Pre-lab quiz 10: Spinal cord, plexi, reflexes
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
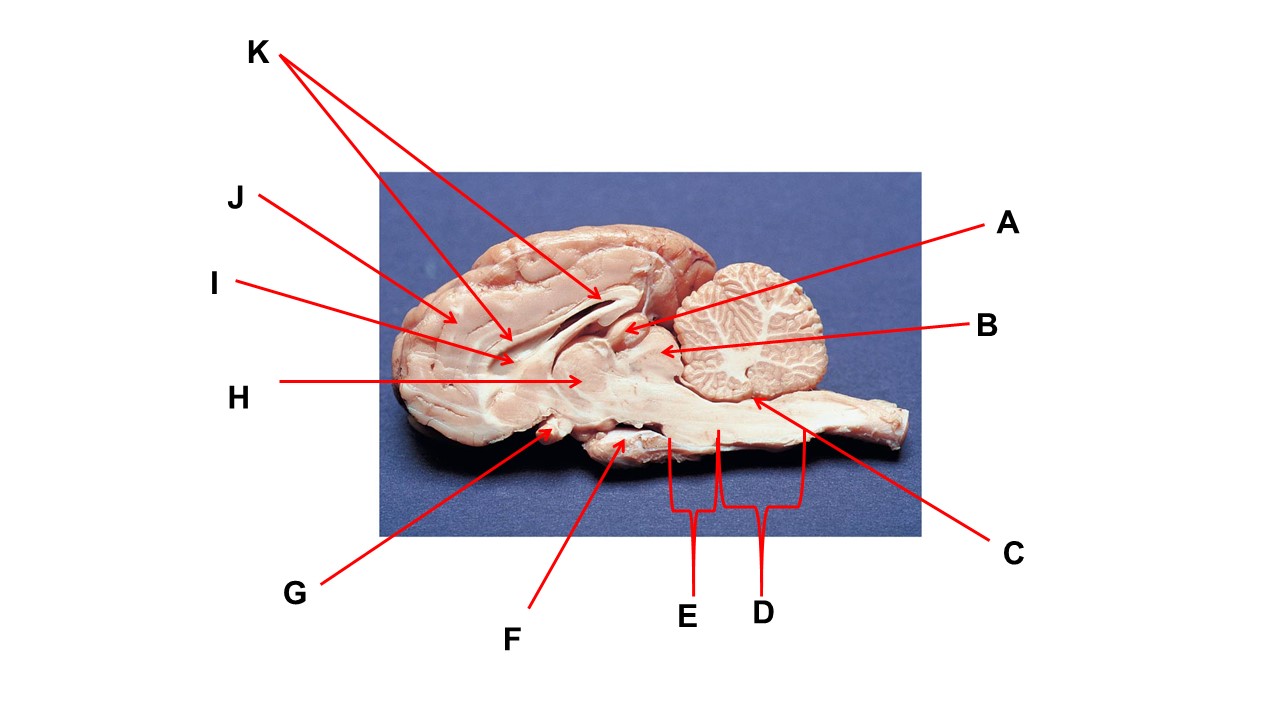
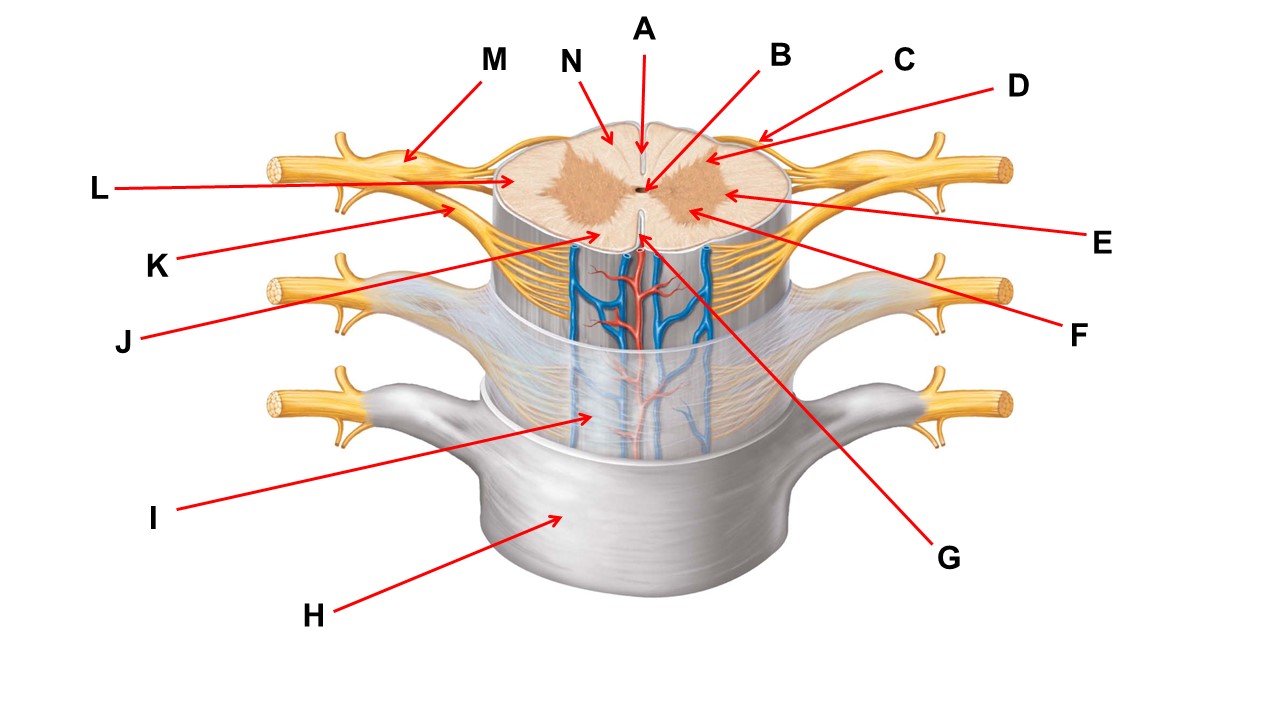
Name the region within bracket D.
medulla
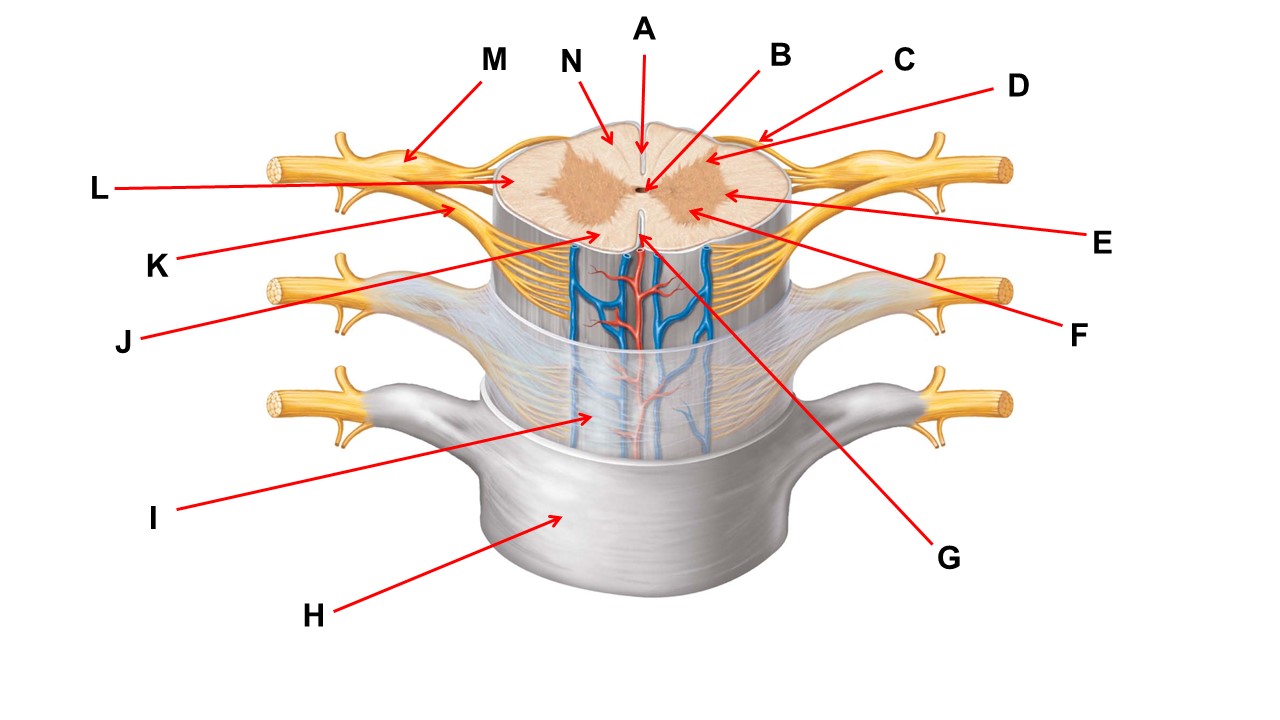
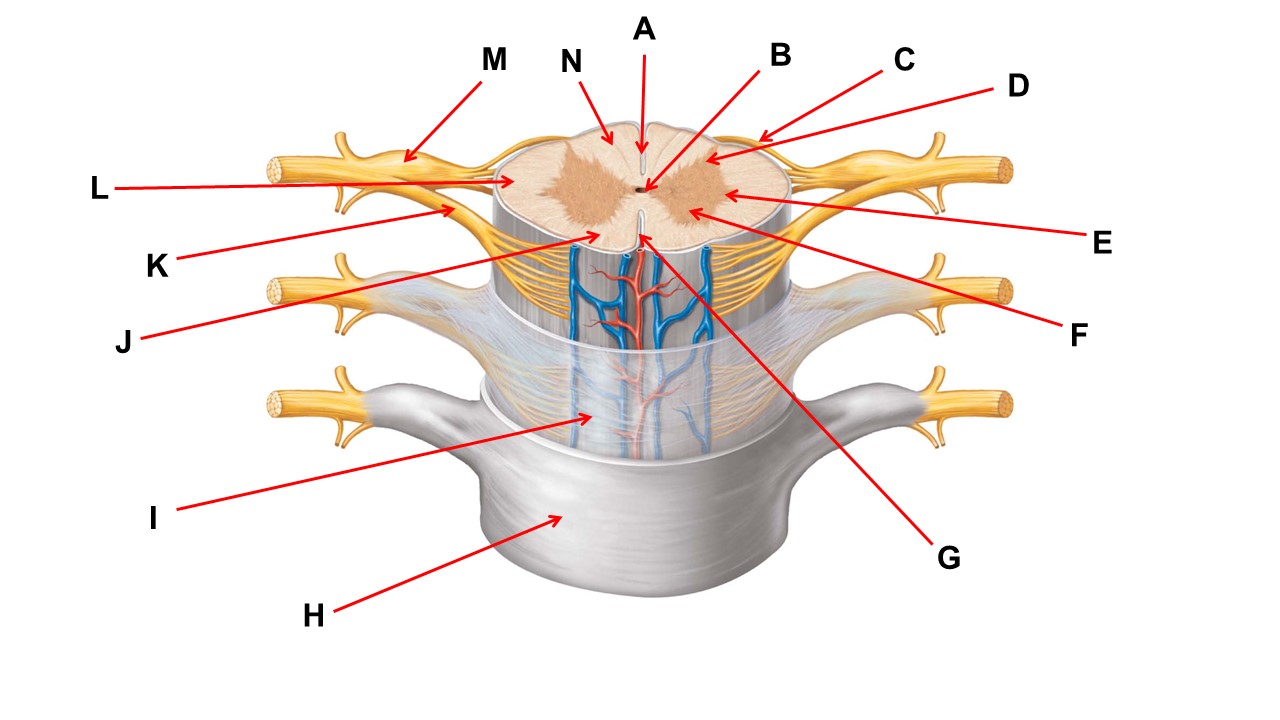
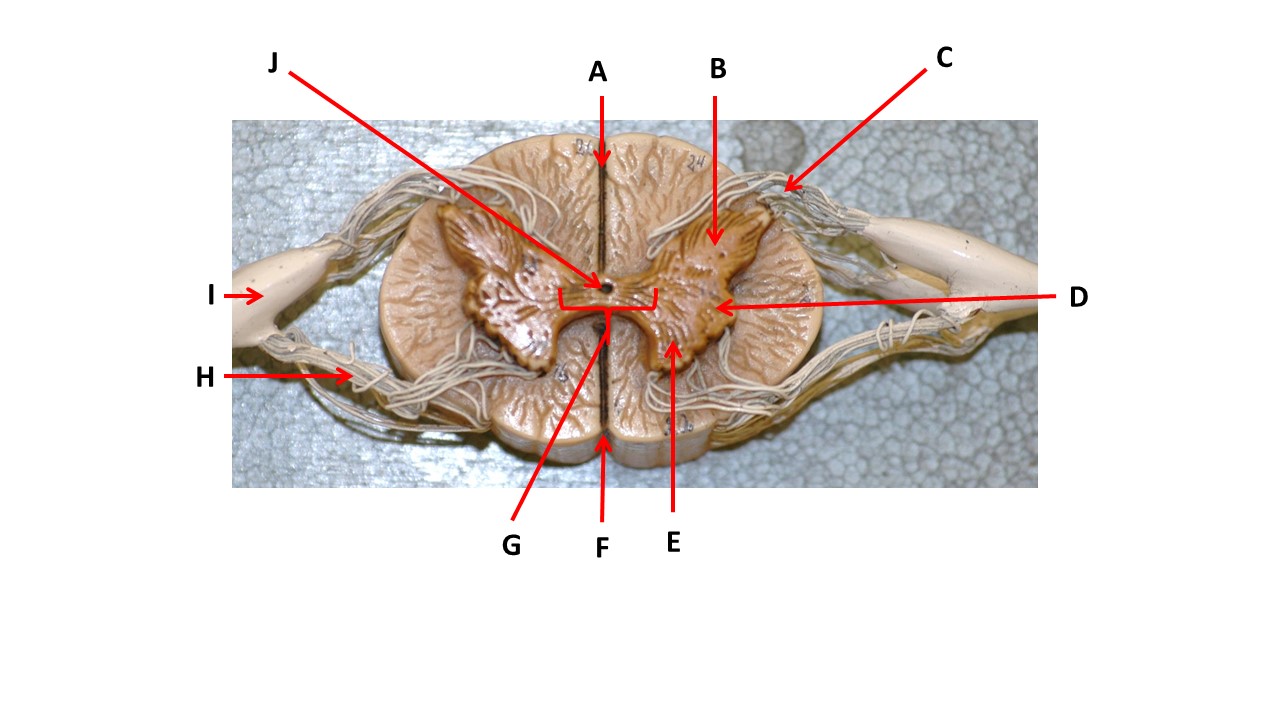
Name the region of tissue surrounding the tip of arrow E.
