PDA Lecture 21: Muscarinic Receptor Agonists and Antagonists
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Are muscarinic receptors fast or slow acting?
slower acting G-protein coupled receptors activated by ACh
How many muscarinic receptor subunits are there?
5- M1, M2, M3, M4, M5
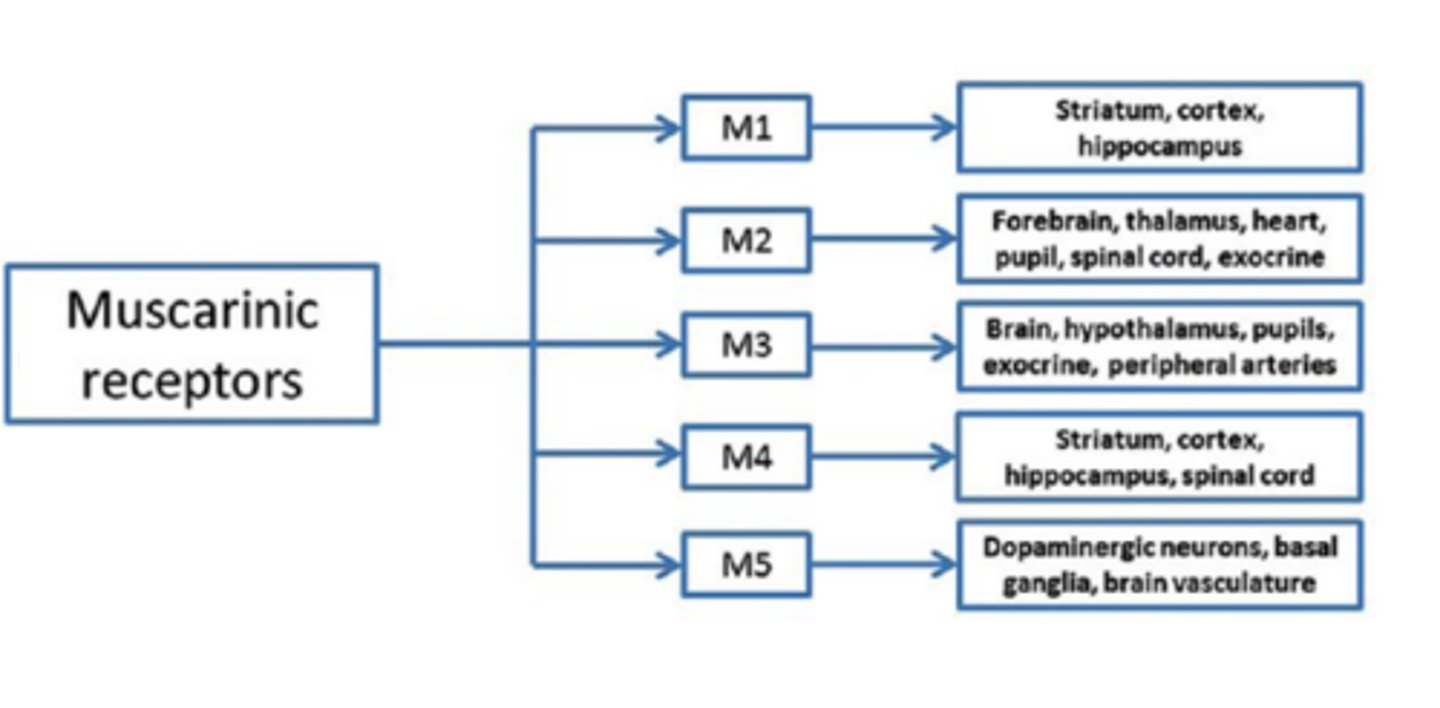
What do M1, M3, and M5 activate?
activate Gq, leading to the activation of phospholipase C, generally excitatory
What do M2 and M4 activate?
Gi/o, leading to the inhibition of adenylate cyclase, generally inhibitory
M2 and M4 can be found...
pre- and post-synaptically (as auto-receptors)
Which muscarinic receptor subunits are implicated in ANS function?
