Pitot, Static, failures, VG Diagrams, ANDS, UNOS, Vacuum,
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flight Controls
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
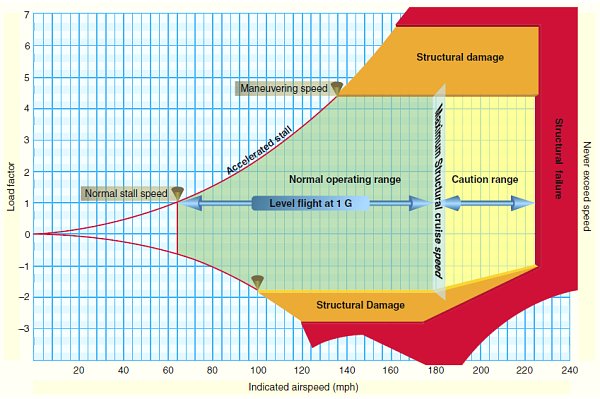
Vg
Velocity versus G loads of load factors
What Koleman uses Pitot and Static
Airspeed indicator
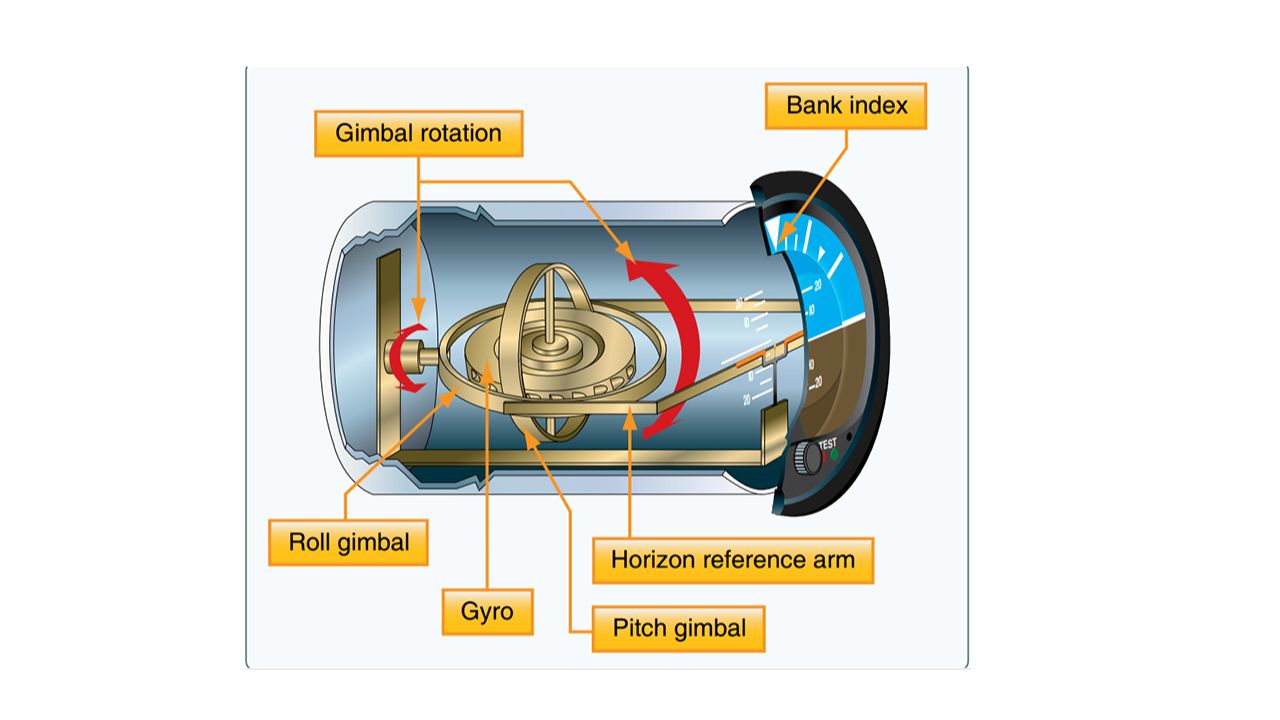
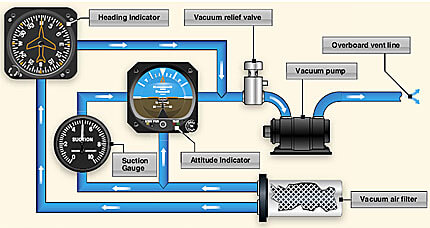
What Koleman uses vacuum/gyro
Attitude indicator, heading indicator,
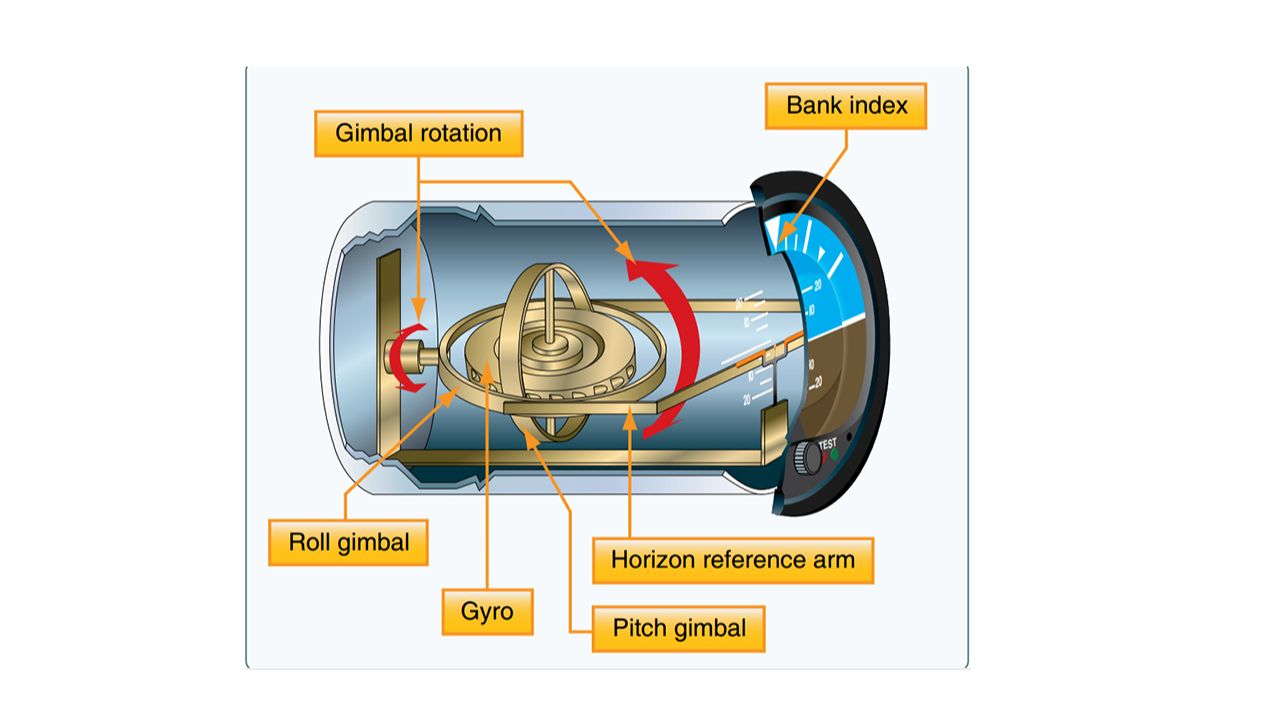
How does a gyro work?
