1.1 Meeting customer needs
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Niche Market
A small segment of a larger market where customers have specific needs
Mass Market-
An unsegmented market aimed at the main market
Advantages and disadvantages of niche marketing
Ads- Scope to charge premium prices and meet customer needs, Less competition increasing customer loyalty.
Dis- Hard to grow sales- no Economies of scales, Mass market competition requires a perfect marketing mix
Advantages and disadvantages of Mass marketing
Ads- Economies of scale- high sales volume, very high for potential revenue
Dis- High investment costs and start up costs, high levels of competition
Branding definition
Used to differentiate a product/ service away from rivals
Why is branding important in a mass and niche market?
Mass- lots of competitors, creates advertisement
niche- Building connections, increase barrier to entry for competitors- not very useful though
Economies of scale
Falling unit costs experienced by a business as it increases in size.
Purchasing economies -
falling unit costs that a growing business can achieve when it buys raw materials or other inputs in larger quantities, allowing bulk-buying discounts.
Technical economies -
falling unit costs that a growing business can achieve by investing in more efficient machinery and equipment and spreading this cost over a larger output.
Marketing economies -
falling unit costs that a growing business can achieve as output increases, e.g. by spreading the cost of promotion campaigns over a larger output.
Managerial economies -
falling unit costs that a growing business can achieve by employing specialist, more efficient managers, and spreading the cost over a larger output.
Internal economies of scale
As a business grows and increases its output its total costs will increase. But sometimes business find that at the same time, unit costs (the cost of making one product or providing one service) actually fall.
Why do economies of scale matter?
Lowering cost per unit is very important, Lowering prices make it more attractive for consumers if they are price sensitive.
Market size equations
Value= selling price x number of units sold
Market share eqaution
(Sales of a business/total market sales) x100
Market growth
(Change/ original) x100
Market size
the potential sales volume/ revenue and helps businesses decide on the best strategy
Market share
Indicates how the overall market is split between the existing competitors.
Typically measured by value, although can also be measured by volume.
Market growth
Measures the rate of change in market size which might be rising, declining or stable.
Can be calculated using either value or volume.
Dynamic market -
A market that is subject to rapid/continuous change.
Innovation -
Putting new ideas/designs into action.
Product innovation -
The creation and development of new or improved products or services
Process innovation -
The implementation of new methods, techniques, or practices that improve the efficiency, effectiveness, and productivity of business operations.
Some markets are static/stable
This means they change little from year-to-year, or change only slowly/gradually.
What are the key drivers of a changing market?
Technological advancements
Consumer behaviour preferences
Intensity of rival
External business environment (PESTLE)
change in market size
Businesses can adapt to change better if they
market research
encourage intrapreneurship
quick decision making
flexible workforce
Continuous improvement
Ads and dis for product innovation
Ads- Source of competitive advantage, higher profit margins
Dis- Imitated products, research and development costs
Ads and dis of Process innovation
Ads- cost minimisation, improved product/service and quality
Dis- Large upfront investment, disruptions to operations
Online retailing -
selling via the internet, e.g. via a website or app (e-commerce or m-commerce).
Pros and cons of online retailing
Pros- Increased revenue, lower costs
Cons- Prefer personalised service, large upfront costs
Competition -
rivalry among sellers, where sellers try to increase sales, profit and/or market share.
Direct competition -
between rivals that sell similar goods, e.g. Papa Johns & Domino's
Indirect competition -
between firms that sell substitute goods, e.g. KFC & Domino's
Competitiveness -
the ability of a business to outperform rivals and achieve sustainable competitive advantage
Competitive advantage -
features of a business and/or its products that enables it to generate more sales or to be more profitable than its rivals.
Factors when assessing competition
intensity of rivals
threat of new entrants
Threat of substitutes
power of customers
power of suppliers
How does competition affect the market?
Changing their marketing mix, controlling costs to maintain profitability
Risk -
when the probabilities of different outcomes are known or can be estimated.
Uncertainty -
when the probabilities of different outcomes are not known or cannot be reliably estimated
Common business risks
Issues with cyber security
supply-chains shocks
employee related risks
Market orientation -
where businesses design and develop products based on understanding and meeting customer needs and preferences.
Product orientation -
designing and developing products based on the business's capabilities and expertise rather than specific customer needs or market demands.