lateral horn
In nervous system physiology, the definition of a reflex is a ________.
rapid, predictable, involuntary motor response to a stimulus
Name the layer at the tip of arrow H.
dura mater
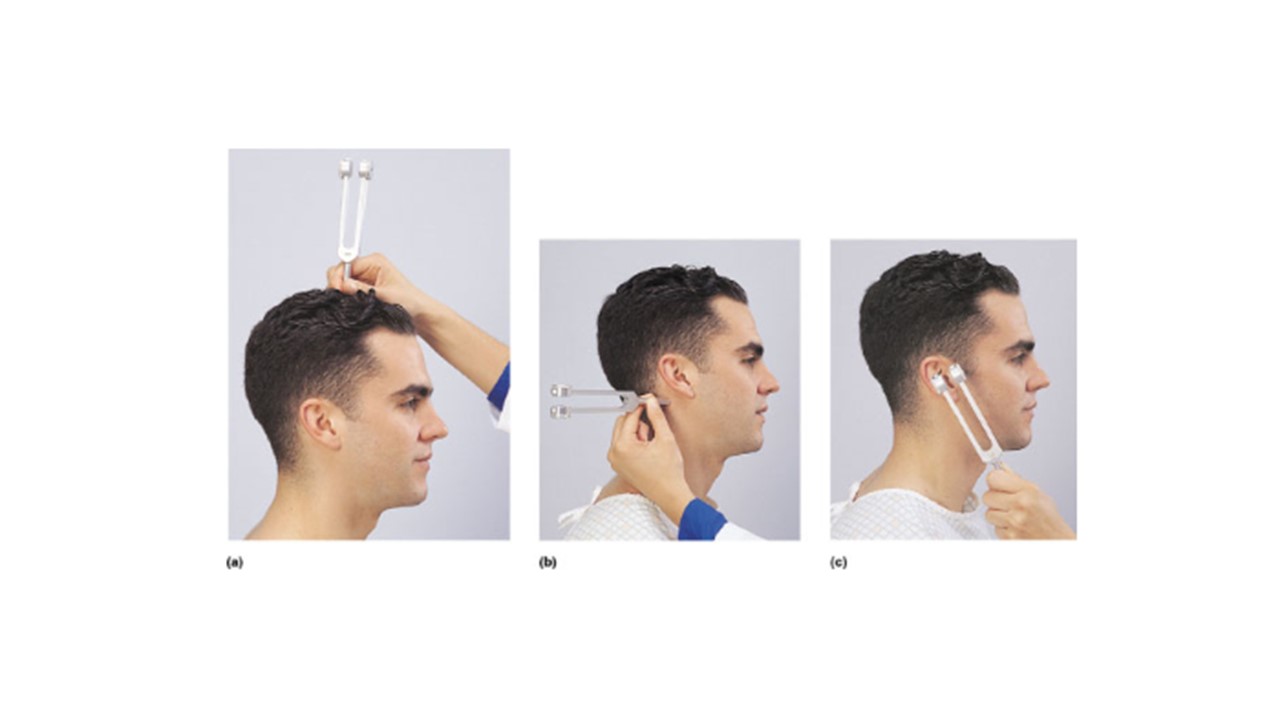
Which lettered image(s) above demonstrates the proper administration of the Weber Test?
a
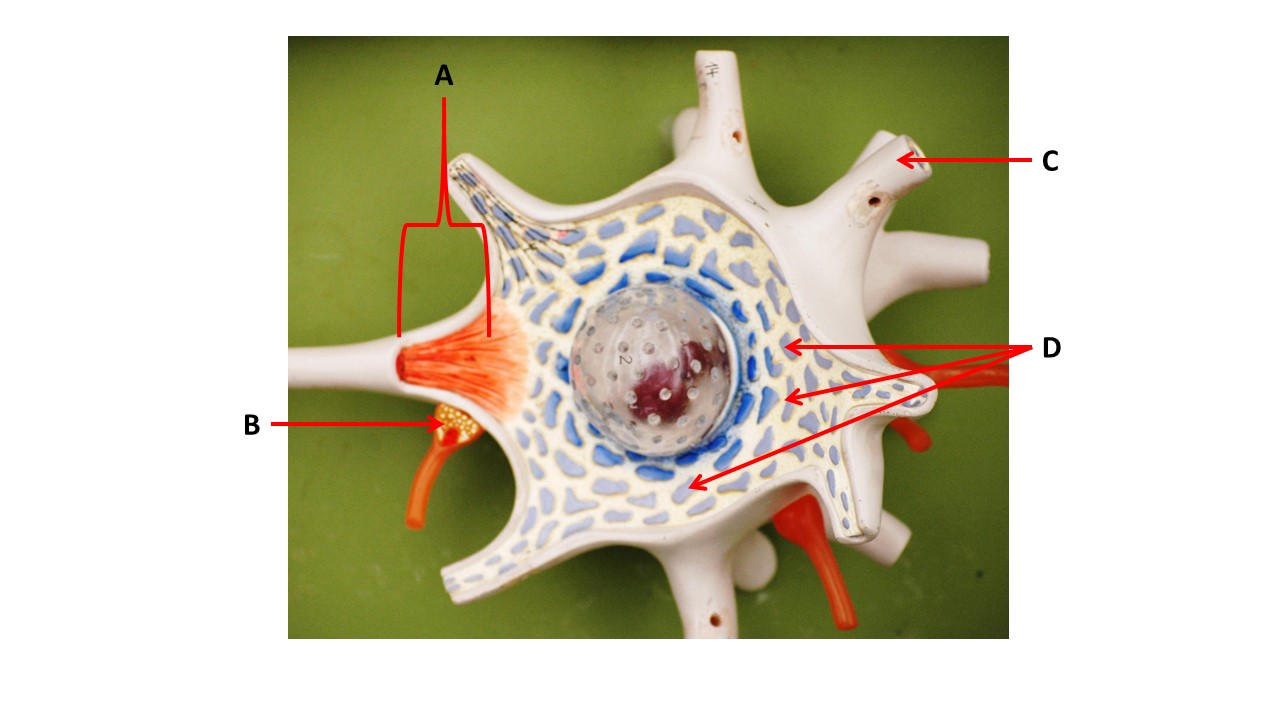
The structures at the tips of arrows D are _____.
Nissl bodies
The two-point discrimination test is used to determine ________.
