Visual Psychophysics: Midterm 2
1/239
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
240 Terms
Who came up with the Absolute threshold experiment?
Hecht, Shlaer, Pirenne (HSP)

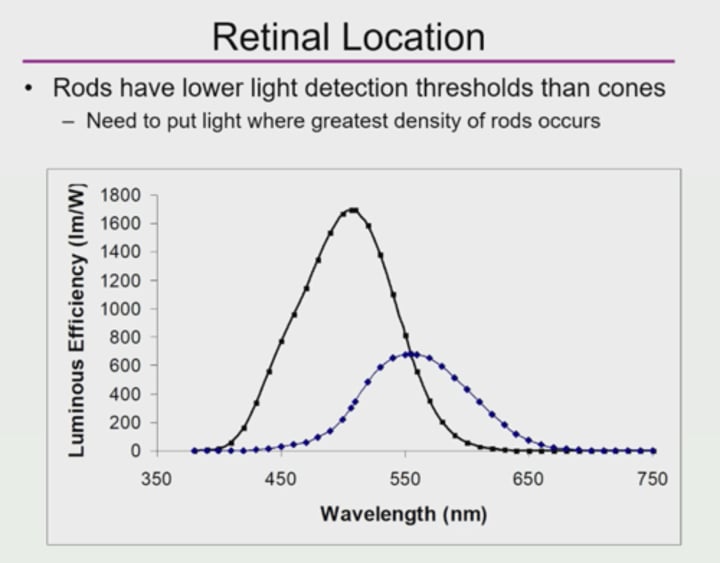
What is the luminous efficiency of rods and at what wavelength?
1700 lumens/watt at 507 nm
What is the luminous efficiency of cones and at what wavelength?
683 lumens/watt at 555 nm
What is the absolute threshold?
10 photons
What is the lowest limit for scotopic vision?
1*10^-6 candelas/m^2
1.What photoreceptors has a lower light detection threshold?
2.Where do you need to put a light?
1.Rods have lower light detect thresholds than cones
2.Need to put a light where there is the greatest density of rods occurs
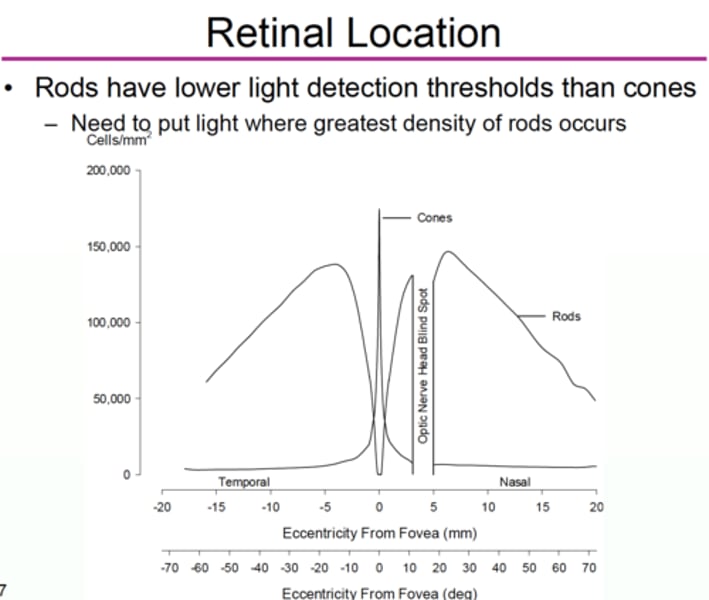
Where do rods have the most density?
15 to 20 degrees eccentrically from the fovea
What location was tested/ where the red light placed on when HSP decide to do the absolute threshold experiment?
20 degrees on the temporal retina
*occurs at all major meridians of the retina
*optic nerve head
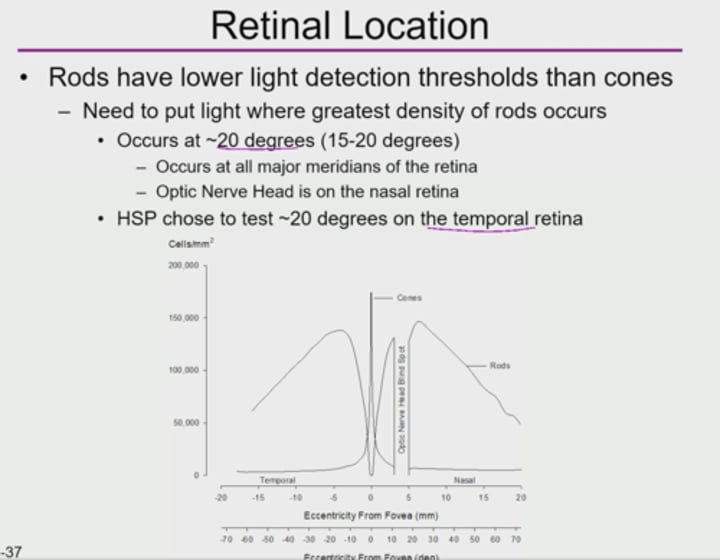
Where is the optic nerve head located (in degrees eccentricity)?
15 degrees nasally
3 to 5 mm nasally
What is found 15 degrees temporally ?
15 to 20 degrees temporally = max rod density
Can you test rods on the inferior or superior retina for greatest rod density in the absolute threshold experiment?
Yes
greatest density of rods occurs at all major meridians of the retina !
15-20 degrees eccentric
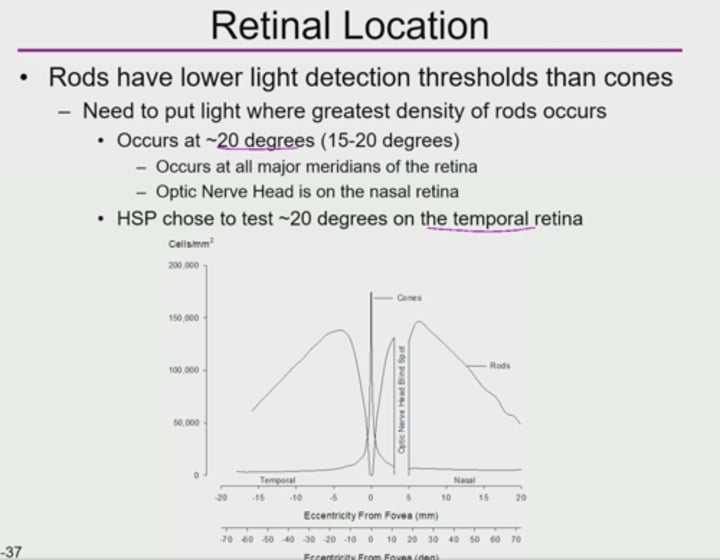
Where is the optic nerve head?
optic nerve head is on the nasal retina
Who were the subjects of the absolute threshold experiment?
H, S, & P
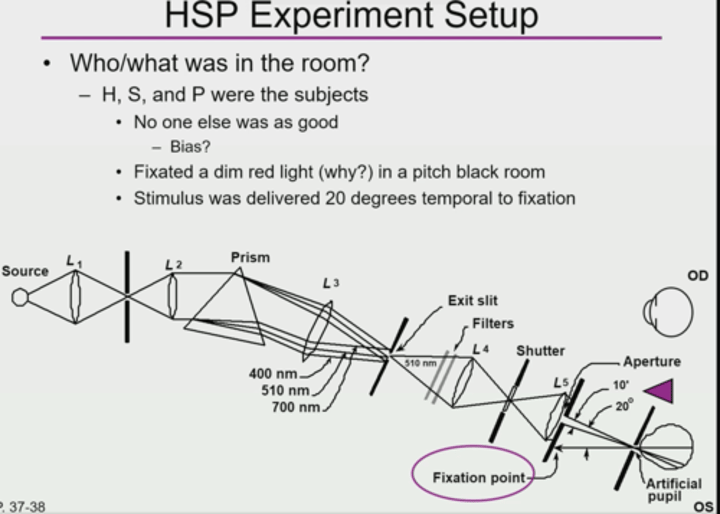
Is there bias if the experimenters are also the subjects?
No
not significant where it will change results
What was the fixation target of the H,S,P absolute threshold experiment?
