Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is meant by the quantum of energy ?
The smallest fixed amount of energy required for a change
How can energy be described?
discrete or quantised
How are electrons arranged?
in energy levels that are quantised
What is the ground state?
The state at which the electrons are in the lowest energy levels possible for each of them.
What is the effect of the ground state?
The atoms are most stable
What is the excited state?
When an electron temporarily occupies an energy state greater than its ground state
How does an electron become excited?
When an electron absorbs a quantum of radiation it can move up to a higher energy level.
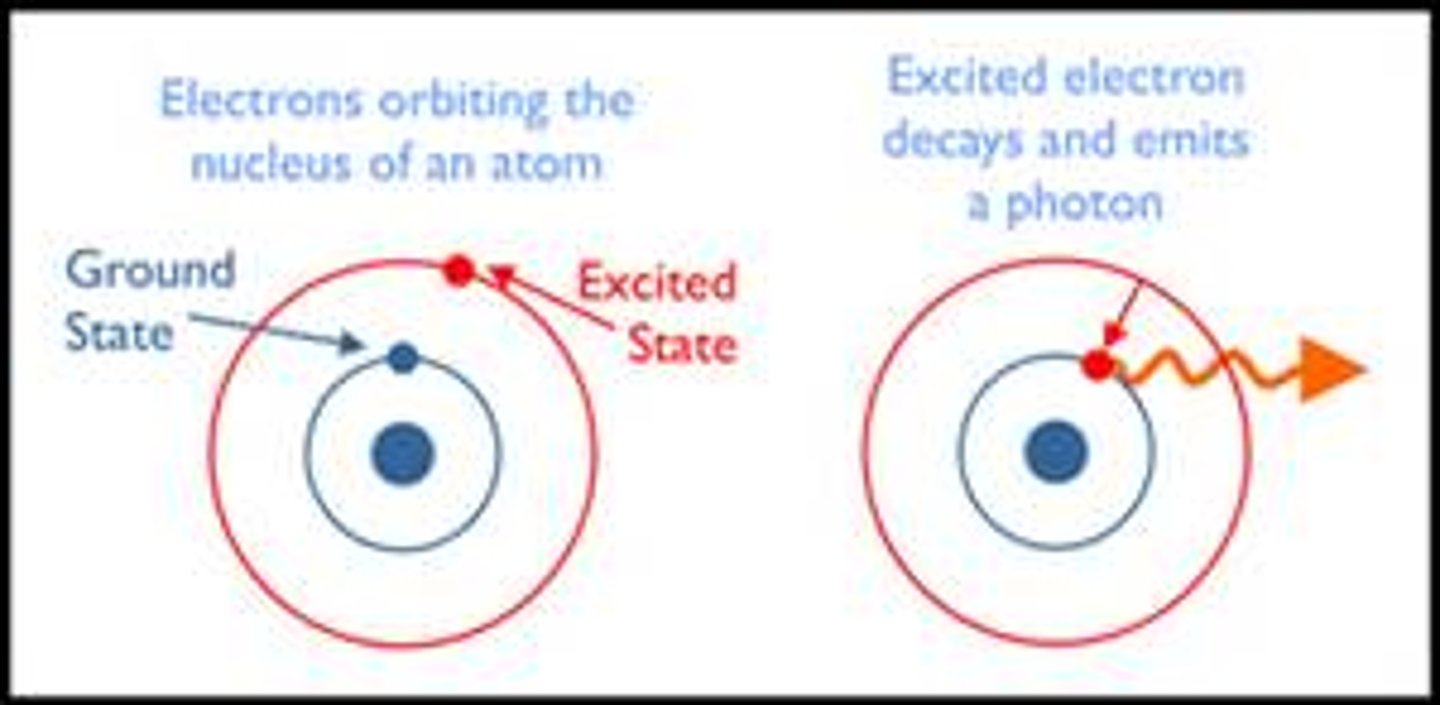
What happens when an excited electron falls to a lower energy level?
a quantum of radiation is given out.