the density of touch receptors
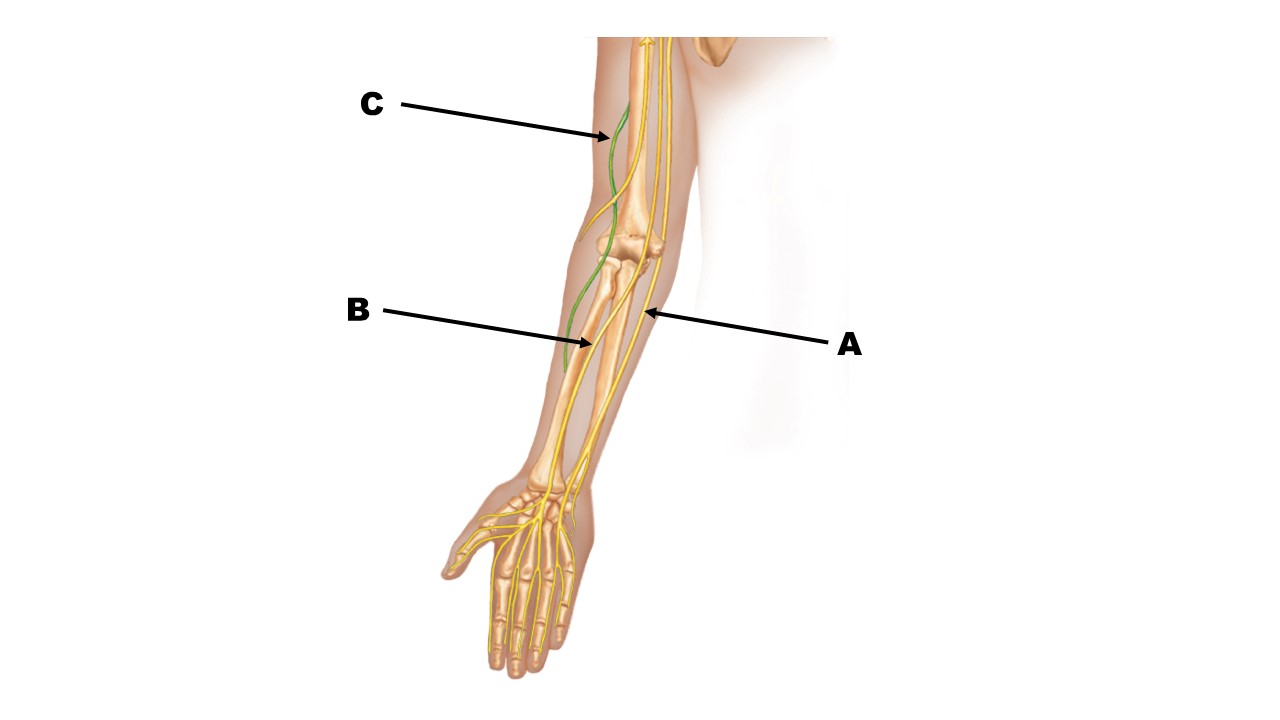
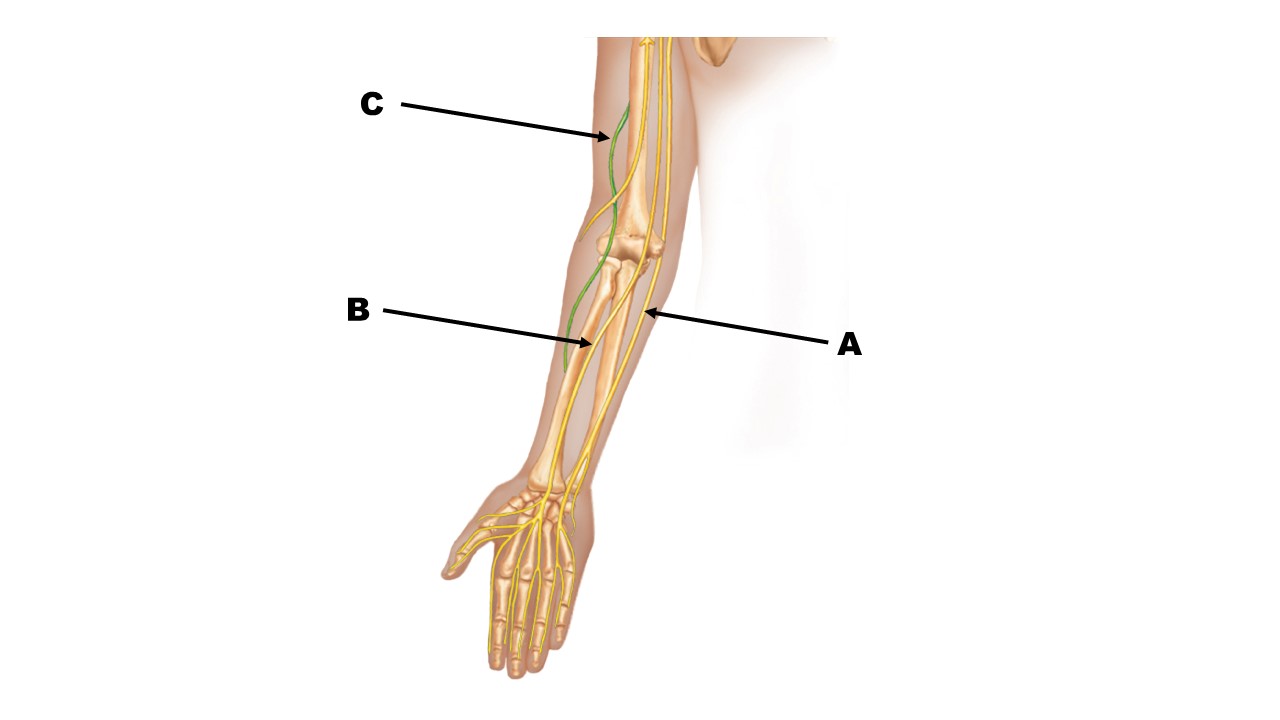
The nerve at the tip of arrow B is the _______ nerve.
median
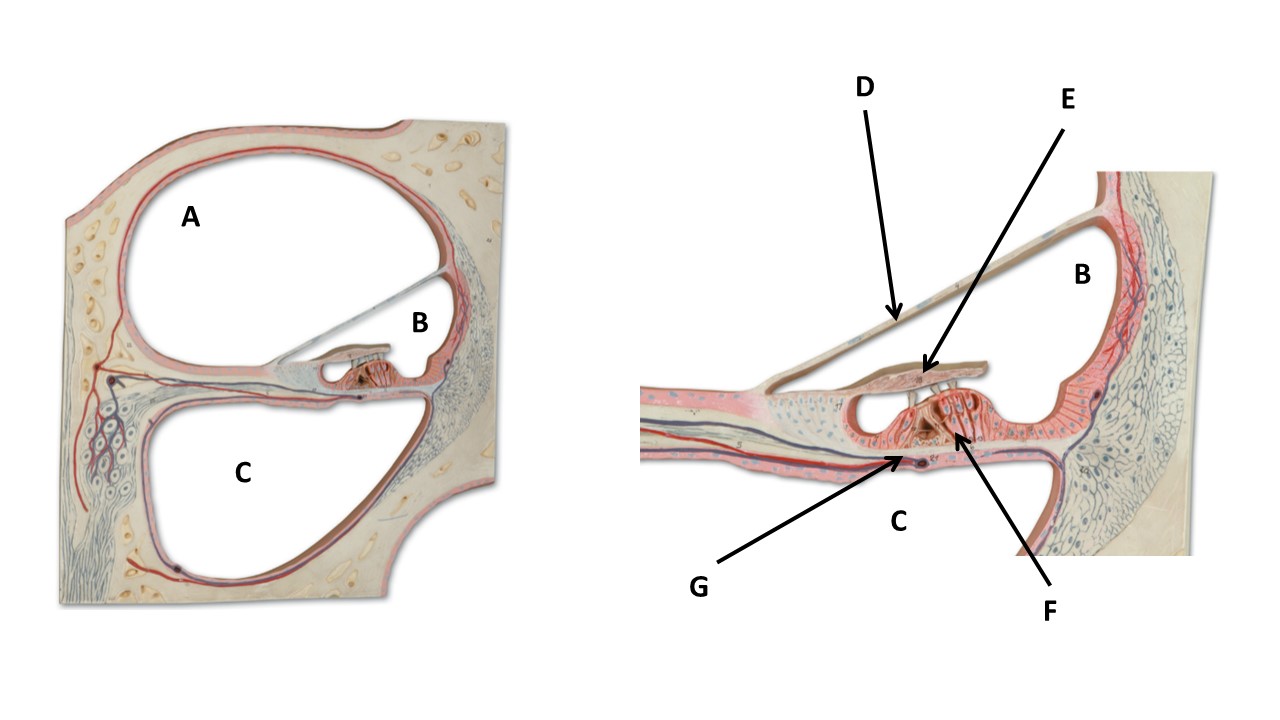
The chamber labeled B is filled with _____.
endolymph
Cranial nerve IV is a _____ nerve.
motor
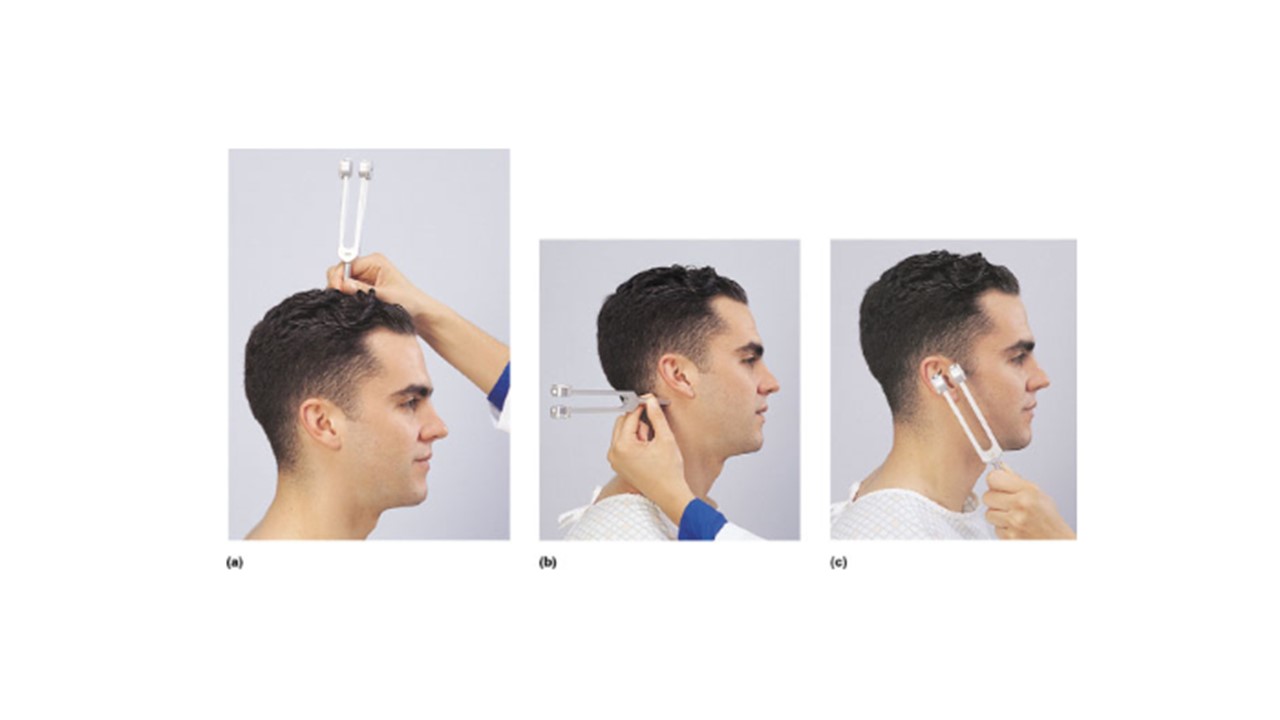
If the man in image a hears the tone in his left ear but not his right he is experiencing __________________ deafness in his right ear.
sensorineural
Which nerve innervates the skin and muscles of the shoulder?
axillary
Which nerve innervates the posterior portion of the thigh?
sciatic
Name the region of tissue surrounding the tip of arrow B.
dorsal horn
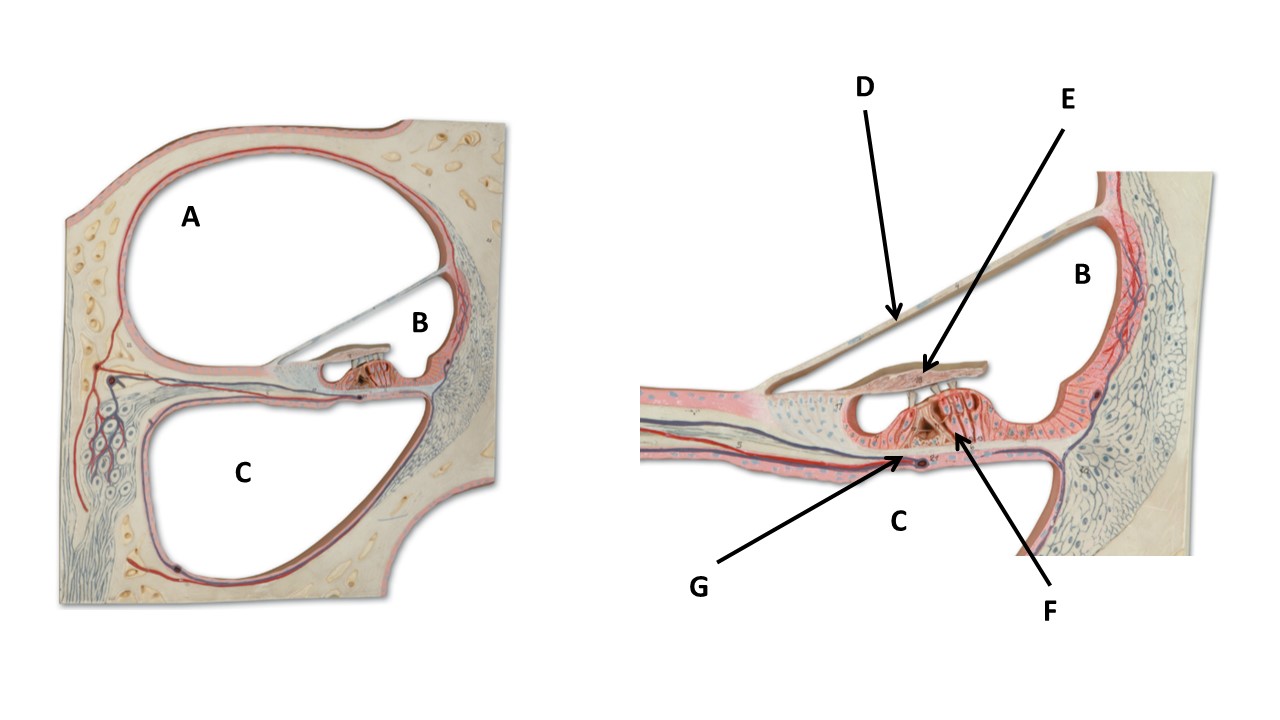
Name the structure at the tip of arrow F.
