L02: Anaerobic Metabolism: Phosphagen System + Glycolysis
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What are energy systems
Biochemical processes that harness energy from fuel substrates to resynthesize ATP.
What does the power of an energy system refer to?
The rate at which it can resynthesize ATP.
What does the capacity of an energy system refer to?
The amount of ATP that it can resynthesize.
What is the phosphagen system known for?
Highest power and lowest capacity among energy systems.
What is anaerobic glycolysis characterized by?
Intermediate power and capacity.
What is aerobic metabolism characterized by?
Lowest power and highest capacity.
What is a universal rule of biochemistry regarding energy?
Energy is conserved but can be transformed.
What happens to usable energy during transformations?
Some usable energy is always lost, usually as heat.
What is an enzyme?
A molecule (usually a protein) that catalyzes (speeds up) a biochemical reaction.
What is the significance of enzyme concentration?
Higher enzyme concentration can lead to faster reactions and quicker ATP supply.
What is the primary pathway for strength and power activities?
The phosphagen system, also known as the ATP-PCr system.
What is phosphocreatine (PCr)?
A high-energy molecule used in the phosphagen system to resynthesize ATP.
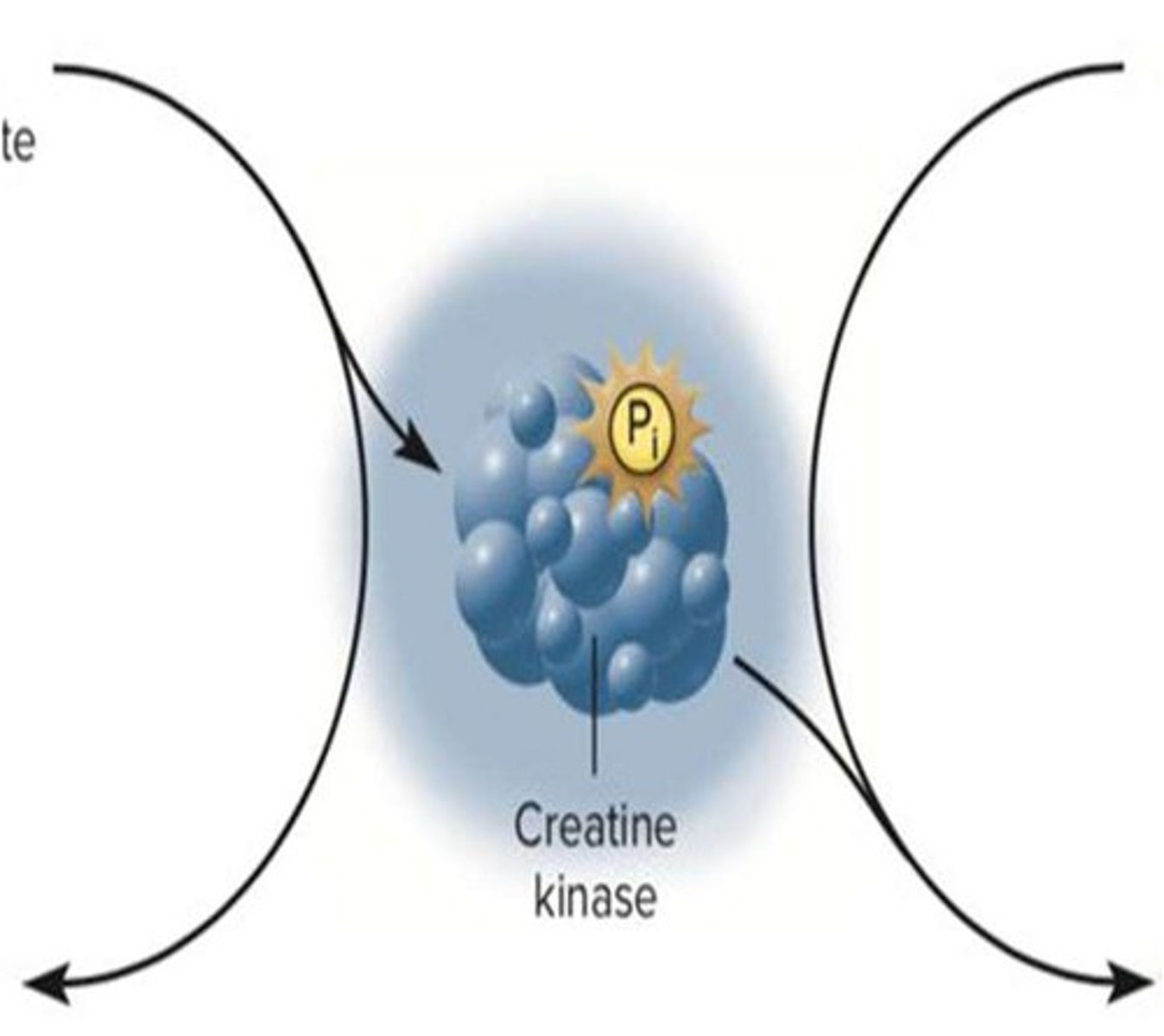
What is the creatine kinase reaction?