What are the energy levels of an atom called?
principal quantum levels/principal energy levels/electron shells
What notation are energy levels given?
n=1; n=2; etc.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The whole range of frequencies of the electromagnetic radiation
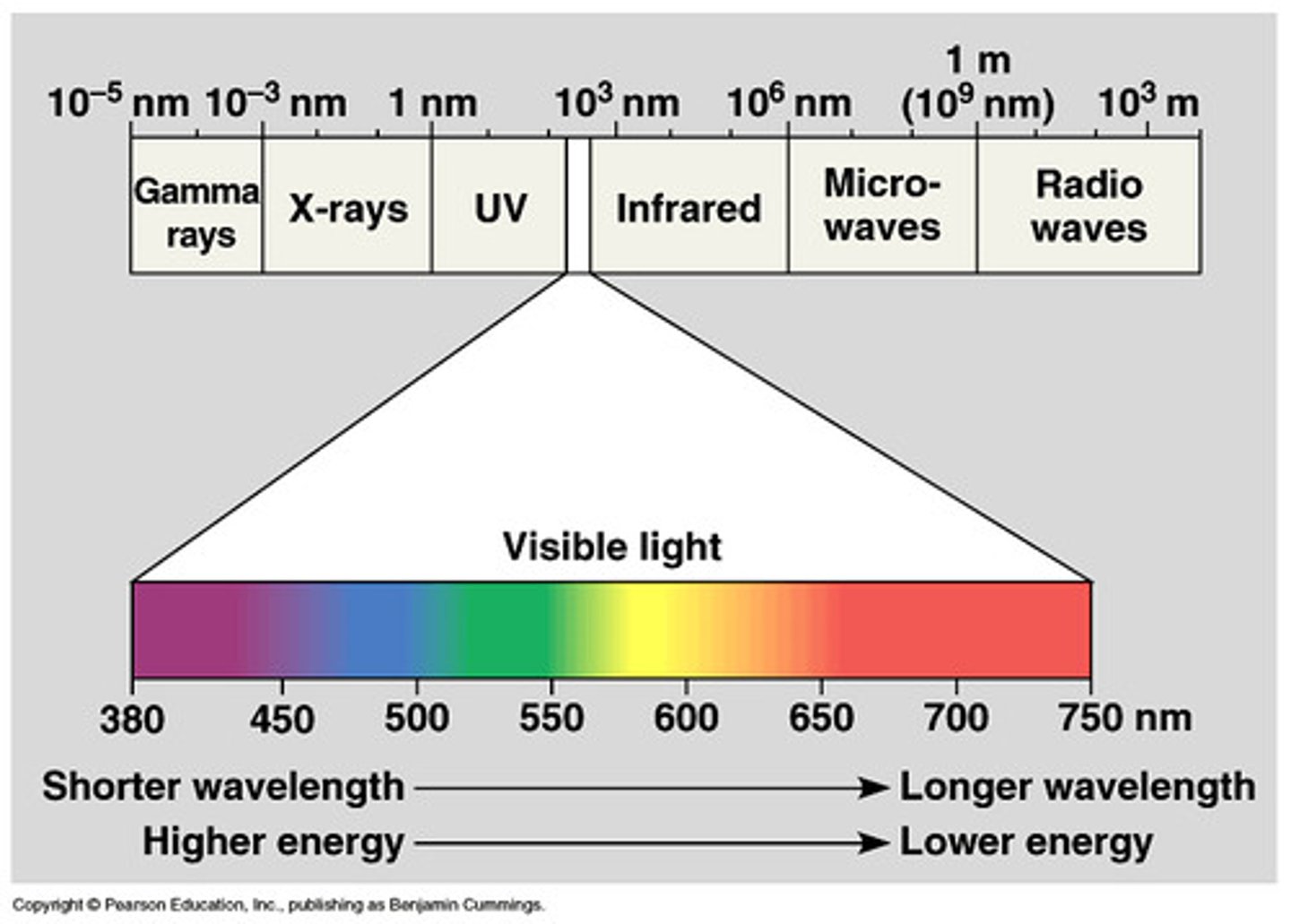
What is a continuous spectrum?