spinal organ
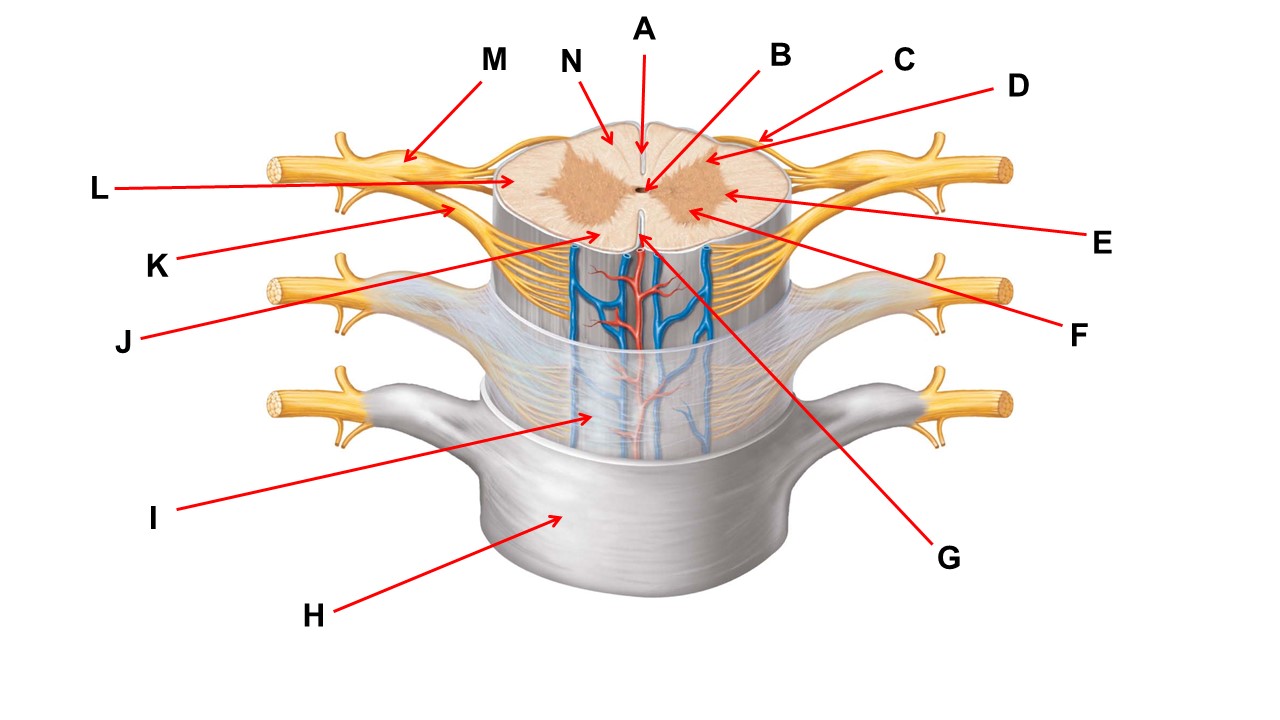
Name the structure at the tip of arrow K.
ventral root
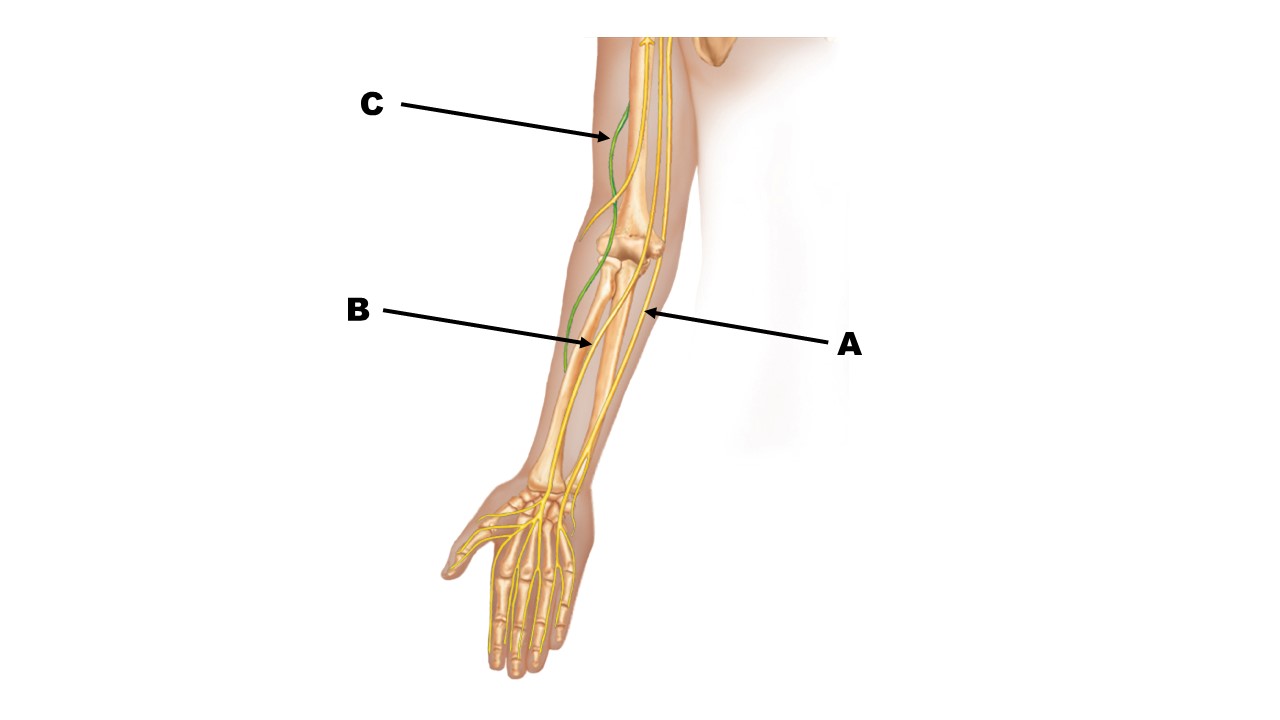
The nerve at the tip of arrow A is the _______ nerve.
ulnar
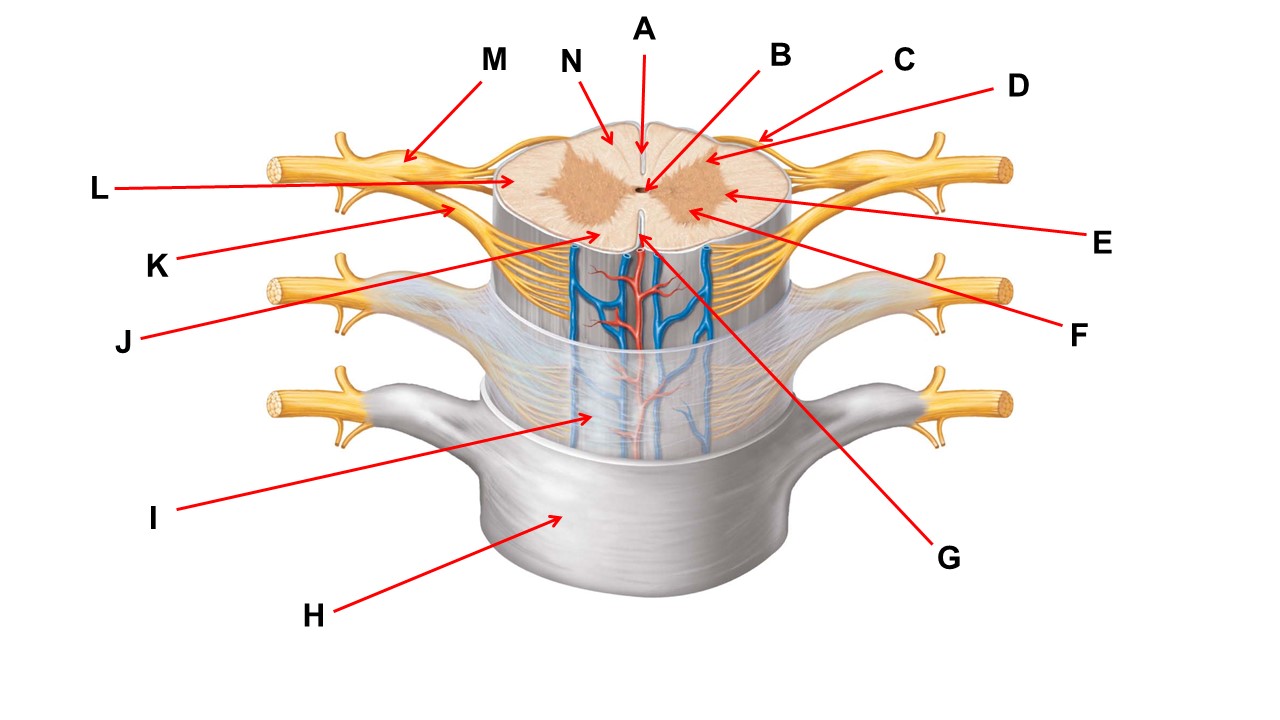
Name the region of tissue surrounding the tip of arrow J.
ventral column
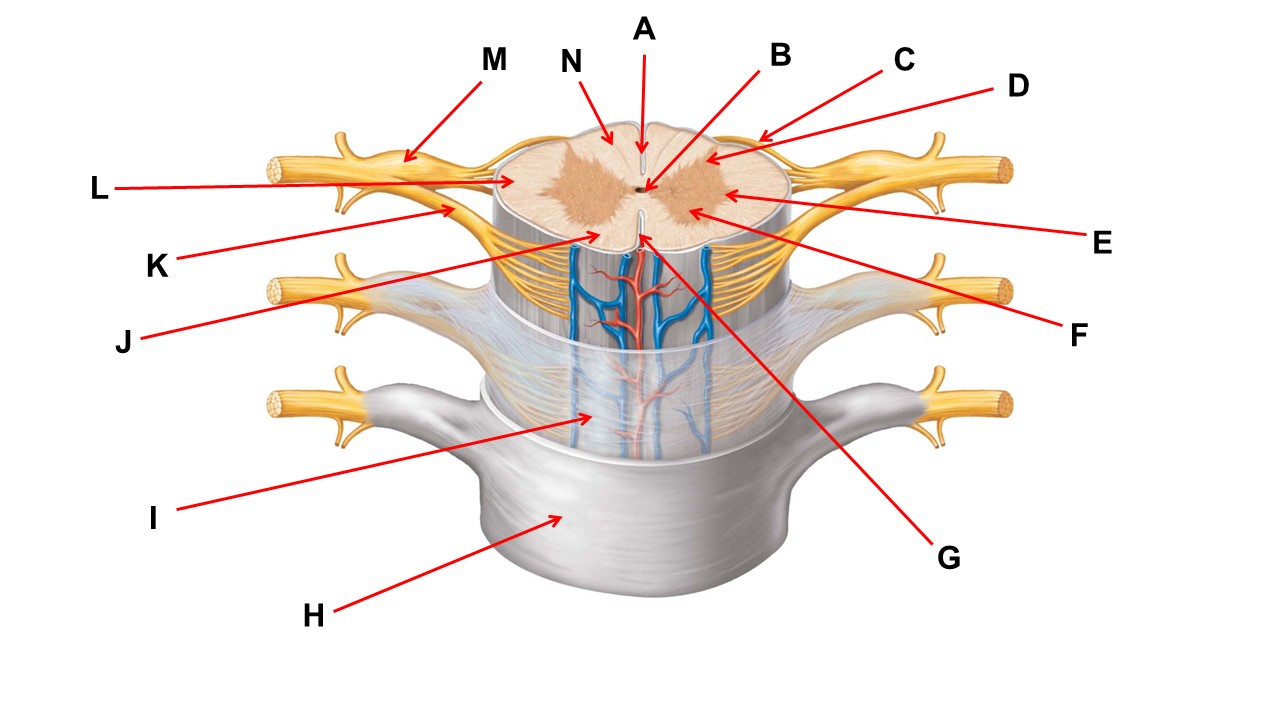
Name the layer at the tip of arrow I.