M1, M2, and M3
- found on smooth muscle tissue and sweat glands
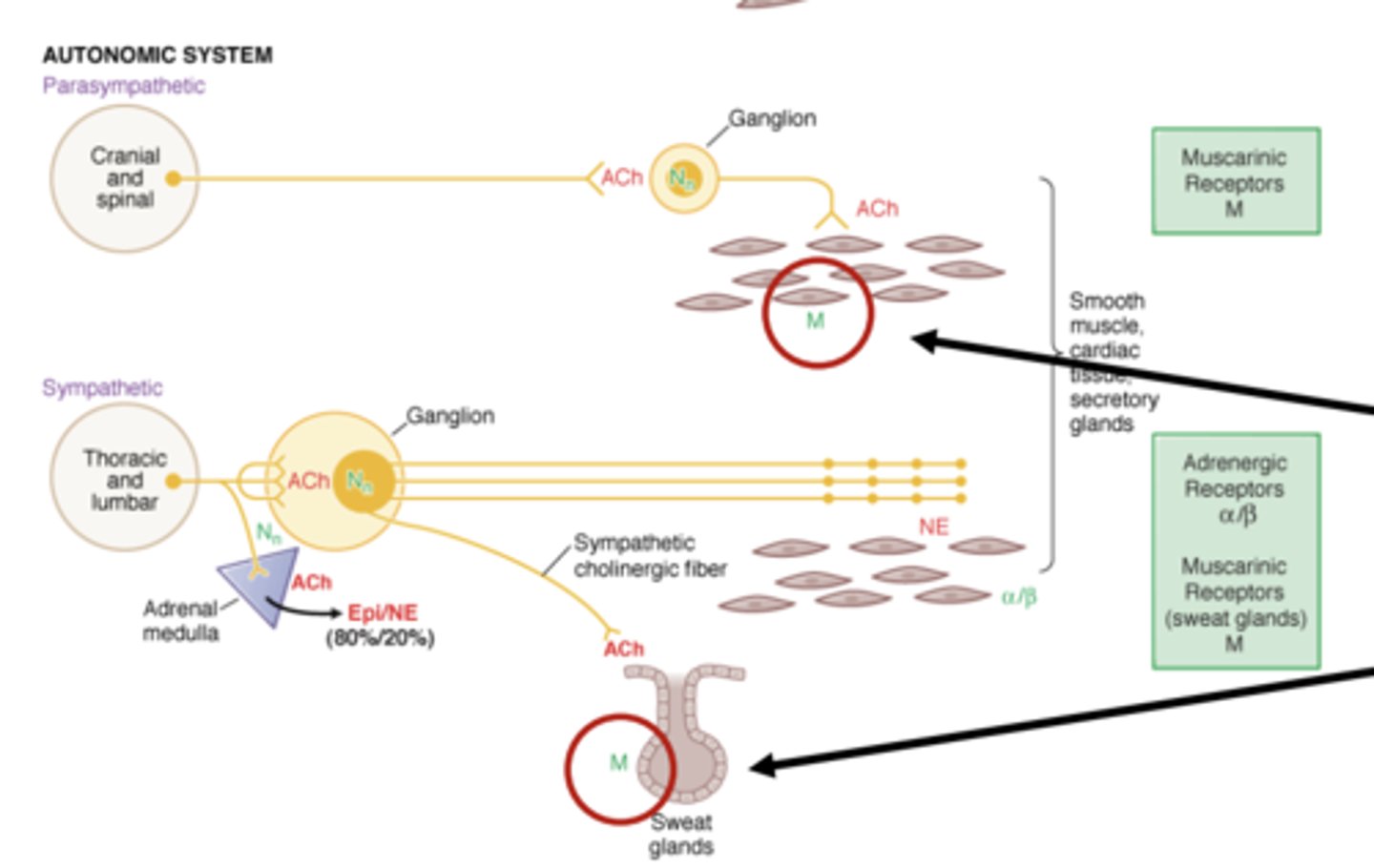
M2-pathway (diagram)
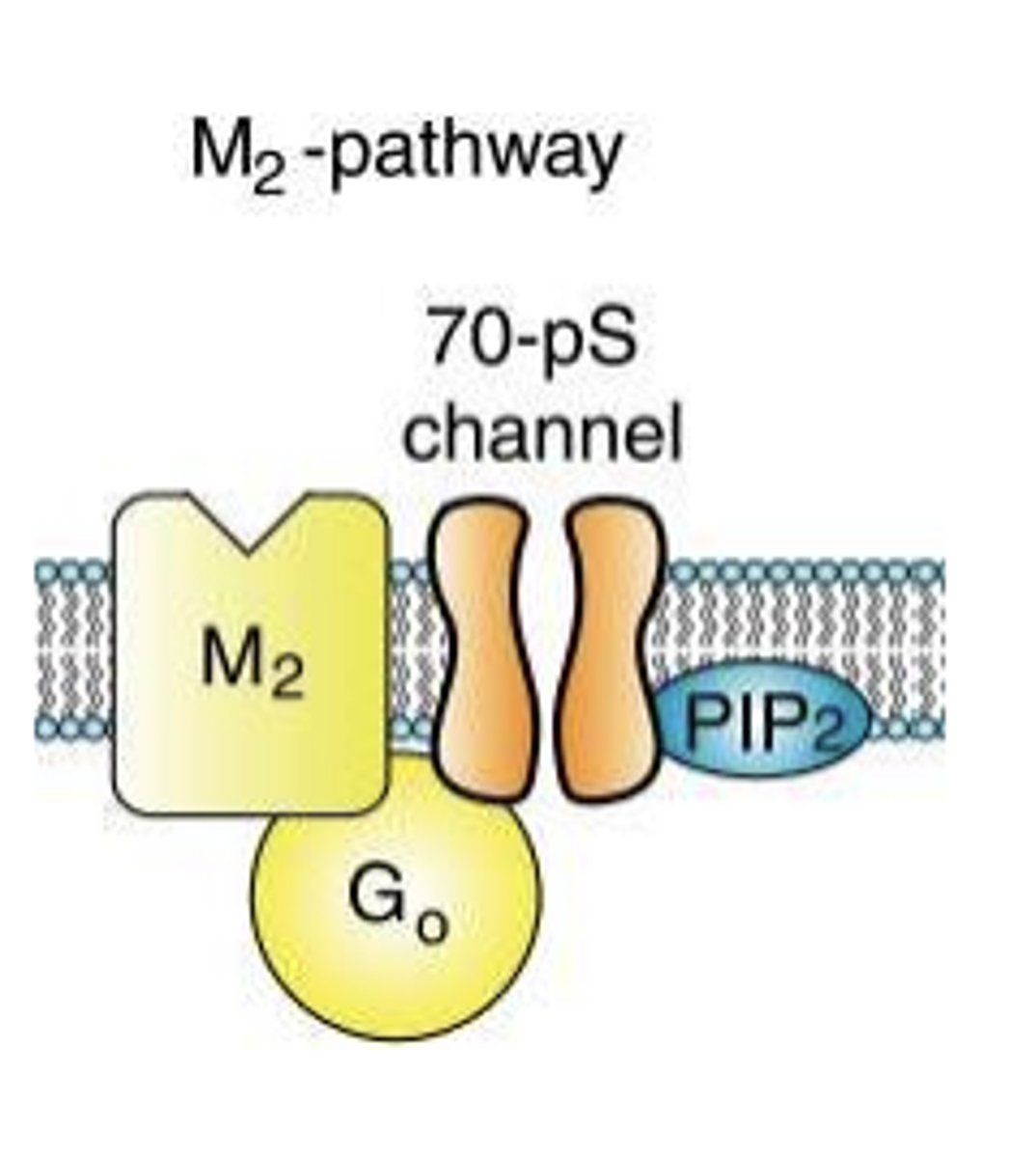
M3-pathway (diagram)
What do direct muscarinic receptor agonists do?
