AP Macro Unit 2 Test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:24 PM on 9/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
Gross Domestic Product
is the dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders in one year
2
New cards
GDP
Consumer Consumption + Investment + Government Spending + Net Exports
3
New cards
% Change in GDP
YEAR2-YEAR1/ YEAR1 x 100
4
New cards
GDP Per Capita
GDP /by the population
-it identifies on average how many products each person makes
-is the best measure of a cation's standard of living
-it identifies on average how many products each person makes
-is the best measure of a cation's standard of living
5
New cards
Why do other countries have higher GDPs?
1. Economic System: Capitalist countries have historically had more economic growth
2. Property Rights: if protectd
3. Capital - the amount
4. Human capital: knowledge
5. Natural Resources
2. Property Rights: if protectd
3. Capital - the amount
4. Human capital: knowledge
5. Natural Resources
6
New cards
Expendentures Approach
add all the spending on final goods and services produced in a given year
7
New cards
Income Approach
add up all the income that resulted from selling all final goods and services produced in a year
Labor Income + Rental Income + Interests Income + Profit
Labor Income + Rental Income + Interests Income + Profit
8
New cards
Shortcomings of GDP
-Certain important work is left out of accounting, such as homeworkers and carpenters
-GDP does not measure the total quality of life
-Does no reflect improved product quality
-GDP does not measure the total quality of life
-Does no reflect improved product quality
9
New cards
Things not included in GDP
1. intermediate goods
2. used goods
3. financial transactions (stocks and bonds)
4. transfer payments
- Public (social security)
- Private (birthday money)
5. unreported legal activity
6. illegal activity (underground economy)
7. US corps producing overseas
2. used goods
3. financial transactions (stocks and bonds)
4. transfer payments
- Public (social security)
- Private (birthday money)
5. unreported legal activity
6. illegal activity (underground economy)
7. US corps producing overseas
10
New cards
Nominal GDP
GDP based on the prices that prevail when the outputs was produced is called unadjusted GDP
11
New cards
Real GDP
GDP that has been deflated or inflated ttp reflect changes in the price level
12
New cards
GDP Deflator
is a measure of the level f prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy
13
New cards
Business Cycle
- largely systematic ups and downs of real GDP
- trend line shows that over the long term, the economy is gradually growing despite cycles of expansion and recession
- trend line shows that over the long term, the economy is gradually growing despite cycles of expansion and recession
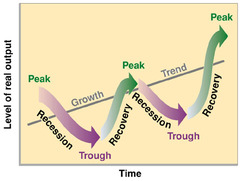
14
New cards
Recession
6 month period of decline in real GDP
15
New cards
Depression
18 month period of decline in real GDP
16
New cards
Macroeconomics
-measures these fluctuations and guides policies to keep the economy stable
-The government has the responsibility to
-promote long-term growth
-Prevent unemployment
-Prevent inflation
-The government has the responsibility to
-promote long-term growth
-Prevent unemployment
-Prevent inflation
17
New cards
Limit Unemployment
-workers that are acteively looking for a job but aren't working
-Rate: the percent of people in the labor force who want a job but are not working
# of unemployed / # in labor force x 100
-Rate: the percent of people in the labor force who want a job but are not working
# of unemployed / # in labor force x 100
18
New cards
Labor Force
-16 years old and up
-Able and willing to work
-not institutionalized
-not in military, in school full time, or retired
-Able and willing to work
-not institutionalized
-not in military, in school full time, or retired
19
New cards
Frictional Unemployment
temporary unemployment or being between jobs; individuals are qualified workers with transferable skills
20
New cards
Seasonal Unemployment
is a specific type of frictional unemployment which is due to time of ouear and the cature of the job
21
New cards
Structural Unemployment
Changes in labor force make some skills obselete; do not have transferable skills
-THESE WORKERS DO NOT HAVE TRANSFERABLE SKILLS and these ojbs will never come back, workers must learn new skills to get a job
-"creative destruction" - the permanent loss of these jobs
-THESE WORKERS DO NOT HAVE TRANSFERABLE SKILLS and these ojbs will never come back, workers must learn new skills to get a job
-"creative destruction" - the permanent loss of these jobs
22
New cards
Technological Unemployment
type of structural unemployment where automation and machinery replace workers
23
New cards
Cyclical Unemployment
Unemployment caused by recession
-as demand for goods and services falls, demand for labor falls and workers are fired
-this is called "demand deficient unemployment"
-as demand for goods and services falls, demand for labor falls and workers are fired
-this is called "demand deficient unemployment"
24
New cards
Natural Rate of Unemployment (NRU)
The amount of unemployment that exists when the economy is healthy and growing
Frictional and structural unemployment
Frictional and structural unemployment
25
New cards
Full Employment
4-6% in the U.S.
