulae
rhomboid major
rhomboid minor
muscles that elevate the scapula
trapezius (descending fibres) (P)
levator scapulae (P)
muscles that depress the scapula
trapezius (ascending fibres) (P)
pectoralis minor (A)
pectoralis major (P)
serratus anterior (A)
muscles that retract the scapula
trapezius (horizontal fibres) (P)
rhomboid major (P)
rhomboid minor (P)
muscles that protract the scapula
serratus anterior (A)
muscles that rotate the scapula
upward rotation:
trapezius (descending + ascending) (P)
serratus anterior (A)
downward rotation:
levator scapulae (P)
pectoralis major (P)
rhomboid major (P)
how can we group shoulder muscles that move the arm and distally attach to the humerus
extrinsic and intrinsic muscles
extrinsic located on axial skeleton
intrinsic located on scapula and/or clavicle
intrinsic shoulder muscles (6)
deltoid
teres major
teres minor (rotator cuff)
subscapularis (rotator cuff)
supraspinatus (rotator cuff)
infraspinatus (rotator cuff)
what are the rotator cuff muscles
teres minor, subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus
tendon surrounds head of humerus
strengthens joint capsule
supraspinatus, infraspinatus + teres minor distally attach onto greater tubercle
not teres major bc doesn’t cross glenohumeral joint
why are shoulder dislocations common
increase of stability within joint comes at a cost of mobility - large range of motion in glenohumeral joint
extrinsic shoulder muscles (2)
pectoralis minor
latissimus dorsi
muscles that flex the arm
deltoid
pectoralis major
coracobrachialis
muscles that extend the arm
deltoid
teres major
latissimus dorsi
muscles that adduct the arm
pectoralis major
teres major
latissimus dorsi
muscles that abduct the arm
deltoid
supraspinatus
muscles that medially rotate the arm
pectoralis major
teres major
latissimus dorsi
deltoid
subscapularis
latissimus dorsi
muscles that laterally rotate the arm
infraspinatus
teres minor
deltoid
what is the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
site of distal attachment for;
pectoralis major
latissimus dorsi
teres major
what is the deltoid tuberosity
site of distal attachment for;
deltoid
what gives rise to brachial artery
subclavian artery - axillary artery - brachial artery
what gives rise to the basilic vein
subclavian vein - axillary artery → cephalic vein and basilic vein
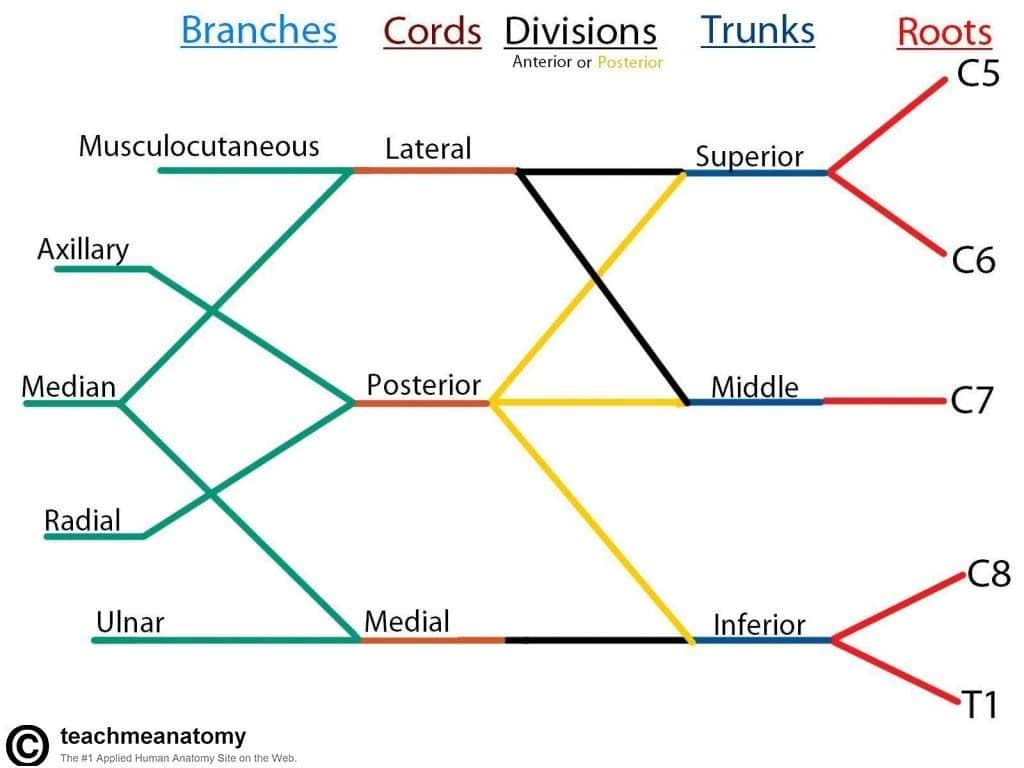
what is the brachial plexus
network of nerves formed by ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1 that join with each other, lateral to vertebral column
5 terminal branches (axillary, musculocutaneous, median, radial + ulnar nerve)
muscles innervated by axillary nerve
teres minor
deltoid