ECEN 414 L5 (Biosensor Characteristics)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Biosensor Characteristics
● Sensitivity
● Limit of Determination
● Background Signal
● Dynamic Range
● Dynamic Response
● Selectivity
● Calibration
● Linearity
● Hysteresis
● Drift and Long-Term Stability
● Temperature Dependence
● Signal to Noise
● Reliability (Accuracy and Precision)
● Resolution
● Lifetime
● Biocompatibility
Sensitivity
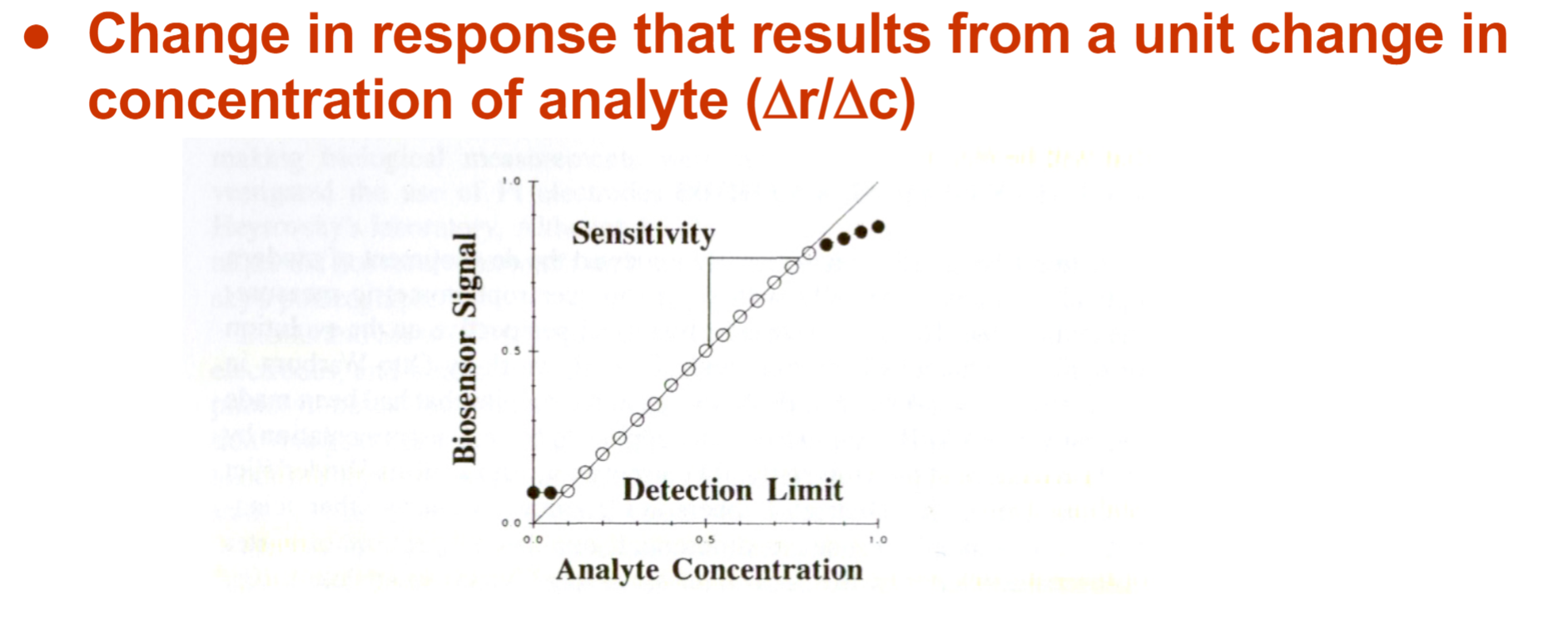
Limit of Determination (Detection Limit)
Ideally: It is extremely low, allowing the biosensor to detect minute quantities of the analyte with high precision and accuracy
Practically: It is often higher due to various factors such as noise, interference from other substances, and limitations in the sensor’s design and materials.
Background Signal
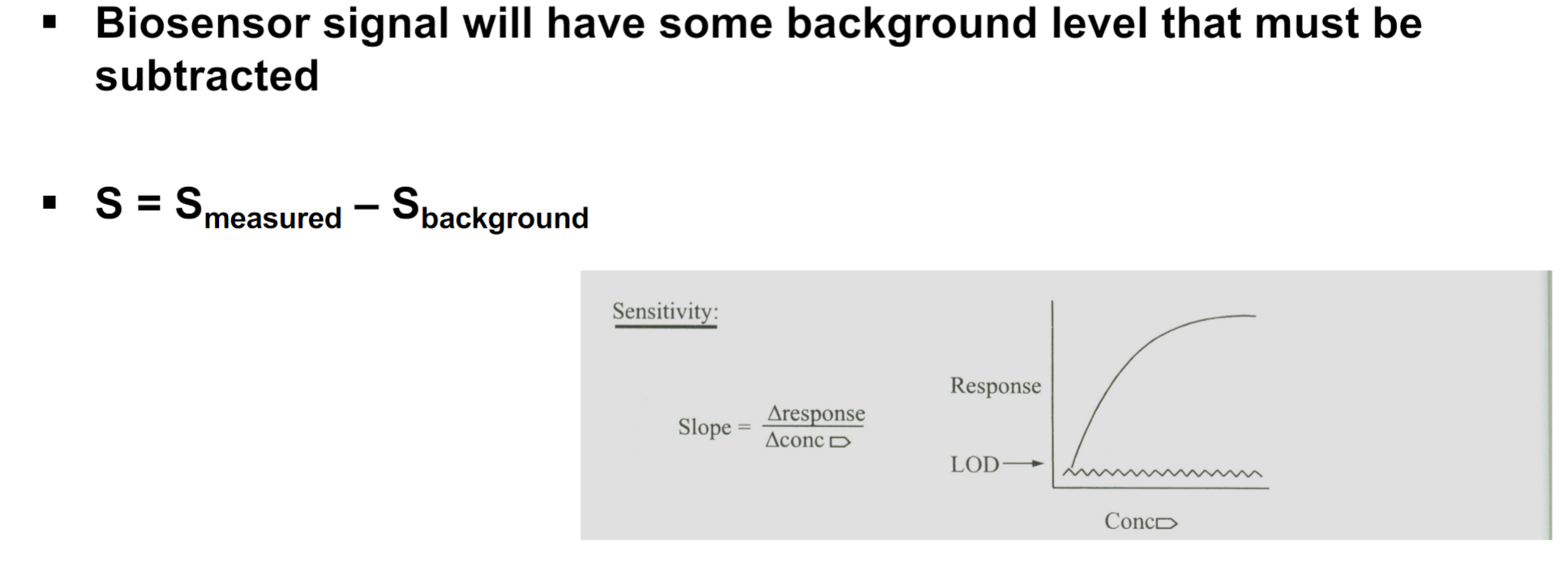
Dynamic Range

