Amino Acids and Peptides
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What are Proteins?
Class of biomolecules which perform vital functions for living organisms
What is the structure of a protein?
Primary structure (linear sequence)
Secondary structure (alpha helix, beta sheet)
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure (multiple subunits)
What are Amino Acids?
“Alphabet” that the structure of a protein is written
How many common Amino acids are there?
20
What joins an amino acid?
Peptide bonds
What is the difference between a Peptide and a Protein?
Determined by weight
What are the parts to an amino acid?
-Carboxyl group
-Amino group
-Hydrogen atom
-R group
What is the common features for Amino Acids?
Alpha carbon and four substituents
Tetrahedral
Chiral alpha carbon
What is an Isomer?
Same formula, different arrangement of atoms
What is a Constitutional Isomer?
(Structural), atoms are bonded differently
What is a Stereo Isomer?
(Spatial), Same structural bonds, rearranged differently in space
What are Enantiomers?
Mirror images of each other
What are Diastereomers?
Not mirror images
What are the two types of enantiomers?
D and L
L are found in real life
What are the classes of Amino Acids?
(Polar) Aliphatic-not aromatic
(Polar) Aromatic-planar, unsaturated rings
(Nonpolar) Uncharged
(Nonpolar) Positively charged
(Nonpolar) Negatively charged
What are the aliphatic R groups?
Glycine, Alanine, Proline, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine
-PROLINE make up beta sheets
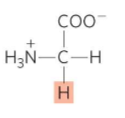
What is this?
Glycine
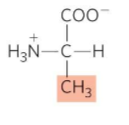
What is this?
Alanine
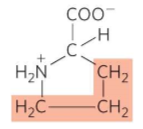
What is this?
Proline
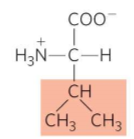
What is this?
Valine
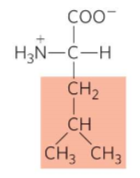
What is this?
Leucine
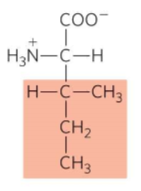
What is this?
Isoleucine
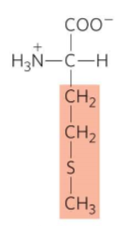
What is this?
Methionine
What are the Aromatic R Groups?
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan
-Absorb UV light at 270-280 nm
-association with “aromas”
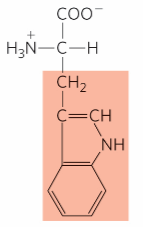
What is this?
Tryptophan
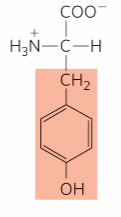
What is this?
Tyrosine
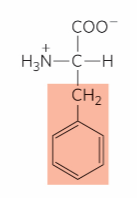
What is this?
Phenylalanine
What are the Polar, Uncharged R Groups?
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine
-CYSTEINE can form Disulfide bonds
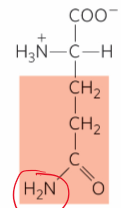
What is this?
Glutamine
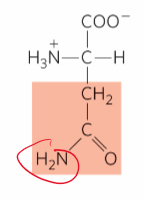
What is this?
Asparagine

What is this?
Cysteine
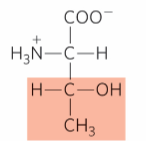
What is this?
Threonine
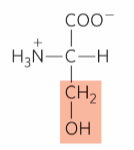
What is this?
Serine
What are the Positively Charged R Groups?
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
-Charge with NITROGEN
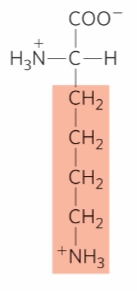
What is this?
Lysine
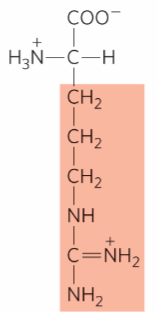
What is this?
Arginine
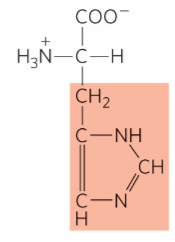
What is this?
Histidine
What are the Negatively Charged R Groups?
Aspartate, Glutamate
-CARBOXYLIC acids on the R group
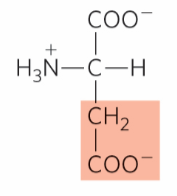
What is this?
Aspartate
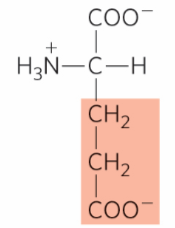
What is this?
Glutamate
What are Bronsted-Lowry acids?
Proton Donors
What are Bronsted-Lowry bases?
Proton acceptors
What is a Zwitterion?
Molecule having separate positive and negative charges at neutral pH
A lower pKa means?
Stronger acid
Higher pKa means?
Stronger base
What is a buffer?
Resist changes in pH
Critical for overall biological function
What do buffers consist of?
weak acid (HA) and conjugate base (A-)
weak base (B) and its conjugate acid (BH+)
What is the Ka equation?
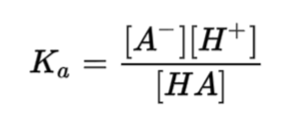
What is a Titration?
Analytical chemistry technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution
What is the isoelectric point?
pH which the net electric charge of a molecule is zero
What is the equivalence point?
amount of added titrant is stoichiometrically equivalent to the amount of analyte in the solution
Are Amino acids natural buffers?
Yes
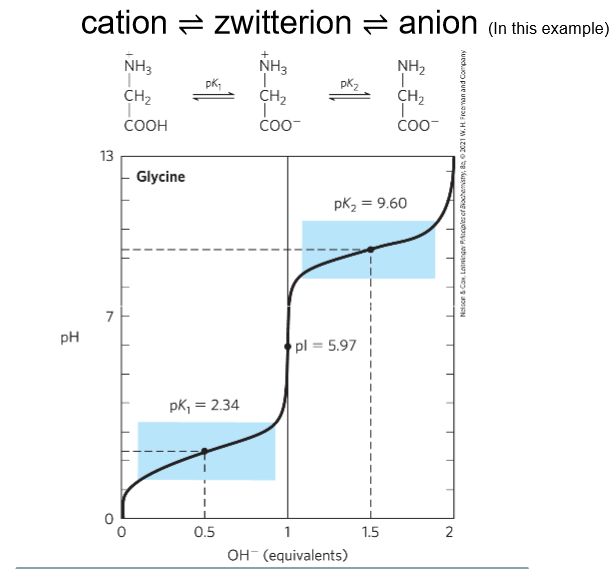
What does a titration curve for Amino acids look like?
Cation—-Zwitterion—-Anion
What can happen with an imbalance in tear film pH?
Dry eye syndrome and other disorders
DES is a degenerative disease of inflammation, cell damage, and biochemical imbalance
What make up Peptide bonds?
Amide linkages
What are characteristics of Peptide bonds?
Covalent bonds
Formed through condensation reactions
Broken through hydrolysis reactions
What are the 3 dihedral angles with peptide conformations?
phi= C-N, free rotation
psi= C-CO, free rotation
omega= CO-N, no rotation
What are Lipoproteins?
Contain lipids
What are Glycoproteins?
Contain sugars
What are Metalloproteins?
Contain metals
What is Taurine?
Non-proteinogenic AA
Helpful for degenerative retinal diseases
What is Glutatione?
Tripeptide antioxidant
Protecting the lens from oxidative damage that leads to cataract formation