Week 12 Gastrointestinal Disorders
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
GI Tract is divided up into portions
Mouth
Esophagus
Stomach
Fundus, cardia, body, pylorus
Small intestine
Duodenum, jejunum and ileum
Large intestine
Cecum, ascending, transverse,
descending, sigmoid colon and rectum
What is the purpose of the GI tract?
Ingestion, digestion, and absorption
Categories of nutrients
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids
Nutrients - Carbohydrates
Amylase in oral cavity; amylase from pancreas; enzymes from brush border.
Nutrients - Proteins
Gastrin; hydrochloric acid converts pepsinogen to pepsin (chyme)
Cholecystokinin in small intestine- pancreatic enzymes (e.g., trypsinogen)
Nutrients - Lipids
Cholecystokinin stimulates the gallbladder (bile) and pancreas and small intestine (lipase)
Peptic Ulcers
Break in mucosa in stomach or duodenum - Potential of perforation
Duodenal and gastric ulcers are commonly caused by Helicobacter pylori
Stimulates the inflammatory process
Increase in hydrochloric acid
Production of urease
Peptic Ulcers Transmission
person-to-person, fecal-to-oral, and contaminated food
Peptic Ulcers Laboratory considerations
Gastroscopy, breath tests, stool antigen tests, and serological tests
GI Ulcers - Diagnosis (Gastroscopy)
Tissue samples, Rapid urease test (phenol red; changes in colour), Microbiological cultures and Histologic tests.
GI Ulcers - Diagnosis (Urea breath test)
High sensitivity (94%) and high specificity (98%)
Most widely used test (noninvasive)
Commonly uses urea with carbon-13
Pathogenic H. pylori produces urease
Breaks down urea and release CO2
Elevated levels of labeled CO2 indicate H. pylori
Detect active infections
GI Ulcers - Diagnosis (Stool test for H. pylori antigen)
Reliable, convenient, and noninvasive test
High sensitivity and specificity (>90%)
Detect active/ recent infections
Use of immunoassays (ELISA)
GI Ulcers - Diagnosis (Serological tests)
Antibodies (IgM, IgA, IgG) to H. pylori
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Associated with mutations; Benign, non-beta-islet cell, gastrin-secreting tumours; Gastrinomas (pancreas or duodenum).
A rare condition characterized by gastrin-secreting tumors (gastronomas) that lead to excessive gastric acid production. This overproduction can cause severe peptic ulcers and gastrointestinal symptoms due to high acidity levels.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (symptoms/signs)
Gastric pain
Fulminant peptic ulcers
Massive gastric hypersecretion
Hypergastrinemia
Diarrhea
Steatorrhea
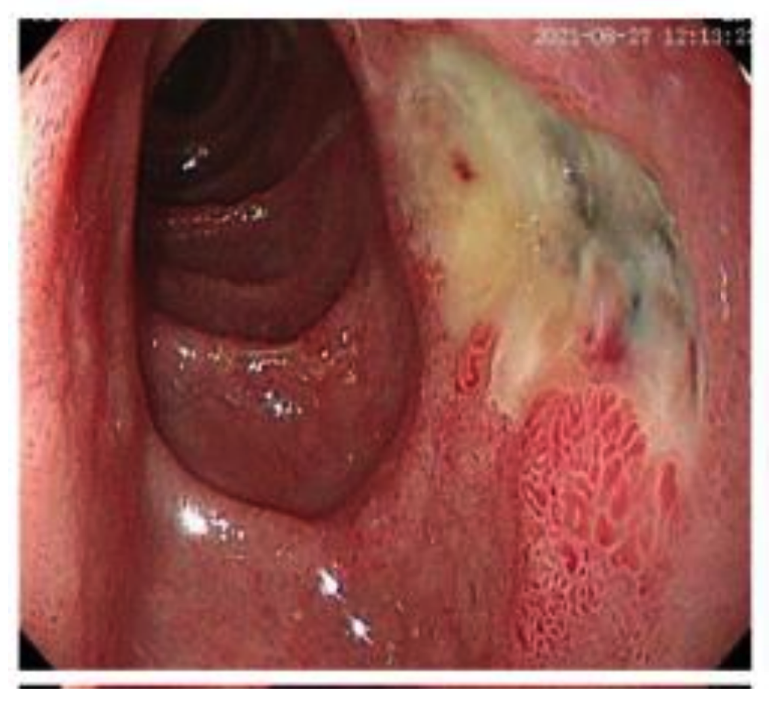
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome - Diagnosis
Gastrin levels
Gastrin levels >10 X RI + gastric acid hypersecretion (diagnostic-gastrinoma)
Imaging techniques (CT scan)
Gastroscopy
H. pylori investigation is negative
Malabsorption Syndrome
Defective absorption of nutrients
Single nutrient malabsorption (i.e., lactose)
Widespread nutrient deficiency (i.e., Crohn disease, Celiac disease)
Common symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, and weight loss
Malabsorption Syndrome- Diagnosis
CBC
Prothrombin time
Vitamin and mineral assays
Serologic tests (celiac disease)
Pancreatic elastase-1 (maldigestion Vs. malabsorption)
Stool cultures (bacteria? Parasites?)