arachnoid mater
Referred pain is ________.
pain perceived as arising in one area when a different area is receiving the painful stimulus
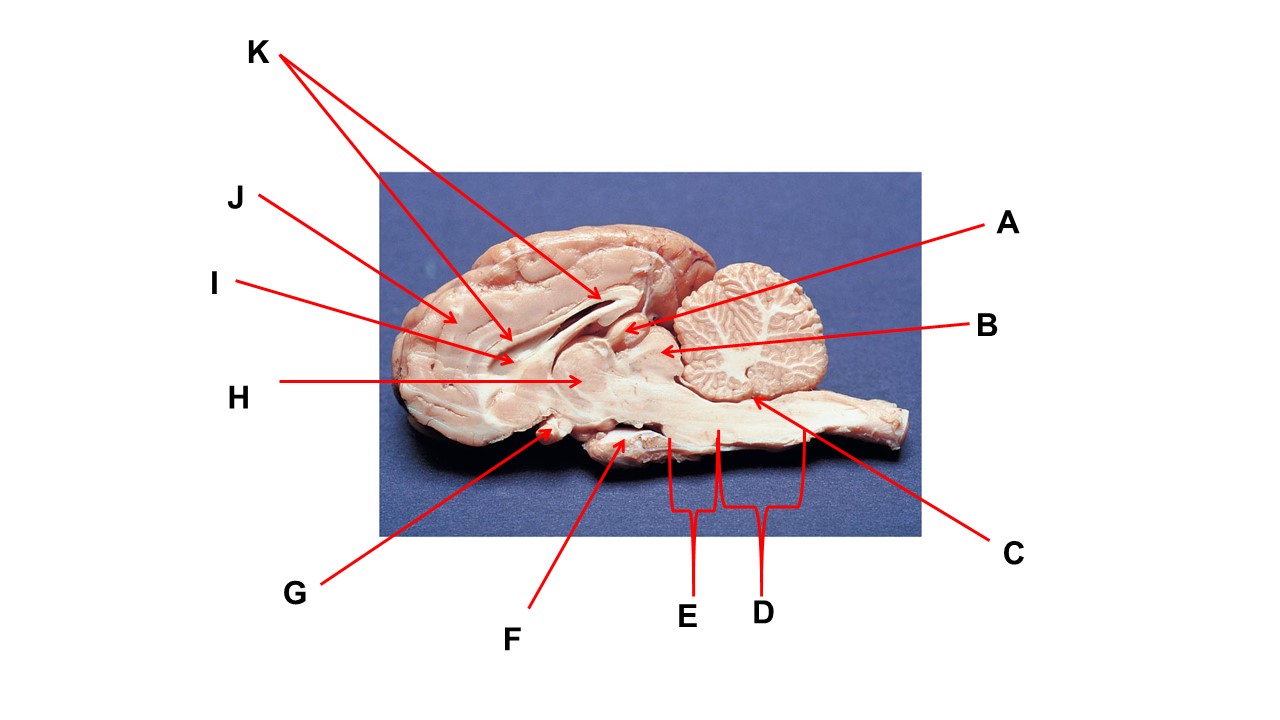
Name the structure at the tip of arrow A.
pineal gland
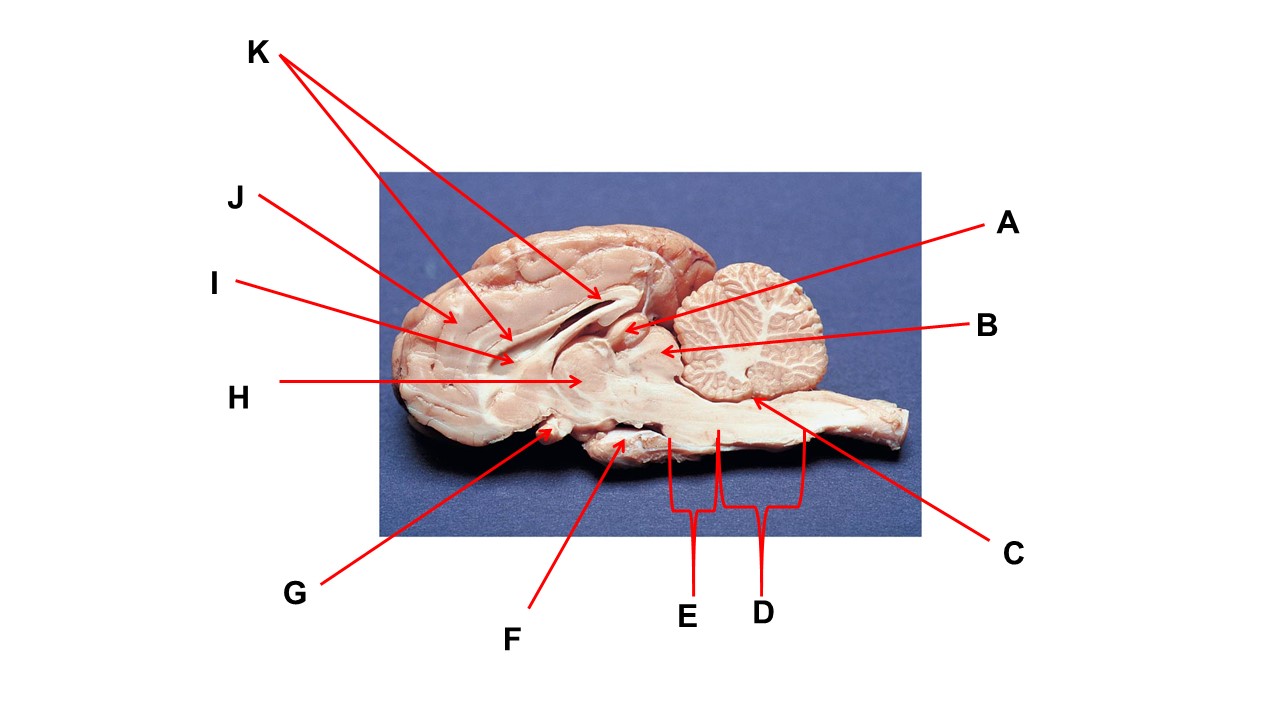
The cavity at the tip of arrow I is the _____.
lateral ventricular
What is true about somatic reflexes?
they activate skeletal muscle
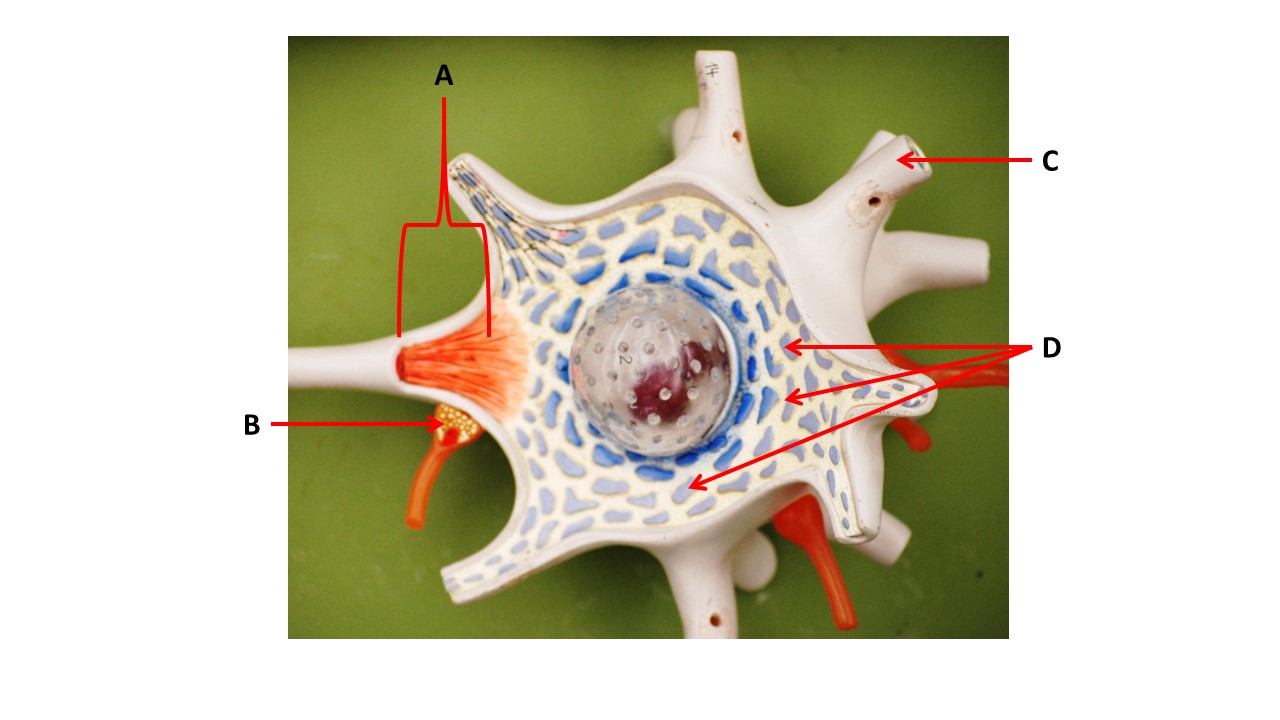
Name the structure of B
synaptic terminal
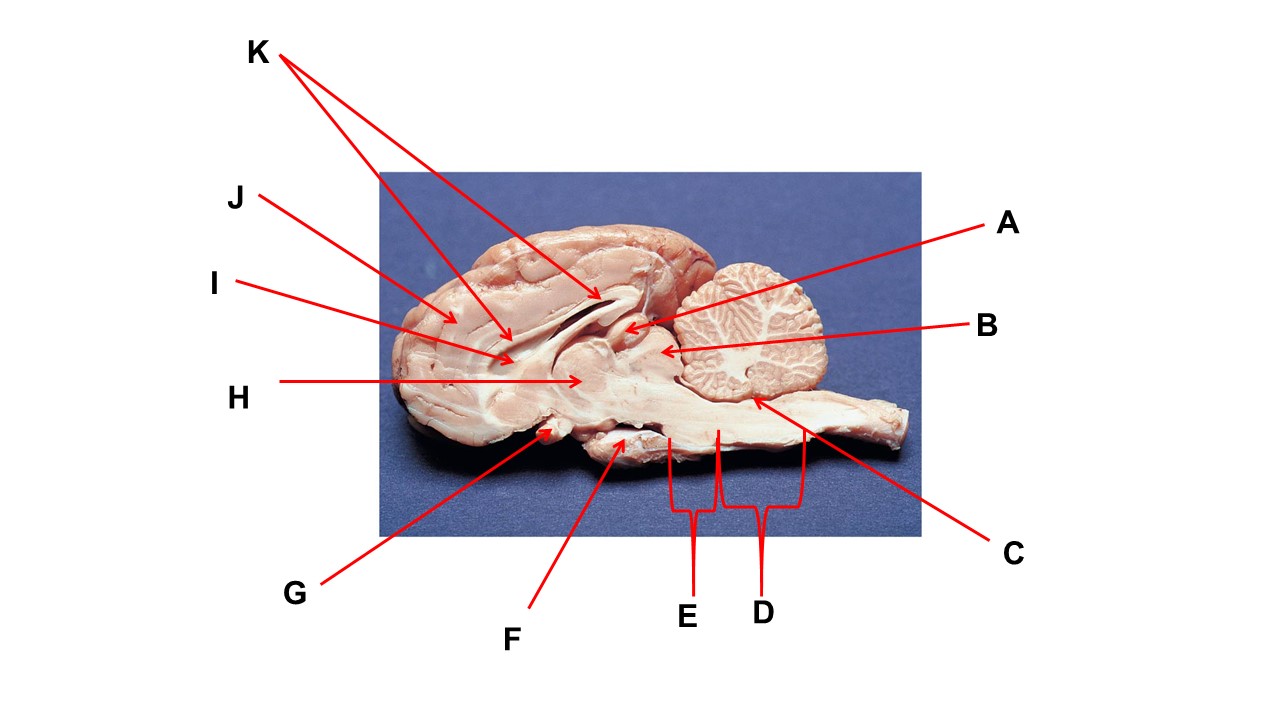
The cavity at the tip of arrow I is filled with ______.