a spectrum of colours made up of all wavelengths of visible light is seen like in a rainbow (there is no distinct division between the colours as they blend in from one to another)
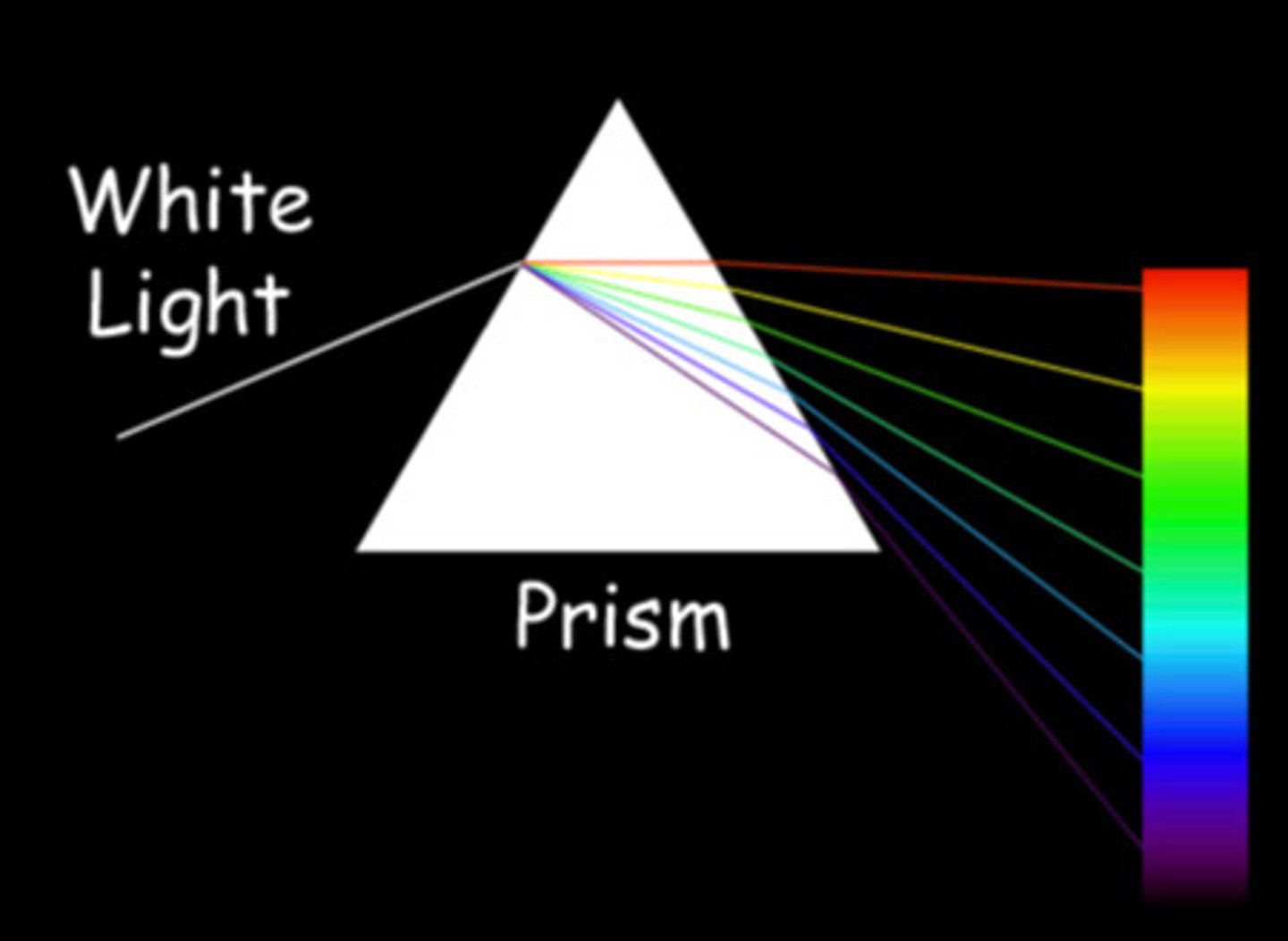
What is a discontinuous spectrum?
a spectrum where there is no distinct division between the colours as they blend in from one to another
What is electromagnetic radiation?
a form of energy that includes radio waves, microwaves, X-rays and gamma rays, as well as visible light.
