Anatomy Lecture 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/232
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:36 AM on 9/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
1
New cards
What is histology?
The study of tissues
2
New cards
Define tissue
A group of similar cells and extracellular products that perform a common function
3
New cards
Describe the extracellular matrix
Produced by the cells and surrounds them
4
New cards
What is the extracellular matrix composed of?
Water, protein fibers, dissolved molecules
5
New cards
What differs in the extracellular matrix across tissues?
Composition, volume, and consistency
6
New cards
What are the four types of tissues in the body?
* Epithelial tissue
* Connective tissue
* Muscle tissue
* Nervous tissue
* Connective tissue
* Muscle tissue
* Nervous tissue
7
New cards
What are the two types of epithelial tissue?
Simple and stratified
8
New cards
How many layers are in simple epithelial tissue?
1
9
New cards
How many layers are in stratified epithelial tissue?
2 or more
10
New cards
What are the types of simple epithelial tissue?
1. Simple squamous epithelial tissue
2. Simple cuboidal epithelial tissue
3. Simple columnar epithelial tissue
4. Pseudostratified columnar epithelial tissue
11
New cards
What are the types of stratified epithelial tissue?
1. Keratinized stratified squamous epithelial tissue
2. Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelial tissue
3. Stratified cuboidal epithelial tissue
4. Stratified columnar epithelial tissue
5. Transitional epithelial tissue
12
New cards
What are the types of muscle tissue?
1. Smooth muscle
2. Cardiac muscle
3. Skeletal muscle
13
New cards
Which type of muscle tissue is voluntary?
Skeletal
14
New cards
What are the types of nervous tissue?
1. Neuron
2. Glial cells
15
New cards
What are the types of connective tissue?
1. Connective tissue proper
2. Supporting connective tissue
3. Fluid connective tissue
16
New cards
What are the types of proper connective tissue?
Loose and dense
17
New cards
What is the difference between loose and dense connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue is low in protein fibers and dense connective tissue is high in protein fibers
18
New cards
What are the types of loose proper connective tissue?
* Areolar connective tissue
* Adipose connective tissue
* Reticular connective tissue
* Adipose connective tissue
* Reticular connective tissue
19
New cards
What are the types of dense proper connective tissue?
* Dense regular connective tissue
* Dense irregular connective tissue
* Elastic connective tissue
* Dense irregular connective tissue
* Elastic connective tissue
20
New cards
What are the types of supporting connective tissue?
Cartilage and bone
21
New cards
What are the types of cartilage supporting connective tissue?
* Hyaline
* Elastic cartilage
* Fibrocartilage
* Elastic cartilage
* Fibrocartilage
22
New cards
What are the types of bone supporting connective tissue?
* Compact bone
* Spongy bone
* Spongy bone
23
New cards
What are the types of fluid connective tissue?
Blood and Lymph
24
New cards
Where is epithelial tissue?
Lines every body surface (epidermis) and all body cavities
25
New cards
What is derived from epithelial tissue?
A majority of glands
26
New cards
Does epithelial tissue have blood vessels?
No. It is avascular
27
New cards
Is the extracellular matrix present in epithelial tissue?
No. It possesses little to no extracellular matrix
28
New cards
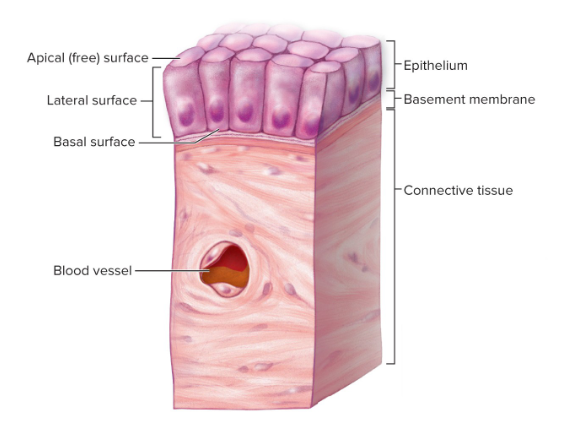
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissue?
