VTNE Review: Urinalysis
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
free catch
voided sample
may include contaminants from the genitalia as the sample passes out of the body
not useful for culture
act of urination known as micturition
cystocentesis
insertion of a needle into the bladder for sterile collection
samples may contain a small amount of iatrogenic blood when obtained
preferred method for urine culture
between the last nipples on midline is the most reliable location for collection
urinary catheterization
sterile procedure to get urine directly from the bladder
color of urine
normal color is yellow
if dark or light yellow it is often a reflection of sample concentration or whether it contains pigment such as bilirubin (bright yellow)
transparency
normal urine is clear in dogs and cats
in large animals it is more turbid or cloudy
causes of cloudiness may be from crystals, infection, mucus, casts, sperm, etc
odor
may smell like ammonia
in ketoacidosis, the urine may smell like acetone
foul odor is sometimes noticed if there is bacteria in the urine
certain medications may cause the urine to have an odor
normal urine production quantity in dogs
12-30 ml per pound normal urine
normal urine production quantity in cats
5-9 ml per pound
normal urine production quantity in cows
8-20 ml per pound
normal urine production quantity in horses
208 ml per pound
normal urine production quantity in pigs
2-14 ml per pound
normal urine production quantity in sheep/goats
4.5-18 mls per pound
urine specific gravity
used to evaluate the concentration of urine
normal: 1.025-1.050
best to perform on a first morning sample
isosthenuria
low urine concentration (1.008-1.012)
hyposthenuria
inability to concentrate urine (less than 1.008)
pH
