Combination - Picashu
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
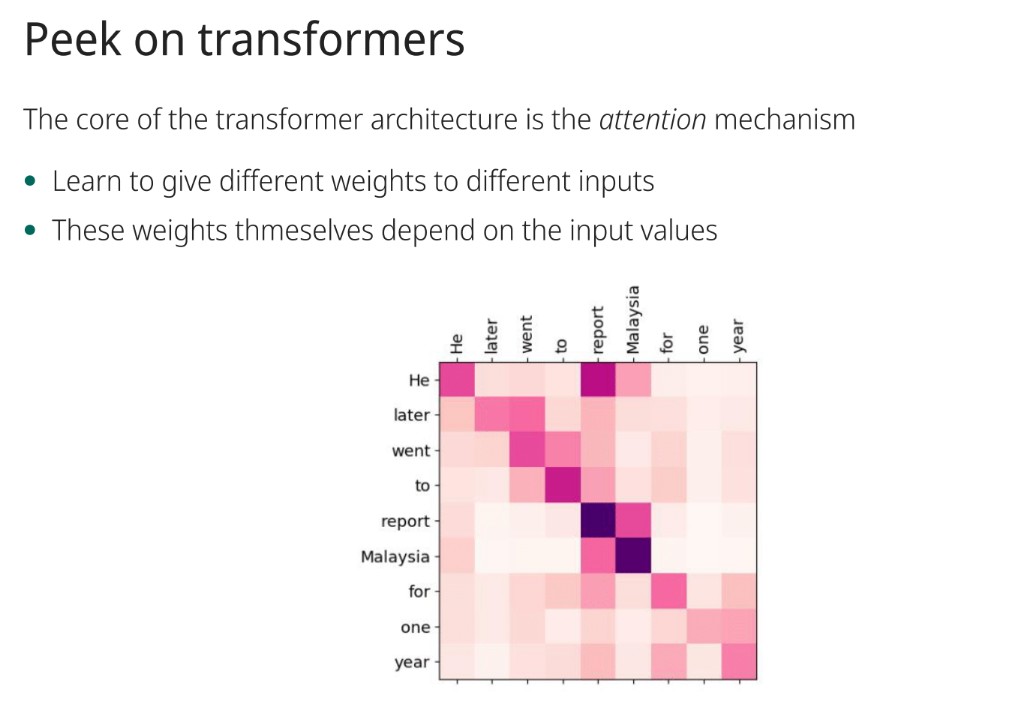
What is the core component of Transformer architecture?
The attention mechanism.
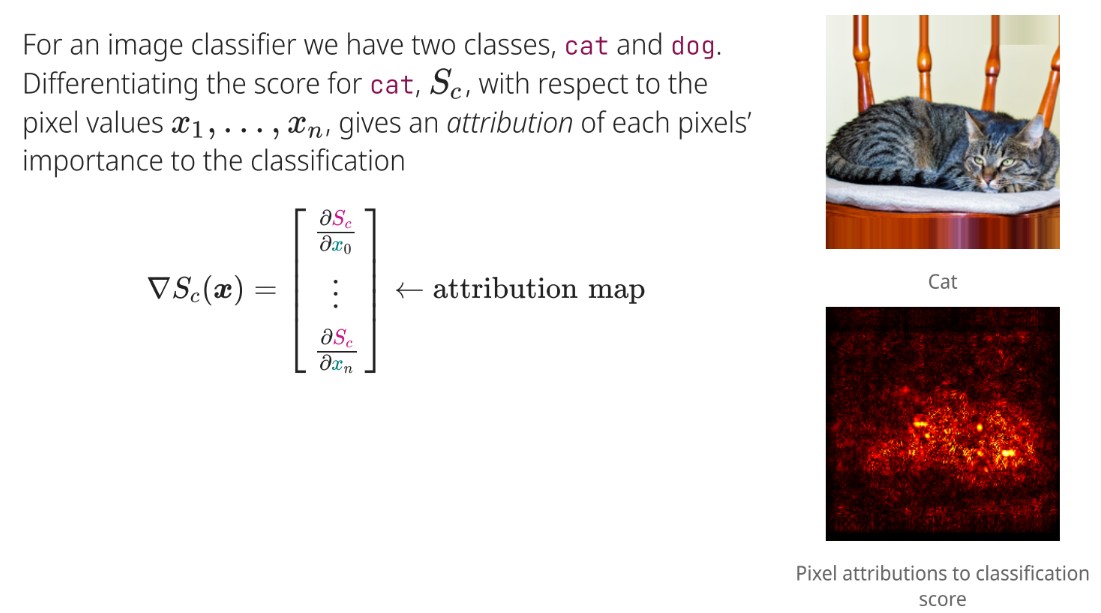
What is the significance of differentiating the score for a class with respect to pixel values in image classification?
