acid-base equilibrium
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
universal indicator pH
below 7 is acidic, above 7 is basic and 7 is neutral
neutralisation
reaction of an acid and base to form salt and water
acid
proton or hydrogen ion donor
base
proton or hydrogen ion acceptor
salt
formed when an acid reacts with alkali, metal oxide or metal carbonate
alkalis
bases that are soluble in water
Bronsted lowry acid
proton (H+) donor
Bronsted lowry base
proton (H+) acceptor
amphoteric
ability to act as both acids and bases
forward arrow —>
reaction goes to completion
equilibrium arrow ←—>
reaction doesnt go into completion
degree of dissociation
extent to which a molecule of an acid ionises in a solvent to form H+ ions or a base forms OH- ions
strong acids and bases
dissociate completely in solution
weak acids and bases
partially dissociate in solution
pH values of strong vs weak acids
strong acids have a lower pH in the same concentration due to a higher concentration of H+ ions
electrical conductivity of strong vs weak acids
strong acids have great conductivity due increased concentration of H+ ions
acid-base indicator
compound that shows colour change based on solution being acidic, basic or neutral
strong acids and strong bases
sharp fall in pH
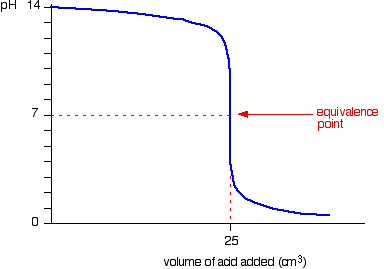
strong acids and weak bases
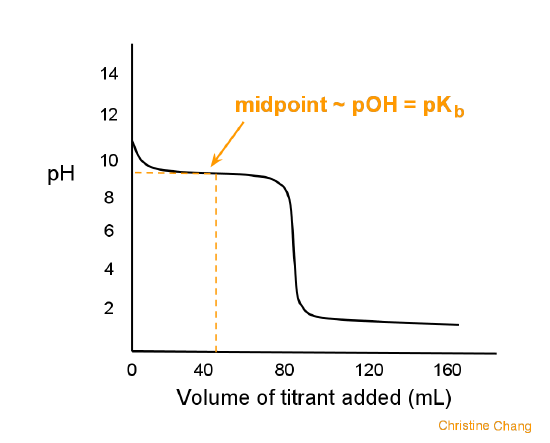
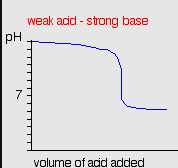
weak acids and strong bases
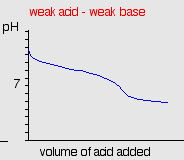
weak acids and bases