* Cellularity
* Polarity
* Attachment to a basement membrane
* Avascularity
* Innervation
* High regeneration capacity
* Polarity
* Attachment to a basement membrane
* Avascularity
* Innervation
* High regeneration capacity
29
New cards
Describe how epithelial tissue possesses cellularity
* Composed almost entirely of cells bound by intercellular junctions
* Little extracellular matrix between cells
* Little extracellular matrix between cells
30
New cards
Describe how epithelial tissue possesses polarity
Epithelia have an apical surface, lateral surface, and basal surface
31
New cards
Define the apical surface
It is exposed and may have modifications like microvilli and cilia
32
New cards
Describe microvilli
Increase surface area for absorption of nutrients
33
New cards
Describe cilia
Help move particles
34
New cards
Define the lateral surfaces
Have intercellular junctions
35
New cards
Define the basal surface
Attached to connective tissue underneath it
36
New cards
Define attachment to a basement membrane as a characteristic of epithelial tissue
Basal surface attaches to a basement membrane, which is a structure produced by both epithelial and neighboring connective tissues
37
New cards
Define avascularity as a characteristic of epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissues lack blood cells. They receive nutrients by diffusion from underlying tissues
38
New cards
Define innervation as a characteristic of epithelial tissue
Epithelia are richly innervated to detect changes in the environment
39
New cards
Define high regeneration capacity as a characteristic of epithelial tissue
Epithelial cells are quickly replaced because the exposed apical surface is frequently damaged
40
New cards
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
* Physical protection
* Selective permeability
* Secretion
* Sensation
* Selective permeability
* Secretion
* Sensation
41
New cards
Describe how epithelial tissue is used for physical protection
It defends against dehydration and abrasion as well as physical, chemical, and biological agents
42
New cards
Describe how epithelial tissue is used for selective permeability
It regulates the passage of molecules in or out of certain regions of the body
43
New cards
Describe how epithelial tissue is used for secretion
It secretes substances for use in the body or for elimination from the body
44
New cards
Describe how epithelial tissue is used for sensation
The tissue possesses nerve endings that can detect light, taste, sound, smell, and hearing
45
New cards
Where is the basement membrane?
Between epithelium and underlying connective tissue
46
New cards
What makes up the basement membrane?
Proteins and carbohydrates into discrete layers
47
New cards
What are the layers that make up the basement membrane?
* Lamina lucida
* Lamina densa
* Reticular lamina
* Lamina densa
* Reticular lamina
48
New cards
What produces the lamina lucida and laminda densa?
Epithelial cells produce the components for the two laminae
49
New cards
What produces the reticular lamina?
Connective tissue
50
New cards
What are the functions of the basement membrane?
* Provides physical support
* Anchors epithelial tissue
* Acts as a barrier regulating passage of large molecules between epithelium and connective tissue
* Anchors epithelial tissue
* Acts as a barrier regulating passage of large molecules between epithelium and connective tissue
51
New cards
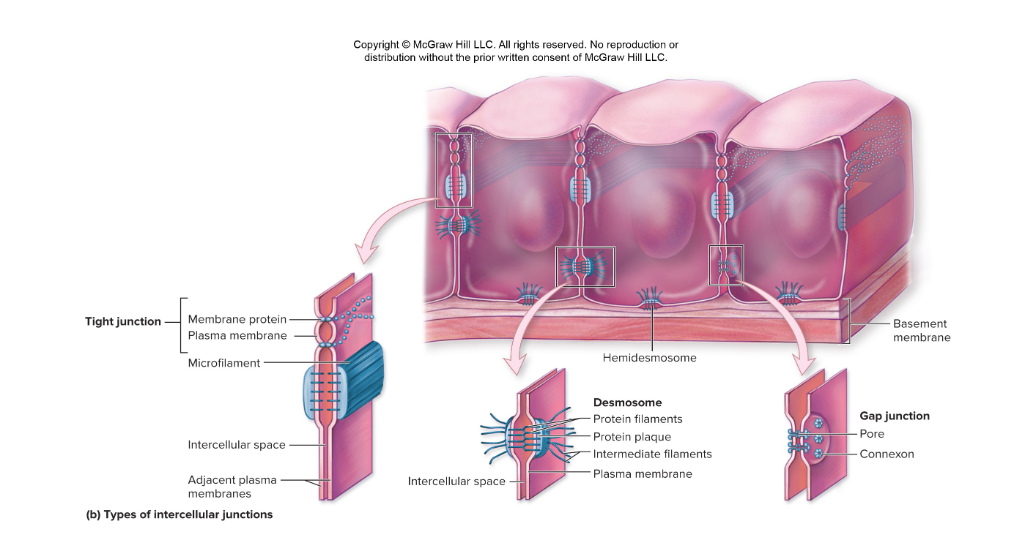
What are the different types of intercellular junctions?
* Tight junctions
* Adhering junctions
* Desmosomes
* Gap junctions
* Adhering junctions
* Desmosomes
* Gap junctions
52
New cards
Describe tight junctions
* Encircle epithelial cells near apical surface and attach each cell to its neighbor
* Prevent molecules from traveling between epithelial cells
* Prevent molecules from traveling between epithelial cells
53
New cards
Describe adhering junctions
Formed around the cell deep to the tight junction and help stabilize the apical surface of the epithelial cell
54
New cards
Describe desmosomes
* Junctions that appear at locations of mechanical stress between cells
* Some basal epithelial cells have hemidesmosomes anchoring them to basement membrane
* Some basal epithelial cells have hemidesmosomes anchoring them to basement membrane
55
New cards
Describe gap junctions
Allow adjacent cells to communicate with each other by the flow of ions and small molecules
56
New cards
What are the different classifications of the epithelium by layer?
