Atoms, Compounds, Mixtures, and Chemical Change
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
What is everything in the Universe made up of?
*matter*
2
New cards
What makes up movement in the Universe?
*energy*
3
New cards
What is energy?
*capacity or power to do work*
4
New cards
What forms can energy exist in?
* *potential*
* *thermal*
* *chemical*
* *nuclear*
* *thermal*
* *chemical*
* *nuclear*
5
New cards
What does the atomic model help us understand?
*structure/interactions/properties of matter*
6
New cards
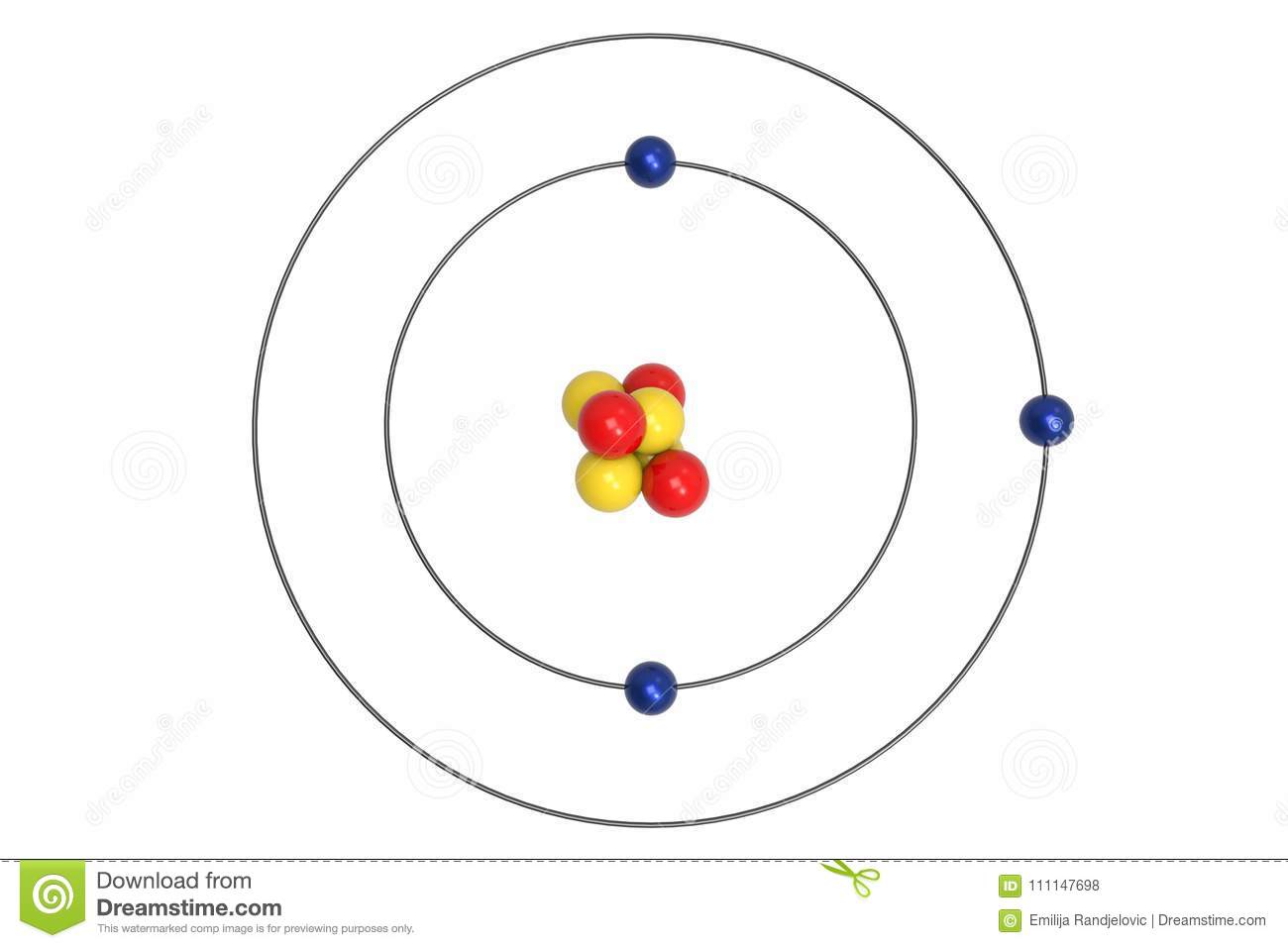
Name this atom
*Lithium Atom*
7
New cards
What is an element?
