Addiction (Week 7)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
DSM-IV requirements:
Must exhibit 3 of the following for the past 12 months
Tolerance
Withdrawl symptoms
Oncreasing doses
Unsuccessful efforts to reduce intake of substance
Considerable amount of time spent obtaining substance/using it
Continuation of use of substance despite recog. phys/psyc issues
How is drug rewards assessed in animals
How motivated/preference to approach drug related stimuli/context
What makes up the mesolimbic dopamine system?
VTA, nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex
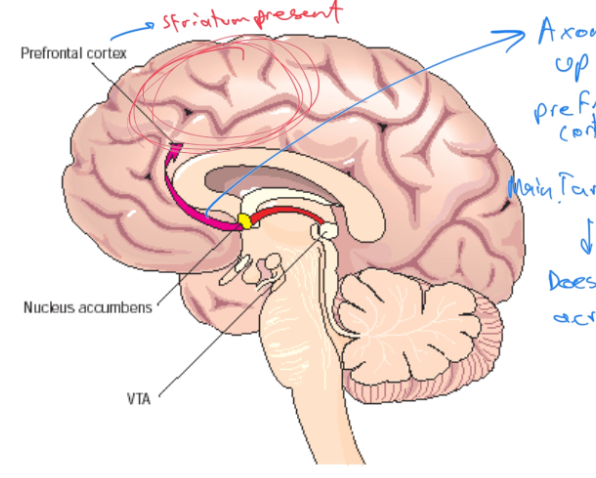
What is the order of the mesolimbic dopamine system
VTA, nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex where the striatum lies
Neurons furthermore disperse it throughout the brain
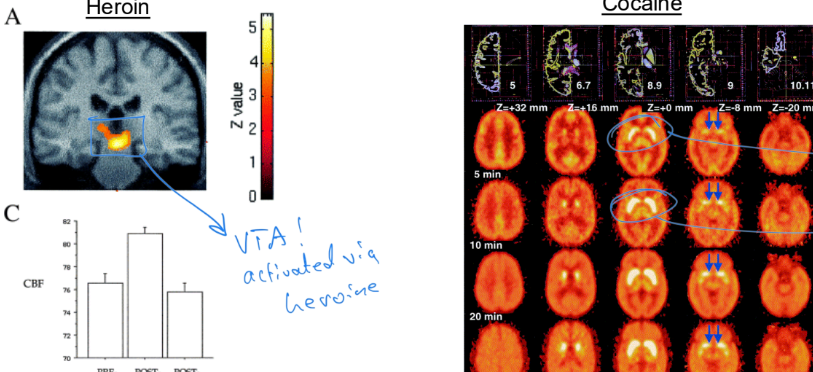
_____ and ____ in the dopamine system are activated when ____ or ____ is used
VTA, striatum; heroin, cocaine
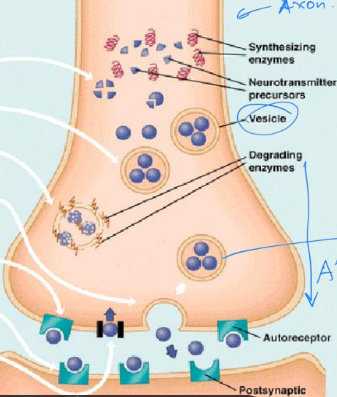
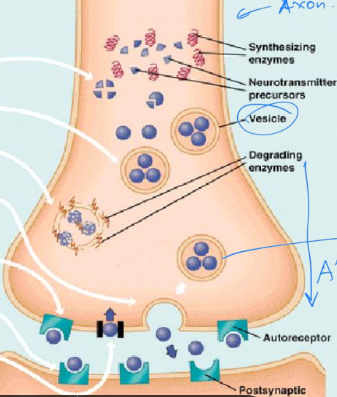
Process of dopaminergic neurotransmission
Tyrosine (amino acid) —> Tyrosine hydroxylase (enz) —> L-DOPA —> DOPA decarboxylase (enz) —> dopamine
What does AP do in dopaminergic neurotransmission
Causes vesicles to fuse & release dop. into synapse
D1 Vs D2 receptors
D1 = Increased cAMP (releases dopamine for reward)
D2 = Decreased cAMP (inhibitory dop)
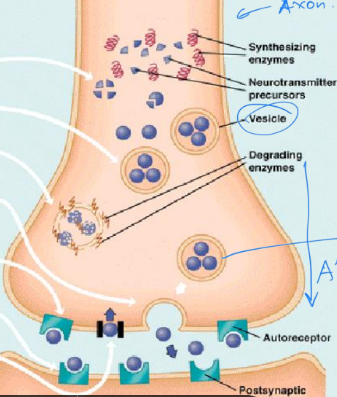
What mechanisms contribute to stop dopamine release
Re-uptake pump = removes from synaptic cleft
MAO enzymes = deactivate dop. within vesicles
D2 = cAMP decrease
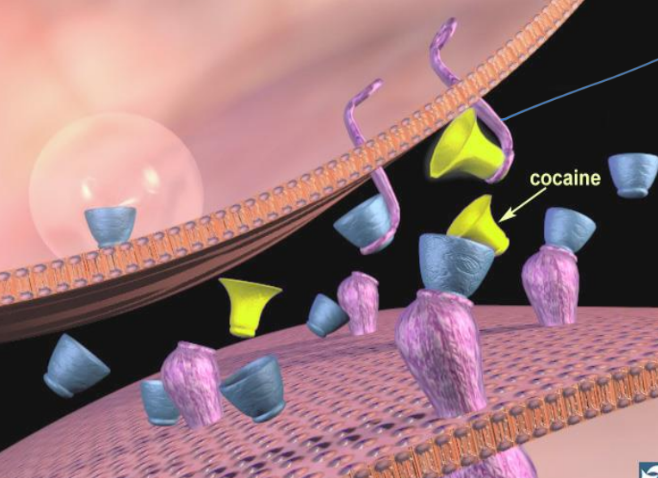
Cocaine’s effect
Prevent’s reuptake of dopamine —> binds to reuptake pumps
Stay within cleft & continue binding w. dopamine
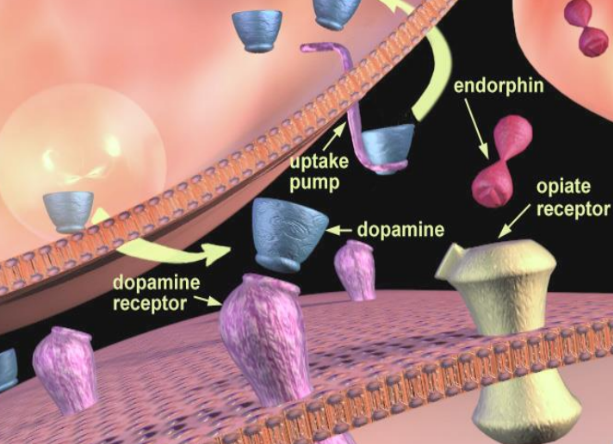
Opioid’s effect
Prevent detection of dop. lvls
Prevent inhibition (can’t detect for homeostasis)
Dop. continues firing
Olds & Milner’s theory of addiction
For pleasure
Dop usually released from normal needs (ie food/sex)
“Hijacks” reward dop system