Dim red light
What was the HSP absolute threshold experiment setup?
dim red light in a pitch black room
IMPORTANT
In HSP absolute threshold experiment, what do subjects use to fixate on their target ?
cones
Why is a DIM red light used as the fixation target in the HSP absolute threshold experiment?
you don't want to contaminate test area
(can't appropriately measure low light levels with a bright fixation target)
Which photoreceptors are more sensitive to red light as used in the dim red fixation target?
cones are slightly more sensitive than rods
cones have peak luminous efficiency (lumens/watt) at 555 nm which is closer to the red wavelength than cones;
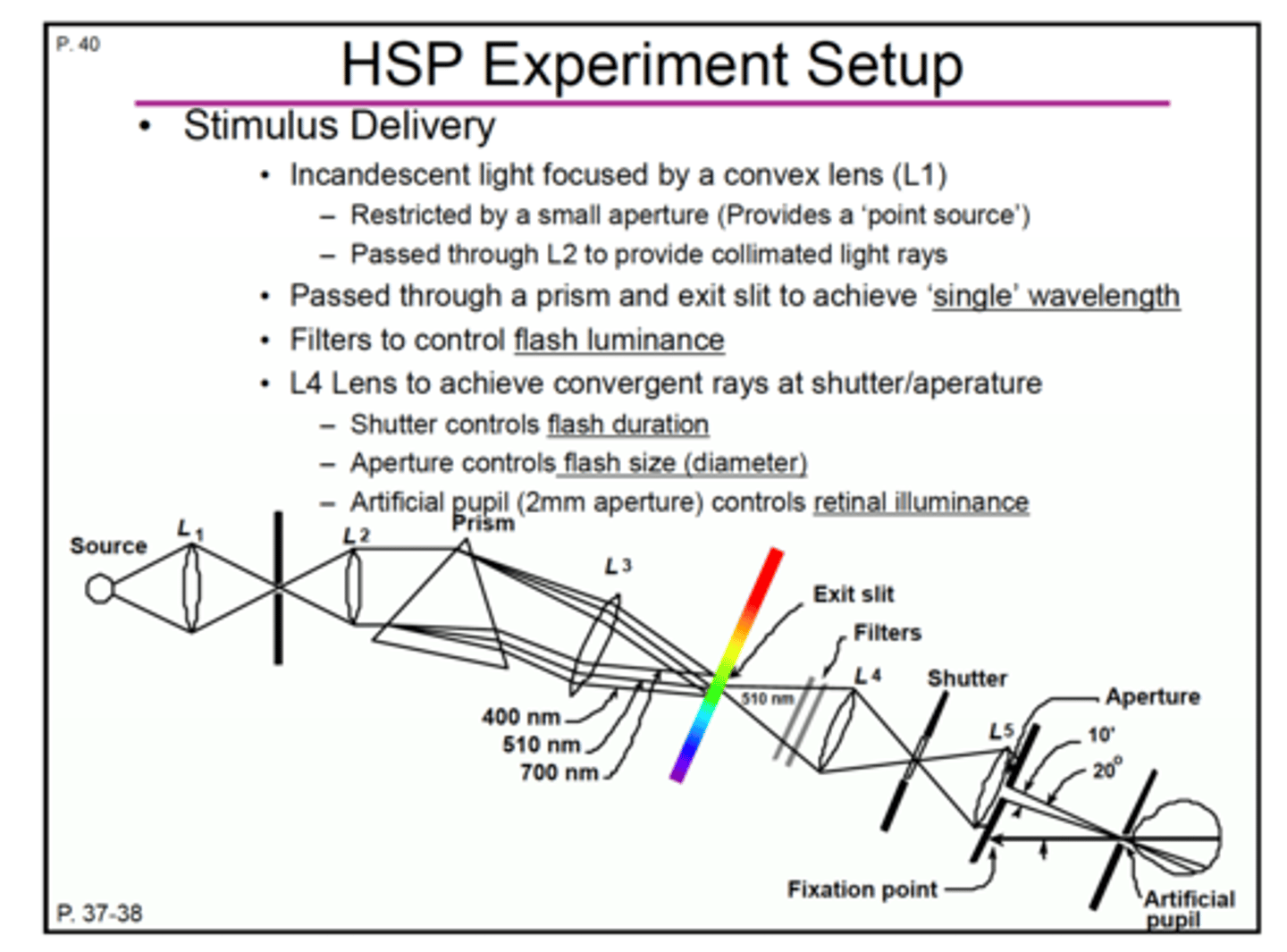
What is the HSP experiment setup using a series of lens and prism? (12)
how many lenses?
1.incadescent light
starts with a point source of light that produces diverging light which then goes through L1
2. L1 : convex lens
converging light then goes through aperture
3. aperture
diverging light exits the aperture creating a point source
then hits another convex lens
4.L2: convex lens
this convex lens produces collimated light rays or parallel light rays
5.prism
parallel light rays enter the prism
6.prism produces transverse chromatic aberration
prism produces several light rays of different colors/wavelengths
7. aperture /slit
a single wavelength of 510 nm passes through an aperture
8. neutral density/optical density filters
510 nm wavelength of light -> filter-> L4 convex lens
9. L4: convex lens achieves converging light at shutter/aperture
10.Shutter/aperture
controls how long the light is left on; controls flash duration
10: L5: convex lens
11. Aperture controls the size of the light/flash size (diameter)
12. Aperture or artificial pupil (2mm)
1)controls the retinal illuminance
2) stimulate the temporal retina
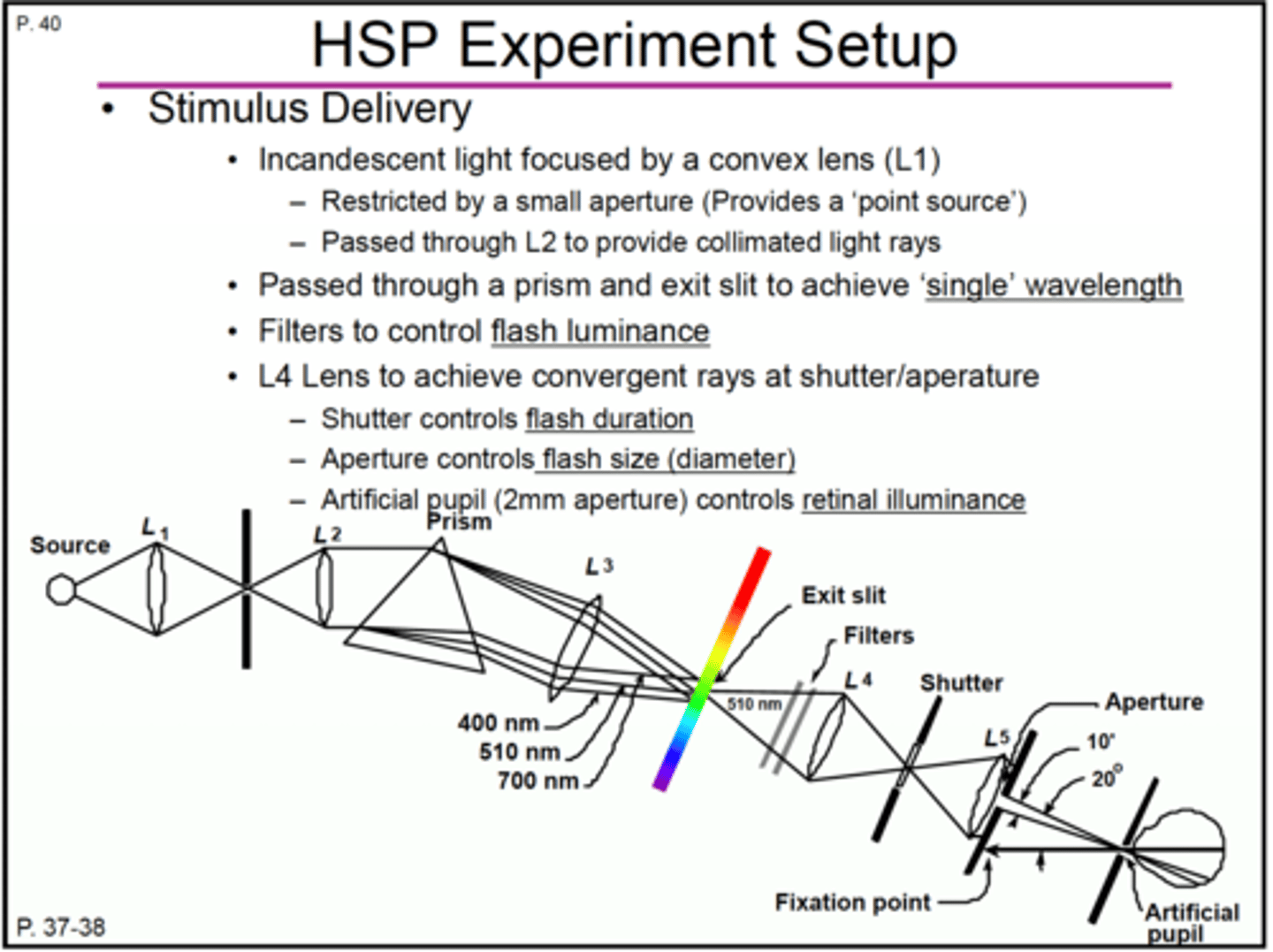
define collimated rays
light has no vergence or are parallel rays;
neither diverging nor converging
define transverse chromatic aberration
(or transverse) chromatic aberration (TCA) occurs when the different wavelengths of light are projected in different positions along the focal plane (same focal point?)