cerebrospinal fluid
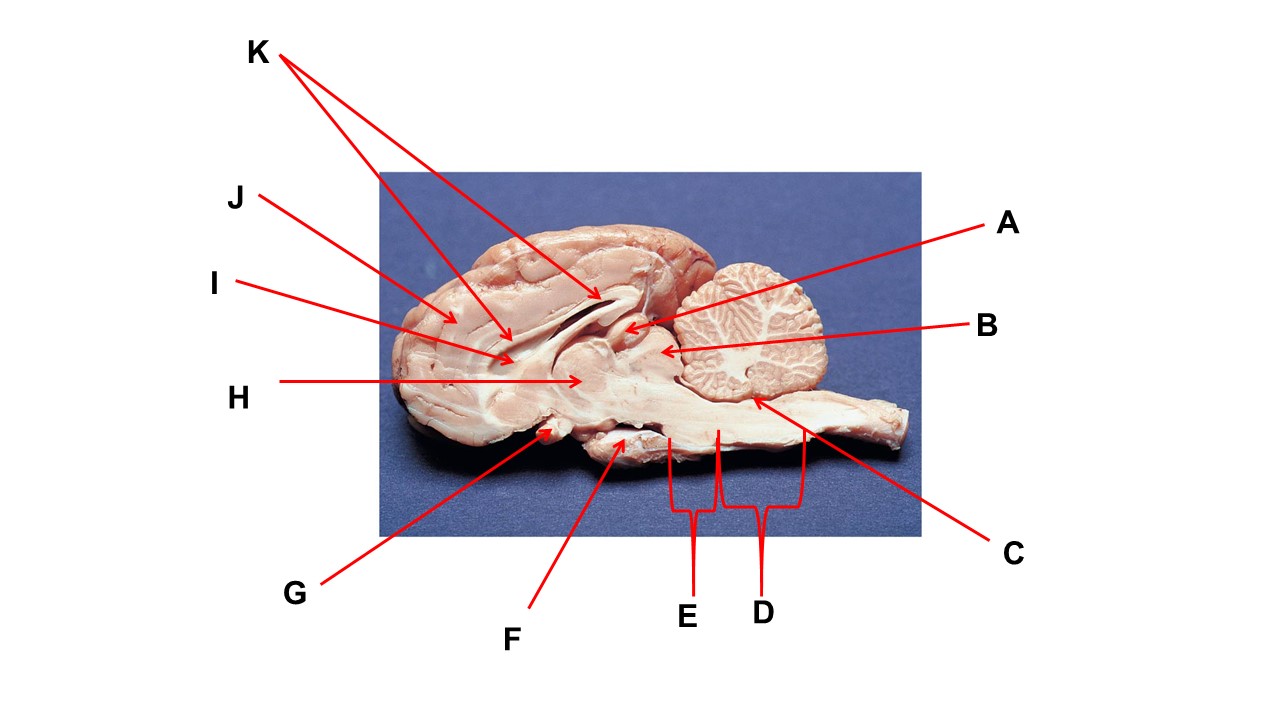
Name the region within bracket D
medulla
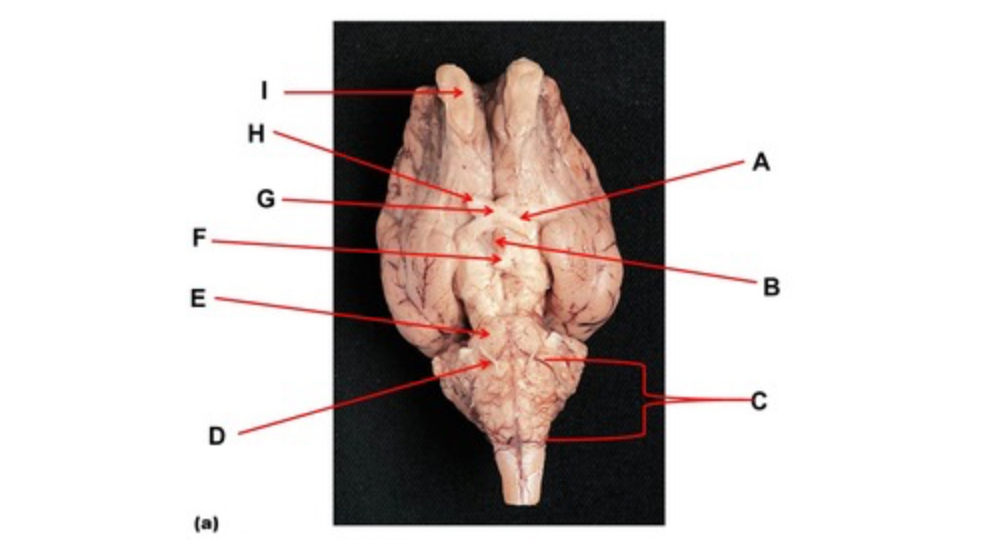
Name the structure at the tip of arrow F
mammillary body
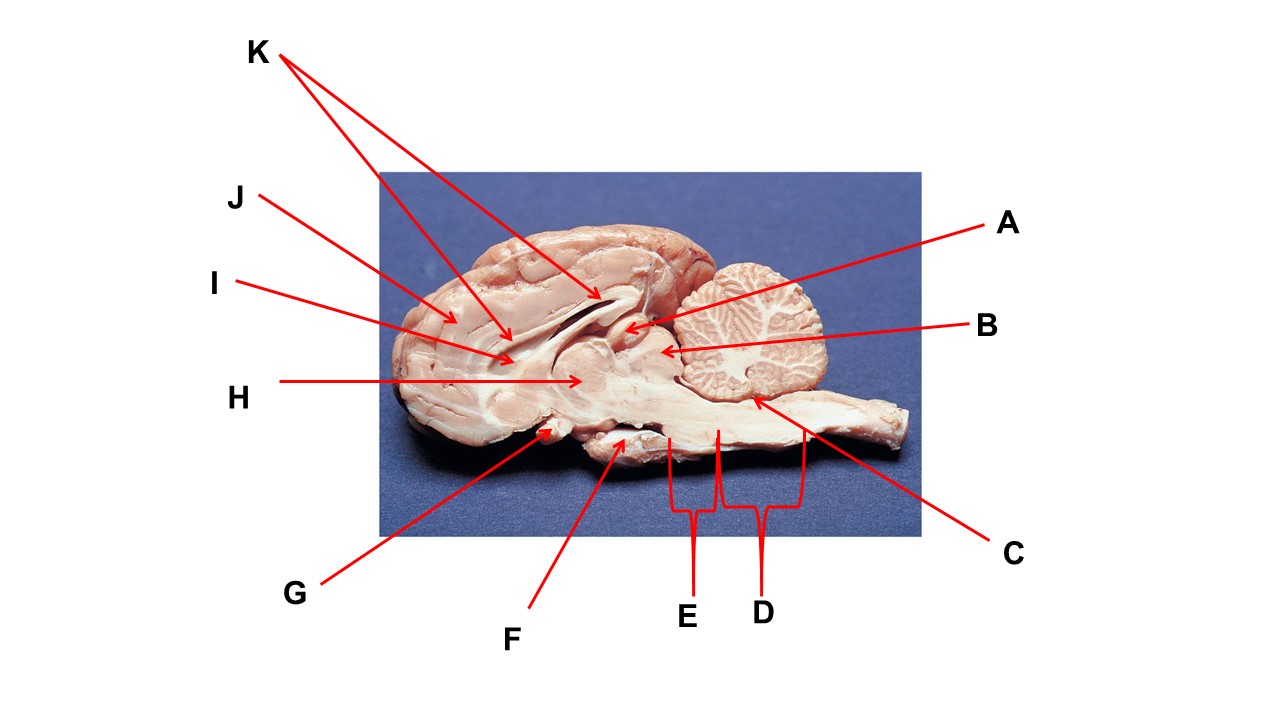
Name the structure at the tip of arrow A.
pineal gland
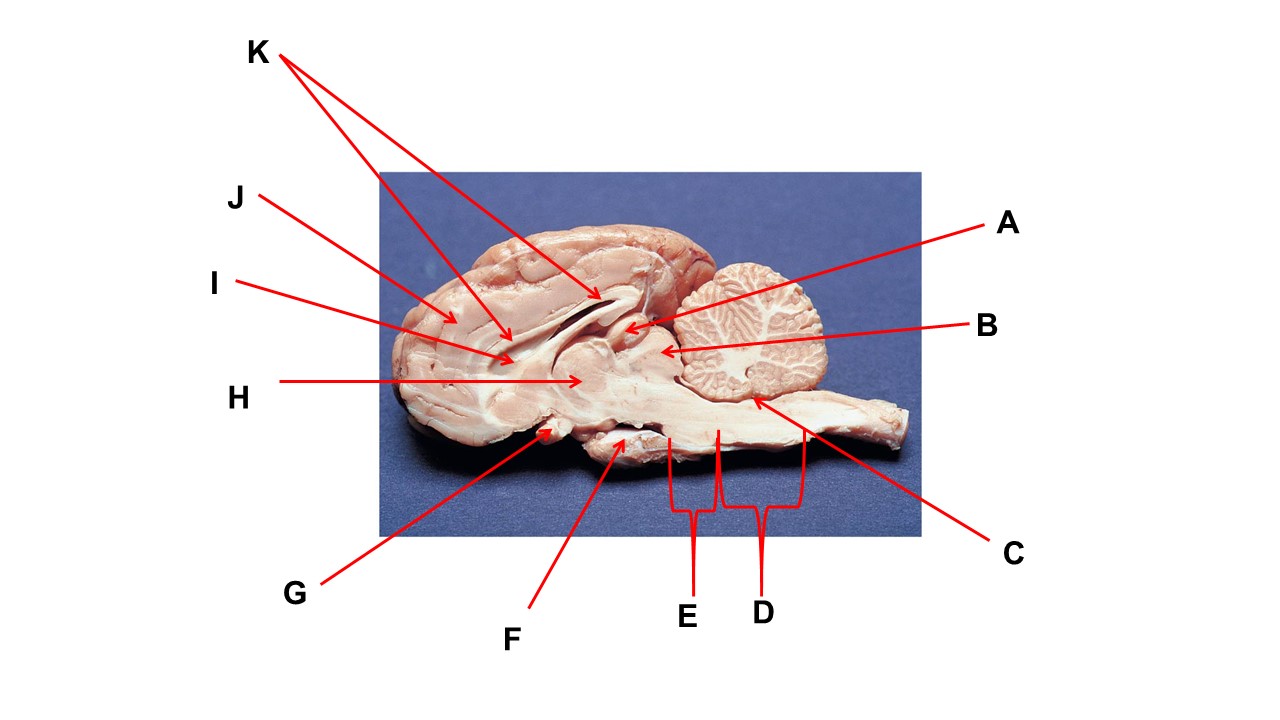
Name the structure at the tip of arrow G
optic chiasma
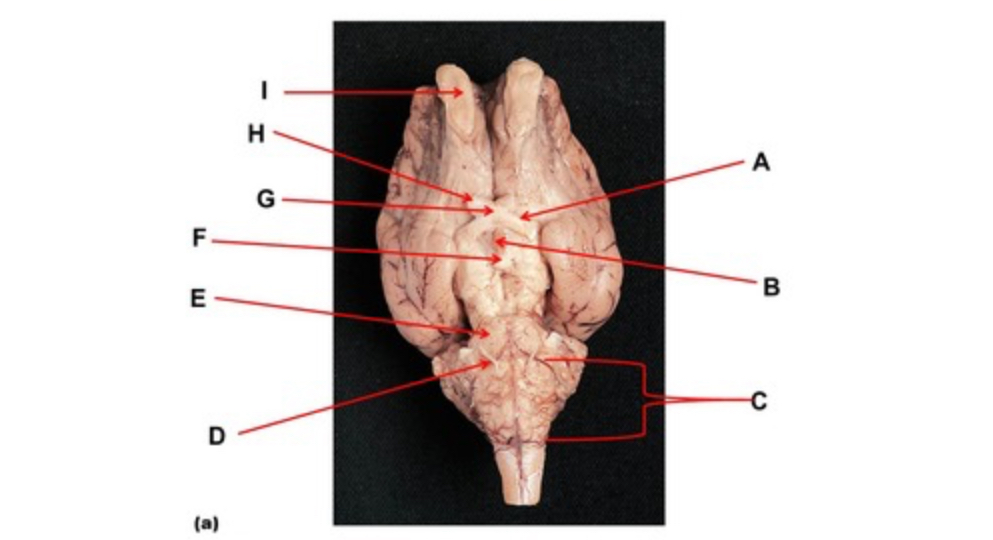
Name the nerve at the tip of arrow H.
optic
In addition to its role in spinal reflex activity, the spinal cord also ______.
contains sensory and motor tracts traveling to and from higher nervous centers
The meninges that covers the spinal cord from outermost to innermost are _____.