Provides an attribution map showing each pixel's importance to the classification.
Name a solution to solve the issue with noisy gradients.
Add noise and average to smooth the gradient (SmoothGrad)

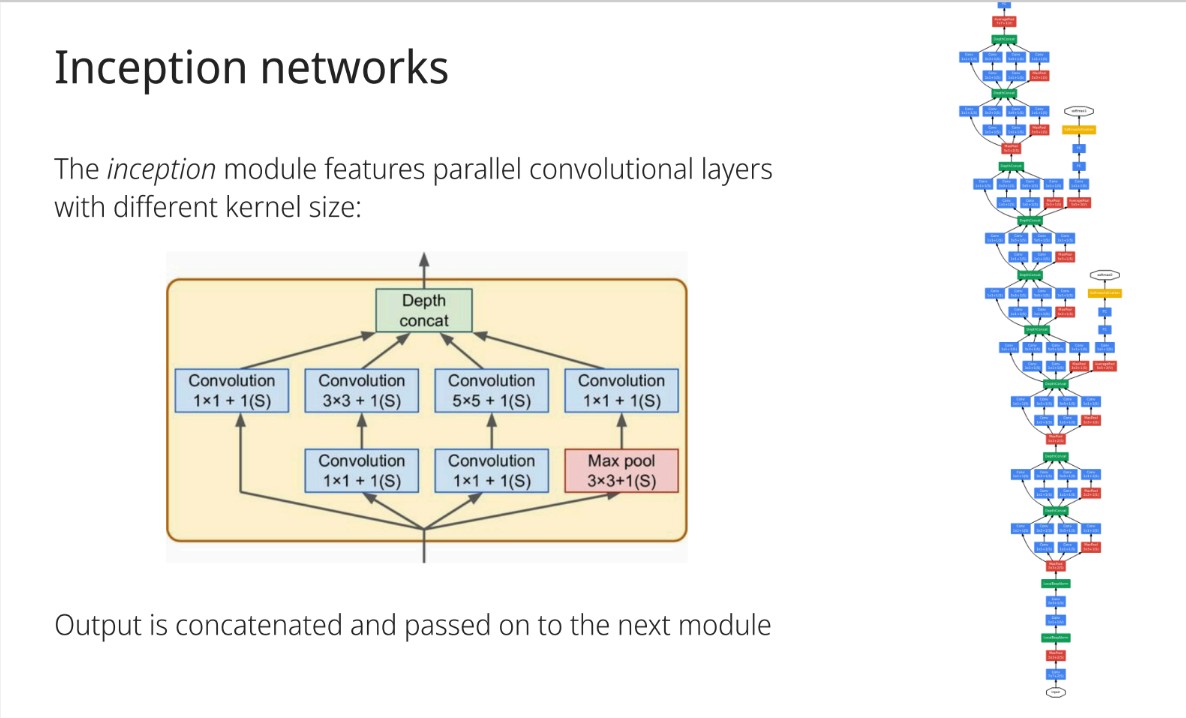
What are the key features of an Inception module?
Parallel convolutional layers with different kernel sizes, concatenated and passed on.