How can electromagnetic radiation be seen?
as a stream of photons (particles with no mass each travelling in a wave-like pattern and moving at the speed of light)
Examples of electromagnetic radiation:
radiation from the sun
What is wave-particle duality?
the fundamental property of matter where, at one moment it appears like a wave, and yet at another moment it acts like a particle
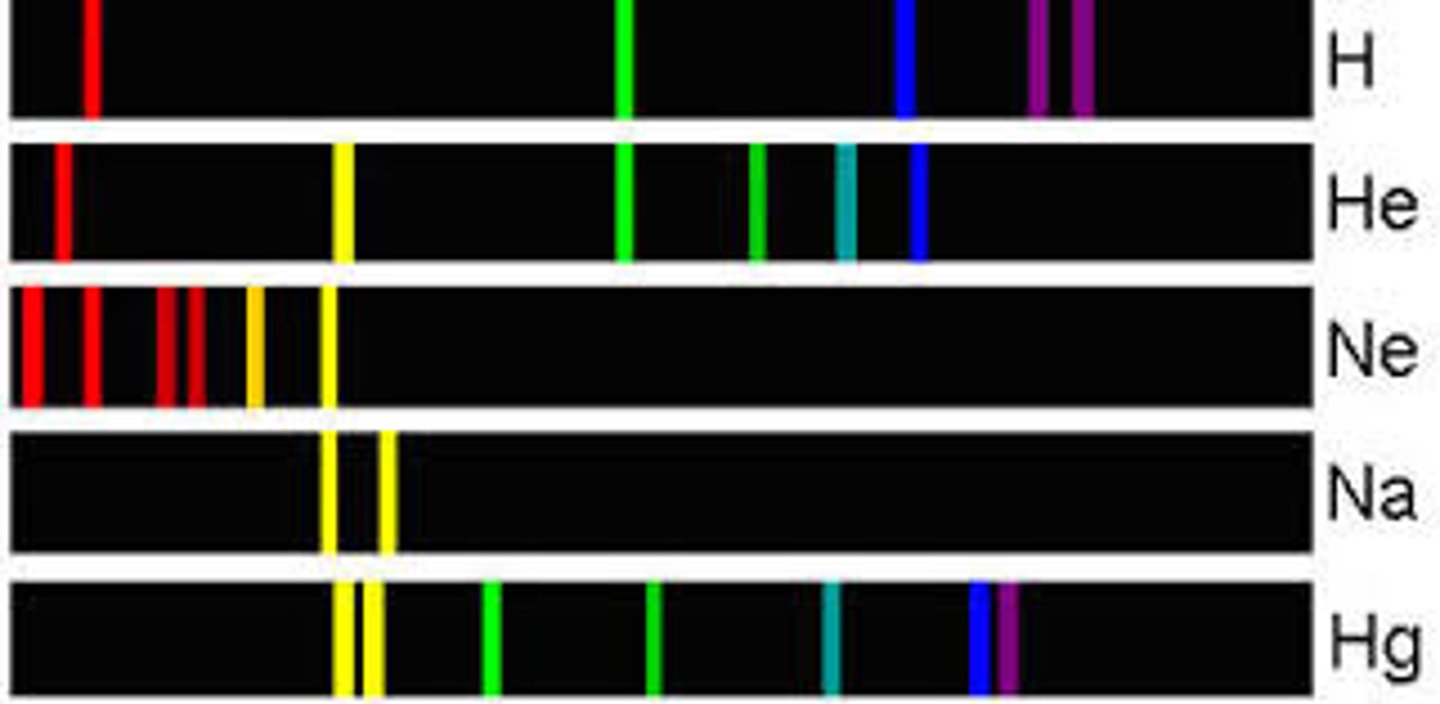
When is an atomic spectrum formed?