Spends based on the perpendicular force
Which Koleman using electricity/gyro
Turn coordinator
which kolseman uses static
Altimeter and Vertical Speed indicator
Pitot tube
reads the Ram pressure which is a combination of Dynamic and Static pressure
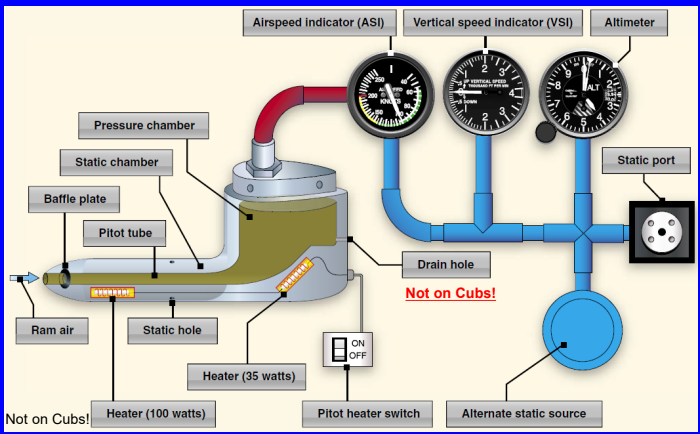
Static Ports
ambient/ sense atmospheric pressure
white arc on airspeed indicator means
flaps operating rang
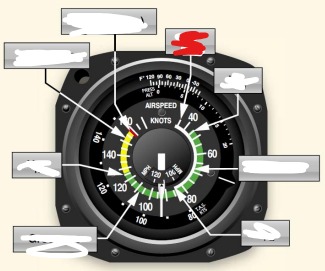
Vs0 (out) power off stalling speed with gear and full flaps extended begins at white arc
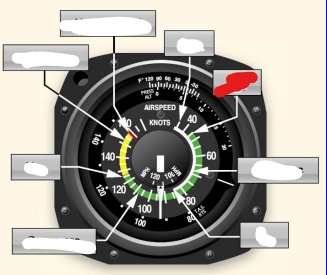
Vs1 (inside) -Stall speed or minimum steady flight speed for which the aircraft is still controllable in a specific configuration. cannot sustain level flight with flaps and landing gear retracted. Used under ideal conditions excluding icing or equipment malfunction before a stall
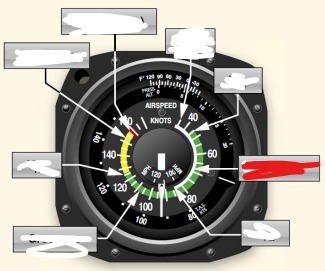
white arc - flaps may only be used in this speed
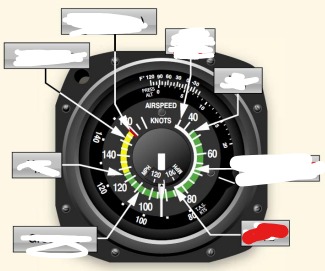
Vfe (flaps extended) -maximum flap extended speed. Do not use flaps above this range.
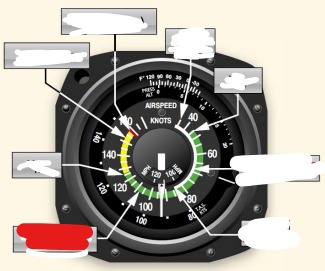
Green arc - normal operating airspeed range
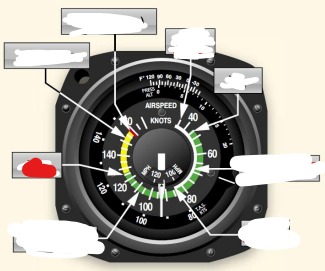
Vno (normal operations)- maximum structural cruise speed. do not exceed except in smooth air
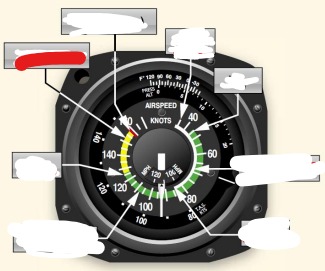
Yellow arc - caution range, only fly in smooth air
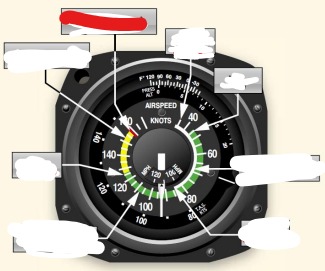
Red line Vne (never exceed speed) - results in structural failure
True altitude
height above (means) sea level
Absolute altitude
height above ground
How to determine blocked pitot tube
ram air (this is the pressure exerted by the air as it is forced into the pitot tube due to the aircraft's forward motion. It's a combination of static pressure and dynamic pressure.) is no longer able to enter therefore ASI decreases to zero because pitot can no longer establish difference between ram and static air.
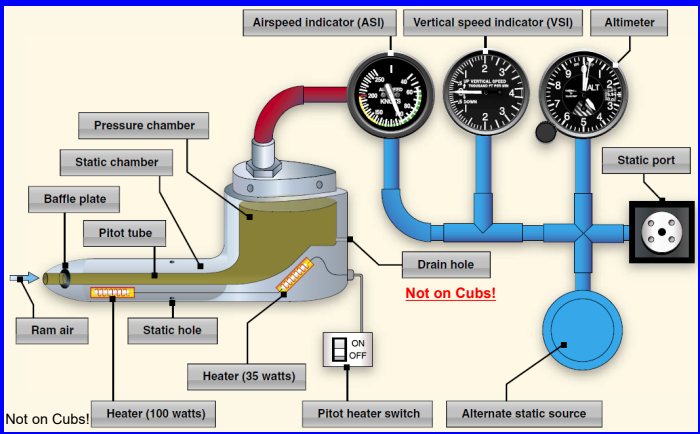
What to do if your pitot tube is blocked?
