Teas Cardiovascular System
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Muscular Organ that pumps blood through the body
Heart
How many chambers are in the heart?
4 chambers
what are the chambers of the heart in order of which receives blood firth?
Right Atrium, Right Ventricle, Left Atrium, Left Ventricle
What separates the left and right parts of the heart?
Septum
Oxygenated Blood away from the heart
- A is for Away from the Heart
Arteries
Deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Veins
Connect Arteries and Veins
- Site of gas exchange
Capillaries
Carries Oxygen and nutrients to cells and carbon dioxide and waste away from cells
Blood
What are the three types of Blood vessels?
Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries
The contraction of the heart
- Peak pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts
- Makes up the "lub" sound of the heart
- Usually the 120 in 120/80
- If this number is too high, it usually indicates hypertension
Systole
Relaxation of the heart
- Represents the lowest pressure in the arteries
- Measures Resistance to blood flow in the arteries
- Makes up the "dub" sound of the heart
- Usually the 80 in 120/80
- Numbers higher than 80 can indicate that the arteries are narrow or too stiff
Diastole
What happens to blood in systole?
Blood is being pumped out of the heart and into the arteries
What is the actual cause of the "lub" sound?
Mitral and Tricuspid valves close
What happens to blood in diastole?
Blood flows into the heart and fills the chambers
What causes the "dub" sound?
Semilunar (aortic, pulmonic) Valves close
Located in the upper right Atrium
Sinoatrial Node
Cause atria to contract which pushes blood into the ventricles
- Primary Pace Maker
Sinoatrial Node Function
located at the junction of the atria and ventricles
atrioventricular node
Acts as a secondary pacemaker if the SA node fails, generating a slower rhythm (40-60 beats per minute).
- Momentarily pauses the SA node to allow the right atrium to fully thoroughly contract
atrioventricular node function
Originates from the atrioventricular (AV) node and travels through the interventricular septum.
- Splits into Left and Right Bundle Branch
Bundle of His
Serves as the pathway that connects the atria and ventricles electrically.
Bundle of His Function
The Bundle of His splits into the left and right bundle branches that run along the interventricular septum.
Left and Right Bundle Branch
The Bundle of His splits into the left and right bundle branches that run along the interventricular septum.
Left and Right Bundle Branches
Spread throughout the ventricular walls, branching from the bundle branches.
Purkinje Fibers
Transmit impulses rapidly to the ventricular muscle cells, triggering a strong and coordinated contraction.
- Essential for pushing blood efficiently into the pulmonary artery and aorta.
- Initiates depolarization in the muscle cell triggering the contraction in the cardiovascular muscle
Purkinje Fibers Function
What are the BPM of the average heart set by the sinoatrial node
60 - 100 BPM
What is the BPM of the average hear set by the AV node?
40-60 BPM
What is the BPM of the average heart set by the Purkinje Fibers
20-40 BPM
Why is the cardiovascular system considered close?
Blood stays within vessels and the respective organs as it circulates through the body
What are all the structures associated with the passageway of deoxygenated blood
Veins, Superior and Inferior Vena Cava, Right Atrium, Tricuspid valve, Right Ventricle, Pulmonary Valve, Pulmonary Arteries, Lung
What are all the structures associated with the passageway of oxygenated blood
Lungs, Pulmonary Veins, Left Atrium, Mitral Valve, Left Ventricle, Aortic Valve, Aorta, Arteries, Capillaries
Function 1 of the cardiovascular system
Delivers oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the body and removes carbon dioxide and waste
Function 2 of the cardiovascular system
Maintains body's blood pressure
Function 3 of the cardiovascular System
Regulates body temperatures
Function 4 of the cardiovascular system
Maintaining the body's pH
Function 5-8 of the cardiovascular system
Transporting hormones, fighting infection, aiding in digestion, assisting in repair of damaged tissues
What is the relation of heat to blood vessel constriction?
conserving heat
What is the relation of heat to blood vessel dilation?