Why was the single wavelength of 510 nm used?
1.best evidence at the time (1922) determined that the peak luminous efficiency for rods was 510nm
2.Wald (1945) found 507 to be the best;
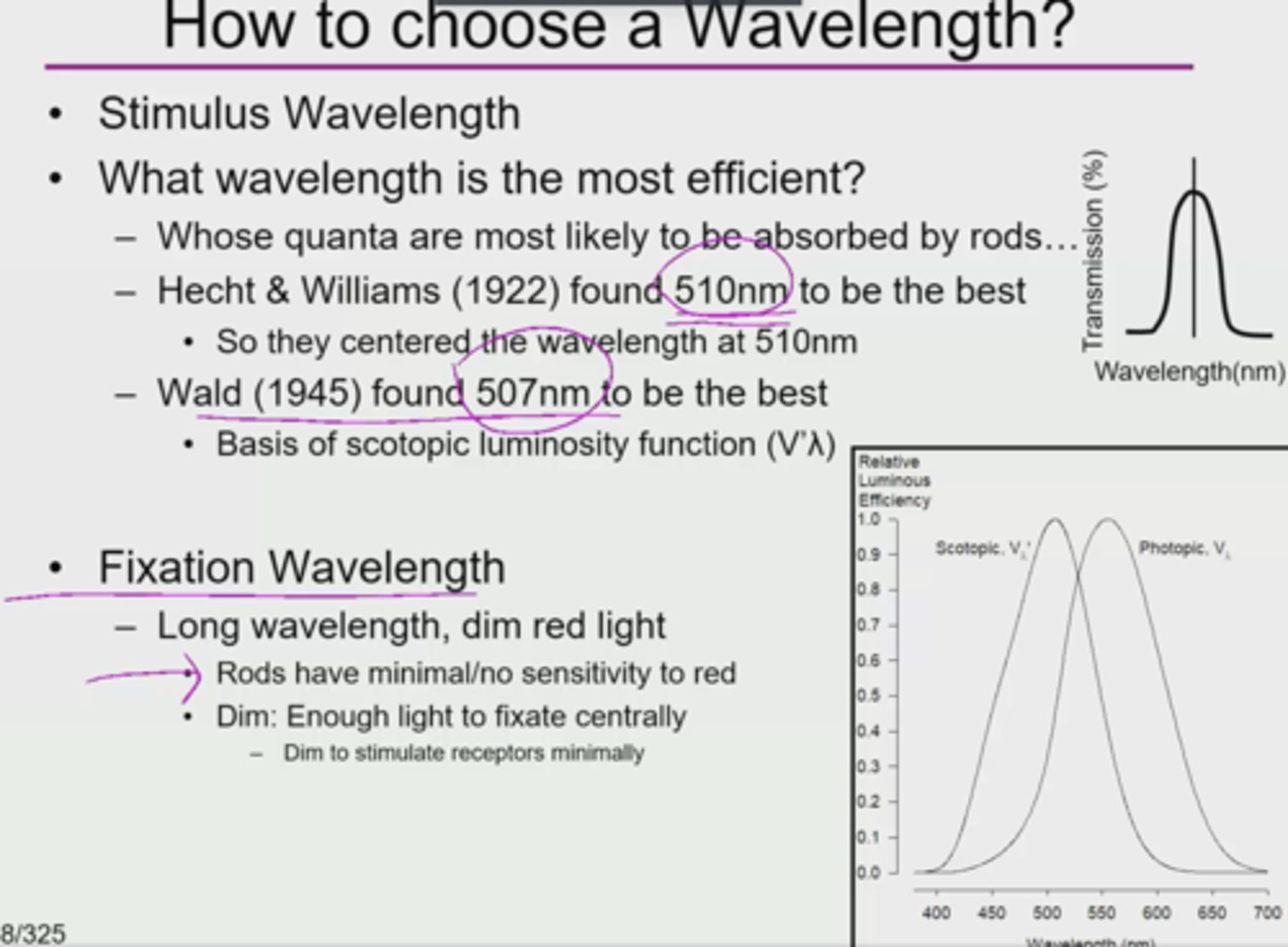
Would there be a difference in the experiment/results if 507 nm were used instead 510 nm for the single wavelength used in the HSP experiment?
No;
rods have minimal sensitivity to the red wavelength
Can rods see the red color?
Yes!
Why is there a 2mm artificial pupil or 2mm aperture used in the last step of the HSP absolute threshold experiment ?
Want all subjects to have the same pupil size in order to control retinal illuminance
What parameters are controlled in the HSP absolute threshold experiment ? (5 parameters controlled)
1.prism with exit slit w/ aperture
produces one wavelength of 510 nm
2.optical density filters
controls flash luminance
3.shutter
controls the flash duration
4.aperture
controls flash size (diameter)
5.aperture or artificial pupil of 2 mm
controls retinal illuminance
Why is a DIM red light used as the fixation target ?
1.need enough light to fixate centrally (only cones fixate)
2.dim to stimulate receptors MINIMALLY
define spatial summation
occurs when stimuli are applied at the same time, but in different areas, with a cumulative effect upon membrane potential. Spatial summation uses multiple synapses acting simultaneously.
What happens if the stimulus size of the stimulus light is too big? (2)
1.if light is too big, quanta will fall under multiple receptive fields
2.the threshold for light detect will be unnnecesarily high;
define neural convergence (2)
1.mutiple photoreceptors-> fewer bipolar cells -> one ganglion cell
2. signal is converging to few and few neurons as it passes;
3. sum up information over that field;
define receptive field
area in space over which one neuron is responsible collecting signals from other neurons
receptive field
vs
receptive field center
receptive field: photoreceptors such as cones and/or rods
receptive field center: ganglion cell
What is an example of spatial summation ?
multisteps (4)
1.person has receptive field on his/her hand
2.person gets stabbed in the hand;
3.person knows that he/she has been stabbed on the hand
4.person doesn't know the exact location on the hand where/he or she got stabbed;
What is an example of spatial resolution?
1.person has receptive field on his/her hand
2.person gets stabbed in the hand;
3.person may know if he/she has been stabbed? &
4. person knows exact location on the hand where/he or she got stabbed; can localize injury;
Where does spatial summation occur?
over a receptive field
Spatial summation & resolution of cones
Cones have great resolution (20/20) but poor summation
Spatial summation & resolution of rods
Rods have poor resolution (20/200) but great summation
What is the opposite of spatial summation ?
spatial resolution
Cones have what in terms of receptive field sizes
many small receptive fields;
example: person has many small receptive fields in order to properly localize injury on the hand on one finger = better spatial resolution
*potential to miss the injury since the receptive field covers less area
Rods have what in terms of receptive field sizes
large receptive fields and less of them;
example: person has limited number of large receptive fields in order to detect the injury at all on the hand= better spatial summation
*won't miss hand injury but can't localize exact location of injury
Can you have both good spatial summation and resolution with either cones or rods?
No
either rods have good spatial summation and poor spatial resolution;
or
cones have good spatial resolution and poor spatial summation.