Dynamic Response (Δr/Δt/Δc)

Selectivity

Calibration
Should be easily calibrated simply by exposing it to prepared standard solutions or gases containing different known concentrations of the target analyte
Hysteresis
Ideal biosensor should not be affected by its past history of measurements, and would have zero ________
Temperature Dependence

Signal to Noise Ratio
Measure of how much a signal has been corrupted by noise
Improving ___ in practice
Controlled environment
When characteristics of noise are known, can use a filter or to process the signal
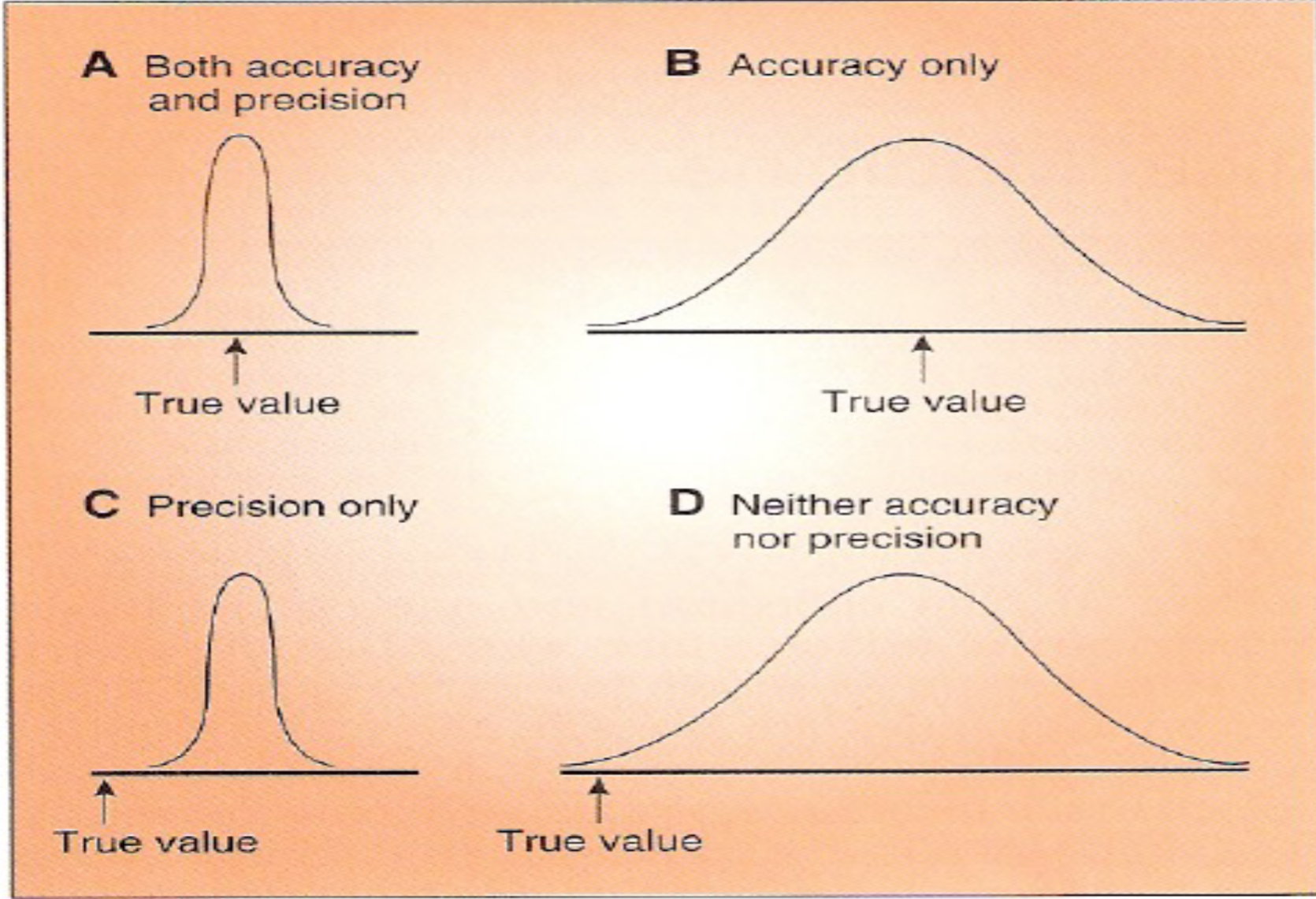
Reliability (Accuracy, Precision ) and Resolution
Lifetime

Biocompatibility
Relevant to biosensors that have medical applications