Expending Heat
-the liquid portion of blood
contains
- water
- proteins
- salts, nutrients
- lipids
- hormones
- vitamins
Plasma
red blood cells, carry oxygen
Erythrocytes
white blood cells, fight infection
Leukocytes
blood clotting
Platelets
Protein in red-blood cells that holds oxygen and carries it from lungs to parts of the body
- also transports some CO2 back to the lungs for removal
Hemoglobin
What is the only pair of veins and arteries that have the reverse role of what they normally do?
Pulmonary Veins and Arteries
What part of the heart holds deoxygenated blood?
Right Side
What part of the heart holds oxygenated blood
Left Side
Do the Atriums or Ventricles have thicker walls?
Atriums
What Vena Cava carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body back to the lungs?
- Legs
- Back
- Abdomen
- Pelvis
Inferior Vena Cava
What Vena Cava carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body back to the lungs?
- Head
- Neck
- Limbs
- Upper Torso
Superior Vena Cava
How does the heart get its own oxygen?
Coronary Arteries which branch from the aorta
How does the heart's own deoxygenated blood make its way back into the right atrium?
Coronary veins
Congenital heart defect where there is an abnormal heart defect where there is an abnormal opening in the interatrial septum.
- Blood flows between the two atria
Atrial Septal Defect
A congenital defect characterized by one or more holes in the interventricular septum.
- allowing blood to mix between the ventricles
Ventricular Septal Defect
What is the mnemonic to remember the order of contingency for the heart's pace maker?
Strong Arteries Benefits Body's Performance
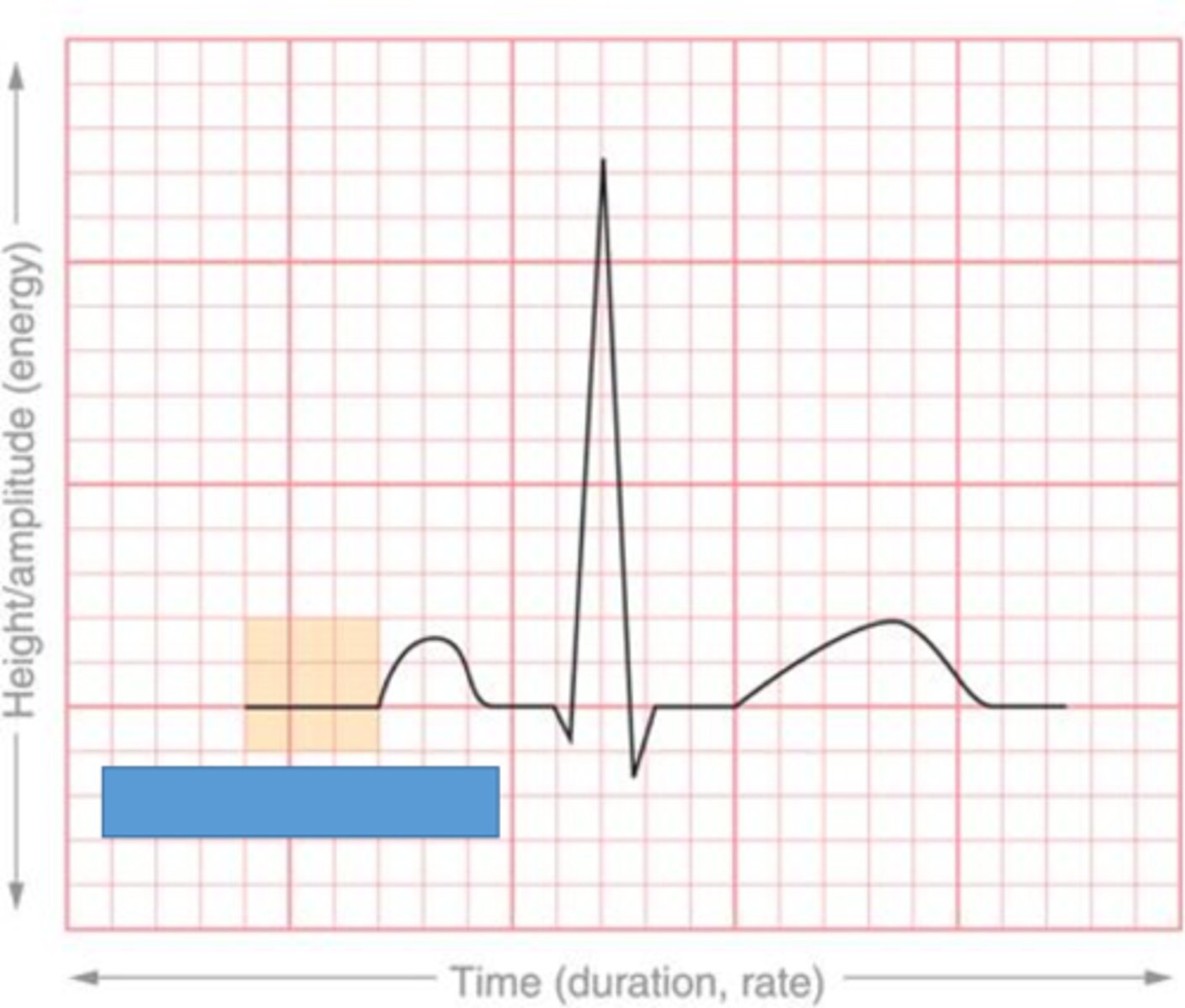
The baseline of the ECG
Isoelectric Line
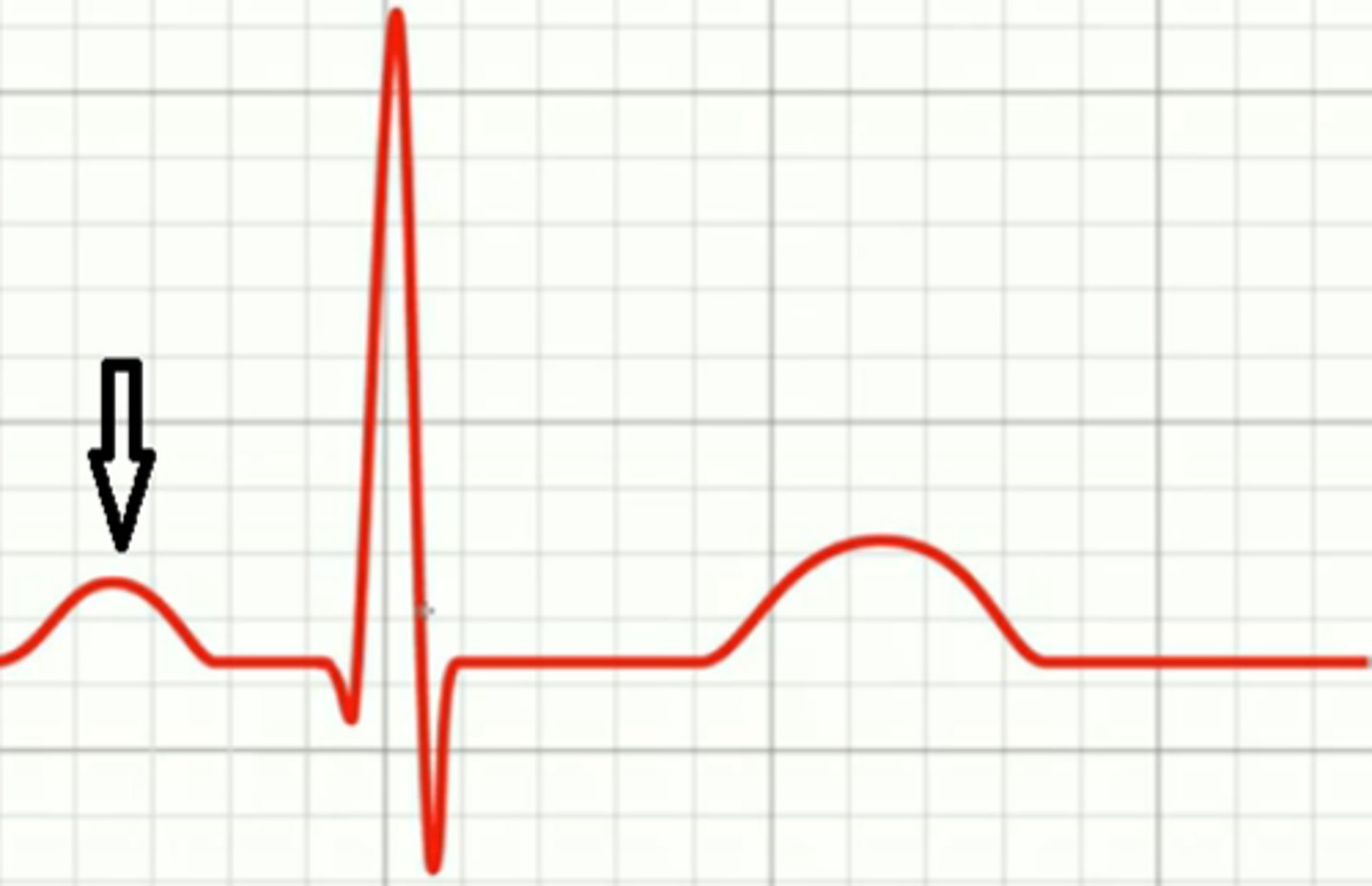
