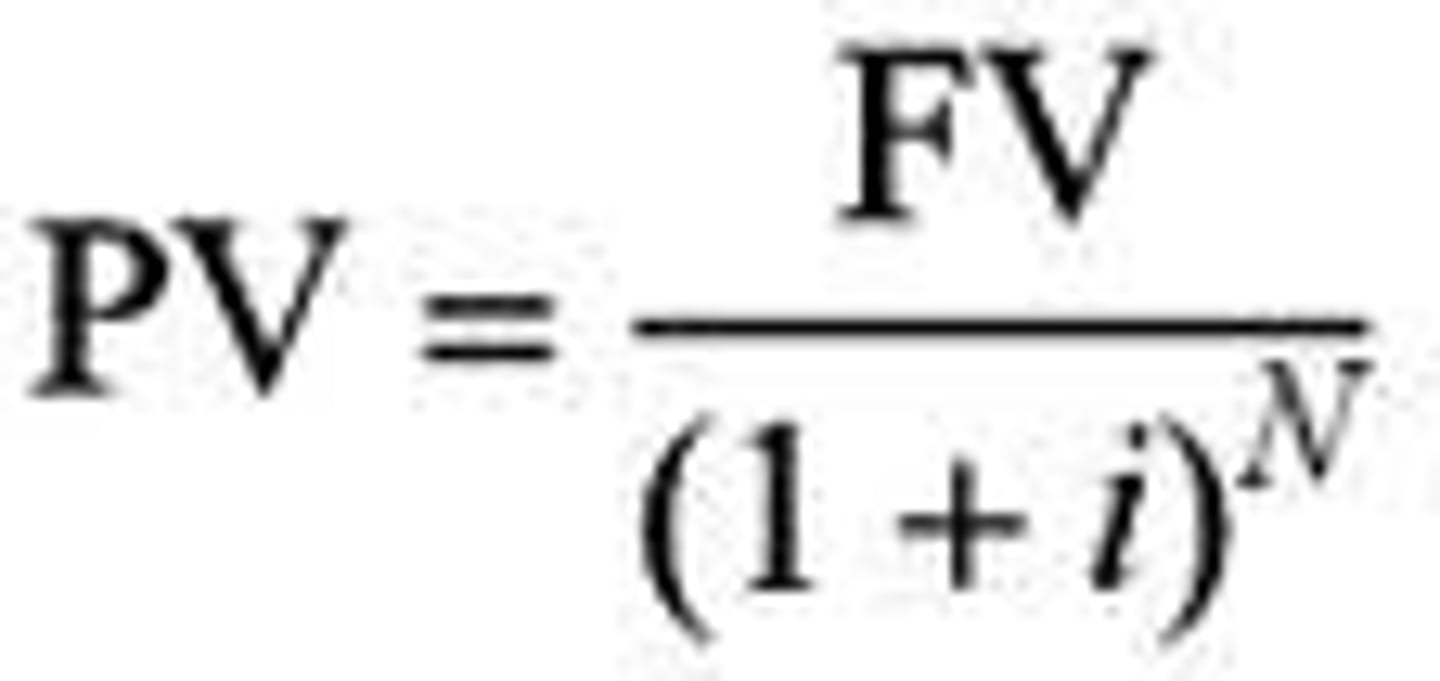ECO2023 FSU Hammock Final Exam
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Scarcity
Stuff is limited.
Choice
One alternative is selected over another.
Opportunity Cost
The value of the best thing given up.
Positive economics
The way the world is
Normative economics
The way the world ought to be
Benefits of trade
- Increased variety of goods
- Increased competition
- Technology transfer
- More efficient large-scale production
Production Possibility Curve
A curve depicting all maximum output possibilities for two goods, given a set of inputs consisting of resources and other factors. The PFF assumes that all inputs are used efficiently.
The Law of Comparative Advantage
An economic law referring to the ability of any given economic actor to produce goods and services at a lower opportunity cost than other economic actors.
Terms of Trade
Refers to the relative price of imports in terms of exports and is defined as the ratio of export prices to import prices. It can be interpreted as the amount of import goods an economy can purchase per unit of export goods.
Law of Demand
As prices rise, quantity demanded falls; negative relationship.
