SHIZOPHRENIA
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:22 AM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
Causes distorted and bizarre thoughts, perception, movements, emotions and behavior. It cannot be defined as a single illness rather schizophrenia is a thought of as a syndrome or a disease process with many different varieties and symptoms much like the varieties of cancer
SCHIZPHRENIA
2
New cards
A mbivalence
A ssociated looseness
D elusions
E chopraxia
F light of ideas
H allucinations
I deas of reference
P erseveration
A ssociated looseness
D elusions
E chopraxia
F light of ideas
H allucinations
I deas of reference
P erseveration
POSITIVE OR HARD SYMPTOMS
3
New cards
Having mixed or contradictory beliefs/feelings
AMBIVALENCE
4
New cards
poorly/fragmented thoughts and ideas
ASSOCIATED LOOSENESS
5
New cards
fixed false beliefs that is not based on reality
DELUSIONS
6
New cards
Imitations of movement/gesture or another person
ECHOPRAXIA
7
New cards
Continues flow of verbalization, jumping rapidly from one topic or another
FLIGHT OF IDEAS
8
New cards
False expression that have special meaning for the person
IDEAS OF REFERENCE
9
New cards
Verbal repetition of sentences, words or phrase resisting to change the topic
PERSEVERATION
10
New cards
L ack of volition
A logia
B lunted affect
A nhedonia
C atatonia
F lat affect
A pathy
A logia
B lunted affect
A nhedonia
C atatonia
F lat affect
A pathy
NEGATIVE OR SOFT SYMPTOMS
11
New cards
absence of will, ambition to take action
Lack of volition
12
New cards
reduced speech output; poverty speech
ALOGIA
13
New cards
restricted range of emotional feeling, tone or mood
BLUNTED AFFECT
14
New cards
Loss of pleasurable feelings
ANHEDONIA
15
New cards
reduced movement; motionless
CATATONIA
16
New cards
Absence of any facial expression
FLAT AFFECT
17
New cards
Feelings of indifference towards people, event and activities
APATHY
18
New cards
**P-** RODROMAL PHASE
**A-** CTIVE PHASE
**R**- ESIDUAL TYPE
**A-** CTIVE PHASE
**R**- ESIDUAL TYPE
TYPICAL STAGES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
19
New cards
**P-** ARANOID TYPE
**D-** ISORGANIZED TYPE (HEBEPHRENIC)
**C-** ATATONIC TYPE
**U-** UNDIFFERENTIATED TYPE (ATYPICAL SCHIZOPHRENIA)
**R-** ESIDUAL TYPE
**D-** ISORGANIZED TYPE (HEBEPHRENIC)
**C-** ATATONIC TYPE
**U-** UNDIFFERENTIATED TYPE (ATYPICAL SCHIZOPHRENIA)
**R-** ESIDUAL TYPE
SUBTYPES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
20
New cards
* Characterized by persecutory or grandiose delusions and hallucinations.
* Do not show disorganized behavior
* Best prognosis of all type
* High familial link than other types
* Intact cognitive skills and affect
* Do not show disorganized behavior
* Best prognosis of all type
* High familial link than other types
* Intact cognitive skills and affect
PARANOID TYPE
21
New cards
* Characterized by grossly inappropriate or flat affect, incoherence and marked disruption of behavior and speech.
* Chronic or lack of remissions, develop early
* Chronic or lack of remissions, develop early
DISORGANIZED TYPE (HEBEPHRENIC)
22
New cards
* Characterized by marked psychomotor disturbances either motionless or excessive motor activity.