What is another word for spatial resolution?
visual acuity
How large does the stimulus light need to be?
the size of the receptive field center or summation area
What defines the spatial summation area?
critical area/critical size
What does the stimulus size need to be less than?
the critical area/critical size
What happens to the spatial summation as you move from the foveola to the peripheral retina?
Spatial summation for both rods and cones
increases with increasing retinal eccentricity
Don't need to know:
i.e. 4-7 degrees eccentric = 20 to 30 minutes of arc;
What did HSP choose as the stimulus size ?
10 minute arc stimulus size
must be limited to one spatial summation area
How many microns is the stimulus size
10 minutes arc = 46 microns
1.pink: cone
2.blue: rod
1.what photoreceptor is the pink arrow pointing to?
2.what photoreceptor is the blue arrow pointing to?
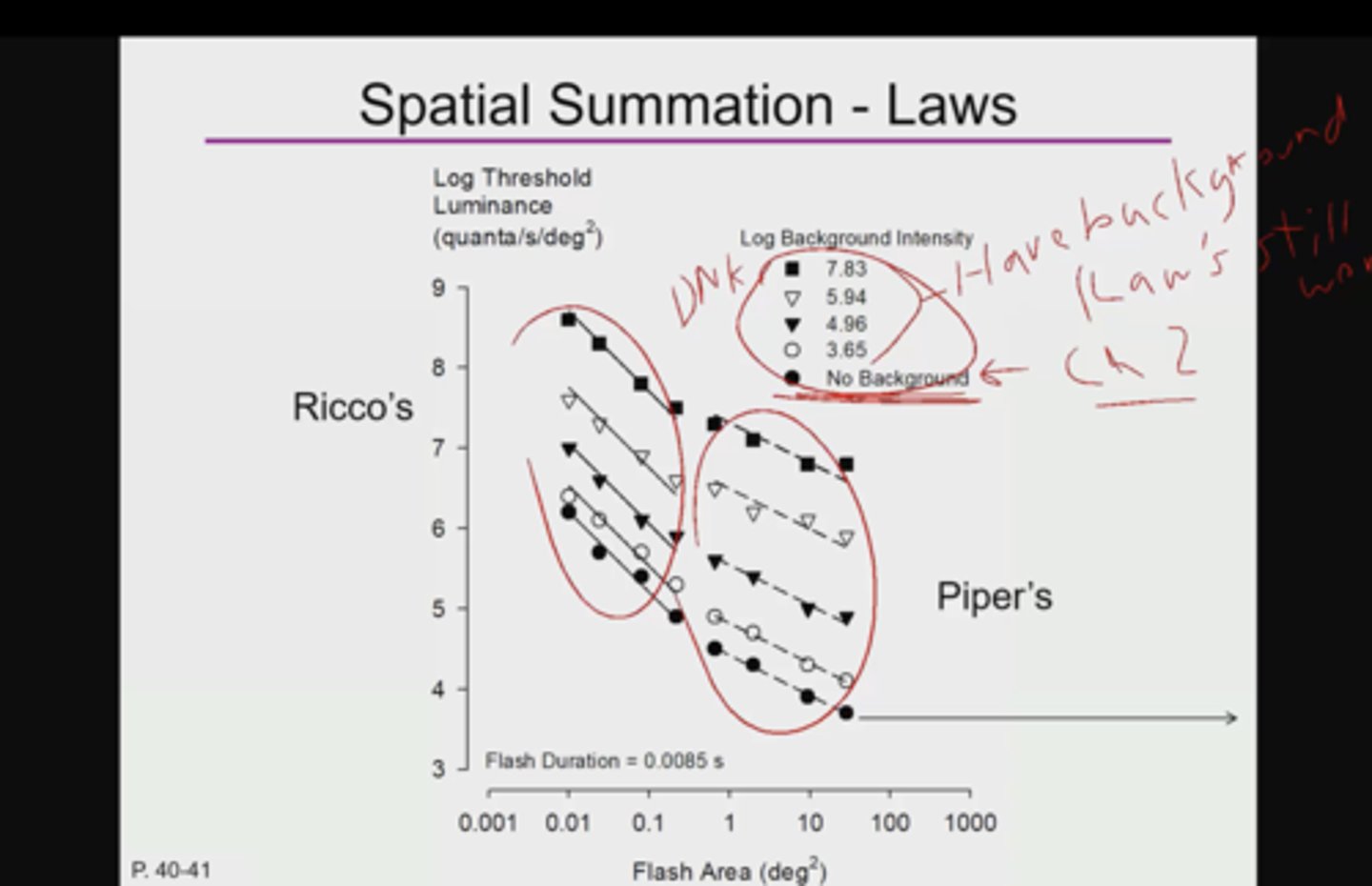
What is Ricco's Law formula?
L x A = C
Luminance x Area = constant (# of quanta at threshold)
What is the constant in Ricco's law?
# of photons at threshold
threshold = 10 photons
1.Example: A 10 cd/m^2 light with a 1 degree^2 is at threshold; what is the constant?
2.If the light is now 5 cd/m^2, how big does the light need to be to reach threshold?
1. constant = 10
2. area = 2 degree^2
According to Ricco's Law,
if the luminance increases or the light is brighter, what happens to the area?
Luminance increases (light is brighter), then the Area decreases
According to Ricco's Law,
if the luminance decreases or the light is dimmer, what happens to the area?
Luminance decreases (light is dimmer), then the Area increases
What is Piper's Law formula?
L x sqrt(A) = constant
Luminance x sqrt (Area) = constant
What are features of piper's law?
1.partial summation
2.still occurs but slower, smaller slope
Ricco's Law vs Piper's Law
Ricco's Law: total summation
Piper's Law: partial summation
define quanta
particle of light
What is the slope of Ricco's Law?
m = -1
(Change in Y)/(Change in X)
REDRAW THIS GRAPH
Spatial Summation: Ricco's and Piper's Law
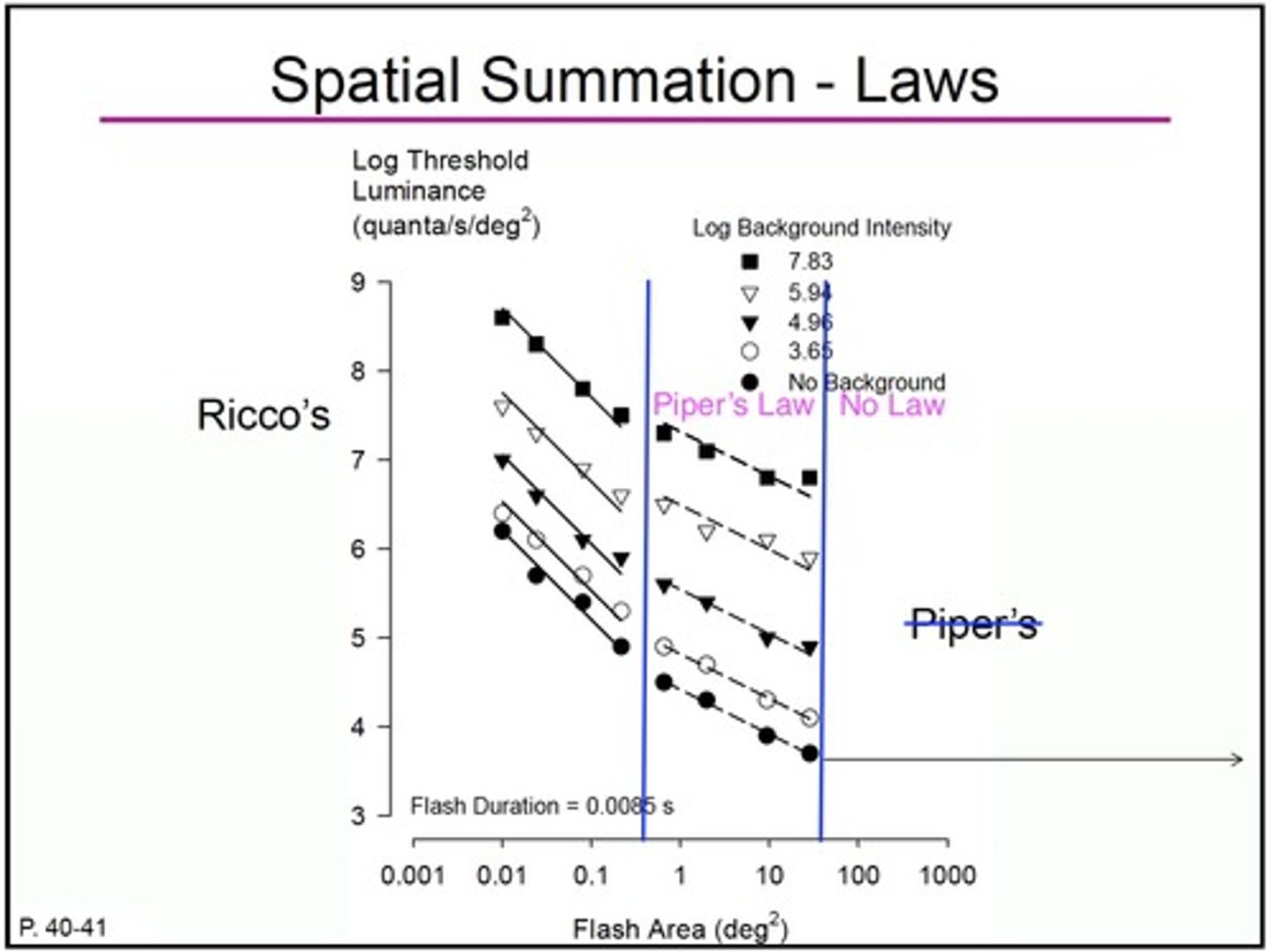
What is the slope of Piper's Law?