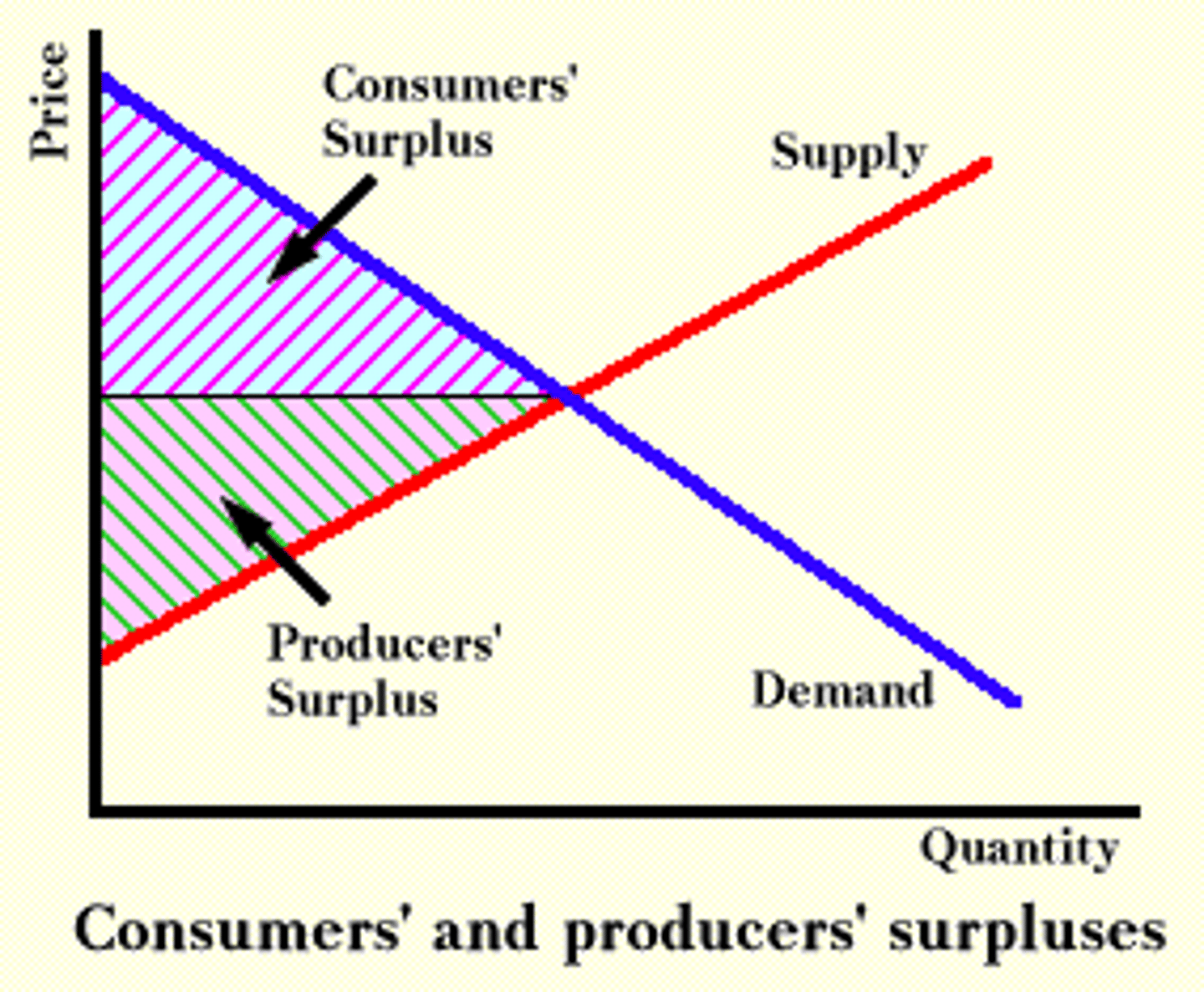
Consumer surplus
The difference between what a consumer is willing to pay, and what the consumer actually pays.
Normal goods.
As income rises, demand for these goes up.
Inferior goods
As income rises, demand for these down down.
Producer surplus
The difference between the price at which a good is sold and its marginal cost.
Substitutes
Goods that can serve as replacements for one another; when the price of one increases, demand for the other increases.
Complements
Two goods for which an increase in the price of one leased to a decrease in the demand for the other and vice versa.
Law of supply
As prices rises, quantity supplied rises; direct relationship.
Equilibrium
The point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.
- Price above equilibrium price = surplus
- Price below equilibrium price = shortage
When we say equilibrium is efficient, we mean that:
- Total surplus is maximized
- Marginal benefits = marginal cost
- Every unit that is produced has a benefit to consumers that is greater than (or equal to) the cost of its production.
Shortage
Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied.
Surplus
Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded.