1. Simple epithelium
2. Stratified epithelium
3. Pseudostratified epithelium
57
New cards
How many layers does the simple epithelium have?
One layer of cells
58
New cards
How many layers does the stratified epithelium have?
Two or more layers of cells
59
New cards
How many layers does the pseudostratified epithelium have?
Appears to have multiple layers, but all cells attach to the basement membrane
60
New cards
Describe the simple epithelium
All cells have an apical surface and attach to the basement membrane
61
New cards
Describe the stratified epithelium
Not all cells have an apical surface nor do all cells attach to the basement membrane
62
New cards
Pseudostratified epithelium is a subtype of what
Simple epithelium
63
New cards
What are the different classifications of epithelial tissue by shape?
* Squamous
* Cuboidal
* Columnar
* Transitional
* Cuboidal
* Columnar
* Transitional
64
New cards
Describe squamous epithelial tissue
Flat, wide, and somewhat irregular in shape
65
New cards
Describe cuboidal epithelial tissue
About the same size on all sides; nucleus is usually centrally located
66
New cards
Describe columnar epithelial tissue
Taller than they are wide, nucleus is oval, and located in basal region of cell
67
New cards
Describe transitional epithelial tissue
Cells change shape depending on degree of stretch
* Polyhedral in a relaxed state
* Squamous when stretched
* Polyhedral in a relaxed state
* Squamous when stretched
68
New cards
Where is transitional epithelial tissue found?
The lining of the urinary bladder
69
New cards
Describe simple squamous epithelium
Single layer of flat cells with a flat nucleus that allows for rapid change
70
New cards
What are examples of simple squamous epithelium?
Lining of alveoli and lining of blood vessels
71
New cards
Define endothelium
What epithelium is called when lining blood and lymphatic vessels
72
New cards
Define mesothelium
The simple squamous epithelium of a serous membrane
73
New cards
Describe simple cuboidal epithelium
Single layer of cells as tall as they are wide with a round or spherical nucleus
74
New cards
Which epithelium tissues allow for absorption and secretion?
Simple columnar and simple cuboidal
75
New cards
What are some examples of the simple cuboidal epithelium?
Kidney tubules and ducts of exocrine glands
76
New cards
Describe simple columnar epithelium
Single layer of tall, narrow cells with an oval nucleus near the bottom third of the cell
77
New cards
What are the forms of the simple columnar epithelium
Ciliated and nonciliated
78
New cards
What could nonciliated forms of simple columnar epithelium have?
Microvilli and goblet cells which secrete mucin
79
New cards
What are examples of nonciliated simple columnar epithelium?
Most of the digestive tract (stomach to anal canal)
80
New cards
What is a ciliated example of simple columnar epithelium?
Uterine tube
81
New cards
Describe pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Single layer of narrow cells with varying heights and both ciliated and nonciliated forms
* Appears stratified but is simple
* All cells touch basement membrane but not all reach apical surface
* Appears stratified but is simple
* All cells touch basement membrane but not all reach apical surface
82
New cards
What is the function of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Protection
83
New cards
What is the function of ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Secretes mucin and moves mucus
84
New cards
What is an example of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Respiratory tract lining
85
New cards
Describe stratified squamous epithelium
Multiple layers with only the deepest layer of cells contacting the basement membrane
86
New cards
What are the shapes of the various cells in the stratified squamous epithelium?
* Apical cells are squamous
* Deeper cells are cuboidal or polyhedral
* Deeper cells are cuboidal or polyhedral
87
New cards
What is the function of stratified squamous epithelium?
Protection
88
New cards
What are the types of stratified squamous epithelium?
Keratinized and nonkeratinized
89
New cards
Describe keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Apical cells are dead, flat, and filled with the tough protein keratin. Dry
90
New cards
Where is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium found?
In the epidermis of the skin
91
New cards
Describe nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Apical cells are flat, moist, and alive. Wet
92
New cards
Where is nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium found?
The esophagus and vagina
93
New cards
What is rare epithelial tissue?
Stratified cuboidal epithelium and stratified columnar epithelium
94
New cards
Describe stratified cuboidal epithelium
* Multiple layers of cells
* Apical cells are as tall as they are wide
* Apical cells are as tall as they are wide
95
New cards
What is the function of stratified cuboidal epithelium?
Protection, secretion, support the walls of some ducts
96
New cards
Where are stratified cuboidal epithelium found?
Lining of sweat gland duct
97
New cards
Describe stratified columnar epithelium
Multiple layers of cells with elongated apical cells
98
New cards
What is the function of stratified columnar epithelium?
Protection, support, and secretion
99
New cards
Where is stratified columnar epithelium found?
Part of male urethra, ducts of some salivary glands
100
New cards
What is the general purpose of stratified epithelial tissues?
Protection