What are examples? (4)
- increase "rest and digest" functions and decrease "fight or flight" functions
- methacholine
- bethanechol
- cevimeline
- pilocarpine
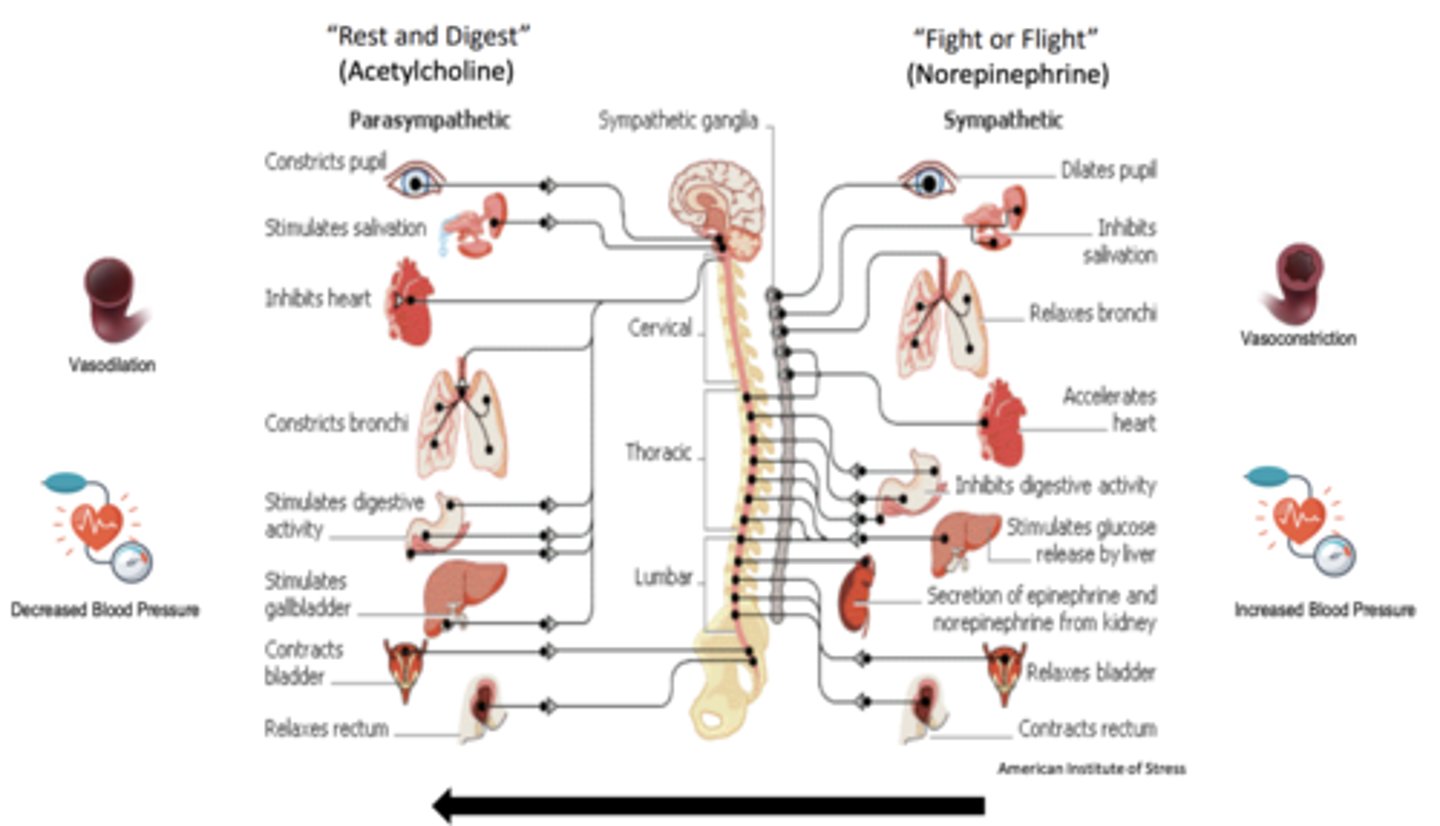
What do direct muscarinic receptor antagonists do?
What are examples?
- decrease "rest and digest" and increase "fight or flight" actions
- atropine, scopolamine, glycopyrrolate, propantheline, pirenzepine, methscopolamine, ipratropium, tiotropium, oxybutynin, tolerodine, fesoterodine, trospium, darifenacin, solenacin
Are muscarinic or nicotinic receptor agonists/antagonist more commonly prescribed?
