Cardiovascular Measurements
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What makes the “lub” heart sound (S1)?
Tricuspid and Bicuspid valves closing (Beginning of systole)
What makes the “dub” heart sound (S2)?
Aortic and pulmonary valves closing
(End of systole/ Beginning of diastole)
Heart rate is the same as what?
Heart Rate = Pulse Rate
What is it called when the blood vessel wall isn’t obstructed so blood can flow naturally?
Laminar Flow
What is it called when the blood vessel wall is obstructed so blood can’t flow naturally?
Turbulent Flow
How do you calculate pulse pressure?
Systolic blood pressure - diastolic blood pressure
(SBP - DBP)
What is the pressure unit for pulse pressure
mmHg
How do you calculate the Mean Blood Pressure (MBP)?
⅔DBP + ⅓ SBP or DBP + ⅓ PP
What is Stroke volume?
Volume of blood ejected by 1 ventricle per beat
How do you calculate Stroke Volume?
Pulse pressure x 2 (PP x 2)
What is the pressure unit for pulse pressure?
mL/beat
What is cardiac output?
Volume of blood ejected by 1 ventricle per minute
What is the pressure unit for cardiac output?
mL/min or L/min
How do you calculate Cardiac Output?
Stroke Volume x Heart Rate (SV x HR)
What causes the sounds heard during blood pressure measurement?
Blood flows back through the artery it is turbulent causing the sound of a pulse or systolic blood pressure
How do you calculate the % of change for Heart Rate?
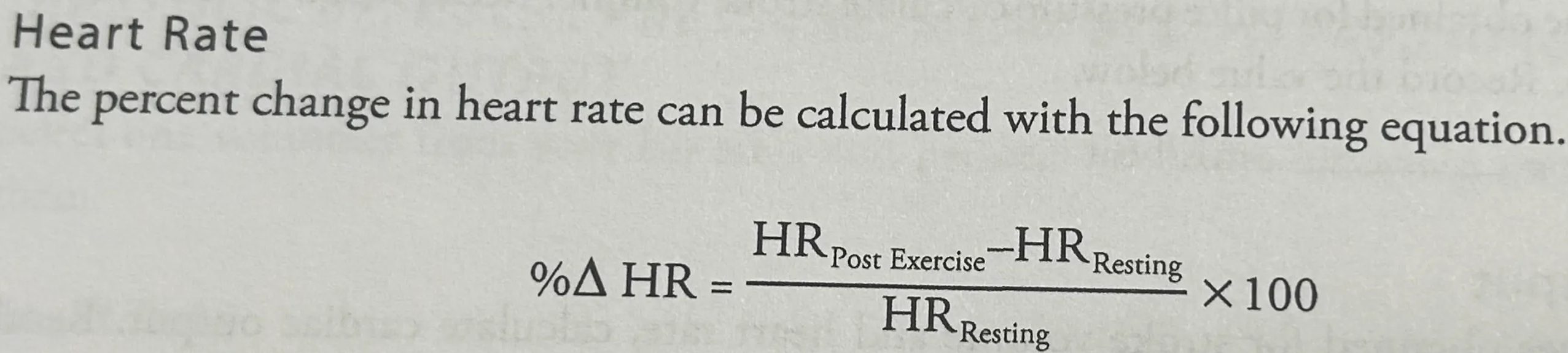
How do you calculate the % of change for Stroke Volume?