The reaction where PCr and ADP are converted to ATP and Cr.
What type of pathway is the phosphagen system?
Anaerobic pathway.
What is the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and reactant concentration?
The rate is proportional to the concentration of reactants.
What happens to PCr during the creatine kinase reaction?
PCr is broken down, transferring Pi to ADP to create ATP.
What is the effect of body temperature on ATP resynthesis?
A slight increase in body temperature can increase the rate of ATP resynthesis.
How can intramuscular PCr stores be increased?
By supplementation, which can increase stores by 10-40%.
What is the role of aerobic metabolism in relation to the phosphagen system?
Aerobic metabolism is necessary to replenish PCr stores after exercise.
What is the relationship between the complexity of a process and the power of an energy system?
Higher power is associated with simpler processes.
What is the outcome of the creatine kinase reaction in terms of energy?
Energy is released from PCr, some of which is used to resynthesize ATP.
What is the primary function of the phosphagen system?
To supply ATP rapidly for muscular power and explosiveness.
How does the phosphagen system relate to athletic performance?
It is crucial for activities like jumping, throwing, kicking, and sprinting where peak velocity matters.
What is the impact of increased capacity of the phosphagen system?
It allows for sustained high power output during anaerobic endurance activities.
What factors influence the effectiveness of phosphocreatine (PCr) supplementation?
Individual response, kidney health, pregnancy, lactation, and age considerations.
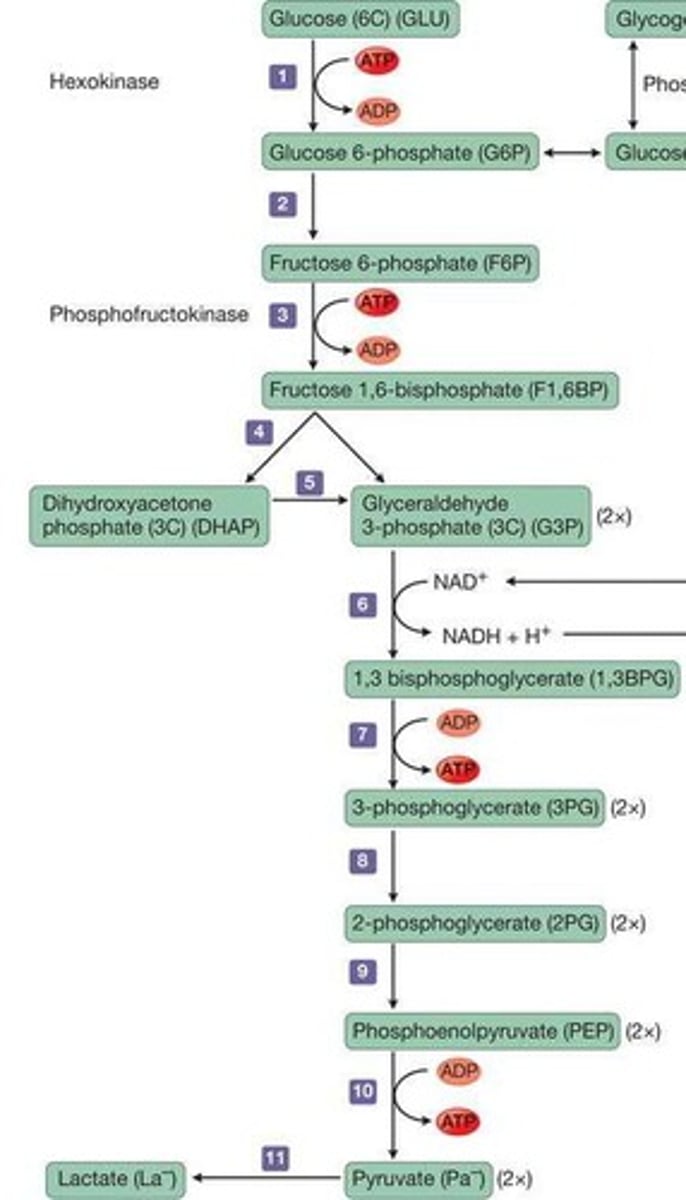
What is glycolysis?
The metabolic process of breaking down glucose into two pyruvate molecules, releasing energy to resynthesize ATP.
What is the net ATP yield from glycolysis per glucose molecule?
2 ATP.
What is the chemical formula for glucose?
C6H12O6.

How does glucose enter cells?
In response to insulin signaling.
What are the two phases of glycolysis?
Investment phase (costs 2 ATP) and Pay-off phase (produces 4 ATP).
What role does NAD+ play in glycolysis?
It acts as an electron carrier, helping to produce NADH from intermediates.
