AP Human Unit 1 Vocab
4.8(4)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Thinking geographically
Last updated 7:46 PM on 4/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
**map**
a representation with an area of land or sea showing physical features, cities and roads.
2
New cards
**cartography**
the science of mapmaking
3
New cards
**map scale**
the relationship between distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground
4
New cards
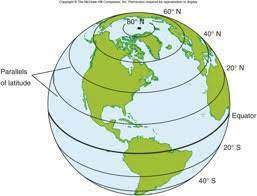
**parallel**
a circle drawn around the globe parallel to the equator and at right angles to the meridians
5
New cards
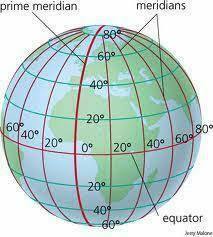
**meridian**
a circle of constant longitude passing through a given place on earth's surface and terrestrial poles.
6
New cards
**prime meridian**
designed as 0 degrees longitude, that passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England.
7
New cards
**region**
geographically, an extensive area of the world defined by its physical and human similarities.
8
New cards
**distortion**
an error in presentation that gives a false representation.
EX: DISTORTION THAT OCCURS FROM TAKING A CIRCULAR GLOBE AND PUTTING IT ON A FLAT MAP
EX: DISTORTION THAT OCCURS FROM TAKING A CIRCULAR GLOBE AND PUTTING IT ON A FLAT MAP
9
New cards
**remote sensing**
studying an object or location without making physical contact
EX: CAMERAS ON SATELLITES
EX: CAMERAS ON SATELLITES
10
New cards
**GIS**
geographic information system, computer system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth's surface.
11
New cards
**GPS**
global positioning system, satellite navigation based on a global network that transmits radio signals from earth.
12
New cards
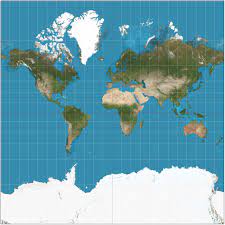
\
**mercator projection ~** an attempt to create a two-dimensional map that maintained accurate and reliable compass points, but sizes are very distorted and inaccurate
13
New cards
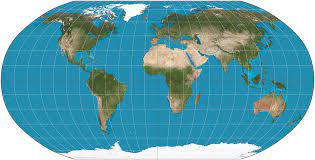
**robinson projection ~** compromise in that it attempts to minimize errors in distance, relative size, and compass direction but does not accurately depict any one of these factors
14
New cards
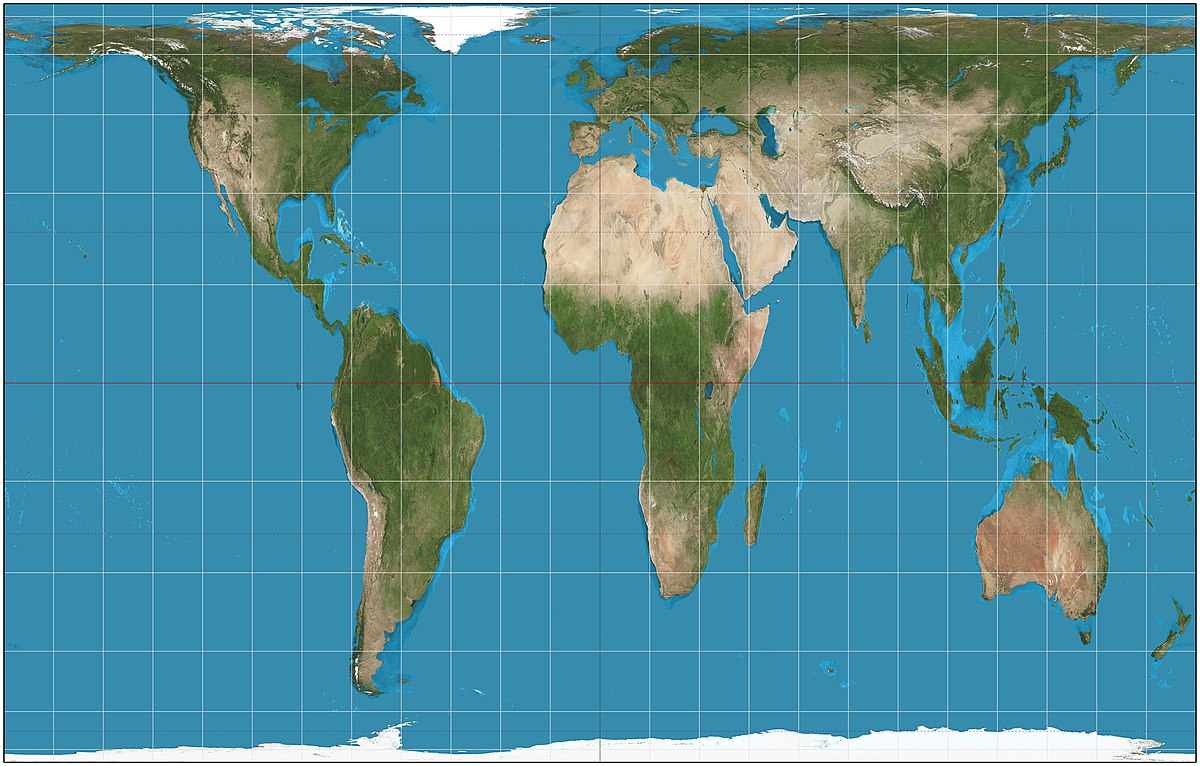
**gall-peters projection ~** reflects the land size of all continents equally, but in doing so it distorts distance and direction.