Fecal fat test (nonspecific)
Lactose tolerance test
No significant increase in blood glucose
Diarrhea
Loose, watery, and frequent stools
Chronic if >4 wks
Diarrhea (Acute)
Bacterial, parasitic, viral causes, antibiotic
Diarrhea (Chronic)
May lead to: dehydration and low potassium levels
Causes
Inflammatory bowel disease
Irritable bowel syndrome
Celiac disease
Food intolerances (E.g., lactose)
Chemotherapy, radiation
Laboratory Tests for Diarrhea
Stool cultures
Immunoassays
C. difficile, rotavirus, and E. coli strains
Ova and parasite test
Fecal fat test (nonspecific)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Primarily including Ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease; Unknown cause; Both exhibit bouts of remission and exacerbations.
Cause chronic inflammation in the digestive tract, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue.
Symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Abdominal pain, Cramping, Anorexia, Bloody diarrhea and Anemia.
Characteristic of Crohn Disease
Area affected: More common in terminal ileum and colon
Stool: Loose, semiformed
Lesion distribution: Transmural, all layers and skip lesions
Presence of granuloma: Common
Fistula, fissure, abscess: Common
Stricture, obstruction: Common
Malabsorption: Yes
Characteristic of Ulcerative colitis
Area affected: Rectum, colon
Stool: Frequent, watery, with blood and mucus
Lesion distribution: Mucosa only diffuse
Presence of granuloma: No
Fistula, fissure, abscess: No
Stricture, obstruction: Rare
Malabsorption: Not Common
Inflammatory Bowel Disease - Diagnosis
CBC (WBC)
C-reactive protein
Calprotectin stool test
High because of inflammation
Fecal examination
Red and white blood cells
Occult blood tests
Imaging (e.g., MRI) and endoscopy / biopsy
Celiac Disease
Autoimmune disease: Antibodies to gluten (gliadin); Inflammation, malabsorption; Avoided through a gluten-free diet
An autoimmune disorder that occurs in genetically predisposed individuals where the ingestion of gluten—a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye—leads to damage in the small intestine.
Celiac Disease - Diagnosis
Signs and symptoms are important
Biopsy (gold standard) -invasive
Endoscopy
Villus atrophy
Serological tests
Signs and Symptoms of Celiac Disease
Diarrhea, weight loss, abdominal pain, bloating, fatigue, and anemia. In children, it can also cause delayed growth and development.
Celiac Disease- Diagnosis
Serological tests:
(EMA) IgA-antiendomysial antibody
(AGA) IgA-antigliadin antibody
(tTG) IgA-antitissue transglutaminase antibody
(DGP) IgA-deamidated gliadin peptide antibody
IgA-antiendomysial antibody (EMA)
Immunofluorescence on monkey esophagus or human umbilical cord
Quantitative ELISA
IgA-antigliadin antibody (AGA)
IgA-antitissue transglutaminase antibody (tTG)
IgA- deamidated gliadin peptide antibody (DGP)
Gastrointestinal Function Tests
Evaluate the function of the digestive system
Fecal fat test
E.g., pancreatitis, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis
24-hour pH monitoring
D-Xylose absorption test
Easily absorbed in intestine
E.g., celiac disease, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, pancreatic insufficiency