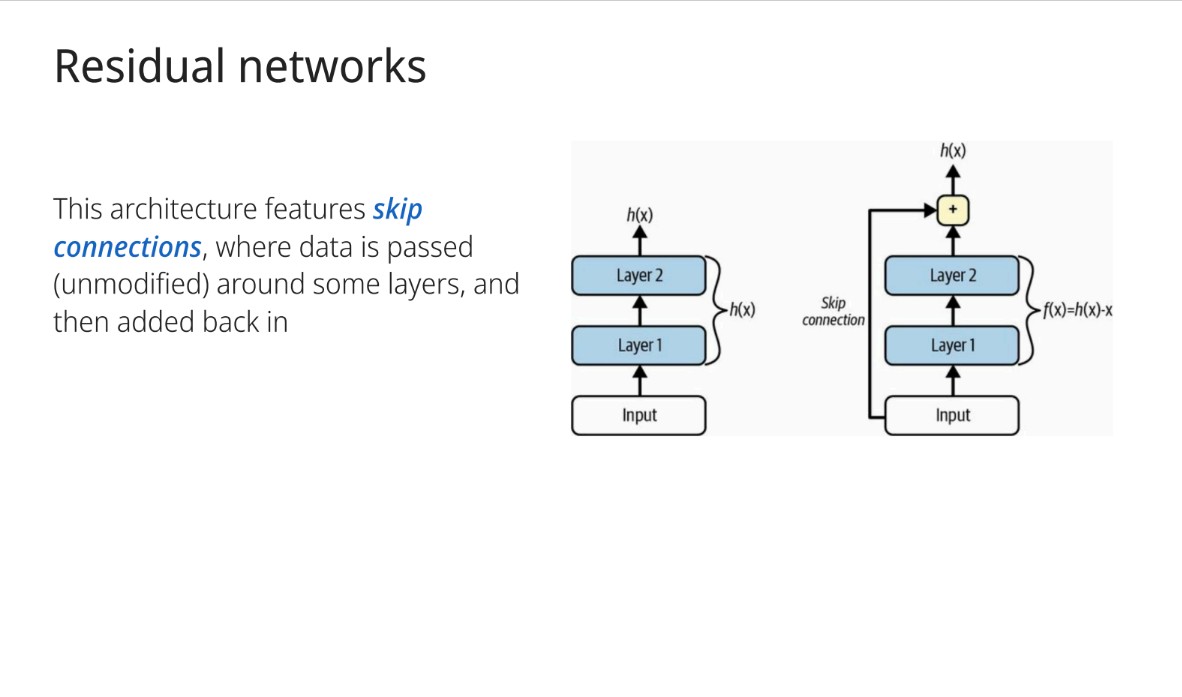
What is the key feature of Residual Networks?
Skip connections where data is passed unmodified around some layers and then added back in.
What is required for segmentation?
Classify each pixel.
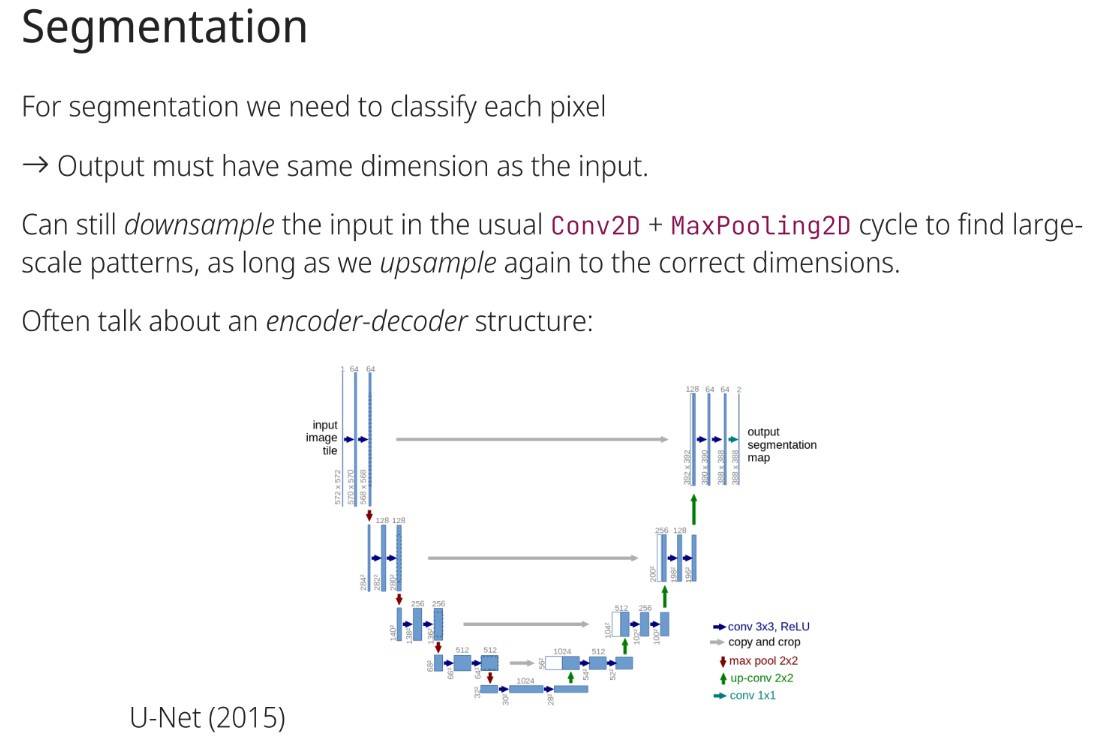
What structure do segmentation networks often use?