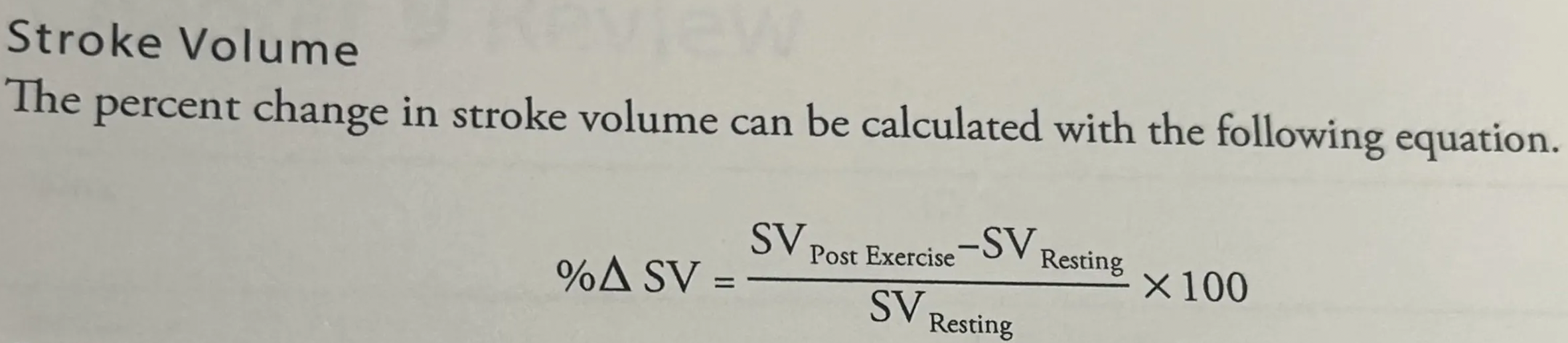
How do you calculate the % of change for Cardiac Output?

Michelle walked 5 kilometers. Prior to walking she had the following:
Pulse rate = 12 pulses / 15 seconds
Systolic BP = 89 mmHg
Diastolic BP = 70 mmHg
At the end of the walk she had the following:
Pulse rate = 21 pulses / 10 seconds
Mean BP = 91 mmHgDiastolic BP = 82 mmHg
Calculate Michelle’s percent change in Cardiac Output
273% increase (for liters)
Given the following:
Cardiac Output = 8.1L/min
Pulse rate = 71 pulses / 30 seconds
Diastolic BP = 89 mmHg
Calculate:
HR
SV
PP
SBP
MBP
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING
HR - 142 bpm
SV - 57 mmHg
PP - 28.5 mmHg
SBP - 117.5
MBP - 98.5
Use the following information to calculate the cardiac output:
pulse = 18 beats every 15 seconds
blood pressure is 125/9
Using the data from question 1, calculate the mean blood pressure.
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING
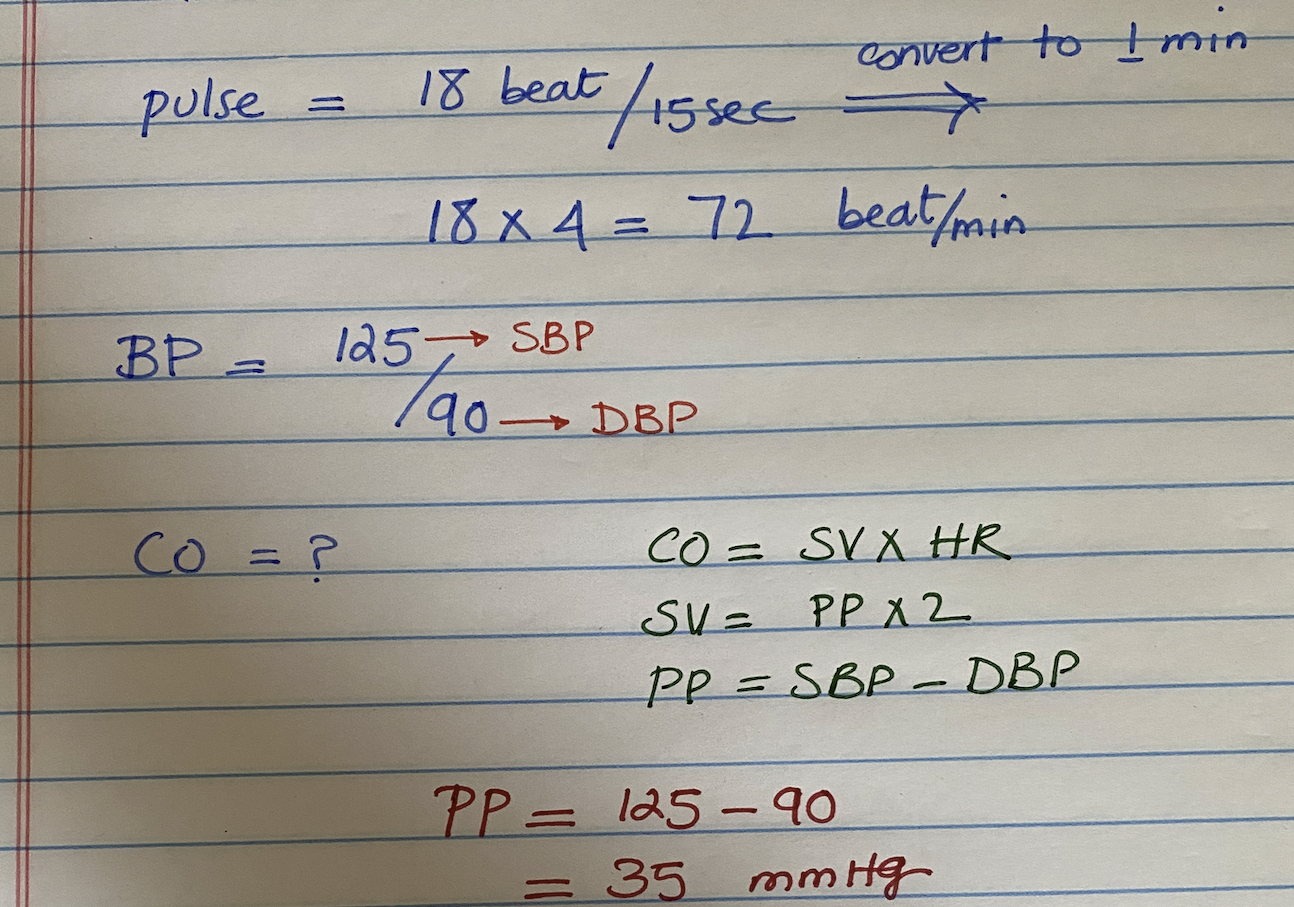
Using the data from question 1, calculate the mean blood pressure.