* *pure substance*
* *atoms are all same*
* *atoms are all same*
8
New cards
What is the fundamental difference between elements?
* *structure of elements*
* *number of protons, neutrons, and electrons*
* *number of protons, neutrons, and electrons*
9
New cards
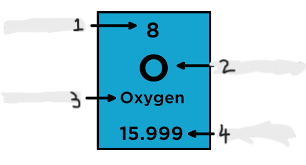
Label the following
1. *Atomic Number*
2. *Element Symbol*
3. *Element Name*
4. *Atomic Weight*
10
New cards
List properties of metals
* *solids at room temp. (except mercury)*
* *conductors of heat and electricity*
* *generally have a high density*
* *lustrous*
* *ductile*
* *malleable*
* *conductors of heat and electricity*
* *generally have a high density*
* *lustrous*
* *ductile*
* *malleable*
11
New cards
List properties of non-metals
* *solids/gases at room temperature (except bromine)*
* *not conductors*
* *generally have a low density*
* *dull (not lustrous)*
* *brittle (crumble/break when bent)*
* *not conductors*
* *generally have a low density*
* *dull (not lustrous)*
* *brittle (crumble/break when bent)*
12
New cards
List properties of semi-metals
* *solid at room temp*
* *semi conductor*
* *usually lustrous*
* *usually ductile/malleable (except silicon)*
* *semi conductor*
* *usually lustrous*
* *usually ductile/malleable (except silicon)*
13
New cards
Compare metals and non-metals
* *metals: dense, lustrous, ductile, malleable*
*non-metals: dull, brittle, low density*
* *metals: conductors of heat and electricity*
*non-metals: not conductors*
*non-metals: dull, brittle, low density*
* *metals: conductors of heat and electricity*
*non-metals: not conductors*
14
New cards

\
Determine whether the following elements are metals, non-metals, or semi-metals
* Lithium (Li)
* Phosphorus (P)
* Argon (Ar)
* Silicon (S)
* Scandium (Sc)
* Hydrogen (H)
Determine whether the following elements are metals, non-metals, or semi-metals
* Lithium (Li)
* Phosphorus (P)
* Argon (Ar)
* Silicon (S)
* Scandium (Sc)
* Hydrogen (H)
* *Lithium (Li) (Metal)*
* *Phosphorus (P) (Non-metal)*
* *Argon (Ar) (Non-metal)*
* *Silicon (S) (Semi-metal)*
* *Scandium (Sc) (Metal)*
* *Hydrogen (H) (Non-metal)*
* *Phosphorus (P) (Non-metal)*
* *Argon (Ar) (Non-metal)*
* *Silicon (S) (Semi-metal)*
* *Scandium (Sc) (Metal)*
* *Hydrogen (H) (Non-metal)*
15
New cards
List an example for a monatomic substance, diatomic substance, polyatomic substance, and lattice.
* *Monatomic - Helium*
* *Diatomic - Oxygen*
* *Polyatomic - Sulfur*
* *Lattice - Graphite*
* *Diatomic - Oxygen*
* *Polyatomic - Sulfur*
* *Lattice - Graphite*
16
New cards
Compare monatomic, diatomic, and polyatomic atom arrangements,
* *monatomic atom arrangement: only one atom in element*
* *diatomic: two atoms in one molecule of element.*
* *polyatomic: more than two atoms in one molecule of element*
* *diatomic: two atoms in one molecule of element.*
* *polyatomic: more than two atoms in one molecule of element*
17
New cards
What is a compound?
* *type of matter composed of different elements*
* *chemically bonded in fixed ratios.*
* *chemically bonded in fixed ratios.*
18
New cards
Explain the differences between the elements that make up compounds and the compounds themselves.
*In H2O, Hydrogen gas and Oxygen gas chemically bond to form H2O molecules, which forms liquid water. The elements that make up water have different properties compared to water.*
19
New cards
Define an ion
* *charged atom or molecule*
* *uneven protons:electrons*
* *uneven protons:electrons*
20
New cards
How are cations formed?
* *after the atom loses electrons*
21
New cards
How are anions formed?
* *after atom gains electrons*
22
New cards
How are ionic compounds formed?
* *positively/negatively charged ions attracted to each other*
23
New cards
Name three cations and anions
*Cations: Lithium, Calcium, Magnesium*
*Anions: Fluorine, Chlorine, Oxygen*
*Anions: Fluorine, Chlorine, Oxygen*
24
New cards
What is a pure substance?
* *chemical composed of one type of atom/molecule/ion (can have more than one particle)*
* *chemically bonded to each other.*
* *chemically bonded to each other.*
25
New cards
What is a mixture?
* *impure substance*
* *particles/substances physically mixed together*
* *not chemically bonded*
* *retain their own chemical properties*
* *particles/substances physically mixed together*
* *not chemically bonded*
* *retain their own chemical properties*
26
New cards
Describe a heterogeneous mixture, with an example.
* *molecules not mixed in even distribution*
* *not the same throughout*
* *example: muddy water.*
* *not the same throughout*
* *example: muddy water.*
27
New cards
Describe a homogeneous mixture, with an example.
* *molecules mixed in even distribution*
* *the same throughout*
* *example: salt water*
* *the same throughout*
* *example: salt water*
28
New cards
How is milk homogenised?
* *large globules of fat form layer of cream*
* *broken down into smaller particles*
* *so tiny they stay suspended in milk*
* *broken down into smaller particles*
* *so tiny they stay suspended in milk*
29
New cards
What is miscibility?
* *ability for two liquid substances to be mixed together*
30
New cards
What is immiscibility?
* *liquid substances don’t mix*
* *form immiscible layers based on density*
* *example: water and oil*
* *oil layer formed ontop of water*
* *form immiscible layers based on density*
* *example: water and oil*
* *oil layer formed ontop of water*
31
New cards
What are alloys?
* *homogeneous mixture of metals*
* *two or more metallic elements.*
* *two or more metallic elements.*
32
New cards
Name 3 alloys and describe their composition.
*Steel is made of Carbon and Iron*
*Nichrome is mde of Nickel and Chromium*
*Bronze is made of Copper and Tin.*
*Nichrome is mde of Nickel and Chromium*
*Bronze is made of Copper and Tin.*
33
New cards
On a particle level, what are the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures?
* *elements: made up of just one type of atom*
*compounds and mixtures: made up of more than one type of atom*
* *compounds: made up of two or more elements chemically bonded*
*mixtures: elements/compounds held together by physical bonds.*
*compounds and mixtures: made up of more than one type of atom*
* *compounds: made up of two or more elements chemically bonded*
*mixtures: elements/compounds held together by physical bonds.*
34
New cards
What is chemical polarity in molecules?
* *electron cloud of atom gains abundance of electrons in particular area*
* *brief negative charge on that end, and brief positive charge on opposing end*
* *brief negative charge on that end, and brief positive charge on opposing end*
35
New cards
What is a solute and solvent in a solution?
* *solute: dissolving solid*
* *liquid in which solute dissolves is solvent.*
* *liquid in which solute dissolves is solvent.*
36
New cards
How does dissolving occur in polar and non polar solutes and solvent?
* *polar solutes only dissolve in polar solvents*
*non polar solutes only dissolve in non polar solvents.*
* *stronger attraction between solute + solvent = more soluble*
* *polar solute is more attracted to polar solvent as the positive and negative poles are attracted to each other*
*a polar solvent/solute has partial negative/positive charges, while a non polar solvent/solute is neutral throughout.*
*polar solvents have bonds between atoms with very different charges, while non-polar solvents have bonds between neutral atoms.*
*non polar solutes only dissolve in non polar solvents.*
* *stronger attraction between solute + solvent = more soluble*
* *polar solute is more attracted to polar solvent as the positive and negative poles are attracted to each other*
*a polar solvent/solute has partial negative/positive charges, while a non polar solvent/solute is neutral throughout.*
*polar solvents have bonds between atoms with very different charges, while non-polar solvents have bonds between neutral atoms.*
37
New cards
Name an example of dissolving being a physical change.
* *sucrose dissolving*
38
New cards
Name an example of dissolving being a chemical change.
* *salt dissolving*
39
New cards
* What are the differences between physical and chemical change?
* *physical change: no new bonds are formed/broken*
*chemical change: new bonds are formed/broken*
* *physical changes: easily reversed*
*chemical changes: not easily reversed.*
***Every chemical goes through varying chemical changes based on their different chemical identities.***
*chemical change: new bonds are formed/broken*
* *physical changes: easily reversed*
*chemical changes: not easily reversed.*
***Every chemical goes through varying chemical changes based on their different chemical identities.***
40
New cards
* What are some characteristics that indicate a chemical change has occurred?
* *Change in colour*
* *Temperature change*
* *Gas is given off*
* *Light is produced*
* *A new solid is formed (precipitation*
* *Temperature change*
* *Gas is given off*
* *Light is produced*
* *A new solid is formed (precipitation*
41
New cards
How do chemical changes relate to chemical reactions?
* *chemical change occurs as a result of chemical reaction*
* *chemical reaction occurs → composition of chemicals change*
* *chemical bonds can be broken or formed*
* *result of a chemical reaction is a chemical change*
* *new chemical substance forming occurs after chemical bonds are broken/formed.*
* *chemical reaction occurs → composition of chemicals change*
* *chemical bonds can be broken or formed*
* *result of a chemical reaction is a chemical change*
* *new chemical substance forming occurs after chemical bonds are broken/formed.*
42
New cards
What is a reactant and product?
* ***reactants****: are the chemicals that are present before the chemical reaction has occurred*
* *react together to form the* ***product****: result of the chemical reaction.*
* *react together to form the* ***product****: result of the chemical reaction.*
43
New cards
How do chemical equations represent a chemical reaction?
* *chemical equation shorter/more efficient way of representing a chemical reaction*
* *easily understand which and how many chemicals are reacting to produce a new substance*
* *chemical equation shows same things as chemical reaction reactant(s) and product(s)*
* *in a simple equation format.*
* *easily understand which and how many chemicals are reacting to produce a new substance*
* *chemical equation shows same things as chemical reaction reactant(s) and product(s)*
* *in a simple equation format.*
44
New cards
Write word equations to represent the following chemical reactions:
* Iron reacts with oxygen to produce iron oxide
* Magnesium reactions with oxygen to produce magnesium oxide
* Zinc reacts with chlorine to produce zinc chloride
* Photosynthesis reaction
* Respiration reaction
* Iron reacts with oxygen to produce iron oxide
* Magnesium reactions with oxygen to produce magnesium oxide
* Zinc reacts with chlorine to produce zinc chloride
* Photosynthesis reaction
* Respiration reaction
* ***Iron reacts with oxygen to produce iron oxide***
*Iron + Oxygen → Iron oxide*
* ***Magnesium reactions with oxygen to produce magnesium oxide***
*Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide*
* ***Zinc reacts with chlorine to produce zinc chloride***
*Zinc + Chlorine → Zinc chloride*
* ***Photosynthesis reaction***
*Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen*
* ***Respiration reaction***
*Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water*
*Iron + Oxygen → Iron oxide*
* ***Magnesium reactions with oxygen to produce magnesium oxide***
*Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide*
* ***Zinc reacts with chlorine to produce zinc chloride***
*Zinc + Chlorine → Zinc chloride*
* ***Photosynthesis reaction***
*Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen*
* ***Respiration reaction***
*Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water*
45
New cards
List chemical equations that describe the process of chemical weathering
* *CO₂ + H₂O → H₂CO₃*
*Carbon Dioxide + Water → Carbonic Acid*
* *H₂CO₃ + CaCO₃ → Ca(HCO₃)₂*
*Carbonic Acid + Calcium Carbonate → Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate*
*Carbon Dioxide + Water → Carbonic Acid*
* *H₂CO₃ + CaCO₃ → Ca(HCO₃)₂*
*Carbonic Acid + Calcium Carbonate → Calcium Hydrogen Carbonate*