15
New cards
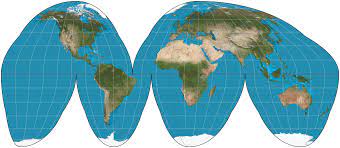
**goode-homolosine projection ~** main disadvantage: most of the angles and directions are distorted, advantage: shape and size of continents being accurate and in proportion.
16
New cards
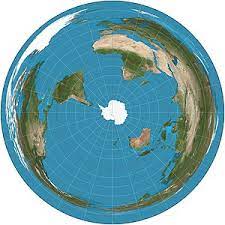
**polar projection ~** polar projection is primarily used to show the north or south polar regions of the Arctic and Antarctica. A polar projection is a type of azimuthal projection.
17
New cards
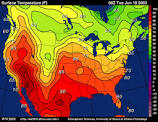
**isoline map (aka isopleth) ~** maps that show lines that join points of equal value. (For example, a topographic map is an isoline map on which lines join points of equal elevation.)
18
New cards
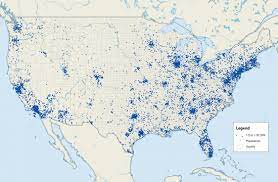
**dot distribution map ~** a type of map that uses the density of dot symbols that are the same size to show the presence of a feature
19
New cards
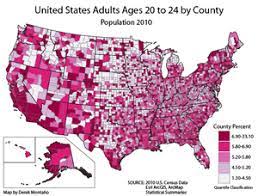
**choropleth map ~** uses different shades to show the variation of the values.
20
New cards
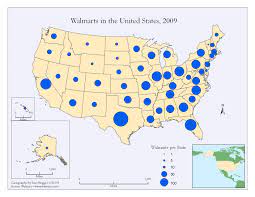
**graduated symbol map ~** used to show quantitative difference between mapped features by varying the size of symbols
21
New cards
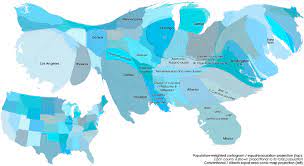
**cartogram ~** a map in which the geometry of regions is distorted in order to convey the info of an alternate variable
22
New cards
**location**
the position of something on the earth’s surface
23
New cards
**toponym**
another word for name, but is specific to locations
EX: USA
EX: USA
24
New cards
**site**
exact location, the site is the land that the city was built upon.
25
New cards
**situation**
the situation of a city relates to its surrounding features, both human-made and natural. the situation of the city includes characteristics that are external to the settlement.
26
New cards
**cultural landscape**
cultural attributes of an area often used to describe a place
27
New cards
**formal region**
an area defined by one predominant or universal characteristic throughout its entire area. formal Regions have well-defined boundaries
28
New cards
**functional region**
an area centered on a node, focal point, or central hub surrounded by interconnecting linkages
EX: CITY AND ITS SURROUNDING SUBURBS
EX: CITY AND ITS SURROUNDING SUBURBS
29
New cards
**perceptual region**
or vernacular region is defined by feelings and prejudices that may or may not be true
EX: THE MIDWEST
EX: THE MIDWEST
30
New cards
**culture**
total way of life held in common by a group of people, including learned features such as language, ideology, behavior, technology, and government
31
New cards
**globalization**
the increasing connection of economic, cultural, and political characteristics across the world.
EX: RAW PRODUCT HARVESTED IN AFRICA, THEN IS USED TO MANUFACTURE GOODS IN CHINA, AND SHIPPED AROUND THE WORLD FOR SALE.
EX: RAW PRODUCT HARVESTED IN AFRICA, THEN IS USED TO MANUFACTURE GOODS IN CHINA, AND SHIPPED AROUND THE WORLD FOR SALE.
32
New cards
**space**
a general, objective location or area
33
New cards
**transnational corporations**
company that conducts research, operates factories, and sells products in many countries, not just where its headquarters or shareholders are located.
34
New cards
**distribution**
arrangement of features in a space
35
New cards
**density**
the no. of people who live in a defined land area
36
New cards
**concentration**
the spread of a feature(dispersed/scattered or clustered/agglomerated)
37
New cards
**pattern**
arrangement of objects on earth's surface in relationship to one another
EX: LINEAR PATTERN OF HOUSES IN A LINE
EX: LINEAR PATTERN OF HOUSES IN A LINE
38
New cards
**distance decay**
theory that states that as the distance between two places increases, the interaction between those two places decreases.
39
New cards
**space-time compression**
the reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place, as a result of improved communications and transportation system
EX: INTERNET
EX: INTERNET
40
New cards
**LDC**
less-developed countries, countries that have low economic growth and little to no industrialization.
EX: COUNTRIES IN SUB SAHARAN AFRICA, AFGHANISTAN
EX: COUNTRIES IN SUB SAHARAN AFRICA, AFGHANISTAN
41
New cards
**MDC**
more developed countries, countries that have advanced socially and economically.
EX: USA, CANADA, JAPAN
EX: USA, CANADA, JAPAN
42
New cards
**NIC**
newly industrialized country, country whose level of economic development ranks it somewhere between developing and highly developed classifications
EX: CHINA, INDIA, MALAYSIA
EX: CHINA, INDIA, MALAYSIA
43
New cards
**environmental determinism**
philosophy of geography that stated that human behaviors are a direct result of the surrounding environment
44
New cards
**possibilism**
theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment.