Physiology II final numbers for memorization
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
sodium
135-145 mEq/L
potassium
4.0-5.0mEq/L
Which of the following metabolic waste products are derived from the catabolism of protein?
urea
hydrostatic capillary pressure
60
what system regulates BP
angiotensin II
what part of the renal system decides in renin is produced?
juxtaglomerular apparatus
Where in the cardiovascular system is the highest pressure concentrated?
arteries
angiotensin II
ADH, constriction
Atrial natriuretic peptide
vasodilator
Where in the cardiovascular system is most of the blood flow?
veins and venules
calcium 2+ blood total value
9.0-10.5 mg/dl
calcium 2+ blood ionized value
4.5-5.5 mg/dl
glucose blood values
60-100mg/dl
glucose blood values for diabetes
125mg/dl
Osmolarity
285-300 mosmol/L
Blood value pH
7.38-7.45
Blood value for PaCO2
35-45mmHg
blood value for PaO2
80-100mmHg
HR
60-100bpm
EF (ejection fraction)
50-75%
Cardiac output
5L
BP
120/80 mmHg
FEV1/FVC (forced Expiratory volume)
>79%
FVC (forced vital capacity) value
5.0L
Breaths
12-20 per minute
Glomerular Filtration Rate
>90ml/min (125 is typical)
HCO3 value
22-28 mEq/L
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) levels
7-20 mg/dL
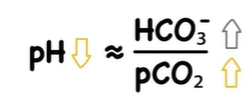
respiratory acidosis
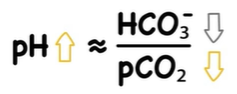
respiratory alkalosis
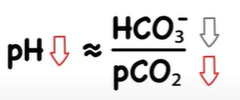
metabolic acidosis
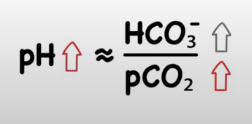
Metabolic alkalosis
Respiratory acidosis
HYPOVENTILATION (not enough air)
CO2 builds up → Carbonic acid increase→ pH decreases
common cause: COPD, respiratory depression, head injury, airway obstruction
compensation: kidneys retain
HCO3- to raise pH
respiratory alkalosis
hyperventilation
effect: CO2 is blown off→ decrease carbonic acid→ pH increases (to more basic) baseline
common cause: anxiety attack, high altitude, fever, pain
metabolic acidosis
cause: buildup of acids or loss of bicarbonate
effect: decrease bicarbonate, pH decreases (more acidic)
common causes: diabetic ketoacidosis, kidney failure, diarrhea, lactic acidosis (loss of HCO3-)
compensation: lungs increase breathing to blow off CO2
Diabetic ketoacidosis
body doesn’t have enough insulin so it breaks down fat for energy producing acidic substances called ketones
high blood sugar levels
can be fatal
metabolic alkalosis
Cause: loss of acid or gain or bicarbonate
effect: increase HCO3-, increase in pH (more alkaline)
common causes: vomiting (loss of stomach acid), diuretics excess antacid use
compensation: lungs slow breathing to reattach to CO2
percentage of plasma in body water
7%
percentage of plasma in blood?
55%
percentage of erythrocytes in blood
45%
plasma
carries blood cells, proteins, nutrients, metabolic waste and other molecules being transported around the body, yellowish liquid component of blood that makes up about 55% of its volume.
3 types of heart control
nerves
endocrine
autonomous