Chapter 26: Nutrition and Metabolism
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merged flashcards from Chapter 26, McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Body weight
Determined by energy balance; gain or loss determined by difference between intake and output around a person’s set point (varies ~30-50% due to heredity, environment, activity, eating)
Appetite
Mechanisms that control feelings of hunger and satiation that can vary with age, weight, and other factors and work over periods of minutes to hours
Appetite regulators
Short-term hormones:
Ghrelin
Peptide YY (PYY)
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Amylin
Long-term hormones:
Leptin
Insulin
Ghrelin
Short-term appetite regulator made in the stomach’s fundus that causes feelings of hunger and stimulates hypothalamus growth hormone production, nutrient absorption preparation
Secretion stopped after an hour of eating
Peptide YY (PYY)
Short-term appetite regulator made in the enteroendocrine cells of the ileum and colon that senses food arrival for satiation
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Short-term appetite regulator secreted in the duodenum and jejunum that simulates bile and pancreatic enzyme secretion for satiation
Amylin
Short-term appetite regulator that promotes satiation and inhibits stomach activity
Leptin
Long-term appetite regulator secreted by adipocytes that indicates fat levels; stimulates nerve fibers to produce norepinephrine for fat breakdown (lipolysis)
Deficient receptors can cause obesity in some cases
Insulin
Long-term appetite regulator secreted by the pancreas to stimulate glucose and amino acid uptake as well as glycogen and fat synthesis; helps index fat stores with weaker effect than leptin
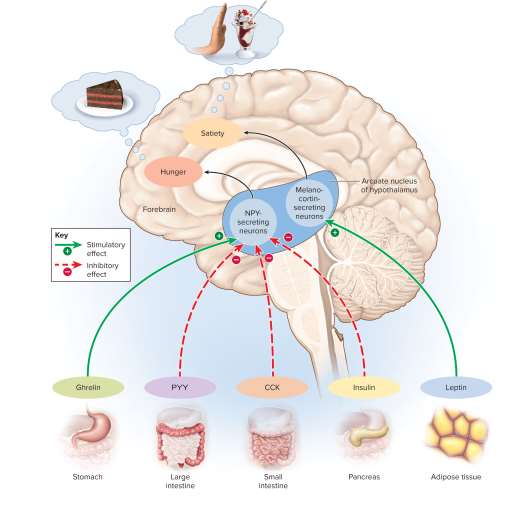
Hypothalamus
An important center of appetite regulation in the brain
Hunger contractions
Contractions within the stomach after emptying that increase in intensity over a period of hours; can be briefly satisfied by chewing and stomach filling but requires nutrition for satiation
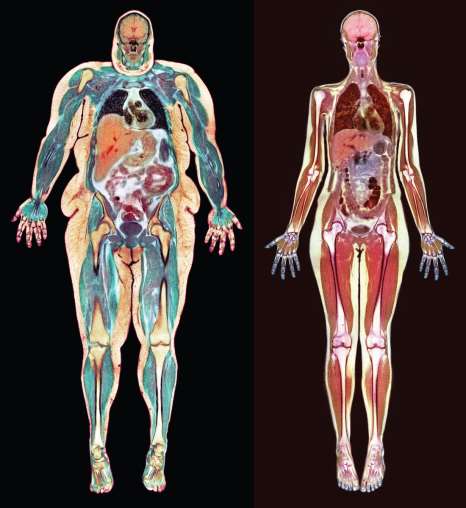
Obesity
Having a body weight more than 20% the recommended norm for one’s age, sex, and height; can be caused by heredity and overfeeding for a shortened life expectancy
Body mass index (BMI)
Number used as an indication of being overweight or obese; calculated based on weight and height
Calorie
A measure of the capacity to do biological work; specifically, the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree celcius
Kilocalorie (kcal)
1,000 calories
4 kcal per gram
The calorie density of carbohydrates and proteins
7 kcal per gram
The calorie density of alcohol and sugars that provide few nutrients and suppress appetite
9 kcal per gram
The calorie density of fats
Nutrient
Any ingested chemical used for growth, repair, or maintenance of the body
Macronutrients
Water, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins — these are required in larger quantities
Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals — these are required in small quantities
Carbohydrate
Macromolecule that serves as an easily absorbed source of fuel in greater amounts for cells; regulated by insulin and glucagon and can be found in plants, grains, and milk
130 grams
The recommended daily allowance for carbohydrates
120 grams
The amount of carbohydrates that the brain consumes each day
Hypoglycemia
Blood glucose deficiency that can cause nervous system disturbances, weakness, and dizziness
Glycemic index (GI)
The effect of dietary carbohydrates on blood glucose levels; higher indexes stimulate higher demands and thus increase obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus risks
Fiber
Fibrous material that resists digestion — not technically a nutrient but allows for smoother digestive function
Lipids (fats)
Macronutrient that accounts for 80-90% of an adult’s resting energy needs through energy stores; very dense at 9 kcal per gram and aids vitamin absorption (lower consumption equates to vitamin deficiency)
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
“Good” cholesterol found in healthier fatty foods; indicates cholesterol is being removed from arteries and transported to the liver for disposal
Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
“Bad” cholesterol found in unhealthy fatty foods; can be increased via smoking, saturated fat intake, coffee, and stress but is lowered via vigorous exercise