m = -0.5 or -1/2
(Change in Y)/(Change in X)
Any point on the line graph of ricco's law is...
at threshold
What is the line dividing piper's and rico's law on the spatial summation graph represent?
where ricco's law stop
where critical area = spatial summation = receptive field size
What happens in the no law zone of the spatial summation graph?
What is the slope?
Luminance and area become independent of each other;
Luminance remains the same; doesn't matter what area is;
m = 0; represented by a horizontal line;
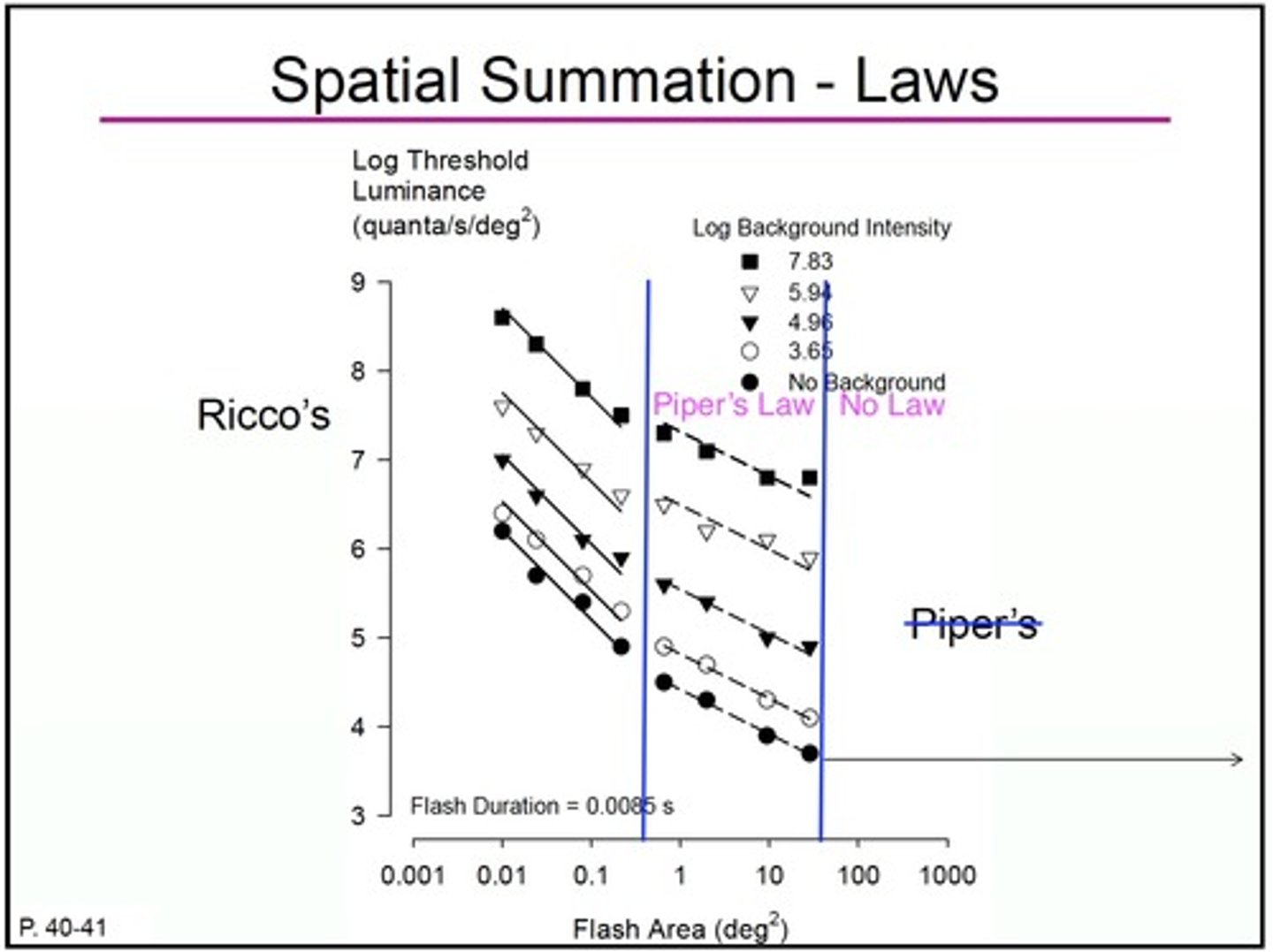
When there is log background intensity, what type of test is this?
discrimination/resolution task
note: spatial summation graphs of rico's and piper's laws don't only apply to HSP absolute threshold experiment settings (dim red light in a pitch black room)
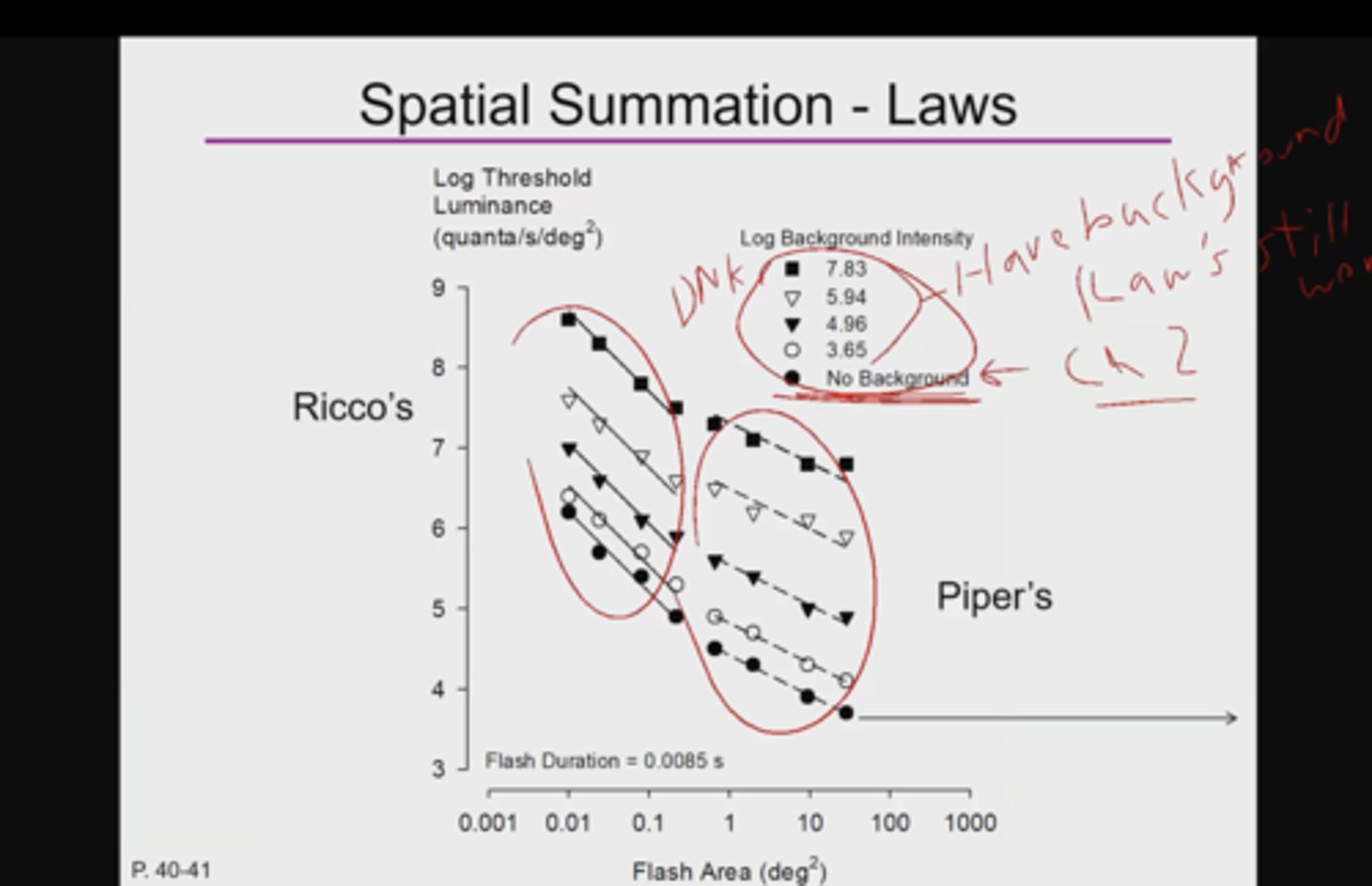
When there is NO log background intensity, what type of test is this?