26
New cards
Discouraged Job Seekers
those who have officially given up looking for work and are discouraged
27
New cards
Underemployed Workers
those with part time or seasonal jobs who would rather have full time
28
New cards
Criticisms of the Unemployment Rate
*-misdiagnose actual unemployment rate*
1. Discouraged workers
2. Underemployed Workers
3. Racial/Age Inequalities: the overall unemployment rate doesn't show disparity for minorities and teenagers
1. Discouraged workers
2. Underemployed Workers
3. Racial/Age Inequalities: the overall unemployment rate doesn't show disparity for minorities and teenagers
29
New cards
Labor Force Participation Rate
Labor force/ Population (16 and older) x 100
30
New cards
Inflation
-is the general rising in the level of prices
-it reduces the "purchasing power" of money
-when inflation occurs, each dollar of income will buy fewer goods than before
-it reduces the "purchasing power" of money
-when inflation occurs, each dollar of income will buy fewer goods than before
31
New cards
Nominal Wage
wage measured by dollars rathe than purchasing power
32
New cards
Real wage
wage adjusted for inflation
33
New cards
How is inflation measured?
Government tracks the prices of specific "market baskets" that include the same goods and services
34
New cards
Market Basket
sets of goods and services that are bought and sold as stables in a functional economy
35
New cards
Inflation Rate
the percentage change in prices from year to year
36
New cards
Price Indexes
index numbers assigned to each year that show how prices have changed relative to a specific base year
37
New cards
Consumer Price Index
CPI = Price of Market Basket / PRice of market basket in a base year x 100
38
New cards
Problems of CPI
1. Subsittution Bias - as prices increases for the fixed market basket, consumers buy less of these products and more substitutes that maby not be part of the market basket
*Result* - CPI may be higher than what consumers are really paying
2. New Products: the CPI market basket may not include the newest consumer products
*Result* - CPI measures prices but no the increase in choices
3. Product Quality: the CPI ignores both improvements and decline in product quality
*Result* - CPI may suggest that prices stay the same though the economic well being has improved significantly
*Result* - CPI may be higher than what consumers are really paying
2. New Products: the CPI market basket may not include the newest consumer products
*Result* - CPI measures prices but no the increase in choices
3. Product Quality: the CPI ignores both improvements and decline in product quality
*Result* - CPI may suggest that prices stay the same though the economic well being has improved significantly
39
New cards
CPI v.s. GDP Deflator
The GDP deflator measures the prices of all goods produced, wheras the CPI measures prices of only the goods and services bought by consumers
An increase in the price of goods bought by firms or the government will show up in the GDP Deflator but not in the CPI.
THe GDP deflator includes only those goods and servuces produced domestically. Imported goods are not a part of GDP and therefore don't show up in the GDP deflator
GDP deflator = Nominal/Real x 100
An increase in the price of goods bought by firms or the government will show up in the GDP Deflator but not in the CPI.
THe GDP deflator includes only those goods and servuces produced domestically. Imported goods are not a part of GDP and therefore don't show up in the GDP deflator
GDP deflator = Nominal/Real x 100
40
New cards
Who are affected by unexpected inflation?
*Helped*
-Borrowers
-Business where the price of the product increases faster than the price
*Hurt*
-Lenders
-People with fixed Incomes
Savers
-Borrowers
-Business where the price of the product increases faster than the price
*Hurt*
-Lenders
-People with fixed Incomes
Savers
41
New cards
Causes of Inflation
1. The government prints too much money (quantity theory)
-government that keeps printing money to pay debts end up with hyperinflation
-*result* - Banks refuse ti lend so investment falls and people don't save up to buy things
2. Demand-Pull Inflation: demand pulls up prices
-"too many dollars chasing tee few goods"
-an overheated economy with excessive spending but same amount of goods
3. Cost-Push Inflation: Higher production costs increases prices
-negative supply shock increases the costs of production and forces producers to increase prices
-government that keeps printing money to pay debts end up with hyperinflation
-*result* - Banks refuse ti lend so investment falls and people don't save up to buy things
2. Demand-Pull Inflation: demand pulls up prices
-"too many dollars chasing tee few goods"
-an overheated economy with excessive spending but same amount of goods
3. Cost-Push Inflation: Higher production costs increases prices
-negative supply shock increases the costs of production and forces producers to increase prices
42
New cards
Real Interest Rate
the percentage increase in purchasing power that a borrower pays
Real Interest = nominal interest - expected inflation
Real Interest = nominal interest - expected inflation
43
New cards
Nominal Interest Rate
the percentage increases in money that the borrower pays not adjusting for inflation
Nominal = real interest + expected inflation
Nominal = real interest + expected inflation
44
New cards
Achieving the 3 goals
-the government roles is to prevent unemployment and prevent inflation the same time
-if the government focuses too much on preventing inflation and slows down the economy we will have unemployment
- if the government focuses too much on limiting unemployment and overheats the economy we will have inflation
-if the government focuses too much on preventing inflation and slows down the economy we will have unemployment
- if the government focuses too much on limiting unemployment and overheats the economy we will have inflation
45
New cards
Quantity Theory of Money Equation
M*V = P*Y
M= money supply
V=velocity
Y= Quantity Output
P= Price level
M= money supply
V=velocity
Y= Quantity Output
P= Price level
46
New cards
Menu Costs
the cost of printing new menus when a restaurant decides to reduces its prices, but lowering prices also creates other costs
when menu costs are present, firms may choose to avoid them by retaining current prices
when menu costs are present, firms may choose to avoid them by retaining current prices
47
New cards
Shoe Leather Costs
refers to the cost of time and effort that people spend trying to counter-act the effects of inflation, such as holding less cash and having to make additional trips to the bank.