muscarinic receptor agonists/antagonists are much more commonly prescribed than nicotinic receptor agonists/antagonists
Non-selective muscarinic agonists
binds to all muscarinic receptors
- bethanechol: treatment of dry mouth
- pilocarpine: treatment of glaucoma (vasodilation help with drainage of aqueous humor) and dry mouth
Selective muscarinic agonists (for M1 and M3 muscarinic receptor)
- cevimeline: treatment of dry mouth
- methacholine: diagnosis of asthma and COPD (bronchoconstriction test)
Side effects of muscarinic receptor agonists (Increasing “rest and digest” in unwanted ways)
DUMBBELLS
D – defecation (diarrhea)
U – urination (uncontrolled peeing)
M – miosis (constriction of the pupil)
B – bradycardia (slow heart beat)
B – bronchospasm (difficulty breathing)
E – emesis (vomiting)
L – lacrimation (tearing)
L – lethargy
S – salivation (excessive drooling)
Atropine (5)
- non-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist (binds to all muscarinic receptors)
- plant derived
- commonly taken by IM injection or eye drops
- crosses BBB
- common clinical uses: bradycardia (<60 bpm), organophosphate poisoning (from nerve gas or pesticide) antidote, prior to eye exams to induce dilation
The vagus nerve of the _________________ releases _______________ to initiate ____________
- parasympathetic system
- acetylcholine
- "rest and digest"
(3, slows down heart)
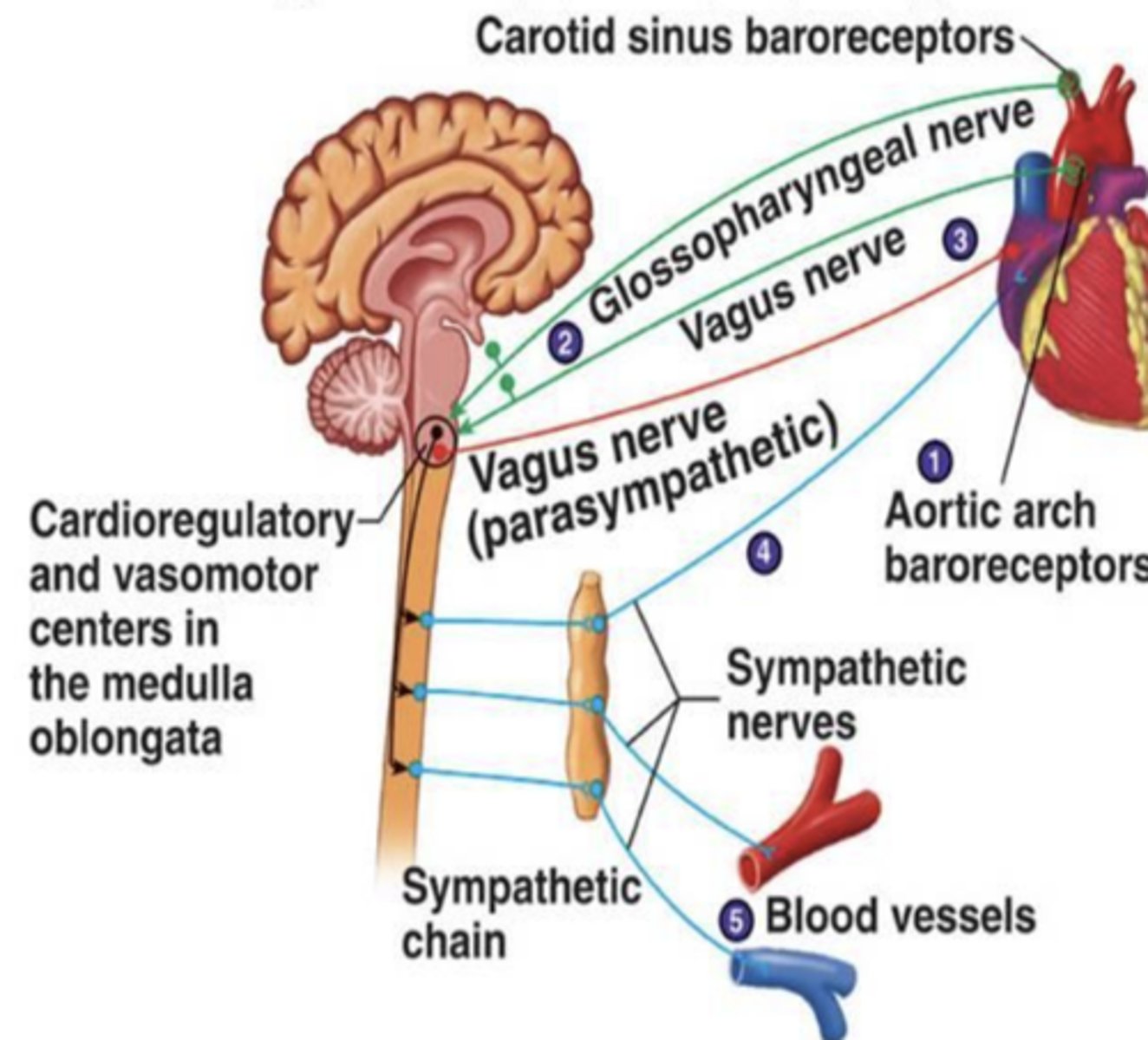
As a muscarinic receptor antagonist, atropine blocks.....