detection test
note: spatial summation graphs of rico's and piper's laws don't only apply to HSP absolute threshold experiment settings (dim red light in a pitch black room)
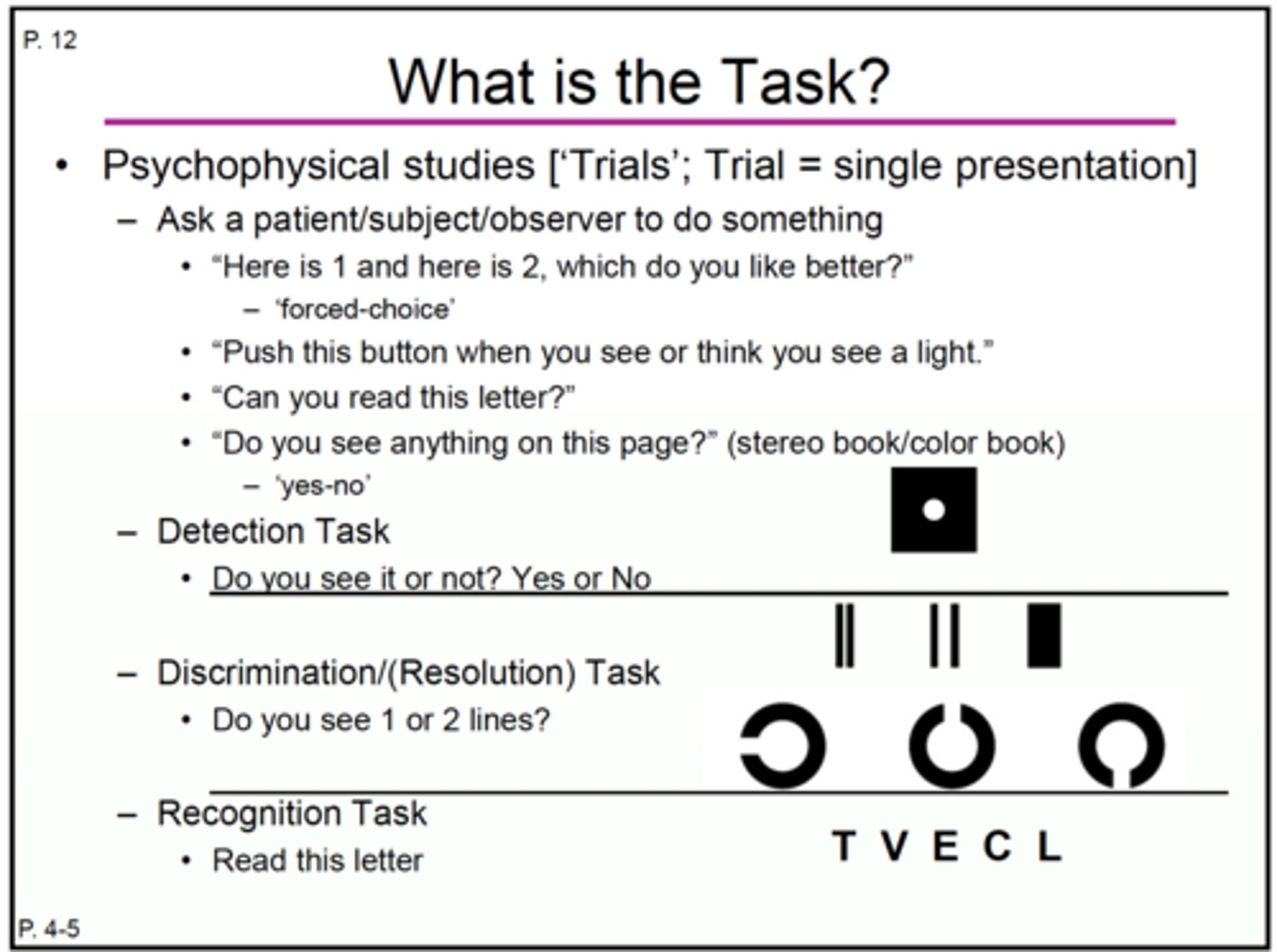
detection task
vs
discrimination/resolution task
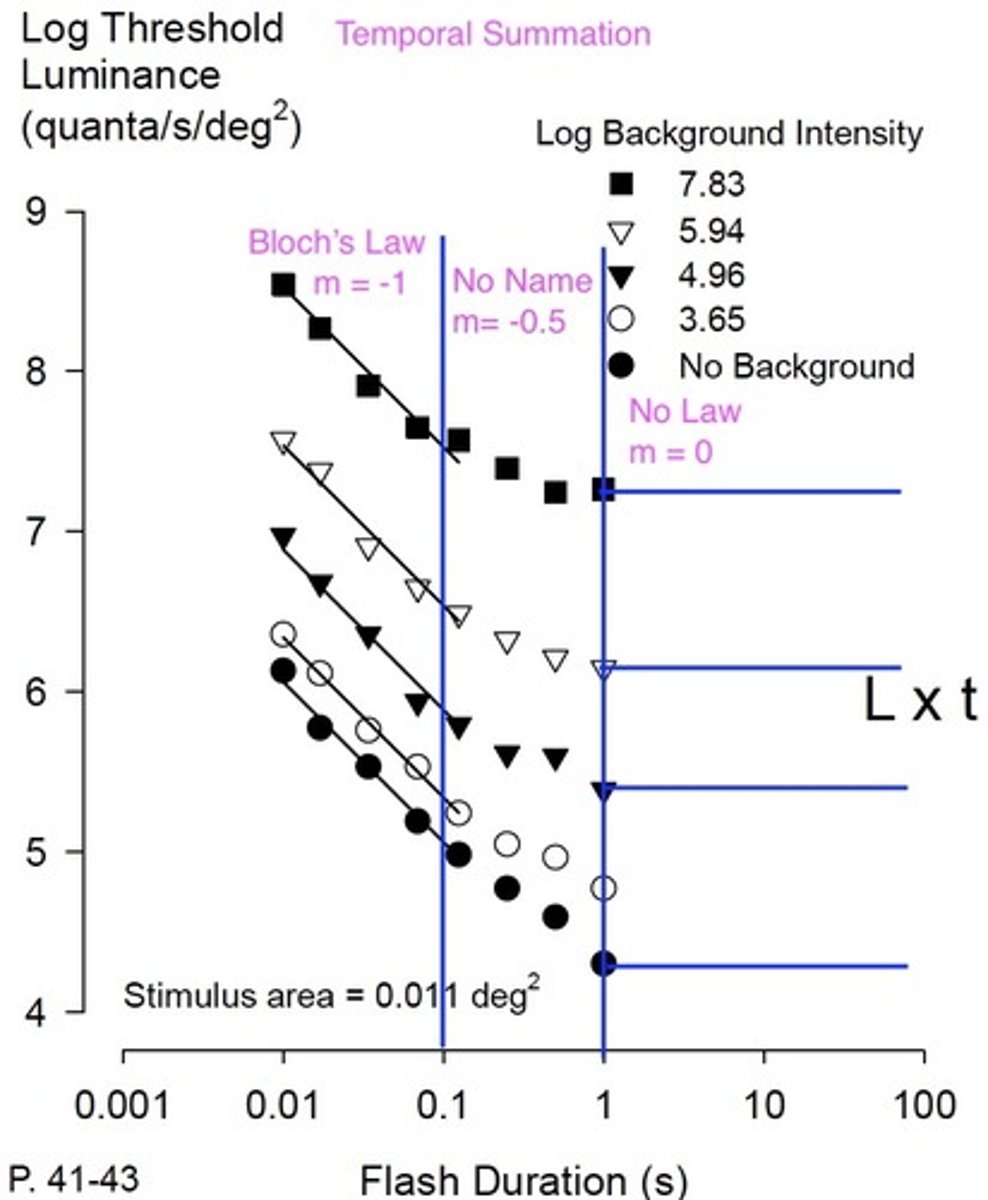
Bloch's Law formula
C = L x t
Luminance x time = constant
What is the slope of bloch's law?