Arc-Own Price Elasticity of Demand
e>0, goods are substitutes
e=0, goods are unrelated
e<0, goods are complements
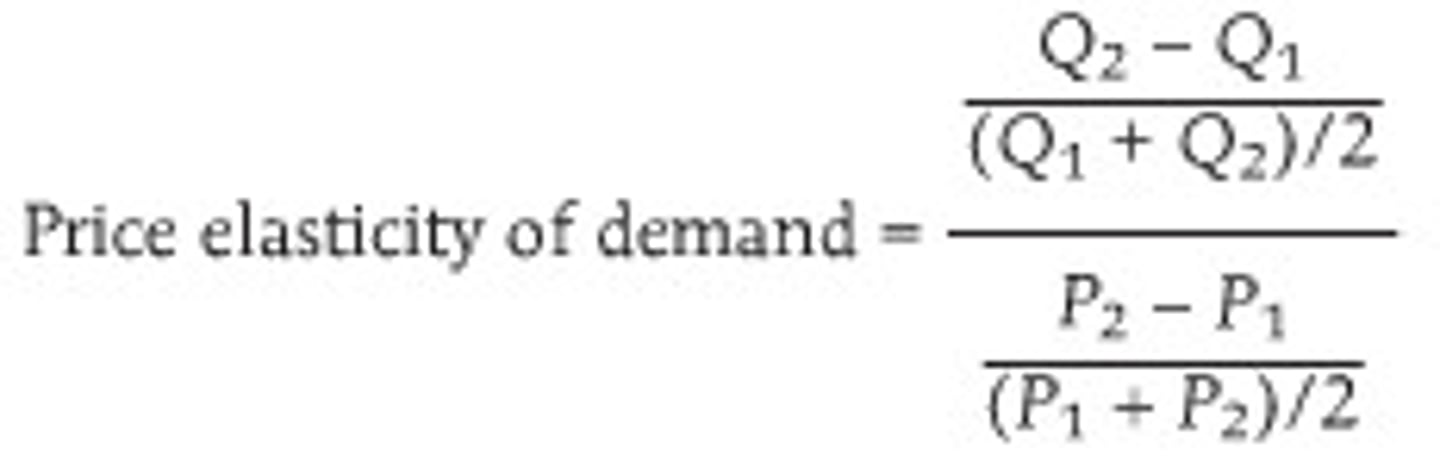
Arc Income Elasticity of Demand
e>0, the good is normal
e=0, income has no effect
e<0, the good is inferior
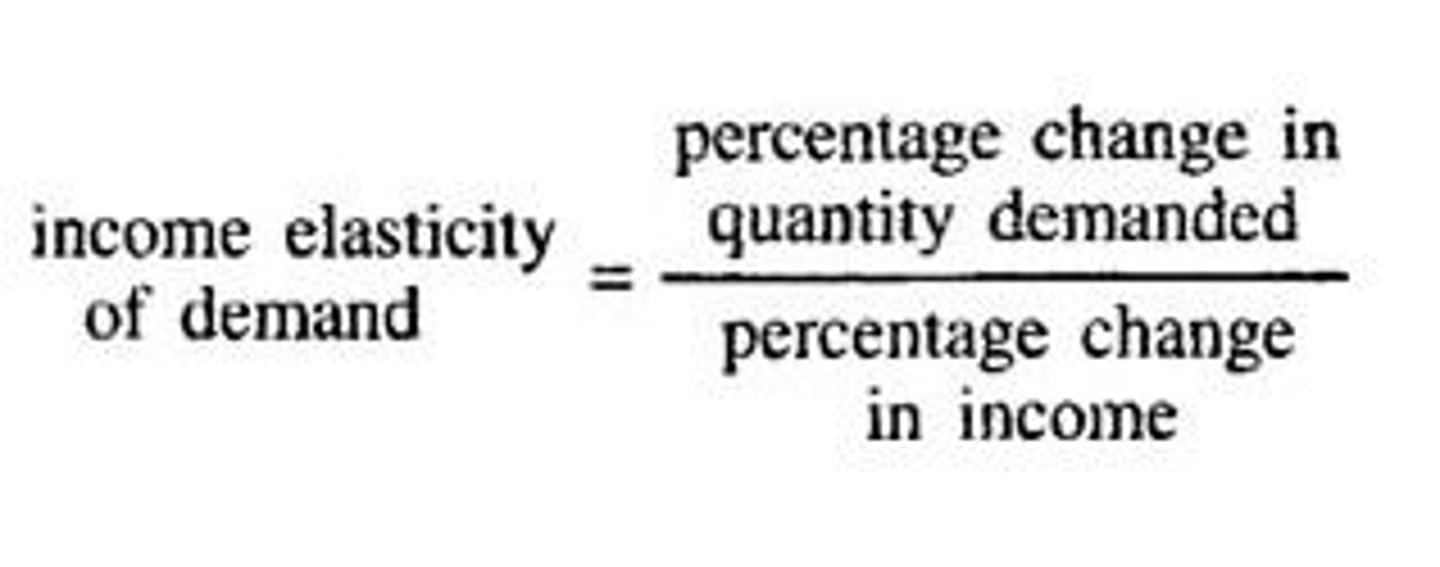
Price Elasticity of Supply
e>1, supply is elastic
e=1, supply is unit elastic
e<1, supply is inelastic
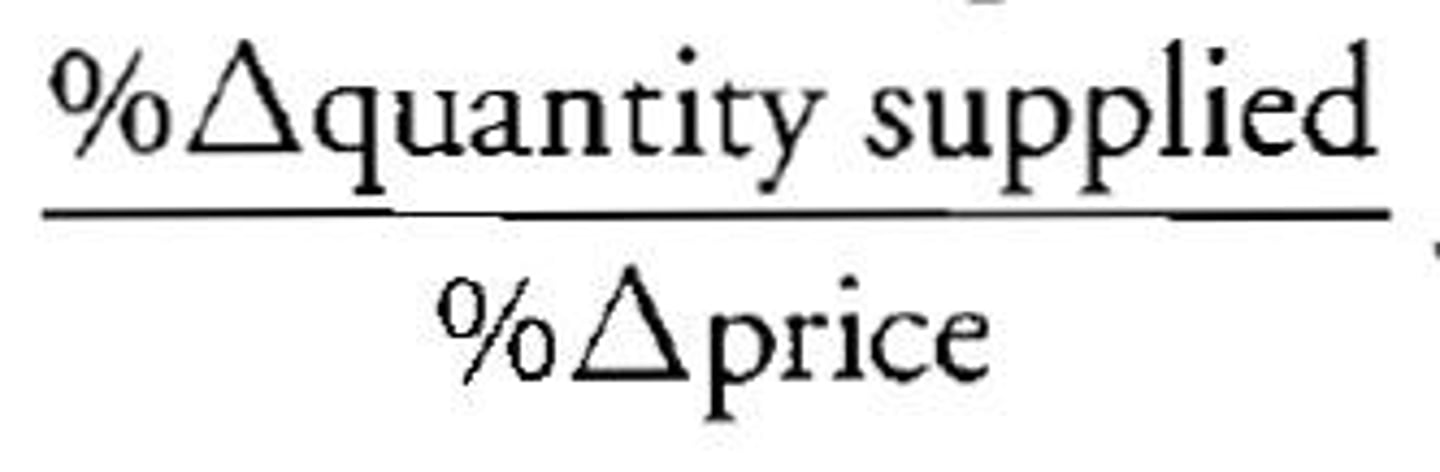
Marginal Product
Change in Output/Change in Labor Input
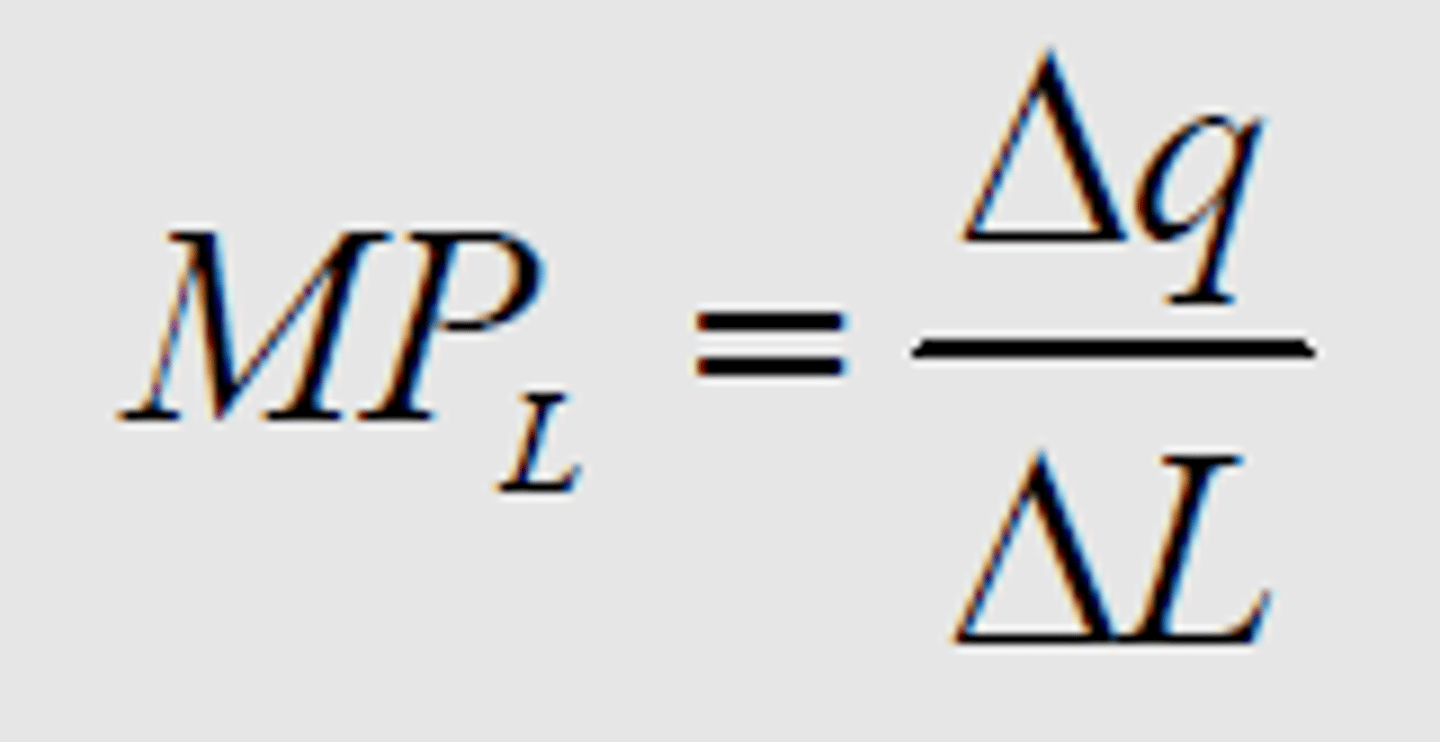
Marginal Cost
Marginal Cost = Marginal Variable Cost
- When MC
- MC
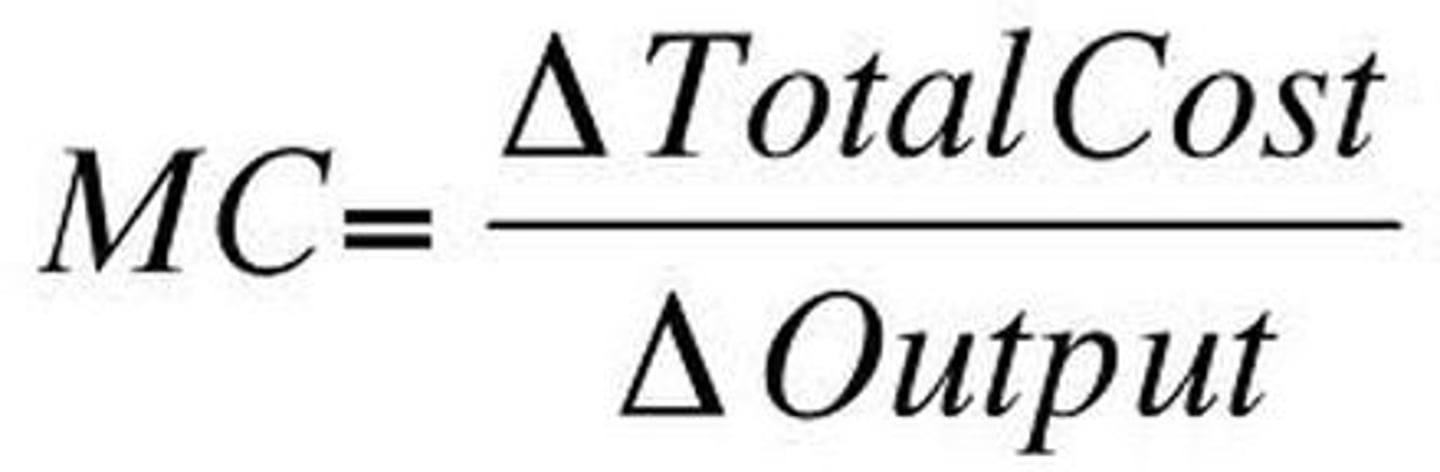