Characteristics of a Product-Oriented Approach:
Assumption of customer demand: businesses often assume that if they create a superior product, customers will automatically want and buy it. The focus is on the belief that customers will recognise the value of the product's features and benefits.
Limited customer input: Customer feedback and market research is given less priority compared to the company's technical vision. The company may believe that it knows what customers want better than customers themselves.
Product-centric marketing: Marketing efforts are centred around highlighting the features and technical capabilities of the product rather than customer needs.
Pros and cons for product orientated approach
Pros- more likely to have development of highly innovative new products
Cons- High risk of failure
Market orientation pros and cons
Pros- New product development is less risky> meeting customer needs
Cons- high costs of market research and will there be an opportunity cost involved
Primary market research -
collecting data first-hand for a specific purpose (sometimes called field research).
Secondary market research -
using data that already exists and was collected for a different purpose (sometimes called desk research).
Sampling -
gathering of data from a subset of respondents, the results of which should be representative of the population (e.g. target market) as a whole.
Primary research methods include
Surveys, Focus groups, consumer panels, observation, test marketing and online analytics
Pros and cons for primary research methods
Pros- Specific and targeted, Competitive advantage
Cons- Risk of bias, time lags
Secondary research inludes
Government publications, Industry reports, trade publications, commercial data bases, social media, competitors websites, past sales, online reviews
Pros and cons of secondary research
Pros- often cheap and free, large sample- wide scope of research
Cons- Retailed market intelligence reports, not tailored to the manager specific market
Sampling
The gathering of data from a set of respondents in the hope that it will reflect the whole sample/ group,
The main risk is bias or that the sample is too small, but its cost efficient and takes less time
Quantitative research -
produces numerical statistics. It usually involves asking closed questions, e.g. via a survey.
Qualitative research
involves collecting opinions. It usually involves asking open questions, e.g. in a focus group.
Pros and cons of quantative research
Pros- Reliable, comparability
cons- quality of the research, lacks depth/ insight
Pros and cons of qualitative data
pros- in depth insights and adaptable
Cons- Sample sizes are small and skilled market researcher
ICT- how do businesses use it>
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in various ways to conduct market research effectively and efficiently. ICT offers tools and technologies that streamline data collection and analysis, providing businesses with valuable insights into consumer behaviour, market trends, etc.
ICT is used by-
Social media, databases, data mining and websites
Market segmentation -
the division of a market into customer groups, each of which has similar characteristics, preferences or behaviours. Common groupings include age, gender, income, hobbies/interests, location, ethnic origin/culture, occupation and lifestyle.
Price discrimination -
charging different prices to different market segments based on their willingness to pay.
Market positioning –
efforts to influence customer perception of a brand or product relative to the perception of competing brands or products.
The market can be segmented into 4 sections
demographics, psychographics, geographics and behavioural
Targeting
Targeting is the process of selecting one or more specific segments to focus on and directing marketing efforts accordingly.
Positioning
Positioning refers to how a company wants its products or services to be perceived by the target market in comparison to rival products or services.
Pros and cons of market segmentation
Pros- Better understanding of customer needs, managers can be differentiated and there’s scope to price discriminate
Cons- risk associated with targeting small segments and there could be high costs- market research ect.
Market mapping -
the process of analysing competition in a market using two key variables that consumers consider when deciding which product to buy, (e.g price and quality) and plotting it on a diagram.