m= -1
What happens in the no law zone of the spatial summation graph?
What is the slope?
Luminance and time are independent of each other
m=o
define temporal summation
Summation by a postsynaptic cell of input (EPSPs or IPSPs) from a single source over time.
define temporal summation in terms of light
add up light over a certain amount of time
What is the critical area for ricco's law?
DONT NEED TO KNOW!
approximately
0.70 degree^2
What is the critical duration for bloch's law?
100 msec
or
.1 sec
Why did HSP pick 1 msec or .001 second for the duration time of their experiment?
HSP was very conservative in choosing the time duration of the experiment
they didn't want to exceed the critical duration at all;
want to accurately test threshold;
What is the critical duration for bloch's law?
100 ms
REDRAW DIAGRAM
temporal summation graphs: Bloch's Law
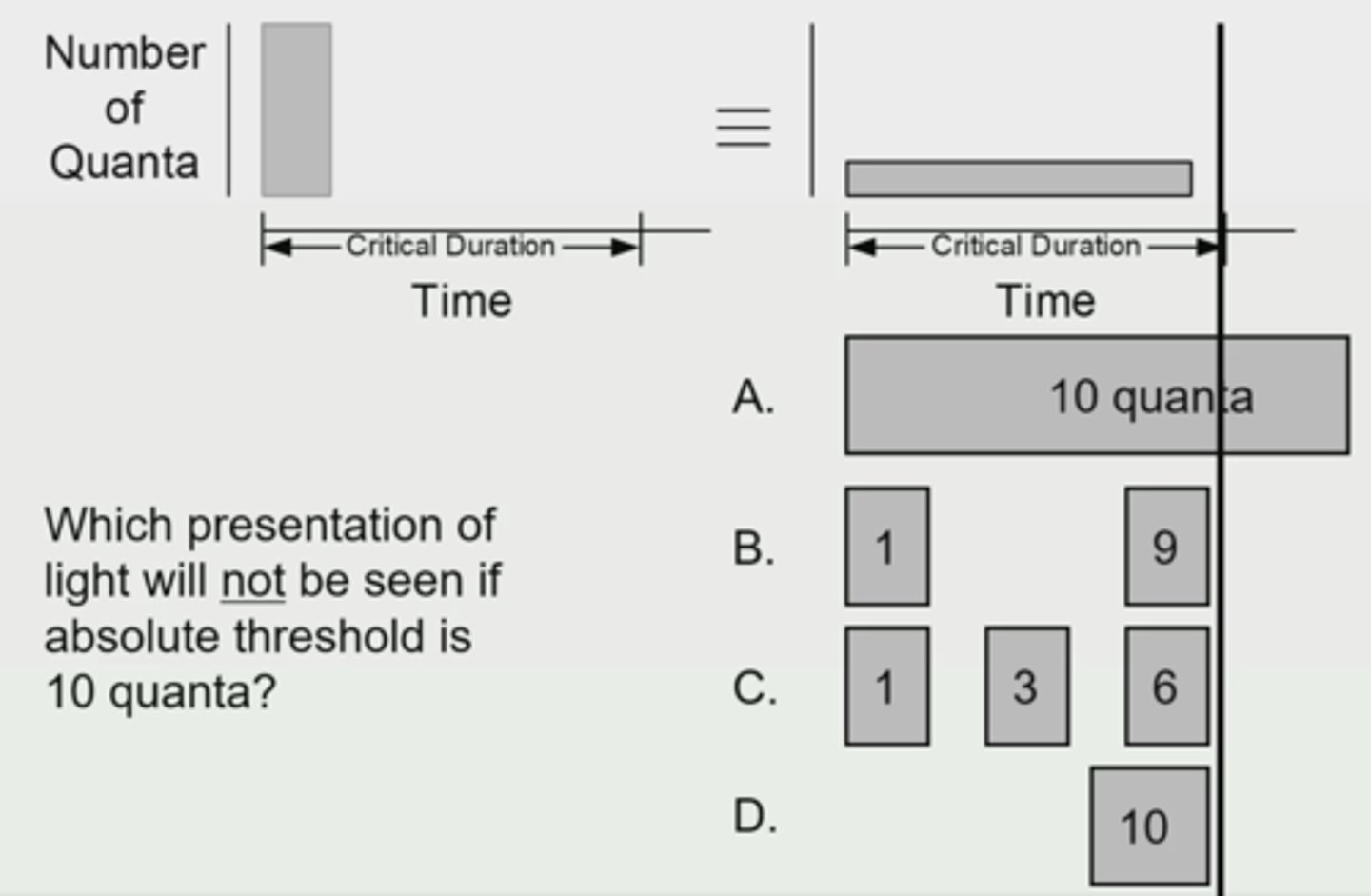
Answer: A
represents bloch's law
Which presentation of light will not be seen if the absolute threshold is 10 quanta?
What does a low threshold mean in comparison to sensitivity?
Low threshold means a high sensitivity
Answer:
D. Grey
What is the color of the stimulus light in the H,S, P experiment?

What does a high threshold mean in comparison to sensitivity?
High threshold means a low sensitivity
1.What happens will you sit in a totally dark room for at least 30 minutes?
2.
1. this allows dark adaption
2.threshold decreases for rods with long time in dark
What is the formula for threshold?
1/sensitivity
What is the formula for sensitivity?
1/threshold
What was the psychophysical method and set up that HSP used?
Use the method of constant stimuli;
What was the set up that HSP used for absolute threshold experiment?