atrial depolarization (atrial contraction)
P Wave
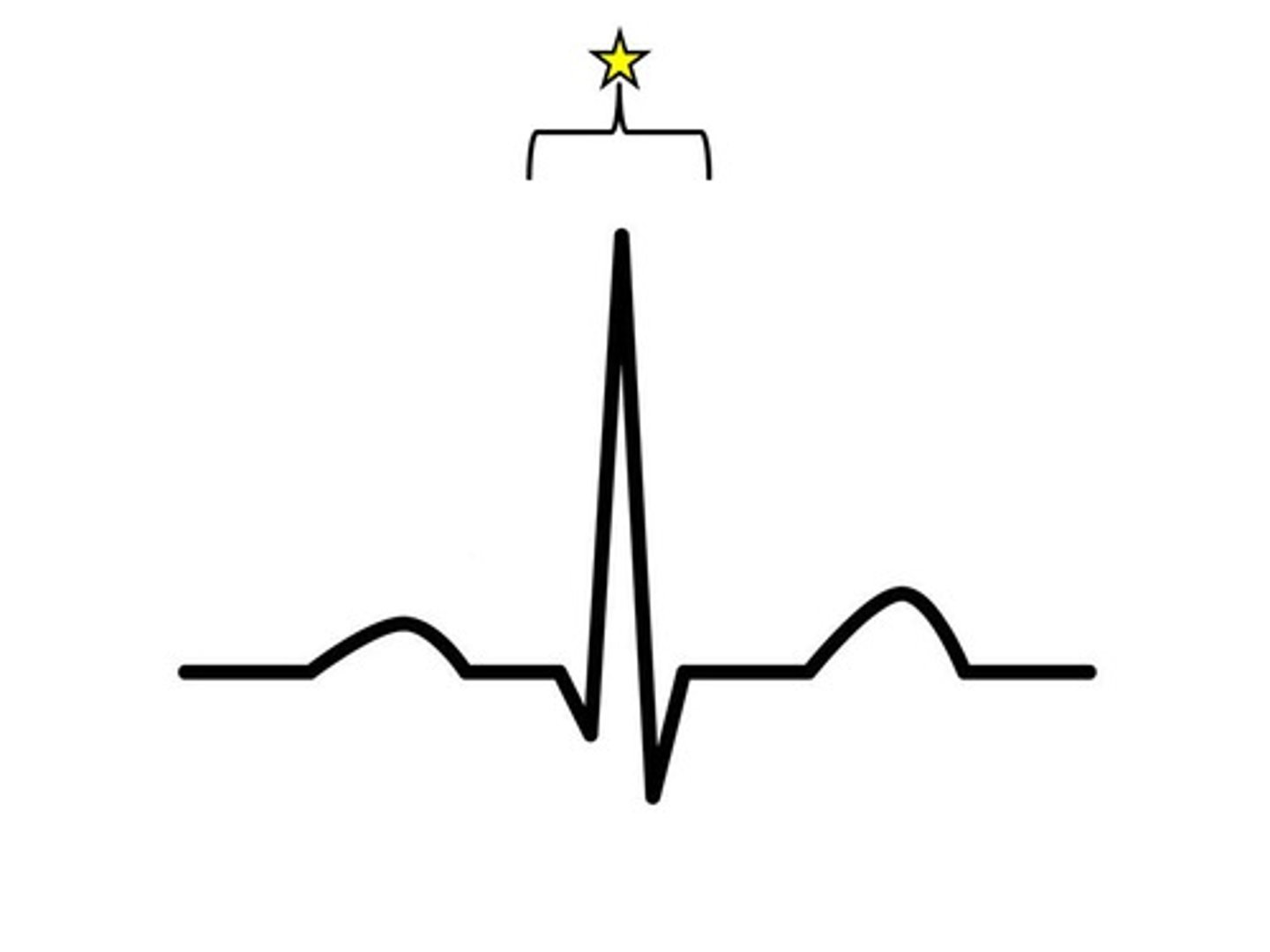
ventricular depolarization
- Range from 0.06 to 0.12 seconds
QRS complex
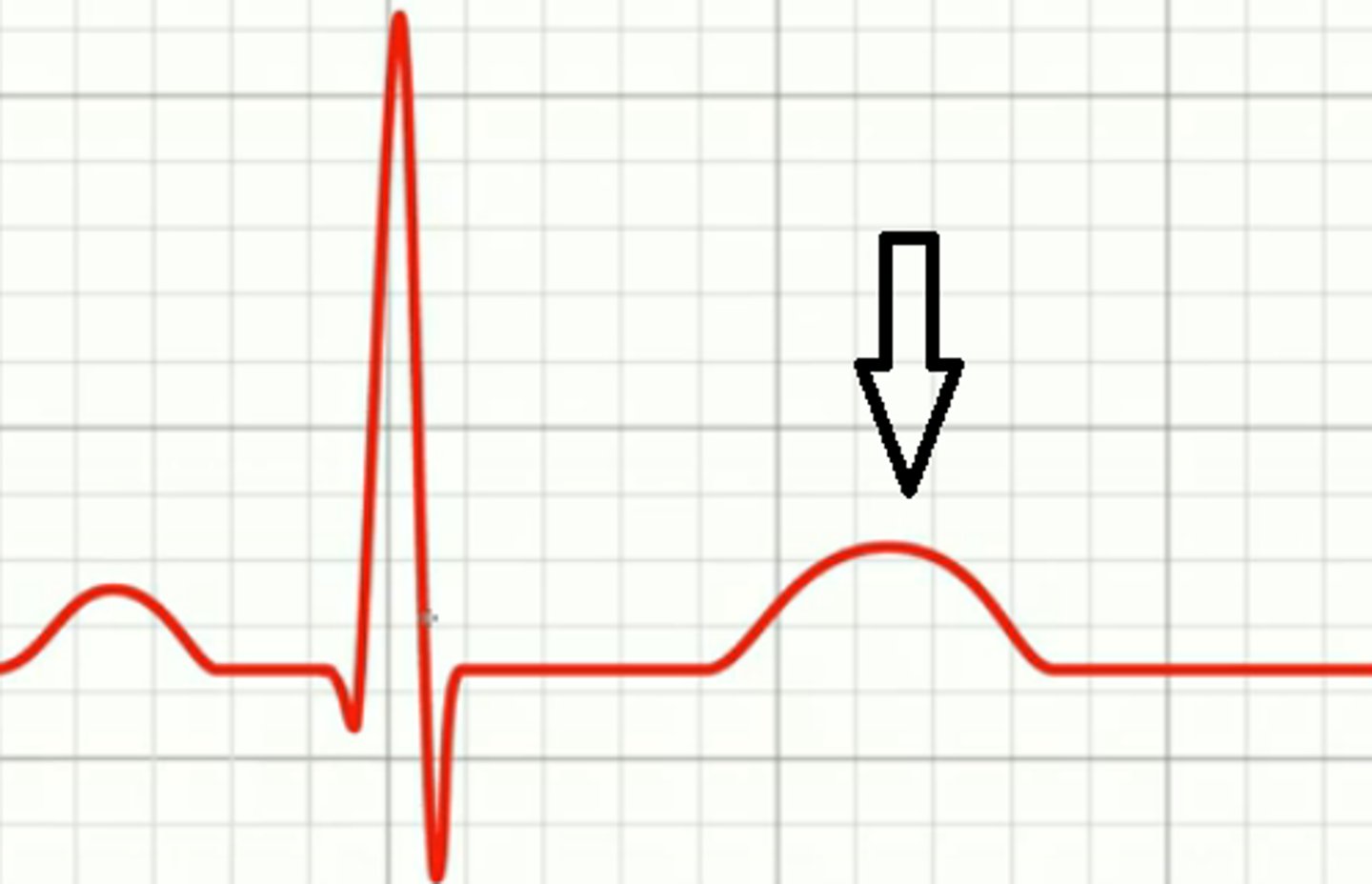
Ventricular Depolarization (Ventricular Relaxation)
T wave
when does atrial repolarization occur?
During the QRS complex
Why is the cardiovascular system considered to be closed?
blood remains enclosed within the heart and blood vessels at all times
Blockage in the coronary arteries (which supply the heart muscle) that cuts off oxygen, causing heart tissue to die
- Chest pain, shortness of breath, arm/jaw pain, and nausea
- Usually caused to plague buildup or a blood clot
Heart Attack or Myocardial Infarction
A sudden interruption of blood flow to the brain, causing brain cells to die
- Ischemic and Hemorrhagic
- Face Drooping, arm weakness, slurred speech.
- High Blood Pressure, atherosclerosis, and arrhythmias