Turn on pitot heat to defrost ice.
Turn on alternate static port. Reads the pressure in the cabin.
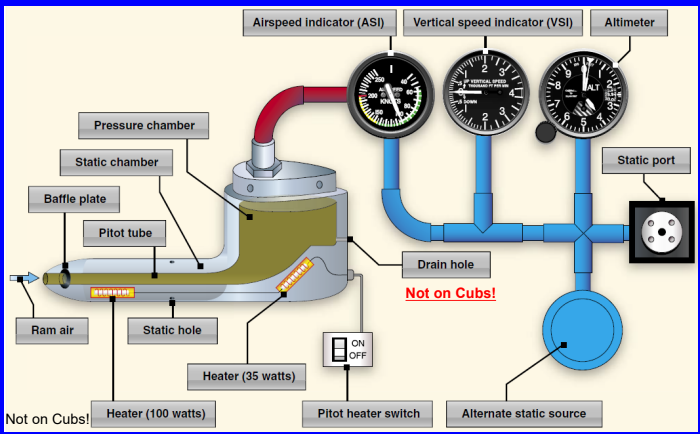
How to determine if the static line is blocked and what to do if that happens?
VSI shoes no rate of change. Static air is trapped and uses the value of the trapped air
Turn on alternate static port.
When should you test your ELT (emergency locator transmitter)
first five minutes after each hour
When do you recharge or change ELT battery
after half its use you recharge it and after one cumulative hour you get it replaced
ARROW
Air worthiness certificate (inspected safe to fly)
Registration (One for who it’s registered under and another that it’s registered in the state)
Radio (radio station licenses) required for international flight
O (Pilot Operating Handbook PHO)
W (Weight and balance)
Va represents
(Velocity of acceleration) maneuvering speed below Vno pilots should be in this speed during turbulence
If an altimeter setting is not available before
flight, to which altitude should the pilot
adjust the altimeter?
The elevation of the departure area.
Prior to takeoff, the altimeter should be set
to which altitude or altimeter setting?
The current local altimeter setting, if available, or the
departure airport elevation.
If the pitot tube and outside static vents
become clogged, which instruments would
be affected?
The altimeter, airspeed indicator, and vertical speed
indicator. (Instruments with “arrows”)
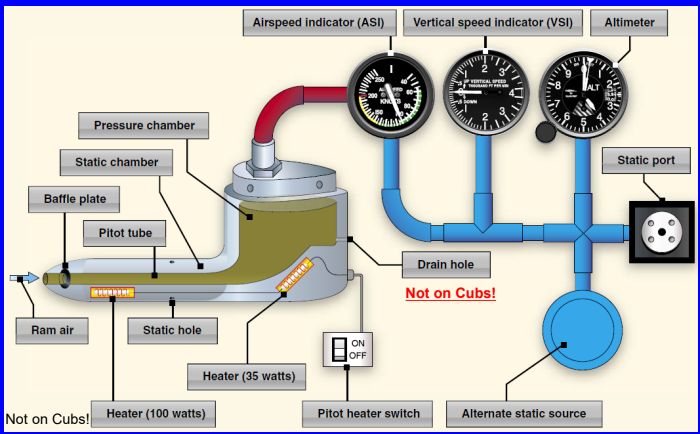
The pitot system provides impact pressure
for which instrument?
Airspeed Indicator.
What should an owner / operator know
about Airworthiness Directives?
They are mandatory.
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic
compass will normally indicate initially a
turn toward the east if...
A left turn is entered from a north heading.
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic
compass will normally indicate a turn
toward the north if...
An aircraft is accelerated while on an east or west
heading.
During flight, when are indications of a
magnetic compass accurate?
Only in straight-and-level unaccelerated flight.
refer back to slides for pressure density and altimeter setting problems
Ambient air pressure,
also known as atmospheric pressure, is the pressure exerted by the air around us. It's the force the air molecules in the atmosphere exert on a surface. This pressure varies depending on altitude and other factors, such as temperature and weather patterns. Essentially, it's the pressure of the surrounding air at a specific location. Typically measured using a barometer.
ANDS stands for
acceleration north, deceleration south
caused by magnetic compass errors
UNOS stands for
undershoot north, overshoot south
caused by magnetic compass errors