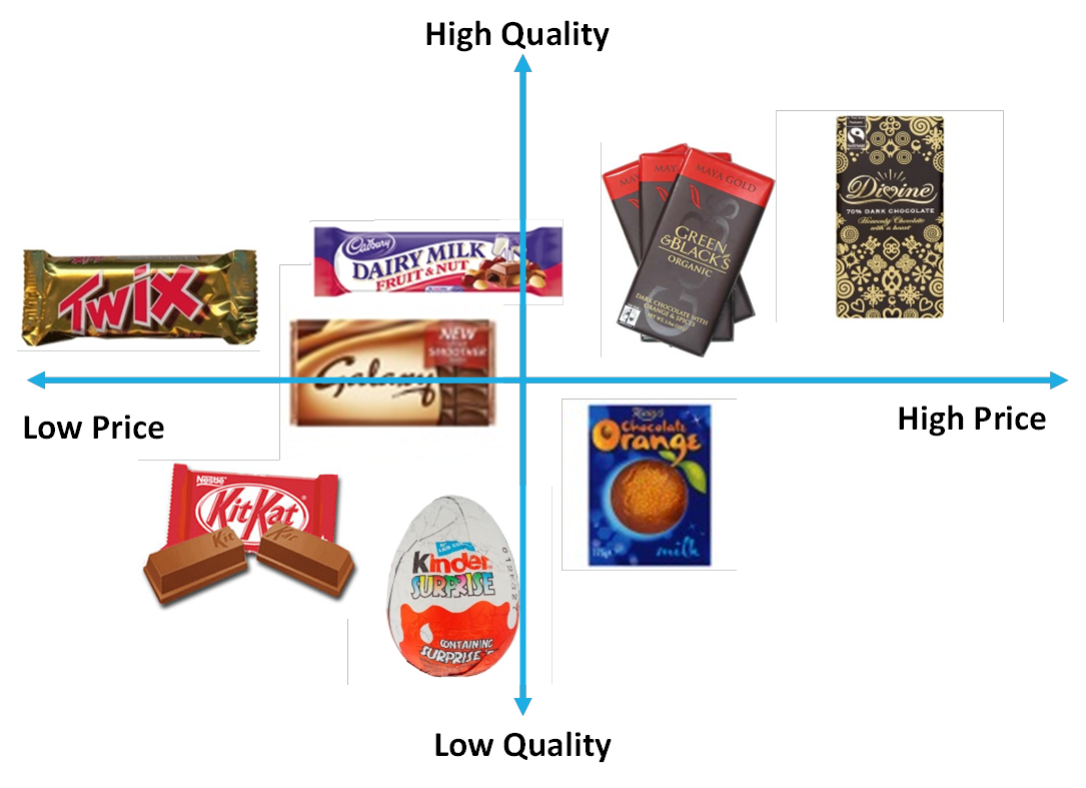
Pros and cons of market mapping
Pros- identifies gaps in the market, improves branding
Cons- Doesn’t guarantee demand where there’s a gap, market maps are very simplistic and might not be accurate.
Adding value -
Activities that allow a business to raise the price beyond the total cost of the inputs required to create the product/service. It might be achieved through improving the product/service itself or improving the way consumers perceive the product/service.
Added value calculation
Added value = Price - unit cost
USP (Unique Selling Point)
- a factor that differentiates a product from its competitors.
Product differentiation -
where a business distinguishes its products/services from rivals. E.g. via a USP or really effective branding.
Competitive advantage
- features of a business and/or its products that enables it to generate more sales or to be more profitable than its rivals.
Corporate strategy –
the medium to long-term plan that a business has chosen to follow in order to achieve its corporate objectives.
Differentiation strategy -
where a business sets out to provide unique benefits that customers value. E.g. via superior product features/performance customer service, reliability, branding, innovation etc.
Cost leadership strategy
- where a business sets out to be the lowest cost producer, for a given level of quality. These businesses focus on improving operational efficiency (e.g. efficient design and production methods, workforce, low overheads, greater economies of scale).
Michael porters strategies- explain
Differentiation strategy
Businesses that pursue a differentiation strategy try to provide products with unique benefits that customers value
Low-cost strategy
Businesses that pursue a low-cost strategy set out to be the lowest cost producer in their market, for a given level of quality.
Getting "stuck in the middle".
This is where a business is neither low-cost nor effectively differentiated. Porter argued that this approach is likely to lead to poor profitability, as unit costs are likely to be relatively high, but without the ability to charge a premium.