when electromagnetic radiation is absorbed or emitted by an element
Plank's equation:
E = hc/λ (e: energy; h: plank's constant; c: speed of light; λ: wavelength)
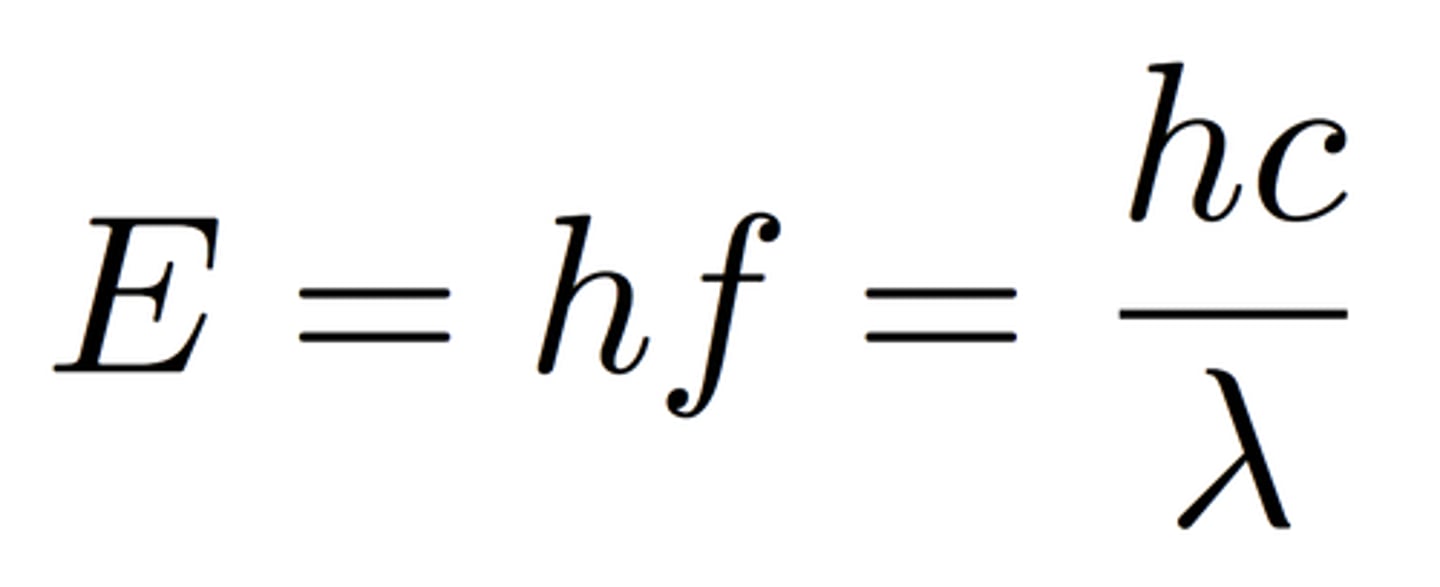
When does the absorption spectrum occur?
when the electron in the ground state is provided w/ energy to lift it to an excited state
Why was hydrogen investigated for the absoprtion spectrum?
it only had one electron
How is it proven that energy levels converge?
in the absorption spectrum, frequency values converge to the higher frequency end of the spectrum