What brain bundle was activated in Olds & Milner’s study?
Medial forebrain bundle (VTA & hypothalamus)
Alternative theory of addiction?
Incentive sensitisation
Drugs enhance transmission within mesolimbic dop. pathway
Increase SALIENCE
ie. sign tracking, craving specific PIT
NB: NOT JUST DRUGS ITS APPLICABLE TOO 😋
What is sensitisation related to?
Associative learning —> attribute incentive value to drug
Advantages of incentive sensitisation
Consistent with role of cravings
Not only applicable to drugs
Limitations of incentive sensitisation
Lack of clinical evidence
DIFFICULTY DISTINGUISHING WANTING & LIKING
Opponent Process Model?
A process (drug) & B process (aversive/withdrawl/homeostasis)
B strengthened & longer w. use, weakened w. disuse
Altering motivation of taking a drug in opponent process models
1st = Positive Affect & tolerance
2nd = withdrawl alleviation
Advantages of opponent process model
Meet DSM criteria
Help understand opioid overdose
Disadvantages of opponent process model
Doesn’t explain drug-taking in drugs without withdrawal states (ie. cannabis)
Tolerance is not an inevitable consequence of drug exposure —> could be drug’s efficacy

What is diacetylmorphine?
Heroine to help morphine addiction
Cocaine properties as a “treatment”
Pain receptor numbed
What is Purdue Pharma & issues it causes
Help with morphine addiction 🤡
synthetic prescribed opioid
If get addicted, cannot receive anymore
Lead to dependency of opioid —> illicitly find opioid
Treating opioid addiction
Methadona —> agonist —> slows drug’s effects —> <craving
Treating alcohol use disorders
Naltrexone —> opioid receptor antagonist —> BLUNTS reward of drug (<A process)
What are agonist based pharmacotherapies?
Mimick effects of drugs w.o the cravings
What are antagonist based pharmacotherapies?
BLUNTS reward effects of drug
Does cue-exposure (extinction) work?
NO

What is contingency management
Alternative ways to treating addiction w.o reliance of pharmaceutical drugs
Individual given rewards for negative drug test
Ie. vouchers/allowed to work
Help rebuild their life
Urine collected multiple times a week —> reinforce abstinence
How does social status influence responses to drugs? (Monkeys)
Subordinate = >usage of drug
dominant monkey = used less