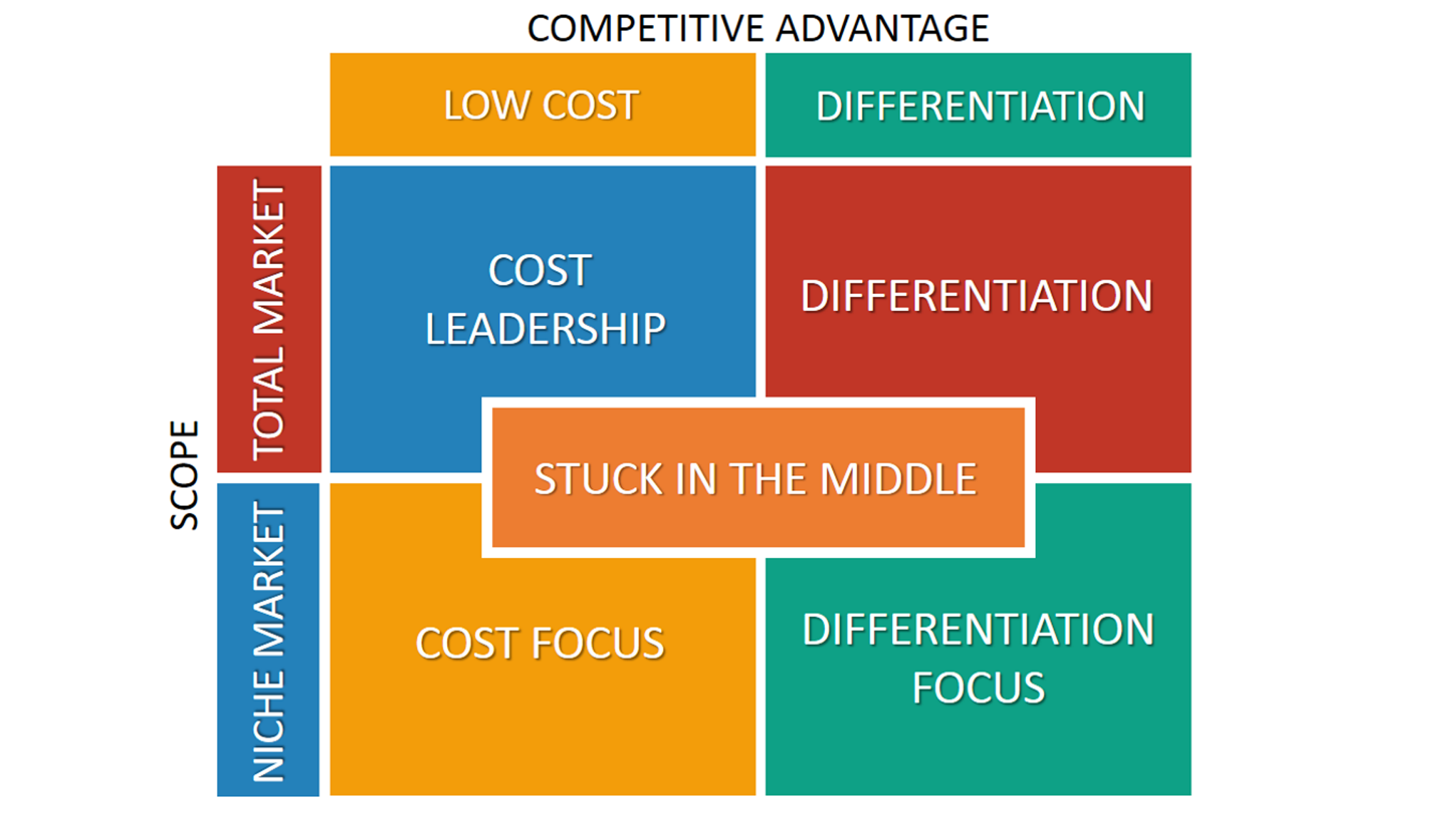
Product design mix
Function, aesthetic, economic
Methods of sampling
Quota sampling non-random, stratified sampling equals random, convenient sampling equals non-random but chosen quickly
Five. Stages of the product life cycle.
Development, introduction, growth, maturity, decline
Advantages and disadvantages of advertising
Advantages, wide coverage, control of message, useful for building brand awareness
Disadvantages, often, expensive, impersonal, one-way communication
Advantages and disadvantages of sale promotion
Advantages, helps to achieve a quick boost of sales, encourages customer to try new products
Disadvantages, the damage, brand image, sales affect may only be short-term, customers may come to expect/anticipate further promotion
Personal, selling advantages and disadvantages
Advantages, persuasive impact, messages, customised, potential for development
Disadvantages, high cost, labour intensive, can only reach a limited number of customers
Direct marketing advantages and disadvantages
Advantages, focus, limited resources on targeting promotion, can make personalised marketing, relatively easy to measure responses
Disadvantages, response rates vary, negative image, e.g. junk mail, databases, expensive to maintain
Factors influencing, promotional decisions and strategies
Target market/market, positioning, stage in plc, nature of the product, competition, marketing, objectives, external influences