muscarinic receptors and acetylcholine’s ability to slow down the heart (heart speeds up)
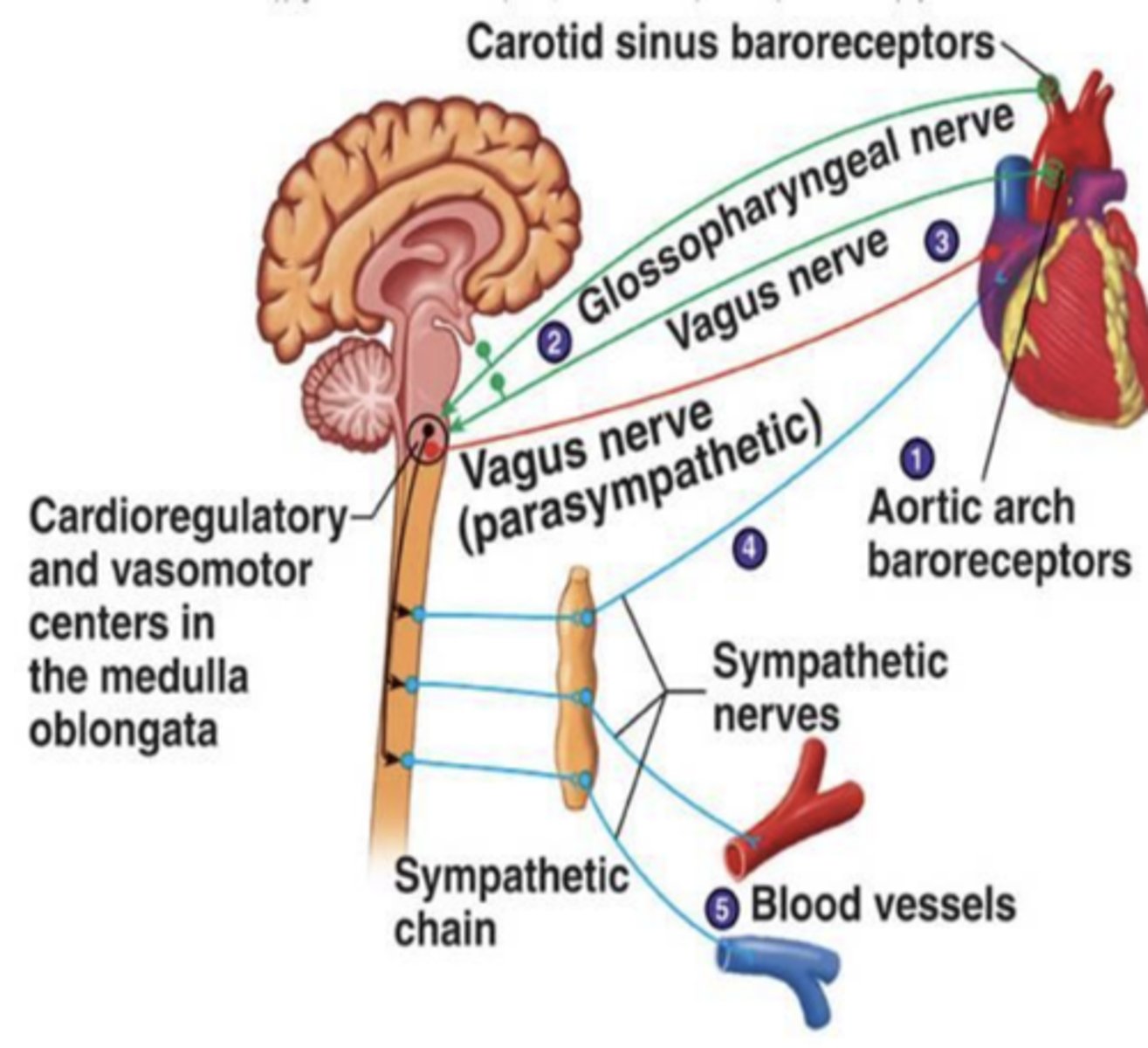
Scopolamine (5)
- non-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist (binds to all muscarinic receptors)
- plant derived
- commonly taken by mouth or transdermally
- crosses BBB. strange psychedelic properties
- common clinical uses: postoperative nausea, organophosphate poisoning (from nerve gas or pesticide) antidote, GI issues (motion sickness, IBS)
Muscarinic antagonists for GI problems
- what route is it administered?
- what kind of drugs are they? what are the effects likely on?
- does it cross the BBB
- what is it mostly used for?
- administered orally
- drugs are non-selective for muscarinic receptors, but effects likely on M1
- does not cross BBB
- mostly used or stomach spasms
ex: glycopyrrolate, propantheline, pirenzepine, methscopolamine