1. 6 different intensities presented randomly (50/trial)
DON'T NEED TO KNOW:
2.subject had control of when presentation would occur
3.subject used a 'bite bar' (dental impression) which forces the head to be still;
4.fixated the red light and attended peripherally
5.set 60% as threshold
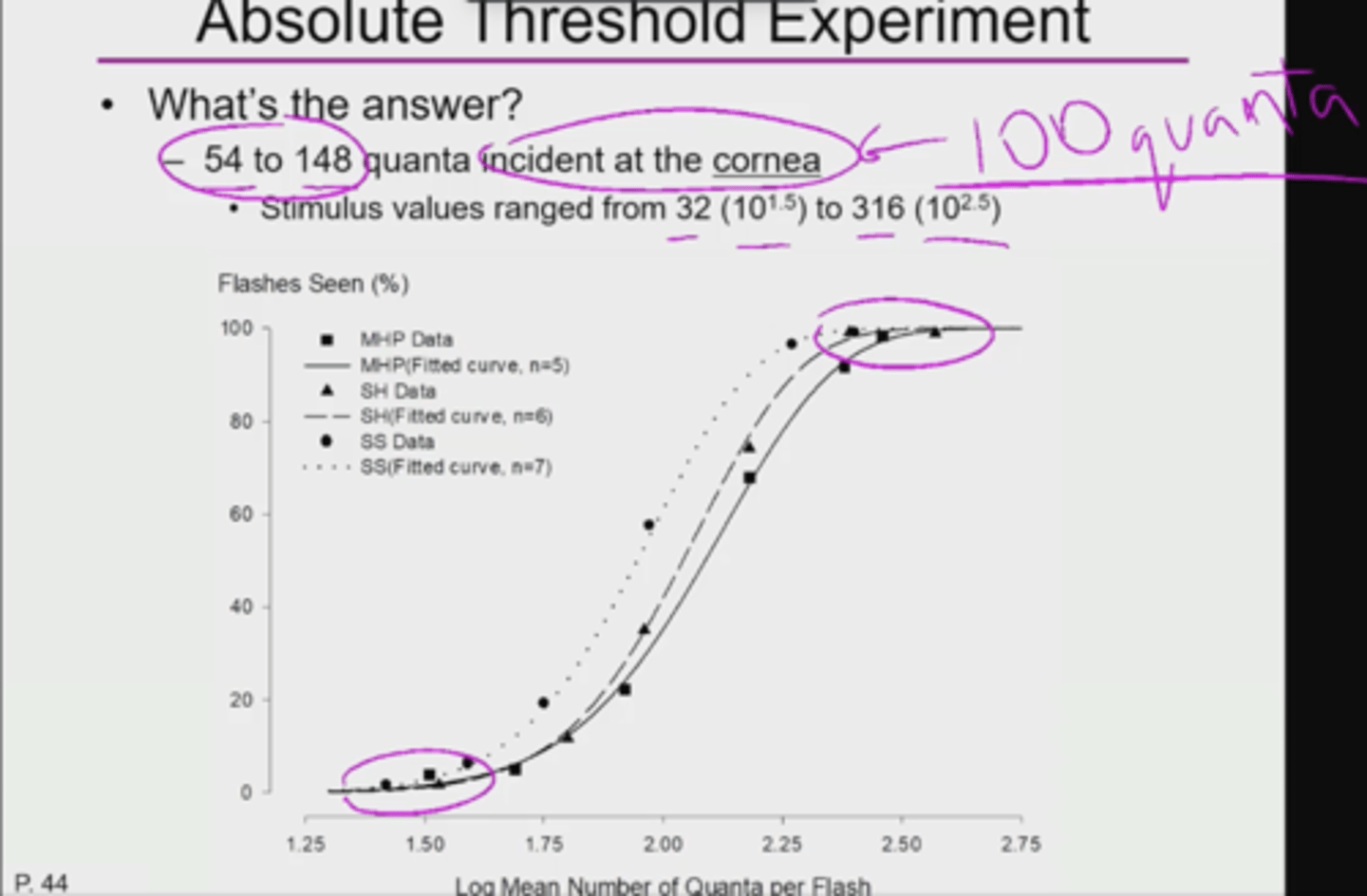
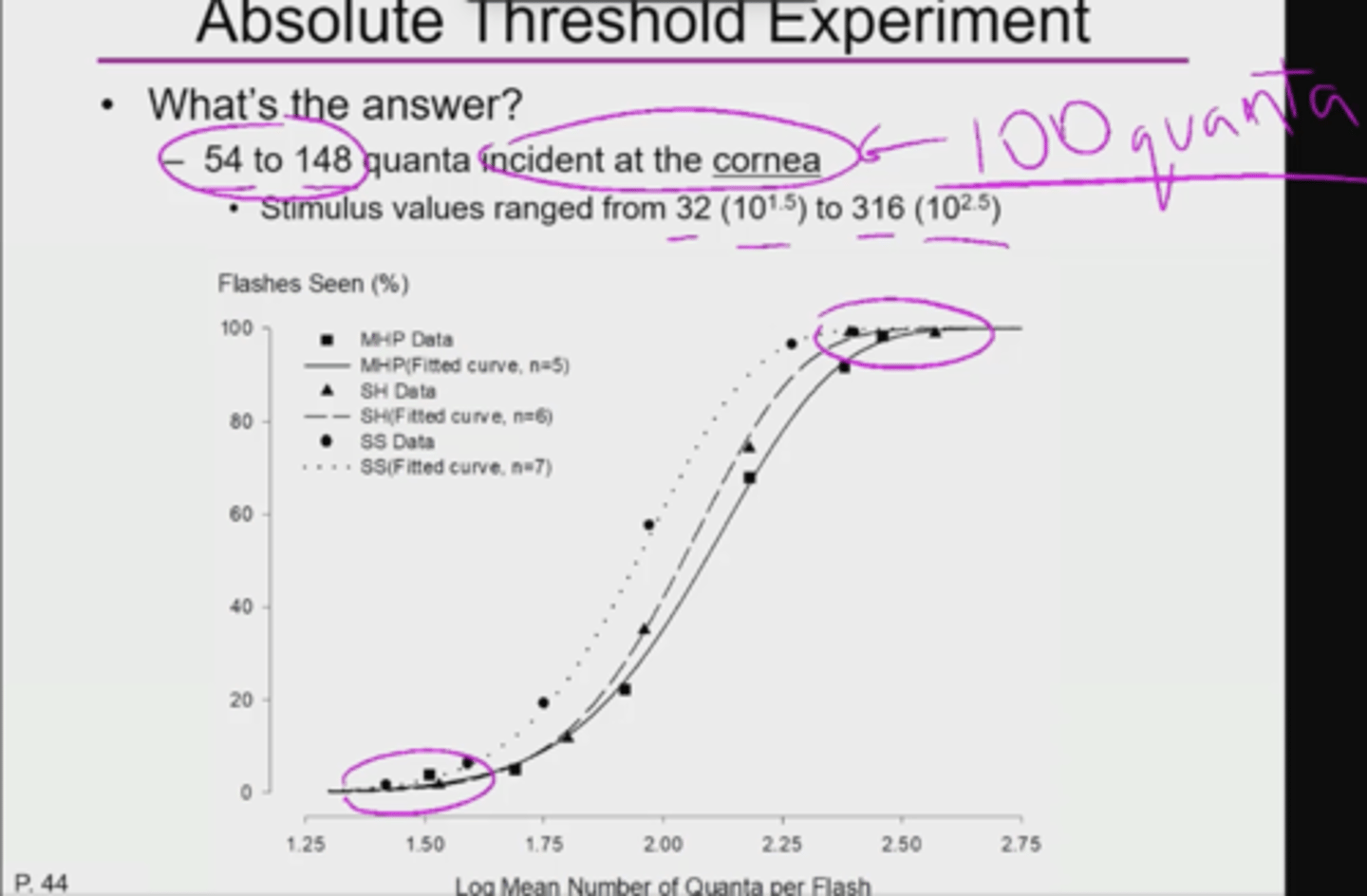
In the HSP absolute light threshold experiment, what is (absolute threshold) of quanta incident at the cornea?
MEMORIZE : 100 quanta incident at threshold;
54 to 148 quanta incident at the cornea;
Since the subject had control of when the presentation would occur in the absolute threshold experiment, what psychophysical method was used?
Adjustment method
Since the subject had 6 different intensities presented randomly (50/trial) in the absolute threshold experiment, what psychophysical method was used?
Constant stimuli method
What number of quanta are incident to the cornea?
100 quanta
Why are 50% of photons are lost when light travels from the cornea to the retina?
(3 factors)
Losses in eye (aqueous, lens, vitreous) due
term-87
1.internal reflection
2.scattering
3.absorption
What percentage of quanta pass through the cornea and make it to the retina?
50 quanta (50% reach the retina from the cornea)
Of the remaining quanta that get to the retina, how many quanta (& percentage) are absorbed by the rods?
10 quanta (20%)
Of the remaining quanta that get to the retina, why is only 20% absorbed by the rods?
1.Absorbed by RPE cells or cones
2.pass through the outer segment of photoreceptors without photo-isomerizing rhodosphin
Can the results of the HSP absolute threshold experiment be trusted?
there was no bias;
even though the subject
What is a perfect observer or subject?
subject/observer has no bias;
In the absolute threshold experiment, were HSP able to control how many quanta were in each flash?
No!
The number of photons in each flash of light weren't always the same!
define Poisson Distribution
uses a small amount of data;
features Poisson Distribution
1.randomly distributed discrete events
2.different distribution for each mean number of quanta;
3.for any given flash, you don't know the actual number of quanta in it;
4.however, the distributions show that there are upper/lower limits;