test the acidity
pH less than 7 is acidic; greater than 7 is alkaline
samples left sitting out may result in increased pH
often related to diet, medications, or time of collection
protein
often indicates urinary tract disease, especially renal disease
may also be positive if contaminants are present in the sample (cells, bacteria)
may be confirmed by the sulfosalicylic acid test
glucose
glucosuria occurs when the renal threshold is exceeded (more than 170 mg/dl in dogs)
most common cause of glucosuria is diabetes
in cats that are stressed/scared, hyperglycemia may occur, exceeding the renal threshold and may cause glucosuria
renal glucosuria (which is rare) may also occur due to decreased resorption of glucose in the renal tubule due to kidney disease
ketones
increased catabolism of fatty acids results in ketonuria
causes include:
pregnancy toxemia: energy requirement for milk production exceeds energy intake and body fat is metabolized, causing ketone production; important cause in cattle and small ruminants
diabetes: lack of insulin leads to inappropriate metabolism of carbs such that fat is broken down and ketones are produced
starvation or prolonged hypoglycemia, low carb diet, or long standing fever
bilirubin
may be normal in dogs and cattle
never normal in cats, pigs, sheep, or horses
presence suggests biliary obstruction or hemolytic anemia (liver cannot excrete the excess bilirubin which is released from the lysed erythrocytes
confirmed with the Ictotest
blood
reagent strip will react to erythrocytes, hemoglobin, and myoglobin
differentiate these with urine sediment
erythrocytes suggest bleeding from urinary or genital tract
hemoglobin suggests intravascular hemolysis
myoglobin suggests muscle damage
nitrate