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
Nerves serving the lower limb tissue form this enlargement of the spinal cord.
lumbar
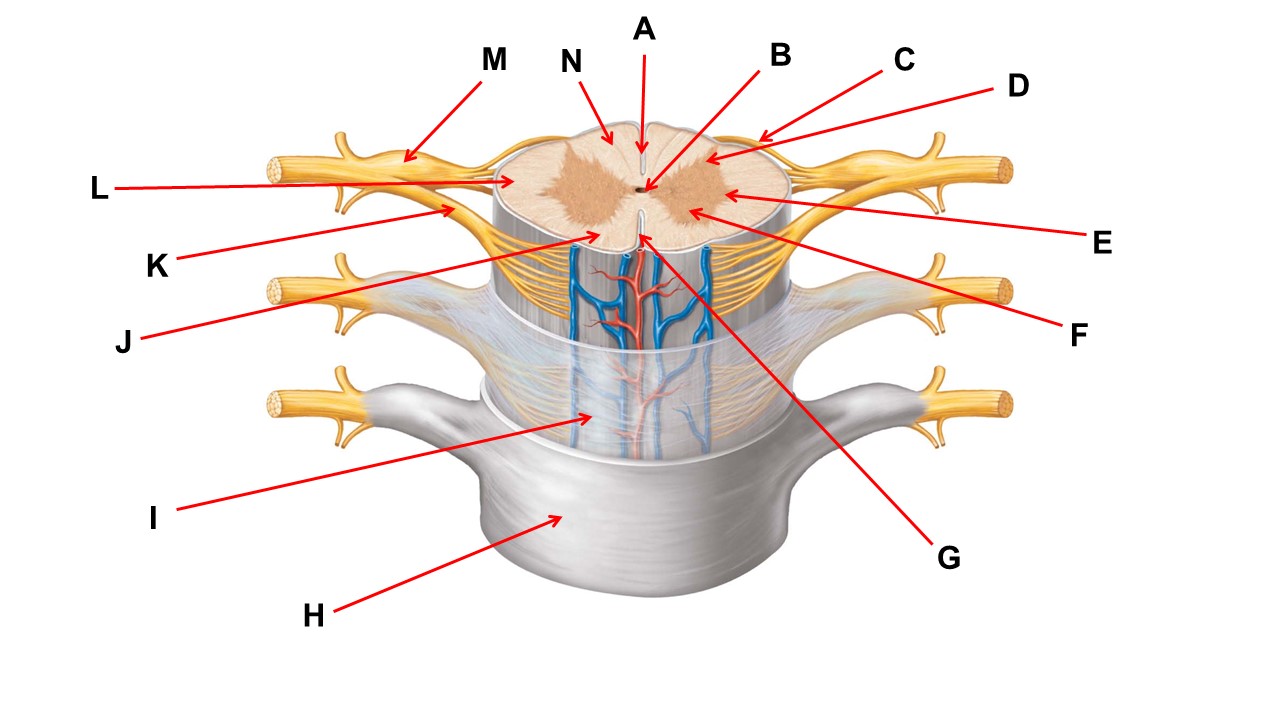
Name the region of tissue surrounding the tip of arrow E.
lateral horn
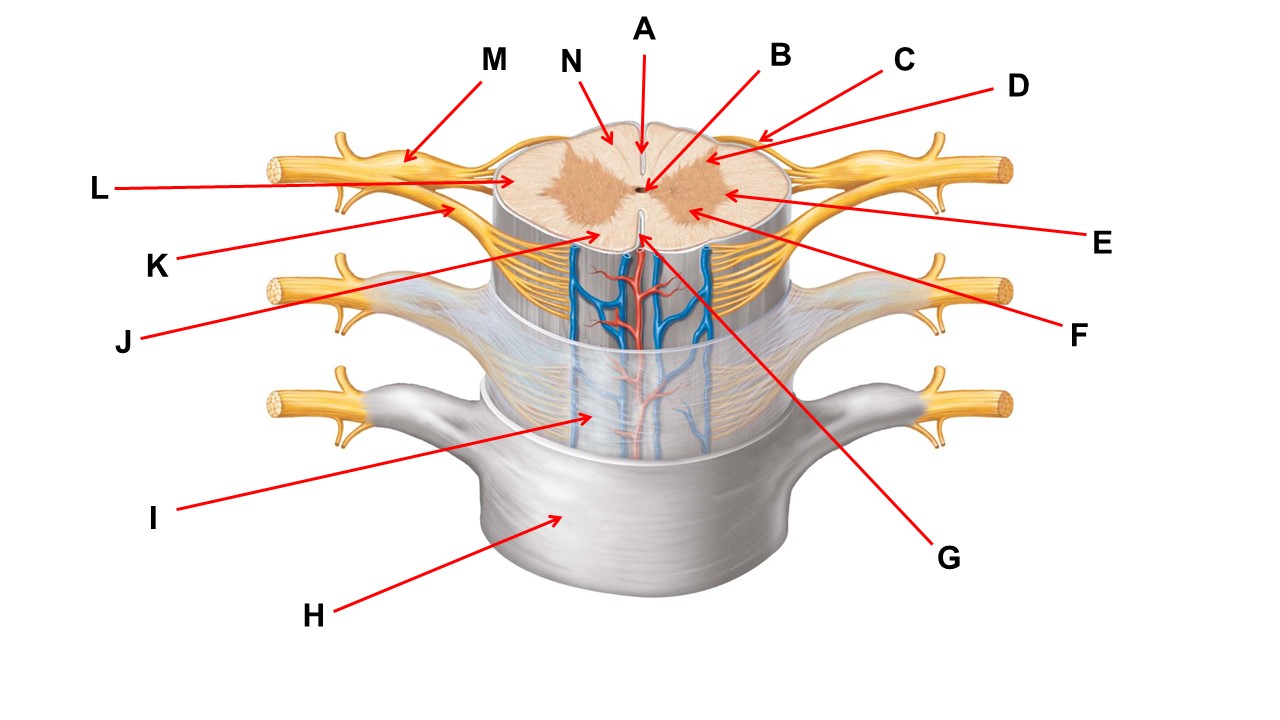
Name the region of tissue surrounding the tip of arrow N.
dorsal column
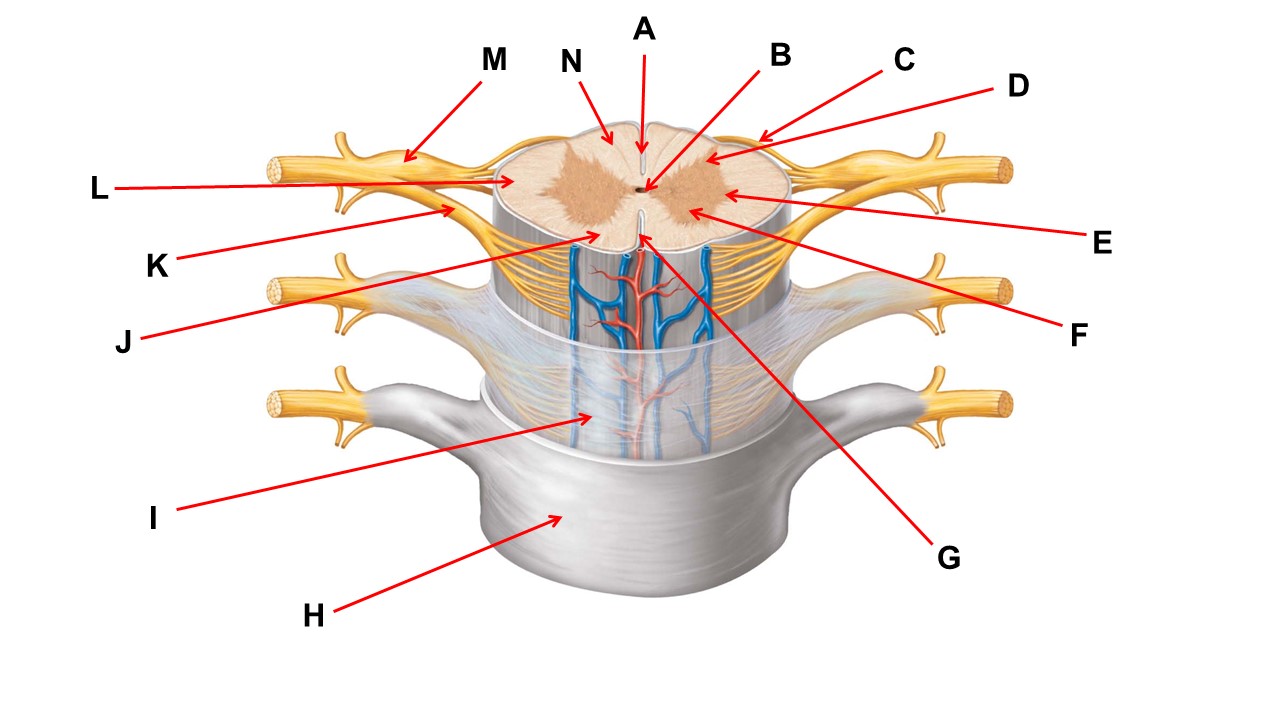
Name the deep groove at the tip of arrow G.