Average Variable Cost
Variable Cost / Quantity
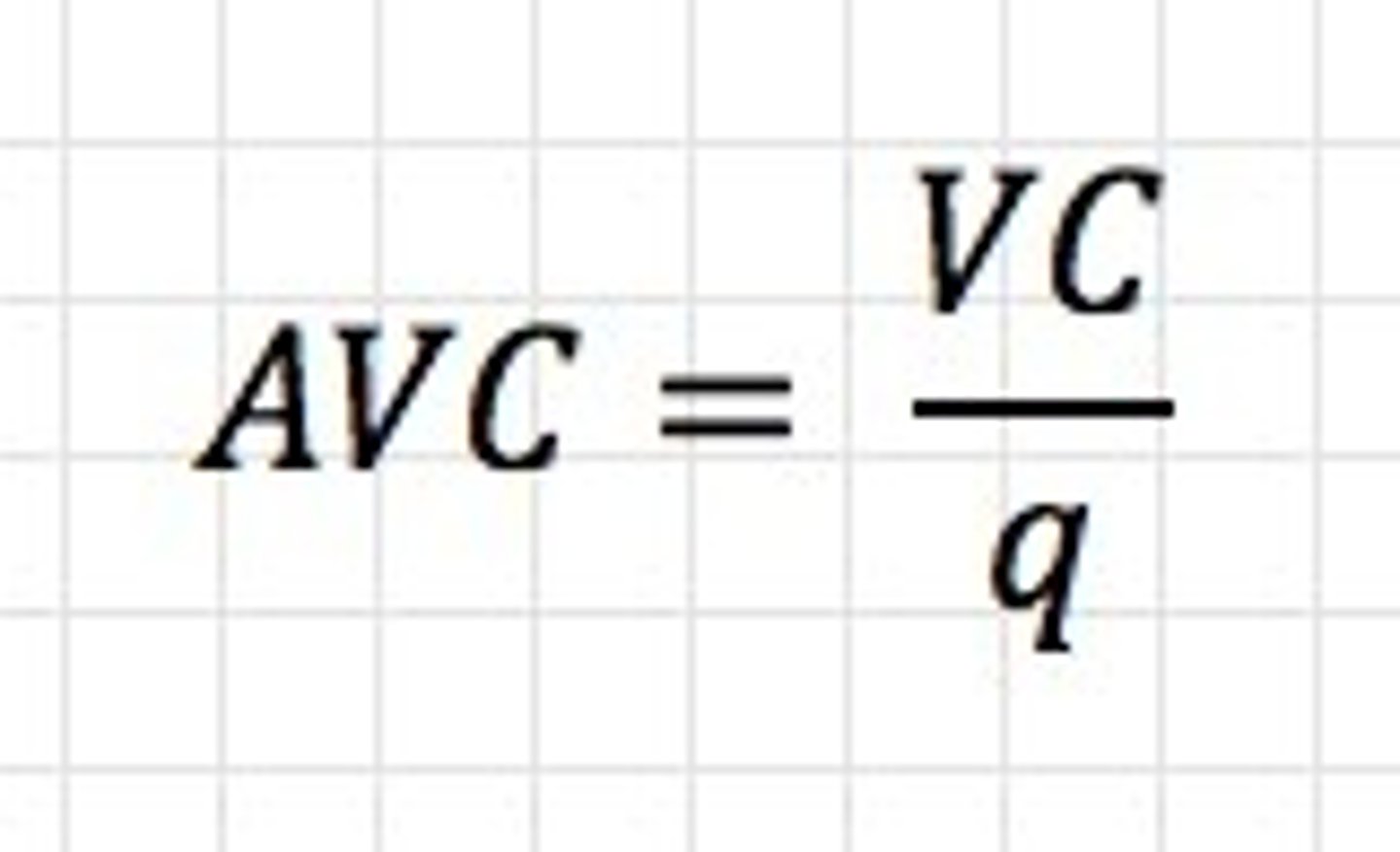
Average Fixed Cost
Fixed Cost / Quantity
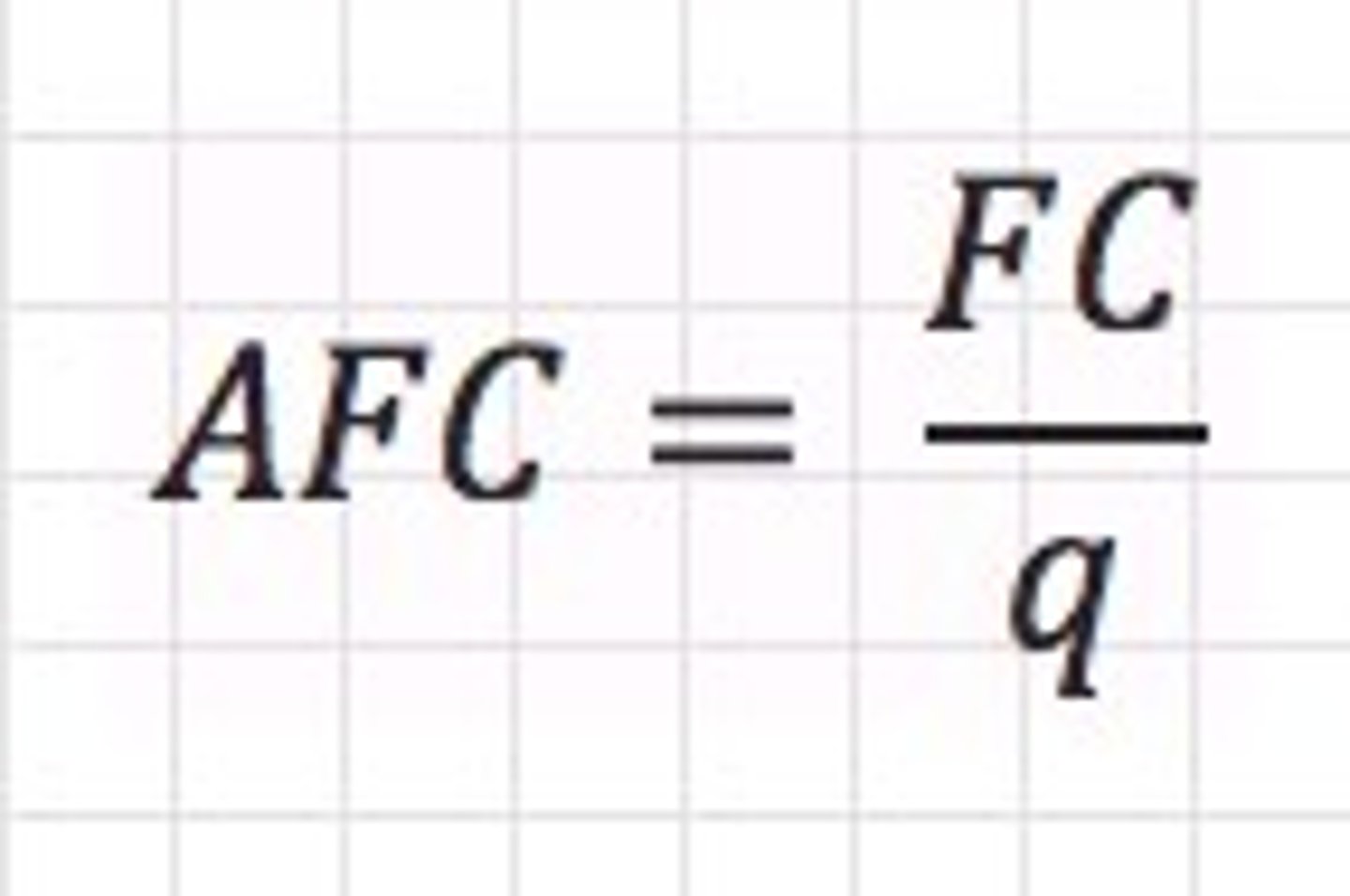
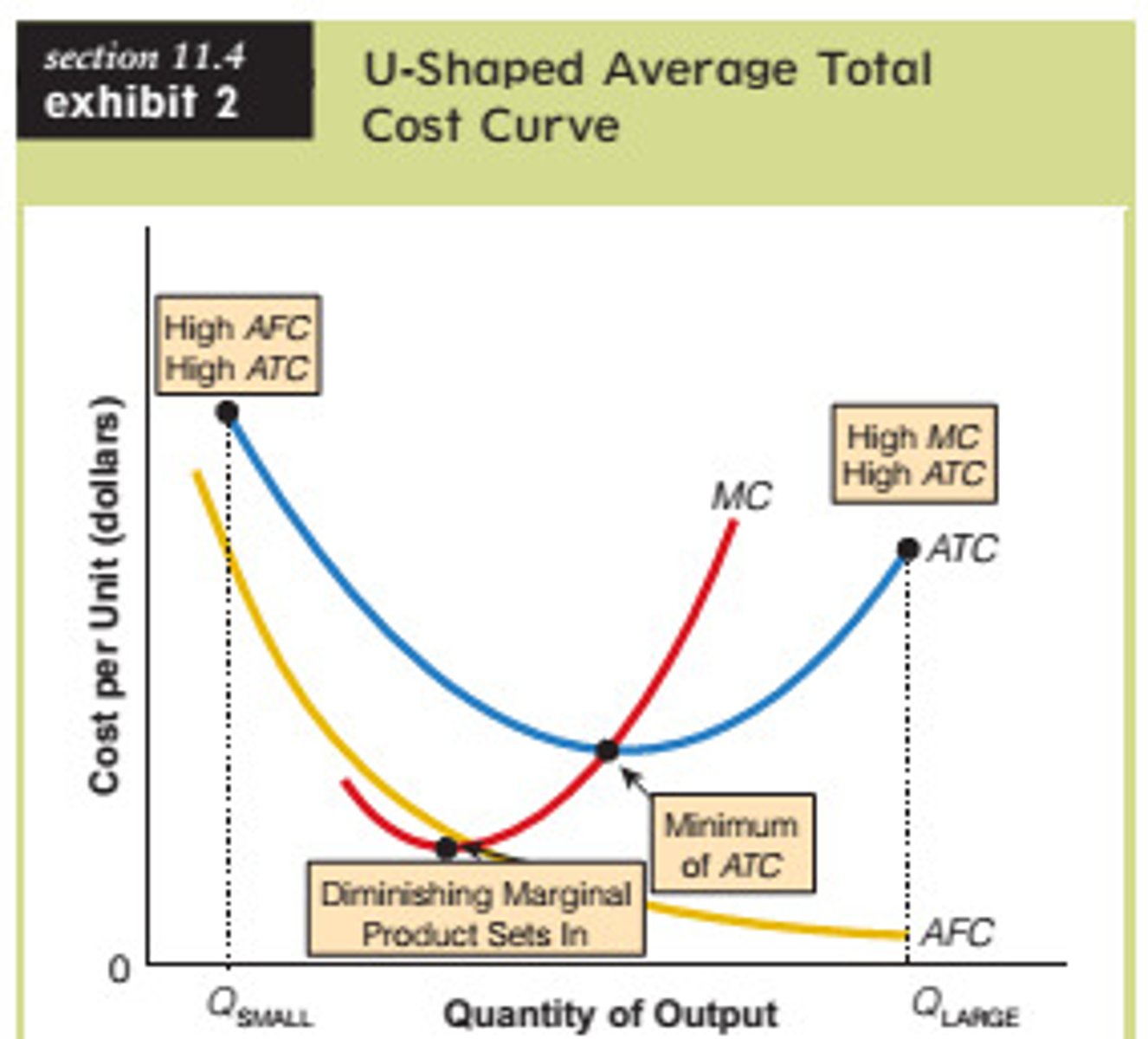
Average Total Cost
Total Cost / Quantity
Marginal Revenue
The additional revenue that a firm takes in when it increases output by one additional unit.
MR=change in total revenue / change in output (q)
Tragedy of the Commons
An economic problem in which every individual tried to reap the greatest benefit from a given resource. As the demand for the resource overwhelms the supply, every individual who consumes an additional unity directly harms others who can no longer enjoy the benefits.