positive reaction suggests bacteriuria, but negative does not rule out the presence of bacteria
leukocytes
more reliable in dogs on a test strip
false positives very common in cats
confirm presence of white blood cells on sediemnt exam
suggest urinary tract infection or inflammation in the urogenital tract
cells found on sediment evaluation
red blood cells
white blood cells
transitional cells (cell type found in the urinary tract)
crystals found in sediment
calcium oxalate, struvite, urate, bilirubin, cystine
may be normal in concentrated urine specimens
animals with ethylene glycol toxicity often have calcium oxalate crystalluria
bacteria on sediment
with presence of leukocytes, infection is likely, or may be from contamination if the sample was voided
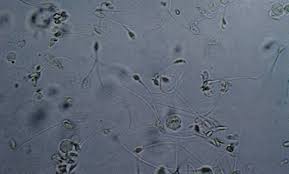
sperm
in free catch intact male samples or females if recently bred
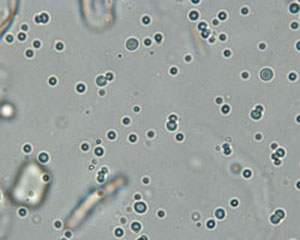
fat droplets
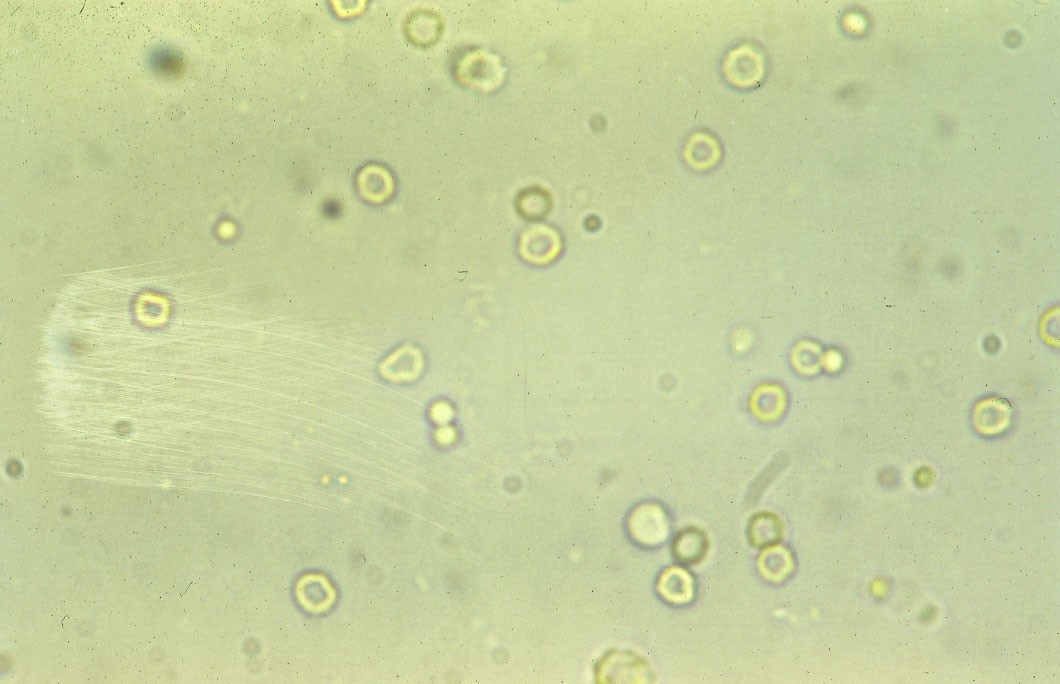
red blood cells
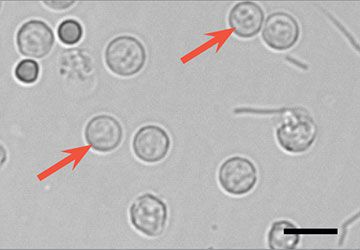
white blood cells
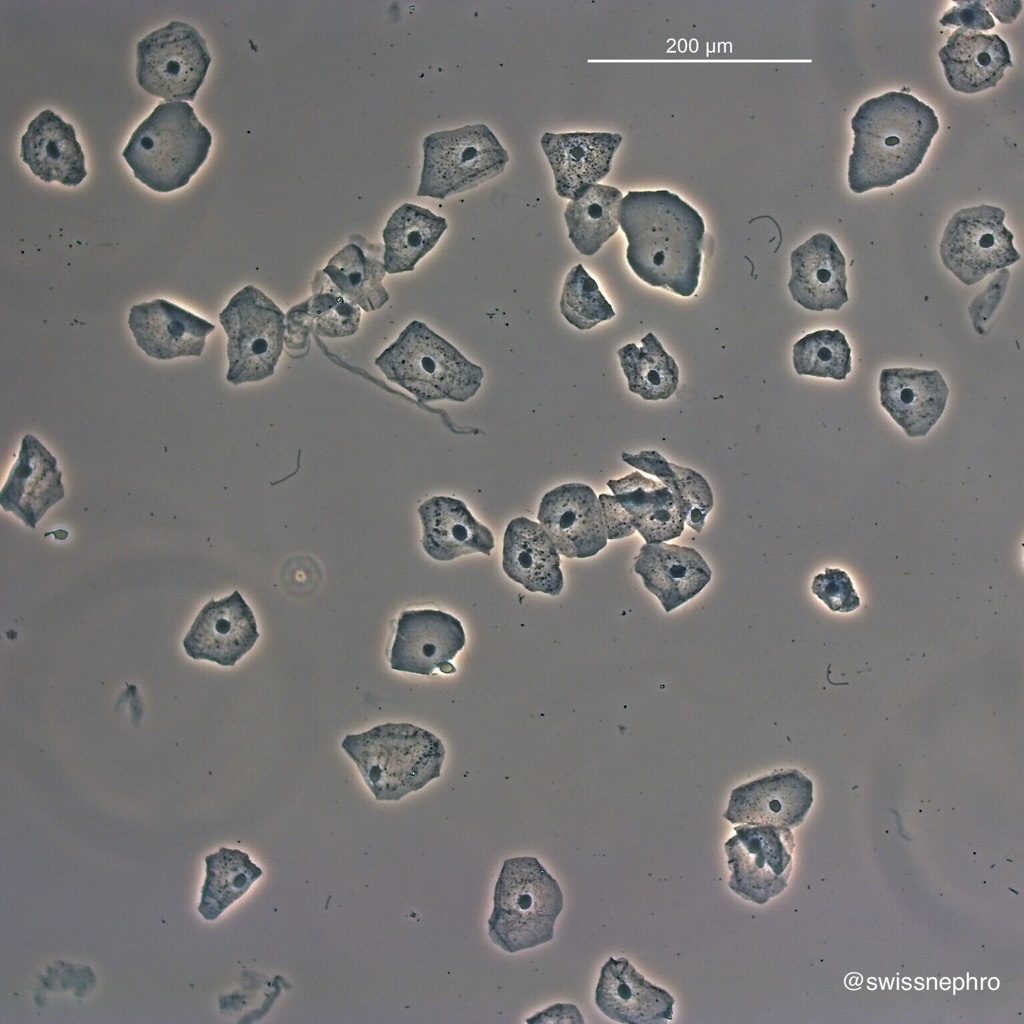
transitional cells
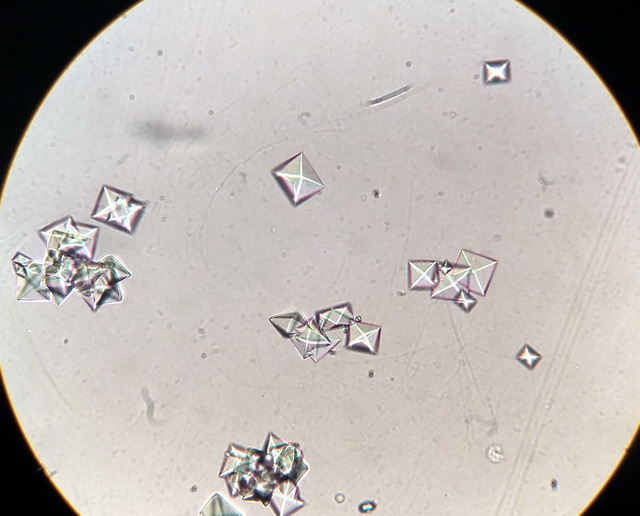
calcium oxalate
casts
cylindrical mold of renal tubules made of protein or cells
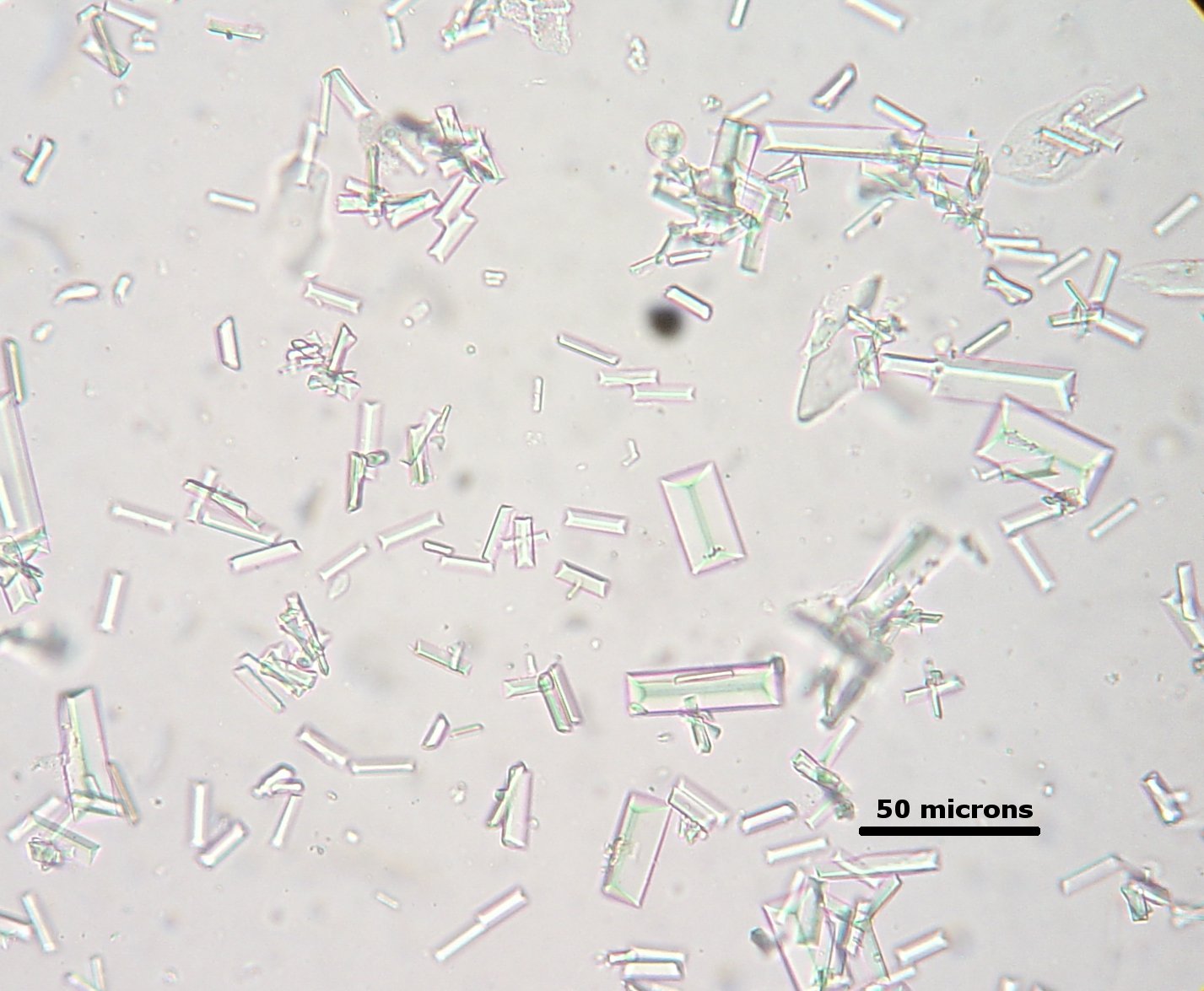

struvite crystals
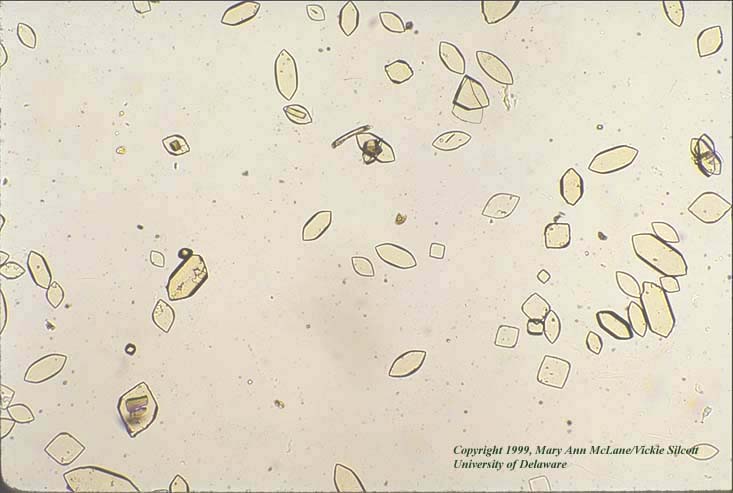
urate crystals (uric acid crystals)
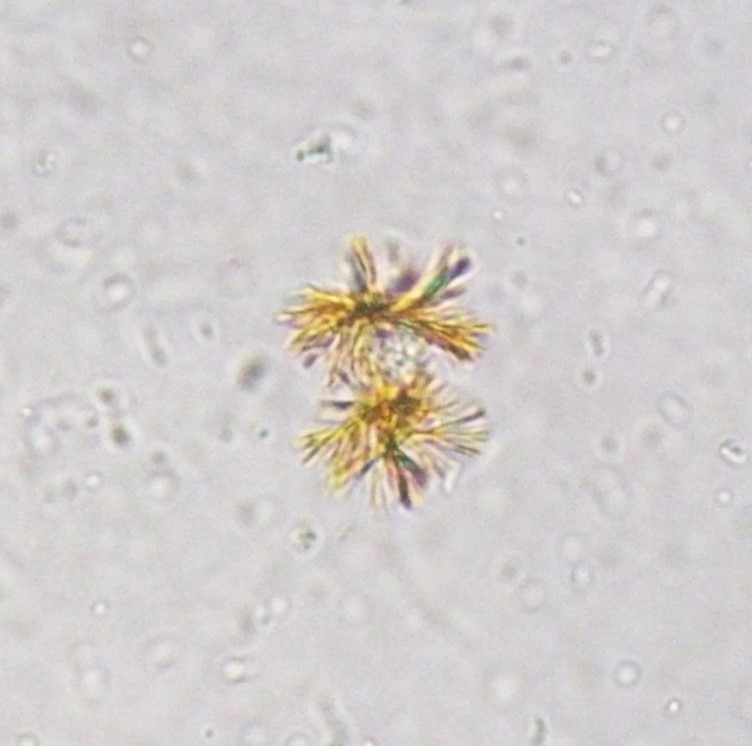
bilirubin
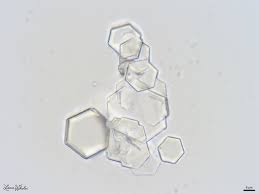
cystine crystals
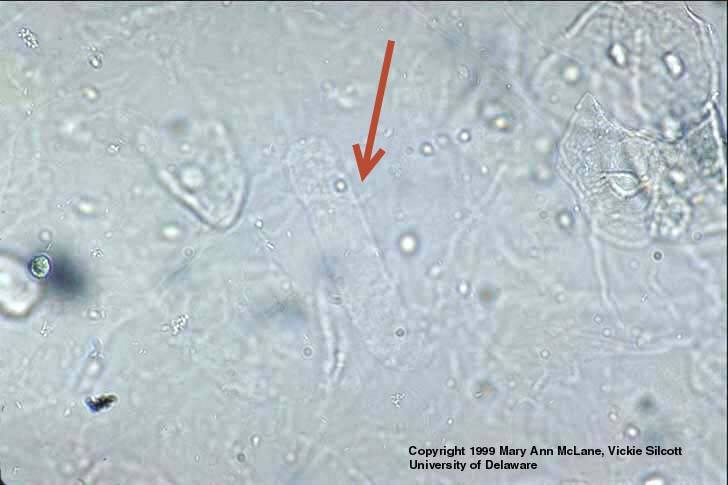
hyaline casts
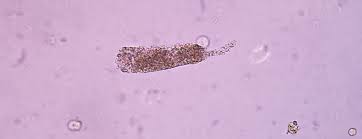
granular cast
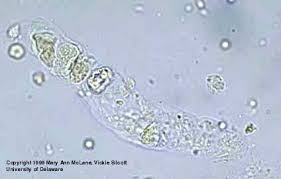
cellular cast
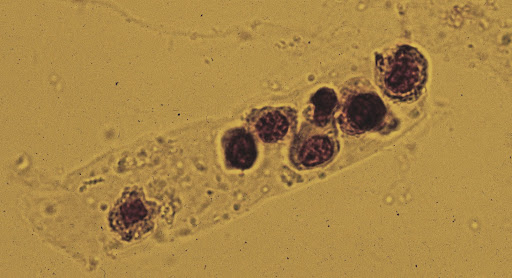
renal tubule cast
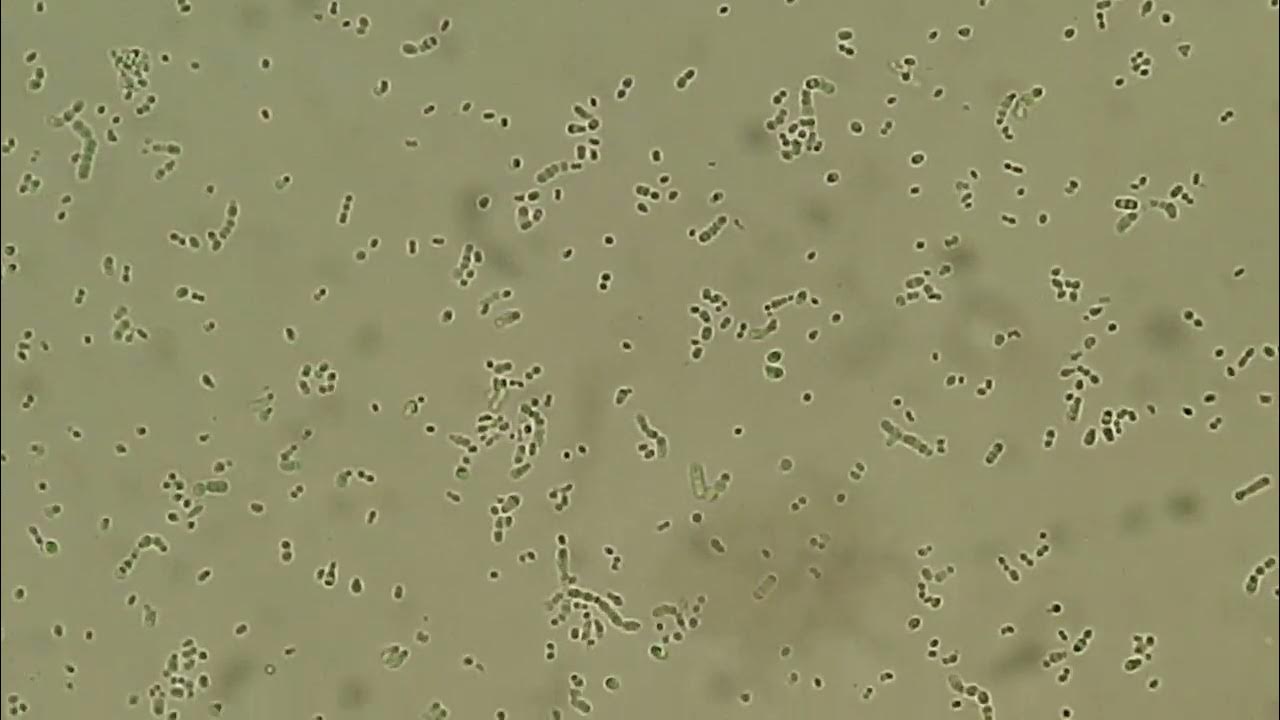
cocci
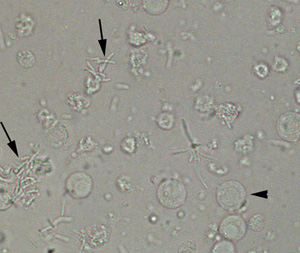
rods