anterior median fissure
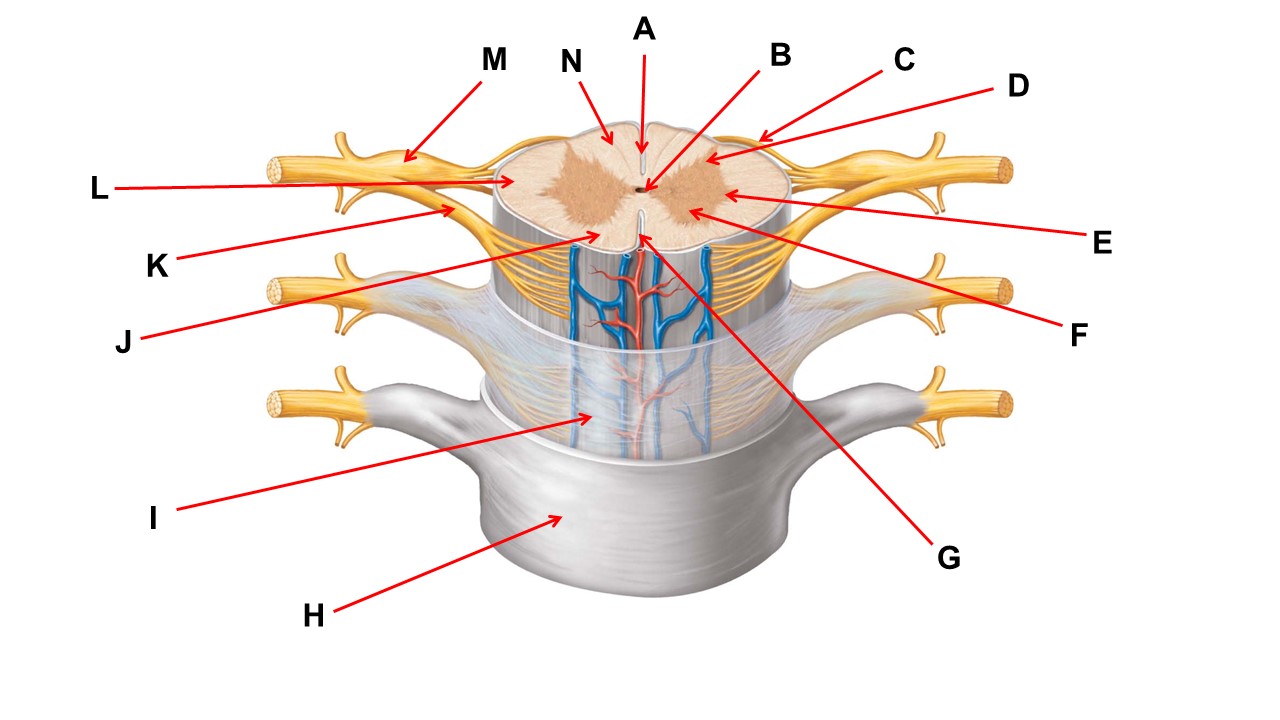
Name the layer at the tip of arrow I
arachnoid mater
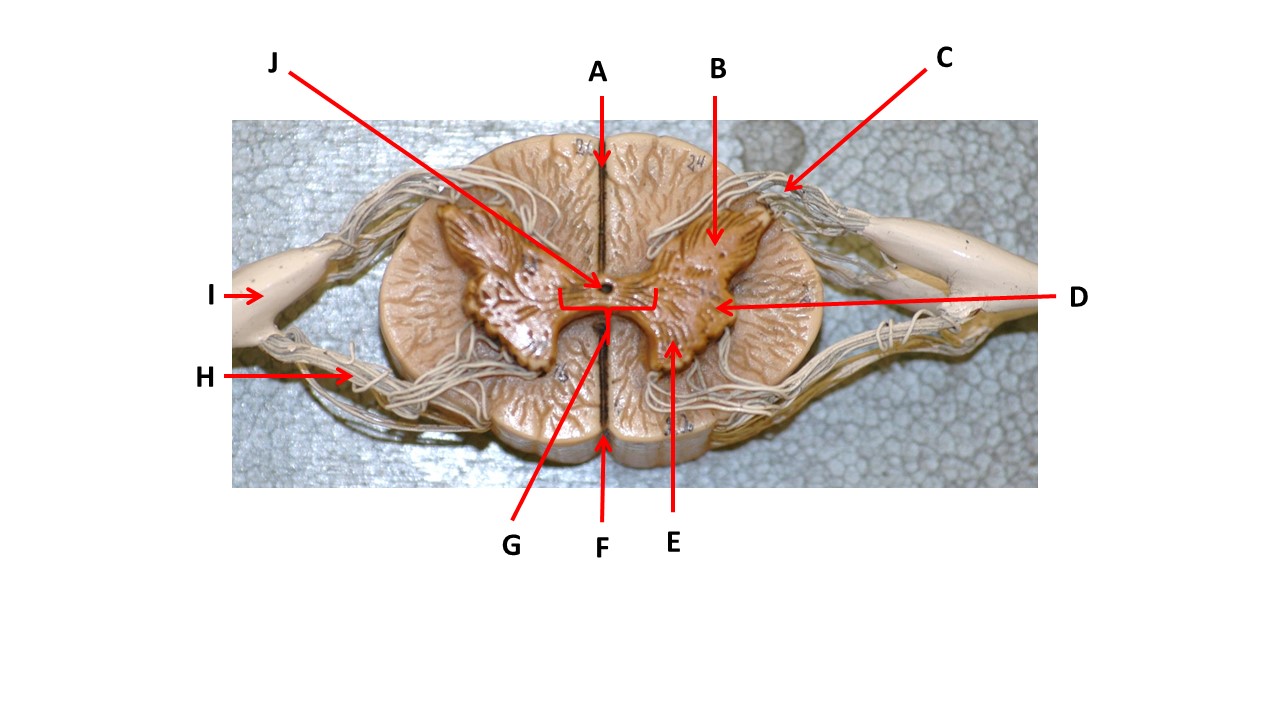
Which structure(s ) would be found in the area at the tip of arrow D.
cell bodies of interneurons
Name the region of tissue surrounding the tip of arrow E.
ventral horn
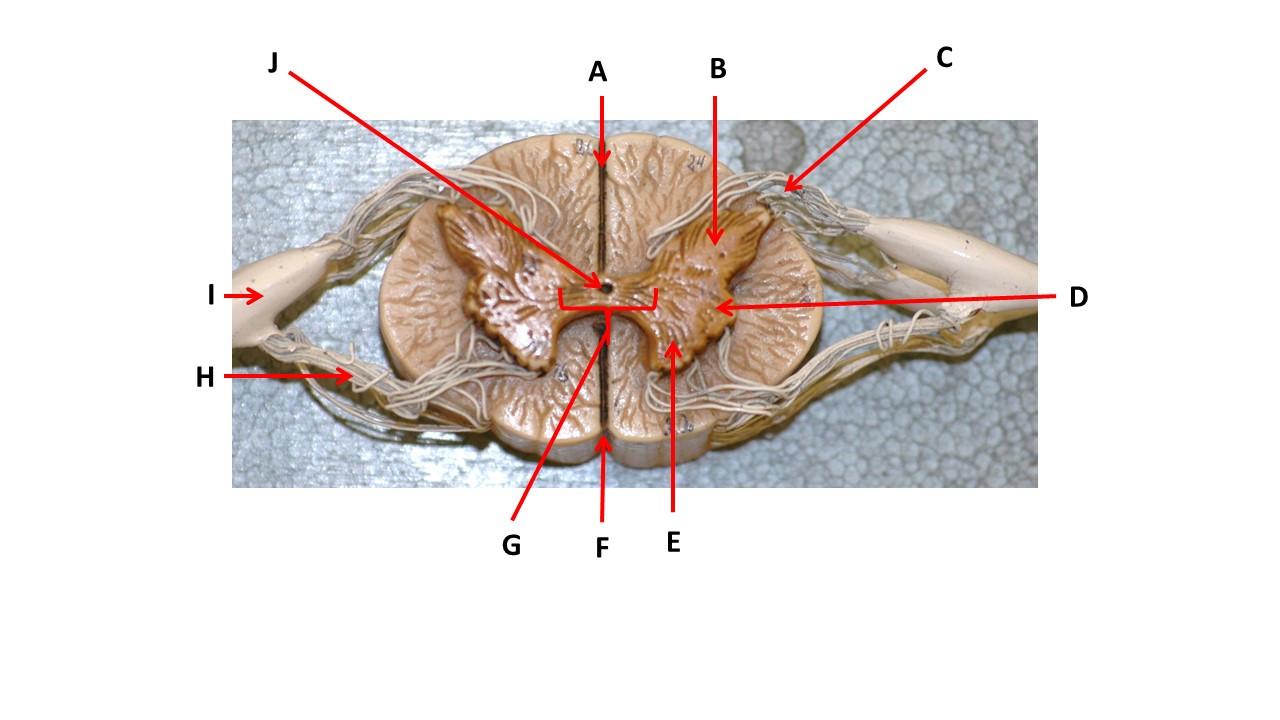
Name the region within bracket G.
gray commisure
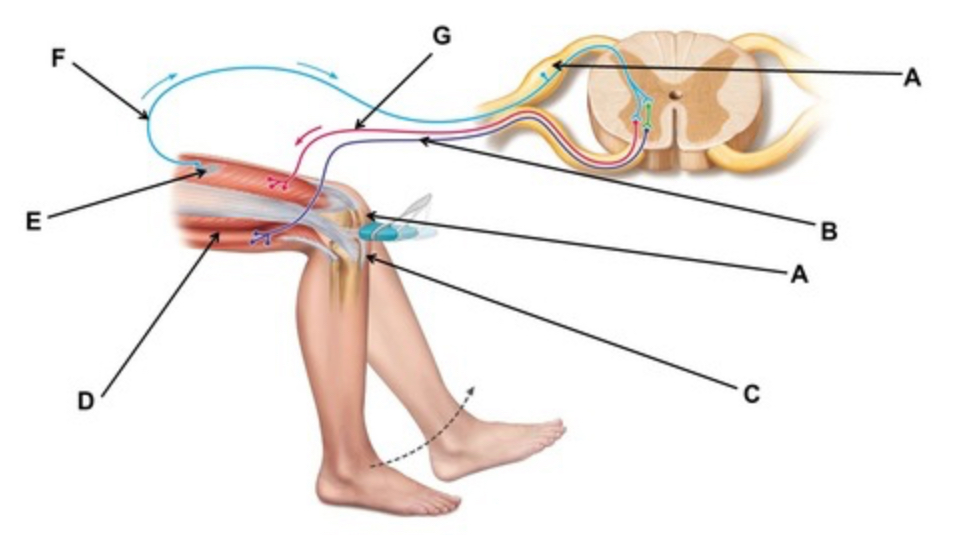
This test could be used to test the functioning of which peripheral nerve?
femoral
the two - point discrimination test is used to determine _____.
the density of touch receptors
The organ involved in the mucturition reflex is the _____.
urinary bladder
The pupillary light reflex is an example of a(n) ____.
autonomic reflex
The function of the pupillary responses include ____.
protecting the retina from damaged by bright light
Lamellar corpuscles are an example of ___.
an elaborate encapsulated nerve ending
True or False: A positive babinski sign is normal in an adult.
false
Which statement about neural reflex arcs is incorrect?
Select one:
they are slowed down by the hormones involved.
What is true about somatic reflexes?
they activate skeletal muscle
Interceptors are located ______.
in internal visceral organs
Which of the following is a receptors for light touch?
hair follicle receptor
Tactile corpuscle and tacticle (merkel) discs are located _____.
in the skin
This receptor for light touch is made up of a free nerve ending associated with a special epidermal cell.
tactile (merkel) disc
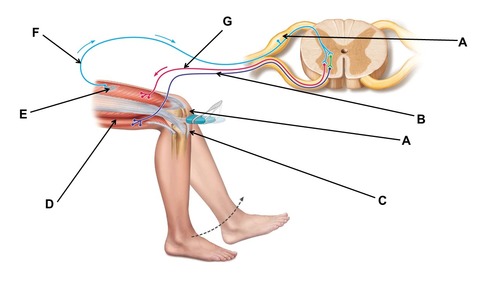
When conducting this reflex, which muscle(s) are inhibited?
hamstrings
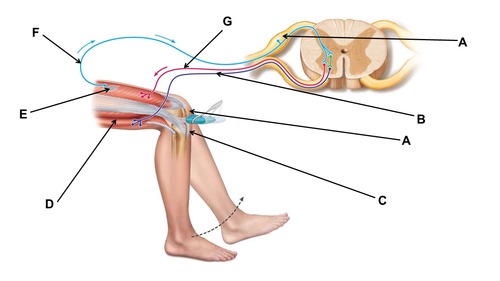
When conducting this reflex, which muscle(s) contracts?
quadriceps
The crossed extensor reflex is an example of a(n) ________.
somatic reflex
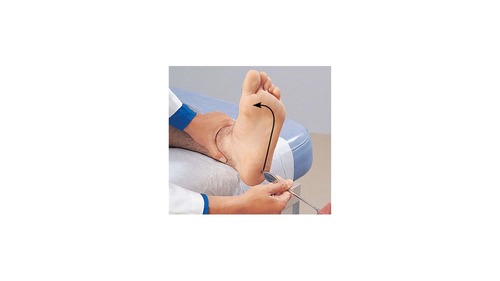
If upon performing this test on an adult the toes are observed to flair this could indicate _____.
damage to the corticospinal tract