Tragedy of the anti-commons
Covers any setting in which too many people can block each other from creating or using a valuable resource.
Elasticity of Supply
Supply is more elastic in the long rung than in the short run.
Market Failure
When individuals pursing their rational self interests result in an outcome that is inefficient.
Public Goods
Nonrivalrous: my consumption doesn't reduce your consumption.
Nonexcludable: not possible to exclude those who don't pay.
Public Interest View
A democratic government acts in such a way as to make it citizens better off; it effectively takes their preferences and translates them into beneficial policy action.
Public Choice View
Governments are made up of rationally self-interested individuals, operating within a system of rules. Their actions are determined by their preferences and the incentives created by the system of rules.
Labor Markets
The equilibrium wage rate in the industry is set by the meeting point of the industry supply and industry demand curves. In a competitive market, firms are wage takers because if they set lower wages, workers, would not accept the wage.
Compensating differentials
The additional amount of income that a given worker must be offered in order to motivate them to accept a given undesirable job, relative to other jobs that worker could perform.
Productivity and Wages
When workers become more productive, the demand for their labor rises, therefore, their wage rises.
This is caused by :
1. Increases in human capital
2. Increases in physical capital
3. Improvements in technology
The rate of time preference
Is usually taken as a parameter in an individual's utility function which captures the tradeoff between consumption today and consumption in the future, and is thus exogenous and subjective. It is also the underlying determinant of the real rate of interest.
How Interest rates are determined.
They are determined by three forces. The first is the Federal Reserve, which sets the Fed funds rate. That affects short-term and variable interest rates. The Second is investor demand for U.S. Treasury notes and bonds. That affects long-term and fixed interest rates. The third force is the banking industry. They offer loans and mortgages that can change interest rates depending on business needs.
Present and future value:
r = the interest rate
t = the number of periods that interest compounds
Use Net Present Value to make decision across time.
Future Value = Present Value (1 + r)^t