Stroke
Caused by a blood clot blocking a brain artery
Ischemic stroke
Caused by a burst blood vessel
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Bulge or weakening in the wall of an artery. If it bursts, can cause severe internal bleeding
- Usually in the Brain, Aorta, or abdomen
- Caused by High Blood Pressure, Trauma, and Genetic Factors
- Usually goes unnoticed
aneursym
Hardening and narrowing of arteries due to plaque build up
- Causes reduced blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes
- Caused by poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and high cholesterol
Atherosclerosis
Irregular Heartbeat - can be too fast (tachycardia, or too slow (bradycardia) or uneven
- Caused by Heart Disease, electrolyte imbalance, and stress
- Causes Palpitation, dizziness, and fainting
Arrhythmia
Consistently high blood pressure in the arteries forcing the heart to work harder
- Can damage arteries, lead to heart attack, stroke, or kidney problems
Hypertension
enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin during coagulation
Thrombin
If the medulla oblongata is damaged, which of the following functions would be most affected?
A) Memory recall
B) Regulation of heart rate and breathing
C) Fine motor control
D) Speech processing
B) Regulation of heart rate and breathing
Which hormone is responsible for increasing blood pressure through vasoconstriction?
A) Insulin
B) Angiotensin II
C) Oxytocin
D) Calcitonin
B) Angiotensin II
Which organ releases renin to activate angiotensin II?
A) Liver
B) Pancreas
C) Kidney
D) Lung
C) Kidney
An occurrence of too high of a concentration of which of the following electrolytes is associated with cardiac arrhythmias?
A) Chloride
B) Phosphorus
C) Potassium
D) Sodium
C) Potassium