Data from question 1
DBP = 90
PP = 35
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING

At rest, Jane’s pulse is 73 beats per minute and her blood pressure is 130/80.
During Jane’s aerobic exercise routine, her heart rate is 160 beats per minute and her blood pressure is 190/100.
Calculate Jane’s cardiac output at rest and during exercise
Calculate the % increase in CO that results from exercise.
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING

Calculate the cardiac output using the following information:
pulse = 60 beats per minute
mean blood pressure = 90 mm Hg
diastolic blood pressure = 80 mm Hg
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING
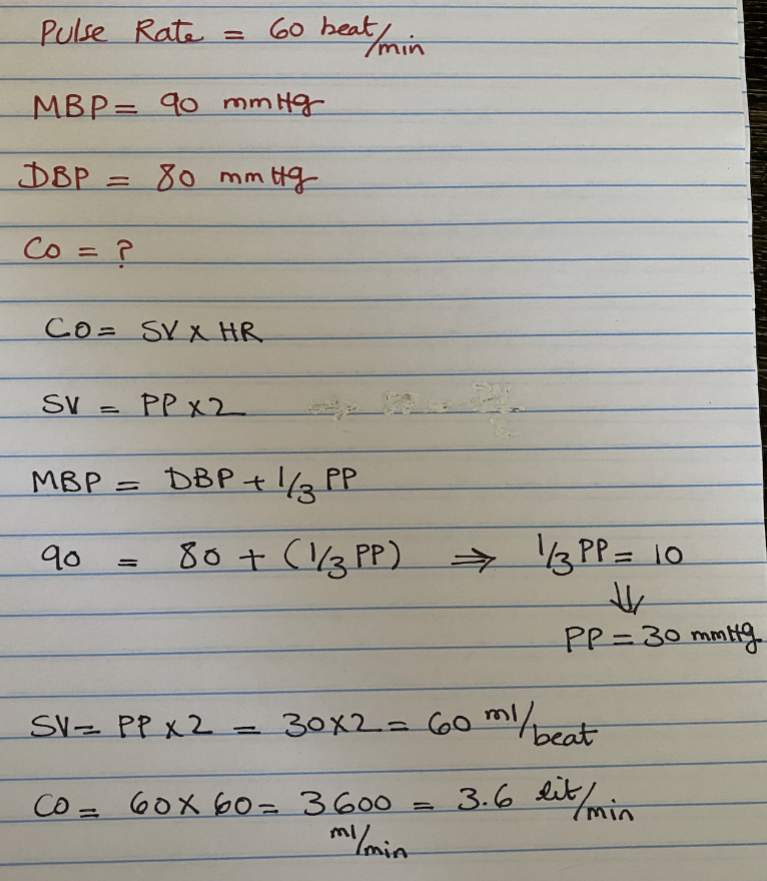
Calculate the mean blood pressure using the following information:
stroke volume = 70 ml per beat
systolic blood pressure = 115 mm Hg
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING

Joe’s resting cardiac output is 4.3 L/min. During exercise, his cardiac output increases by 350%.
