General Terms/Concepts
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering basic principles of kinesiology and gait for exam review.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Kinematics
Branch of biomechanics that describes the motion of the body without regard to the forces that produce the motion.
Translation
When all parts of a “body” move in the same direction as every other part. (Straight line)
Rotation
Describes the arc of movement of a “body” about an axis of rotation. (Around a pivot point)
Origin
The PROXIMAL attachment of a muscle or ligament
Insertion
The DISTAL attachment of a muscle or ligament
Prone
Describes the position of an individual lying face down
Supine
Describes the position of an individual lying face up
Axis of Rotation
The pivot point about which joint motion occurs (always PERPENDICULAR to the plane of motion).
Degrees of Freedom
The numbers of planes of motion allowed in a joint.
Osteokinematics
The path of moving bones
Open-chain motion
Movement of distal segment of bone about a relatively fixed proximal segment
Closed-chain motion
Movement of a proximal segment of bone about a relatively fixed, or stationary, distal segment
Arthrokinematics
Movement that occurs between articular surfaces of joints (roll, slide and spin)
ConVEX on concave
roll/slide in OPPOSITE direction
ConCAVE on convex
roll/slide in SAME direction
Kinetics
Branch of mechanics that describes the effect of forces on the body.
Torque
The rotational equivalent of force. Amount generated depends on: amount of force exerted, distance between the force and the axis of rotation
Line of Pull
The direction of muscular force, typically described as a vector (direction and magnitude of force included)
Anterior-posterior axis
lateral/medial line of pull (LOP)
ex: abduction (lateral LOP), adduction (medial LOP)
Medial-lateral axis
anterior/posterior line of pull (LOP)
ex: elbow flexion (anterior LOP), elbow extension (posterior LOP)
Resultant Force
The result of combining individual force vectors
Gait Cycle Percentages
40% swing
60% stance
STANDING MOST OF CYCLE
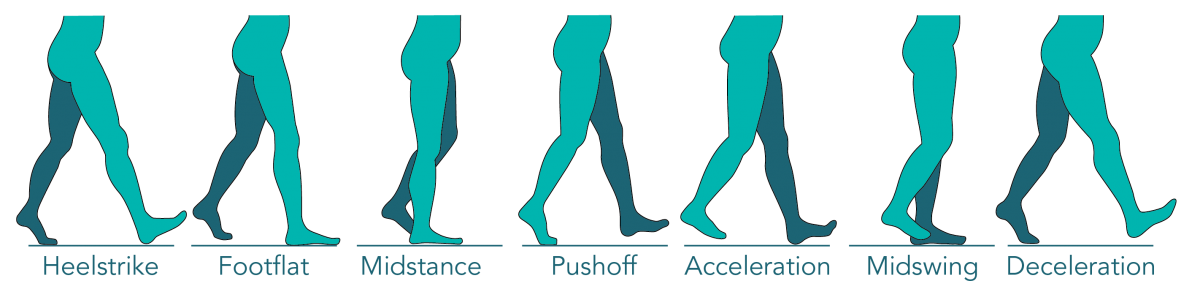
Gait Cycle Order
Heel Contact – Foot Flat – Mid Stance – Heel Off / Toe Off – Early Swing – Mid Swing – Late Swing - Heel Contact
Passive ROM
ROM achieved without expending energy/activating muscles (done for you)
PT doing manual therapy on you
Active ROM
ROM you can achieve yourself using your muscles, without assistance
Intra-articular
Inside a joint
Extra-articular
Outside a joint
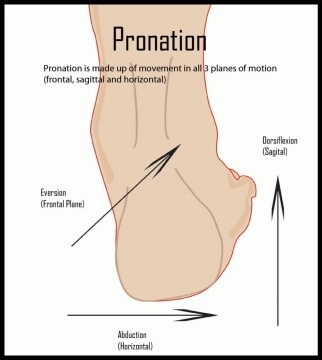
Pronation
Dynamic movement of the foot that includes dorsiflexion, eversion, and abduction
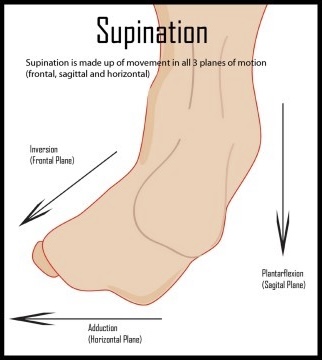
Supination
Hands: the act of turning the palms of the hands upward (“holding a bowl of soup”).
Ankles: a combination of inversion, adduction, and plantarflexion
Bone is what kind of tissue?
Dynamic. Constantly being remodeled in response to internal and external forces.
Will become stronger from forces caused by weight-bearing activities and muscular contractions, or significantly weaker after joint immobilizations.