* Tends to be severe and rare
* Tends to be severe and rare
CATATONIC BEHAVIOR
23
New cards
* Characterized by mixed schizophrenic symptoms of other types along with disturbances of thought, affect and behavior
* Major symptoms symptoms of schizophrenia
* Major symptoms symptoms of schizophrenia
UNDIFFERENTIATED TYPE
24
New cards
* Characterized by at least one previous, though not a current episode; social withdrawal , flat affect, and looseness of association
* still shows “left over” symptoms
* still shows “left over” symptoms
RESIDUAL TYPE
25
New cards
\- Continuous without temporary improvement
\- Episodic with progressive or stable deficit
\- Episodic with complete or incomplete remission
Course of schizophrenia
26
New cards
1\. **T**wo of the following for most of 1 month:
\- Delusions
\- Hallucinations
\- Disorganized speech
\- Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
\- Negative symptoms
2\. **M**arked social or occupational dysfunction
3\. **D**uration of at least 6 months of persistent symptoms
4\. **S**ymptoms of schizoaffective & mood disorder are ruled out
5\. **S**ubstance abuse & medical conditions are ruled out as etiological
**TMDS2 DE HA DE GRO NE**
DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia
27
New cards
is also used in the treatment of schizophrenia, but may be useful when catatonia or prominent affective symptoms are present.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT
28
New cards
\- Chlorpromazine
\- Clopenthixole
\- Levopromazine
\- Thioridazine
\- Droperidole
\- Clopenthixole
\- Levopromazine
\- Thioridazine
\- Droperidole
Conventional antipsychotics – (classical neuroleptics)
29
New cards
- Flupenthixol
\- Zuclopenthixole
\- Zuclopenthixole
Depot antipsychotics: (Fluphenazine deconate-Modecate)
30
New cards
\
\- Amisulpiride
\- Clozapine
\- Olanzapine
\- Quetiapine
\- Risperidone
\- Sertindole
\- Sulpiride
\- Amisulpiride
\- Clozapine
\- Olanzapine
\- Quetiapine
\- Risperidone
\- Sertindole
\- Sulpiride
Atypical antipsychotics – (new neuroleptics);
31
New cards
\- Old age of onset
\- Female
\- Married
\- No family history
\- Good premorbid personality
\- High IQ
\- Precipitants
\- Positive symptoms
\- Treatment compliance
\- Good support
\- Acute onset
\- Presence of mood component
Good prognosis
32
New cards
\- Young age of onset
\- Male
\- Unmarried
\- Family history
\- Personality problems
\- Low IQ
\- No obvious precipitants
\- Negative symptoms
\- Poor treatment compliance
\- Low support
\- Insidious onset
\- No mood component
\- Male
\- Unmarried
\- Family history
\- Personality problems
\- Low IQ
\- No obvious precipitants
\- Negative symptoms
\- Poor treatment compliance
\- Low support
\- Insidious onset
\- No mood component
POOR PROGNOSIS
33
New cards
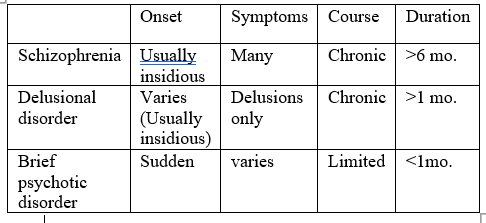
\
PSYCHOTIC DISORDER
34
New cards
S chizophreniform disorder
S hared pychotic disorder (Folie a deux)
S chizoaffective disorder
B rief psychotic disorder
D elusional psychotic disorder
\
**S3BD**
S hared pychotic disorder (Folie a deux)
S chizoaffective disorder
B rief psychotic disorder
D elusional psychotic disorder
\
**S3BD**
OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDER
35
New cards
- Schizophrenic symptoms for a few months **(less than 6 months)**
\- Associated with good premorbid functioning
\- Most resume normal lives
\- The same treatments recommended for schizophrenia may also be utilized here
\- Associated with good premorbid functioning
\- Most resume normal lives
\- The same treatments recommended for schizophrenia may also be utilized here
Schizophreniform Disorder
36
New cards
- Delusion from one person manifest in another person
\- The most common relationships are among parents and children, spouses and siblings
\- - Separation from the dominant person and immersion into normal social interaction
\- The most common relationships are among parents and children, spouses and siblings
\- - Separation from the dominant person and immersion into normal social interaction
Shared psychotic disorder (Folie à Deux)
37
New cards
- Symptoms of schizophrenia and a mood disorder
\- Both disorders are independent of one another
\- Such persons do not tend to get better on their own
\- Long-term outcome of patients is not good as that for patients with a mood disorder, yet not as grave as that for patients with schizophrenia.
\- Both disorders are independent of one another
\- Such persons do not tend to get better on their own
\- Long-term outcome of patients is not good as that for patients with a mood disorder, yet not as grave as that for patients with schizophrenia.
Schizoaffective disorder
38
New cards
- Characterized by eccentric behavior and by deviations of thinking and affectivity, which are similar to that occurring in schizophrenia, but without psychotic features and expressed symptoms of schizophrenia of any type.
\- May affect a less severe form of schizophrenia
\- May affect a less severe form of schizophrenia
Schizotypal disorder
39
New cards
\- Rare disorder, occurring in perhaps less than 1 or 2 per 1000 deliveries
\- It is more common in primiparous than in multiparous women
\- Many of these patients never experience another psychotic illness unless they again become pregnant
\- Symptoms generally appear abruptly within about 3 days to several weeks after delivery
\- Hospitalization is generally indicated
\- It is more common in primiparous than in multiparous women
\- Many of these patients never experience another psychotic illness unless they again become pregnant
\- Symptoms generally appear abruptly within about 3 days to several weeks after delivery
\- Hospitalization is generally indicated
Postpartum psychosis (puerperal psychosis)