An encoder-decoder structure: U-Net
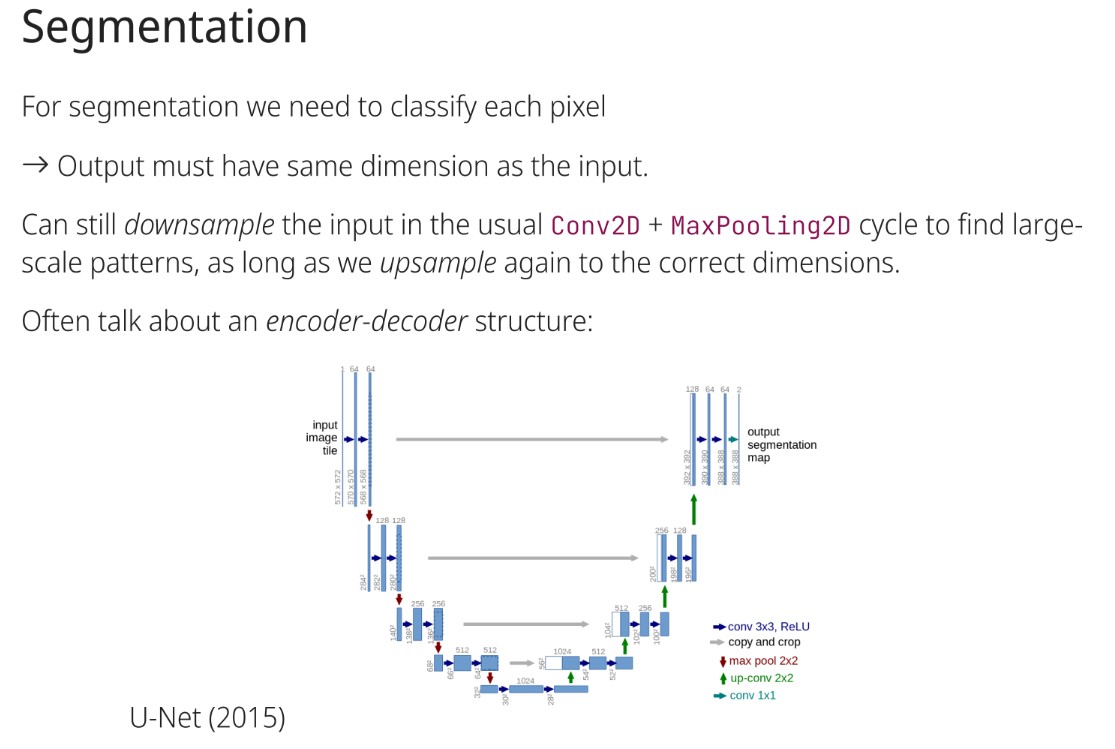
In gradient descent, what does (η) represent?
The learning rate.
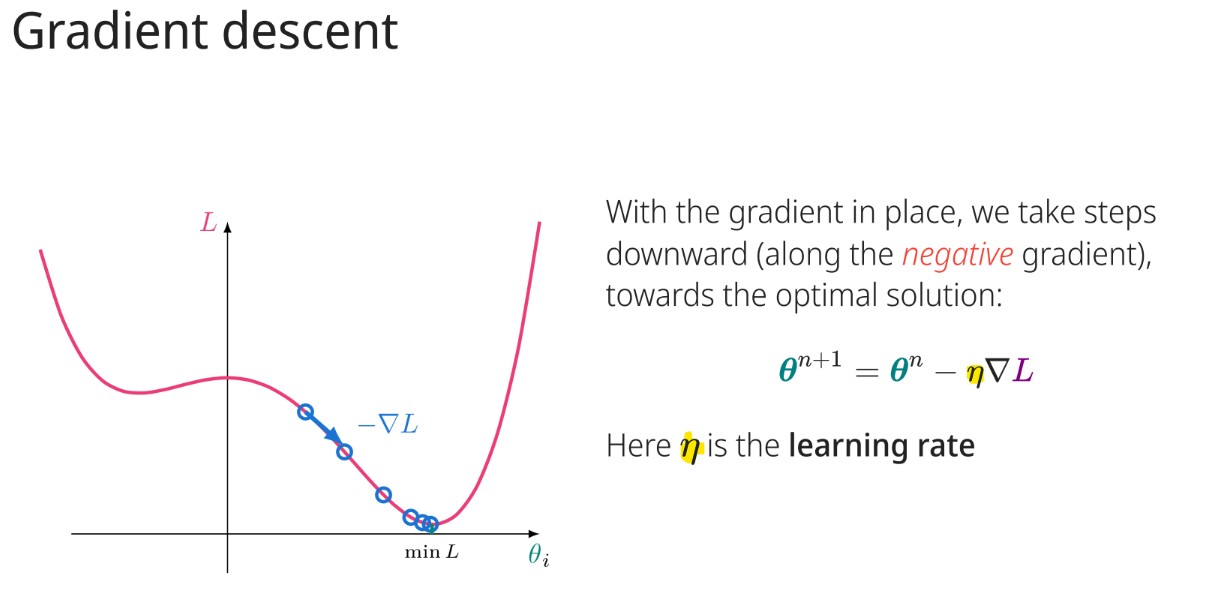
What are the parameters of a simple fully-connected neural network?
