6070- 2nd half of immunity
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
antibodies that have different classes can help identify acute vs chronic conditions.
what would a newly infected disease have, antibody-wise?
what would a chronic disease have, antibody wise?
IgM
IgG
what are the 2 immature types of antibodies?
what are the older types?
IgM and IgD
IgG, IgE, and IgA
what are the secondary lymphoid tissues? x 3
spleen, lymph nodes, mucosa associated lymphoid tissues (tonsils)
where does the class switching take place?
what enzyme does it use?
heavy chain constant region
recombinase
the variable regions of the antibodies normally _____ ____ _____,
but also could have a spontaneous mutation called an _____ _______.
stay the same
affinity maturation
what could affinitiy maturations of antibodies tell us about the length of time this person has had this illness?
could tell us if this is an acute vs chronic condition
what is immunity?
what is this provided by primarily?
state of resistance against infection
adequate levels of circulating antibodies
what is an antibody titer?
what does a high antibody titer mean?
blood test that measures specific serum antibody concentrations;
immunity
how can immunity be acheived?
actively or passively
what is passive immunity?
transfer of preformed antibodies against specific antigen from a protected or immunized individual to an unprotected or nonimmunized individual
what is passive immunity used for ?
B-cell immunodeficiencies
after exposure of indiv. w high susceptibility to a disease w/o adequate time for active immunization
what does an antibody injection do?
alleviate or suppress effects of antigenic toxin
provides immediate but temporary protection
what are the 3 types of passive immunities ?
mother to fetus: IgG can cross placenta
mother to infant: IgA from breast milk
serotherapy: direct injection of antibodies (human or animal)
what is active immunity?
the body in a protected state because of active infection or immunization
what does active immunity require?
memory b cells
what are the timelines looking like for the primary stimulus?
secondary stimulus to immune response?
primary takes much longer to develop and declines rapidly
much quicker and greater antibody response acheived
vaccines that have altered microorganisms or toxins dont have what?
and don’t do what?
pathogenic properties
don’t cause harm to the host
vaccines that contain live or attenuated agents
have live parts of the virus within them
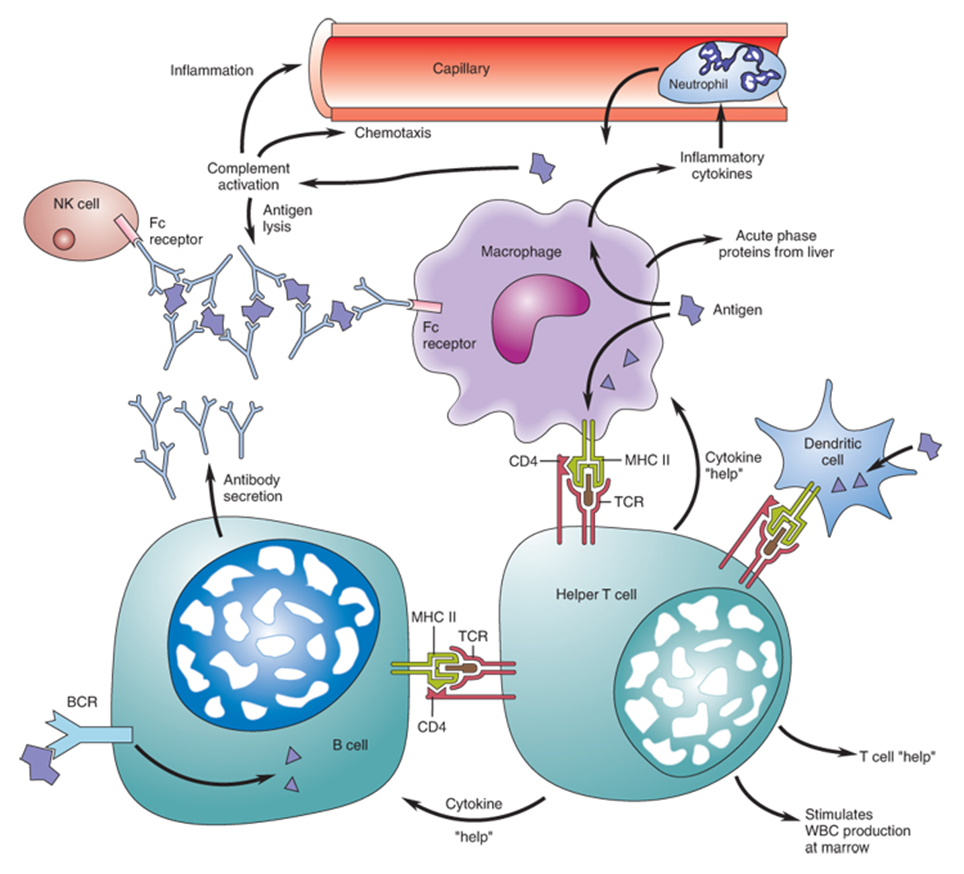
what are the types of alterations to immune response?
excessive immune response
deficient immune response
what are the types of excessive immune response?
autoimmunity
hypersensitivity
t cells that are able to react with self tissue are thought to be what?
destroyed or permanently inactivated during development in the thymus
what is autoimmunity?
immune system recognizing its own cells as foreign and mounts an immune response that injures self tissues
breakdown of self-tolerance
what is the antigenic mimicry thoery of autoimmunity?
self/foreign antigens made of same materials, so small alterations in self tissue lead to attack
what is the release of sequestered antigens theory of autoimmunity?
self antigens not in direct contact with lymphocytes during fetal development
what are the T cell theories of autoimmunity? x 3 components
thymus gland defect,
decreased suppressor T-cell function,
altered T helper cell function
what is the b-cell theory of autoimmunity? x 2 components
b cells lose their responsiveness to suppressor T-cell signals
overactivation of b cells
what is the mast cell theory of autoimmunity?
cytokines are released causing activation of other cells