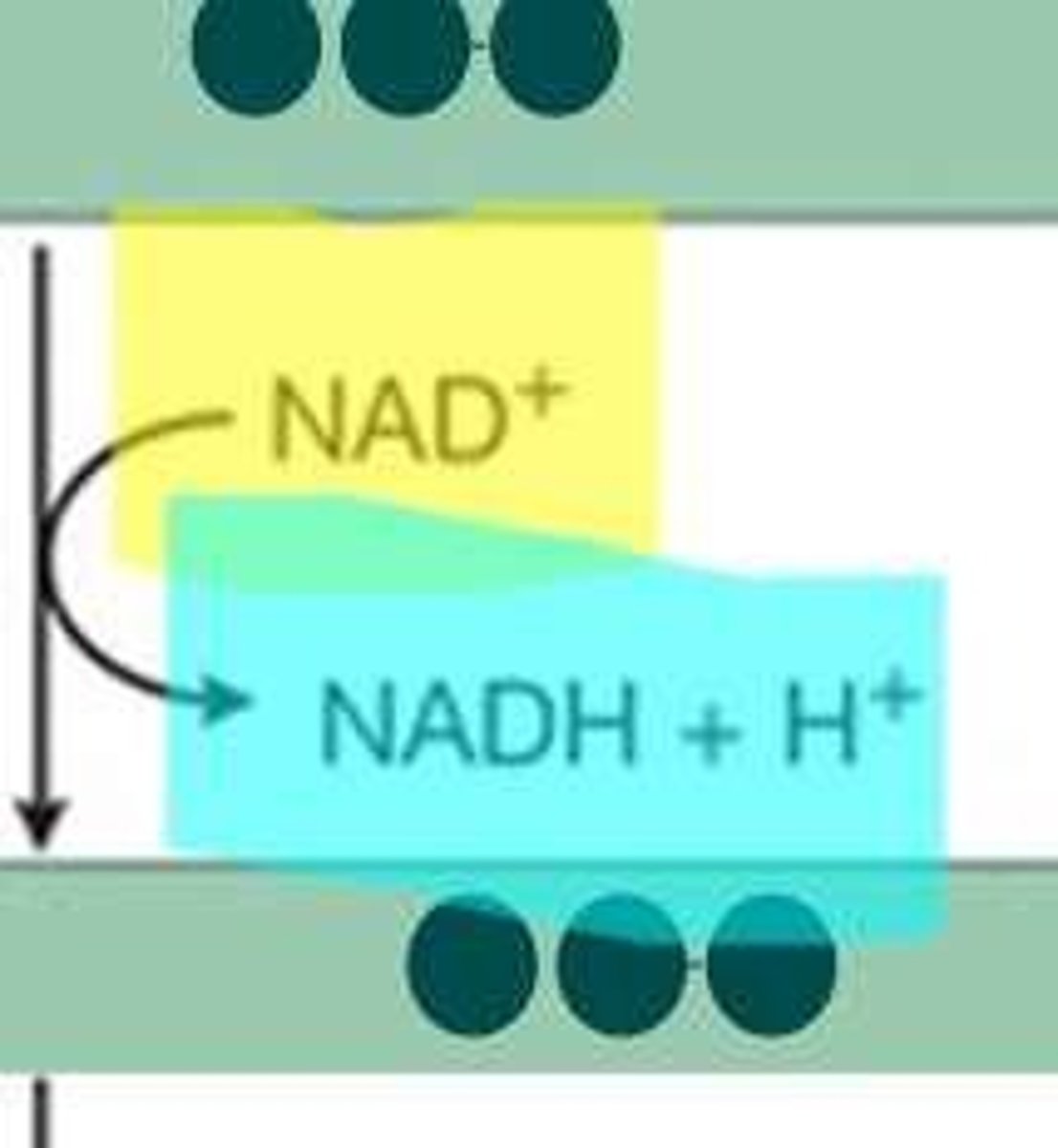
What happens to pyruvate and NADH after glycolysis?
They can be utilized in aerobic metabolism.
What happens to H+ accumulation during glycolysis?
It can lead to decreased pH, slowing down glycolysis and ATP resynthesis.
What is the significance of phosphofructokinase (PFK) in glycolysis?
It is a rate-limiting enzyme that controls the speed of glycolysis.
What factors can deplete glycogen stores in the body?
Fasting, inadequate nutrition, disease, and prior exercise.
What is the relationship between ATP demand and glycolysis speed?
Higher ATP demand increases the speed of glycolysis.
What is the maximum storage limit of PCr in muscles?
160 mmol/kg.
What happens if muscle PCr levels are at the maximum storage limit?
Supplementation will not provide additional benefits.
What is the consequence of self-inflicted acidosis during high-intensity exercise?
It slows down glycolysis and ATP resynthesis, limiting performance.
What is the primary purpose of glycolysis in energy metabolism?
To convert glucose into pyruvate while harnessing energy to produce ATP.
What does the term 'catabolic' mean in the context of glycolysis?
It refers to the breakdown of molecules to release energy.
What is the significance of intermediates in glycolysis?
They are molecules formed during the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, each involved in different reactions.
How does the body replenish low blood glucose levels?
By eating/drinking or breaking down glycogen stored in the liver.
What happens to energy during glycolysis?
Some energy is used to make ATP, some is stored in NADH, and some is lost as heat.
What is the effect of increased H+ concentration on enzyme activity?
It decreases enzyme activity, including that of PFK, slowing glycolysis.