Weight per connection (line) and one bias term per node (circle).
What is convolution in the context of computer vision?
An operation that takes in two functions and returns a new function, used to recognize and localize patterns in data.

Why is convolution easier to implement with discrete data like images?
Because the integral becomes a sum, and we use kernels to find our image patterns.
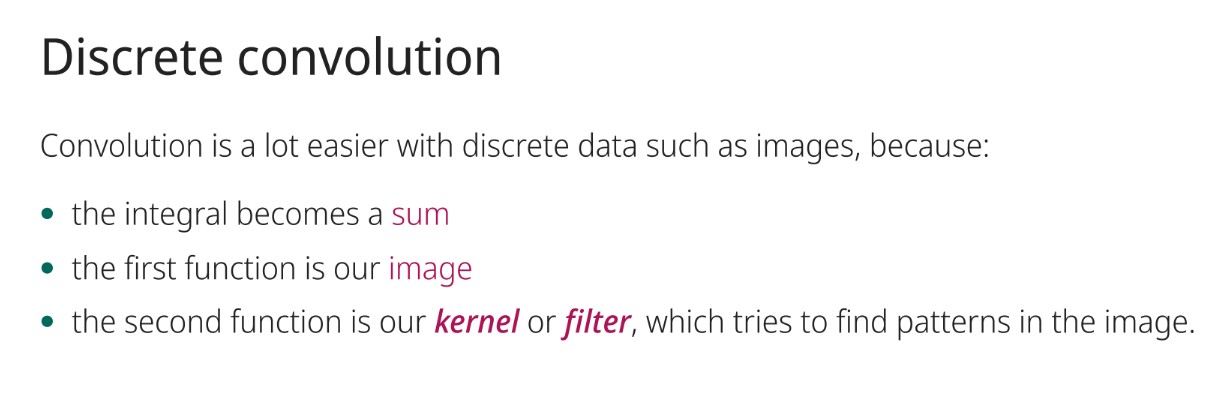
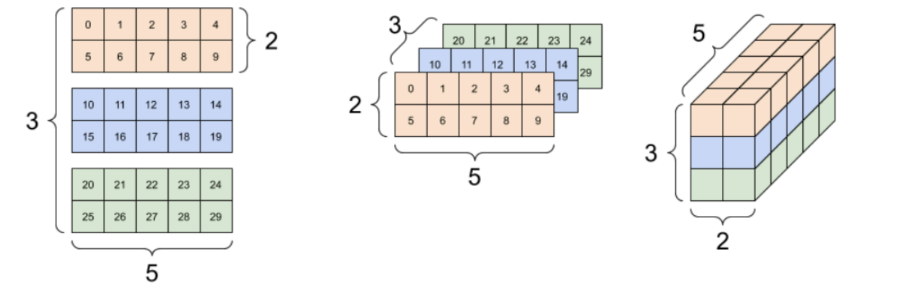
What shape are the images?
A 3-axis tensor, shpe: [3, 2, 5]
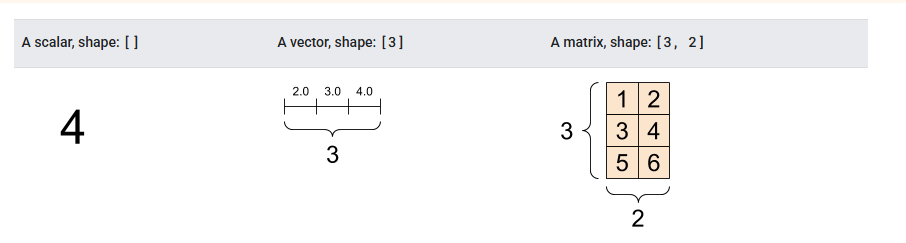
What types of shapes are these:
Shape [], [3] and [3,2]
A scalar, verctor and matrix
How is basic math accessed through operators?
1. a = b + c
2. a = b * c
3. a = b @ c