Protein
Macromolecule that constitutes 12-15% of body mass with 65% in skeletal muscles; contributes to muscle contraction, cell components, pH buffers and are made of amino acids from the diet or synthesized by the body
Minerals and vitamins
Micronutrients that are not used as fuel but nutrient absorption aids that mainly come from the diet in small amounts; function in pH buffering, enzymatic action, blood functions
Catabolism
The breakdown of glucose in small steps to be transferred to ATP and heat generation
Glycolysis
The breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate
Anaerobic fermentation
The reduction of pyruvate to lactate without using oxygen
Aerobic respiration
The more efficient form of cellular respiration that requires oxygen and oxidizes pyruvate to carbon dioxide and water
Enzymes
Proteins that contribute to glucose catabolism and energy production
Glycogenesis
The synthesis of glycogen stimulated by insulin to chain glucose monomers together
Glycogenolysis
The hydrolysis of glycogen to release glucose back into blood
Glycogen
An energy-storage molecule that can aid in glucose level regulation
Glyconeogenesis
The synthesis of glucose from noncarbohydrates, such as glycerol and amino acids, that occurs in the liver and kidneys if necessary
Lipogenesis
The synthesis of fat from other types of molecules, such as amino acids and sugars
Lipolysis
Breaking down fat for fuel in the body; depends on hormone receptors for balance
Proteins
Macromolecules made of amino acids that can be converted to glucose or fat or be used in enzymatic action; synthesis stimulated by growth hormone, thyroid hormone, and insulin with an ample amino acid supply
Liver
Organ that aids in carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism among other nondigestive roles — damage can be life-threatening
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver that is caused by a virus; can range from mild inflammation to more serious progression causing cirrhosis or liver cancer
Cirrhosis
An irreversible inflammatory liver disease with poor prognosis; can result from alcohol abuse, hepatitis, gallstones, or pancreatic inflammation ultimately causing scar tissue, jaundice, ascites, impaired clotting, and liver necrosis and failure
Absorptive state (fed state)
State of metabolism during the four hours during and after a meal with nutrient absorption to meet energy and other needs without the need for stored fuels
Postabsorptive state (fasting state)
State of metabolism after meals in the late morning, afternoon, and overnight with an empty stomach to meet needs from stored fuels
Fed state carbohydrates
Where carbohydrates are transported to the liver for transportation throughout the body with any excess producing glycogen or fat
Fed state amino acids
Where amino acids pass through the liver and go to other cells for protein synthesis (liver cells may use them for fuel or fatty acid synthesis)
Insulin
Hormone that regulates glucose uptake by most cells and causes blood glucose levels to fall and index fat stores; can also transport proteins into cells for protein synthesis
Fasting state fats
Where fats are converted to glucose for energy
Fasting state proteins
Where proteins are used as fuel (particularly muscle proteins) when glycogen and fat reserves are depleted
Cachexia
The extreme wasting away seen in some chronic diseases resulting from the loss of appetite (anorexia) as well as altered metabolisms
Cortisol
A hormone released in response to stress that promotes fat and protein catabolism (breakdown) and gluconeogensis as well as growth hormone secretion and insulin inhibition for higher levels
Metabolic rate
The amount of energy used in the body in a given period of time; measured in kcal per hour or day and can depend on physical activity, mental state, absorptive or postabsorptive status, and thyroid or other hormones
Basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Baseline metabolic rate that minimizes the effects of feeding, activity, and hormone levels around 2,000 kcal per day for adult males (slightly less for females)
Total metabolic rate (TMR)
The sum of basal metabolic rates and energy required for voluntary activities; can be increased by physical activity or states like anxiety, pregnancy, fever, or hormonal levels and decreased by mental state and starvation due to weight conservation