What is Joe’s cardiac output during exercise?
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING
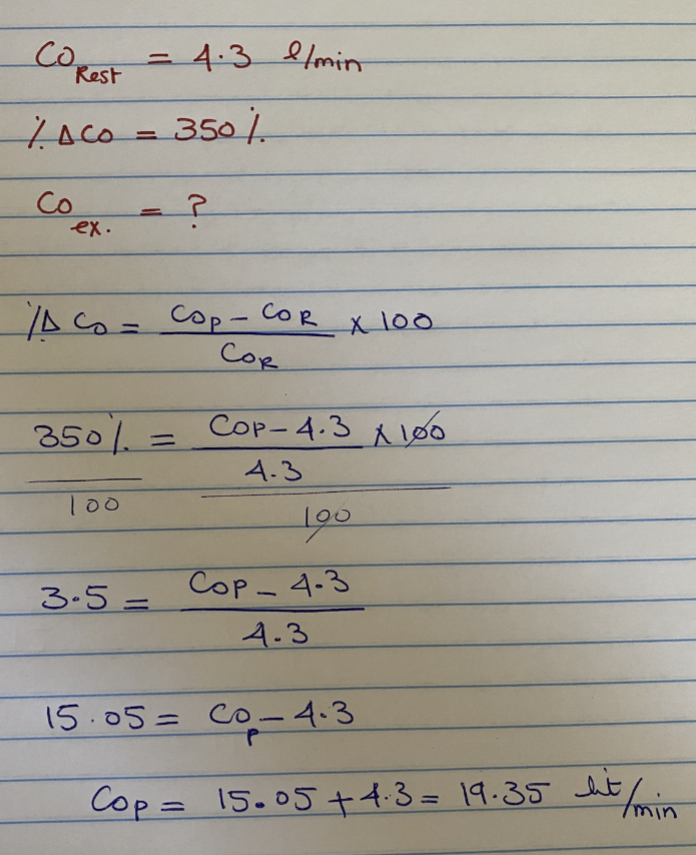
If VIcki has a blood pressure reading of 130mmHg/80mmHg and a heart rate of 70bpm, calculate her cardiac output.
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING
7000mL/min or 7L/min
If Bob’s strove volume is 102mL/beat and his systolic BP os 150 mmHg, calculate his mean blood pressure.
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING
MBP = 116mmHg
Suppose Tom’s cardiac output is 6.8L/min, his heart rate is 100bpm, and his systolic BP is 138mmHg. Calculate his diastolic BP.
DON’T FLIP UNTIL DONE WRITING

What causes the sounds heard during a blood pressure measurement?
Turbulent blood within the semi-occluded brachial artery
What mechanical events within the heart create the first and second heart sound?
The shutting of the AV valves and semilunar valves respectively
Provide reason why an increase in cardiac output is necessary during exercise?
To increase the flow of oxygen and nutrients to working skeletal muscles.
To increase the removal or carbon dioxide and wastes from skeletal muscles
To increase transport of heat to capillaries, so that it may radiate away
During exercise, the increase in skeletal muscle activity causes an increase in the return of blood to the right atrium. How and why does this affect stroke volume?
It increases SV by increasing preload. As the ventricle is stretched (up to a point), the overlap between actin and myosin becomes closer to optimum and more contracile force is generated.