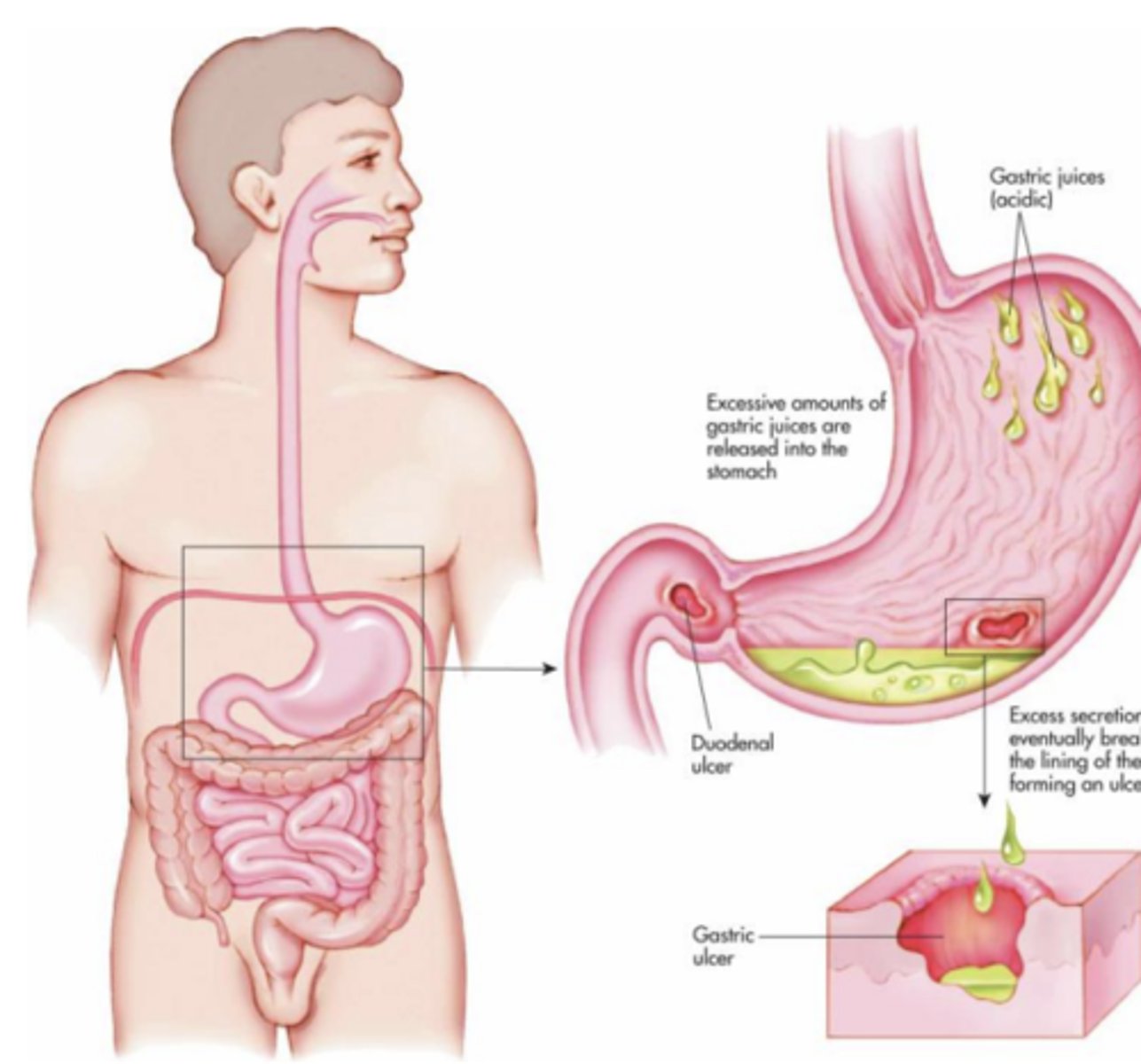
What were Muscarinic antagonists for GI problems previously used for?
peptic ulcers, but PPIs are now preferred
Muscarinic antagonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- what way is it administered through
- what kind of drugs are they? what do they have a high affinity for?
- do they cross the BBB?
- how do they work?
- are they better for asthma or COPD?
- administered through inhalation
- drugs are non-selective for muscarinic receptors, but high affinity for M3
- does not cross BBB
- works by dilating bronchi (increasing air flow)
- better for COPD, than asthma
- ipratropium and tiotropium
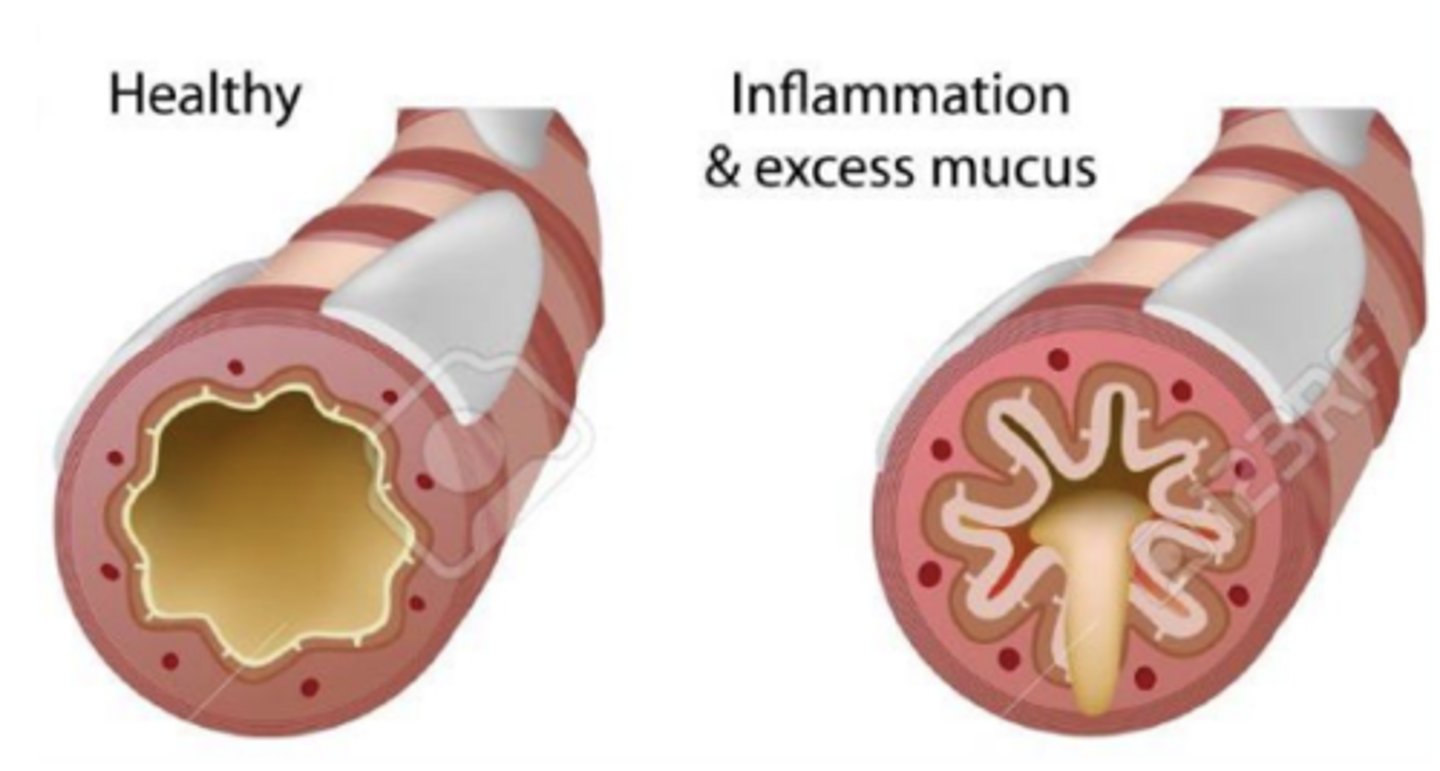
Muscarinic M3 receptor antagonists for the treatment of overactive bladder (urge incontinence)
with urge incotinence, there is over activation of M3 muscarinic receptors in bladder detrusor muscle
- detrusor muscle contracts regardless of how much urine is stored
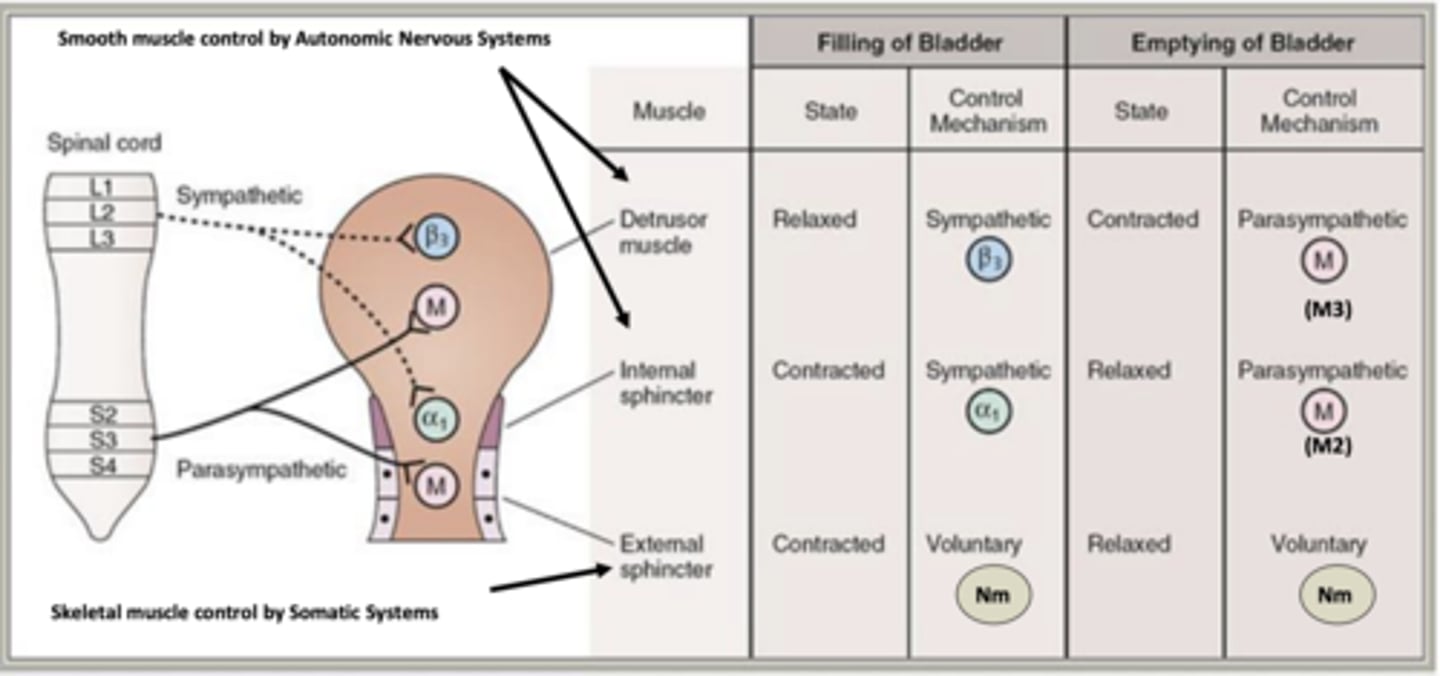
Drugs used for the treatment of urge incontinence block what?
block M3 receptor activation
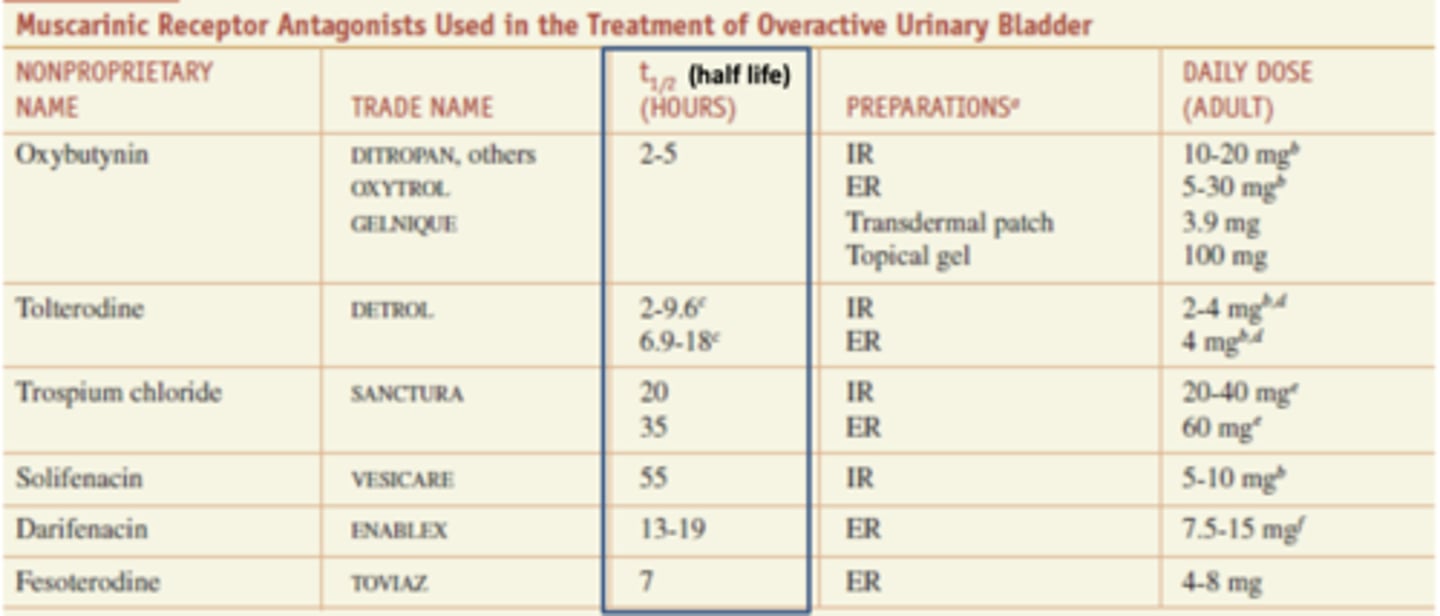
Muscarinic receptor antagonists used in the treatment of overactive urinary bladder
*oxybutynin- 2-5 (shortest)
tolterodine- 1-9c 6.9-1.8c
tospium chloride- 20 and 35
*solifenacin- 55 (longest)
darifenacin- 13-19
fesoterodine- 7
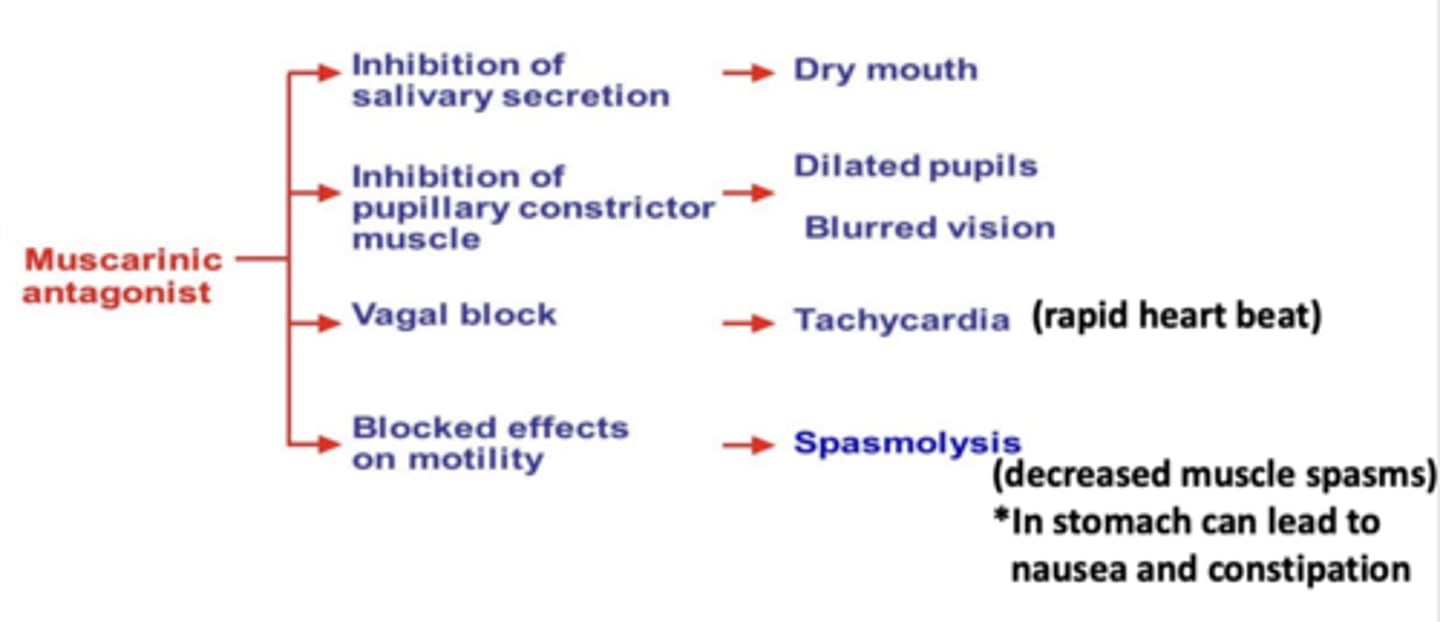
Side effects of muscarinic receptor antagonists (suppressing “rest and digest” in unwanted ways)
- inhibition of salivary secretion --> dry mouth
- inhibition of pupillary constrictor muscle --> dilated pupils, blurred vision
- vagal block --> tachycardia (rapid heart beat)
- blocked effects on motility --> spasmolysis (decreased muscle spasms)* in stomach can lead to nausea and constipation
*Can have toxic effects in CNS
Drugs that block acetylcholine's effects are considered what?
A. Sympathomimetic drugs
B. Parasympathomimetic drugs
C. Parasympatholytic drugs
D. Sympatholytic drugs
C. Drugs Affecting Parasympathetic System
Mimic acetylcholine effects -> Parasympathomimetic
Block acetylcholine effects -> Parasympatholytic
Which of the following muscarinic antagonists can be useful for the treatment of COPD?
A. Ipratropium
B. Oxybutynin
C. Glycopyrrolate
D. Atropine
A. Ipratropium

Which of the following drugs is not used for the treatment of dry mouth?
A. Bethanechol
B. Pilocarpine
C. Cevimeline
D. Methacholine
D. Methacholine: Diagnosis of asthma and COPD
Which of the following is not a side effect of muscarinic antagonists?
A. Dilated Pupils
B. Constrict bronchi
C. Dry mouth
D. Rapid heart beat
B. Constrict bronchi
B. Blockade of muscarinic Ach receptors and rest and digest functions would increase fight or flight functions (including opening of bronchi)