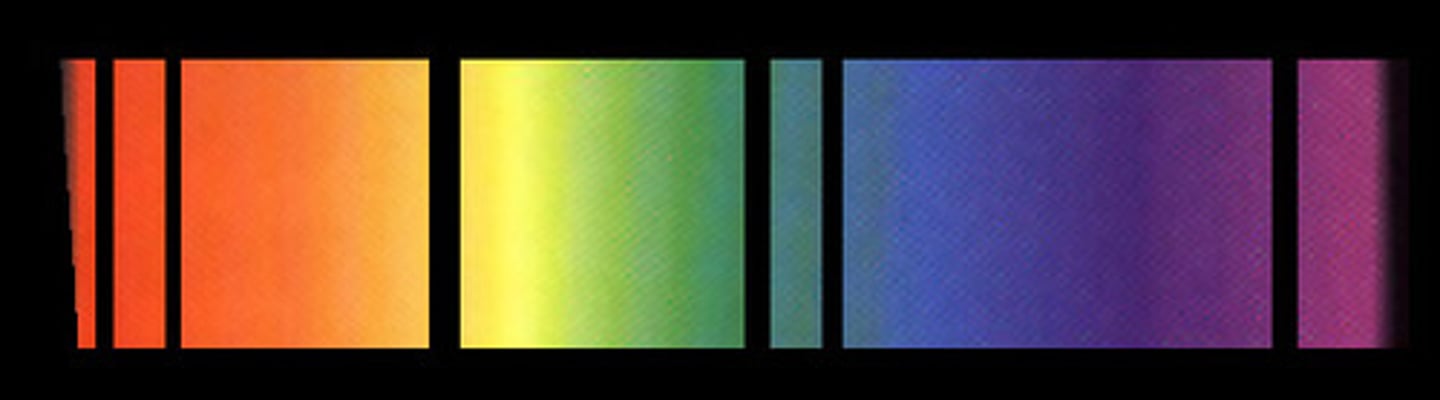
key points about the absorption spectrum:
- higher energies are further from the nucleus
- only a fixed number of transitions are available
- each energy change is shown in the spectrum
- a series of black lines appear on the spectrum
- the final transition corresponds to ionisation
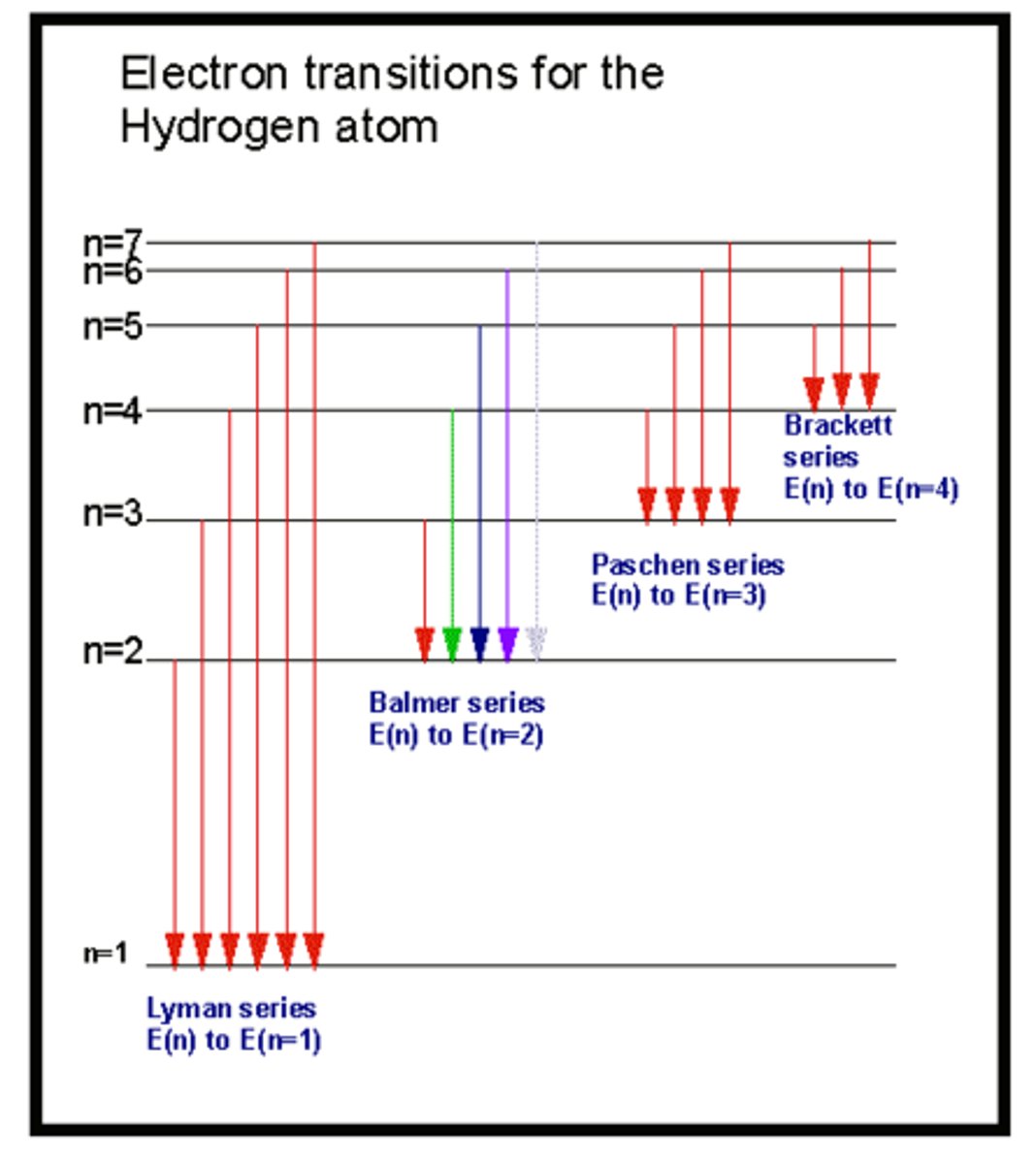
When does the emision spectrum occur?
when electrons, having been excited to higher levels, return to lower ones and give out energy
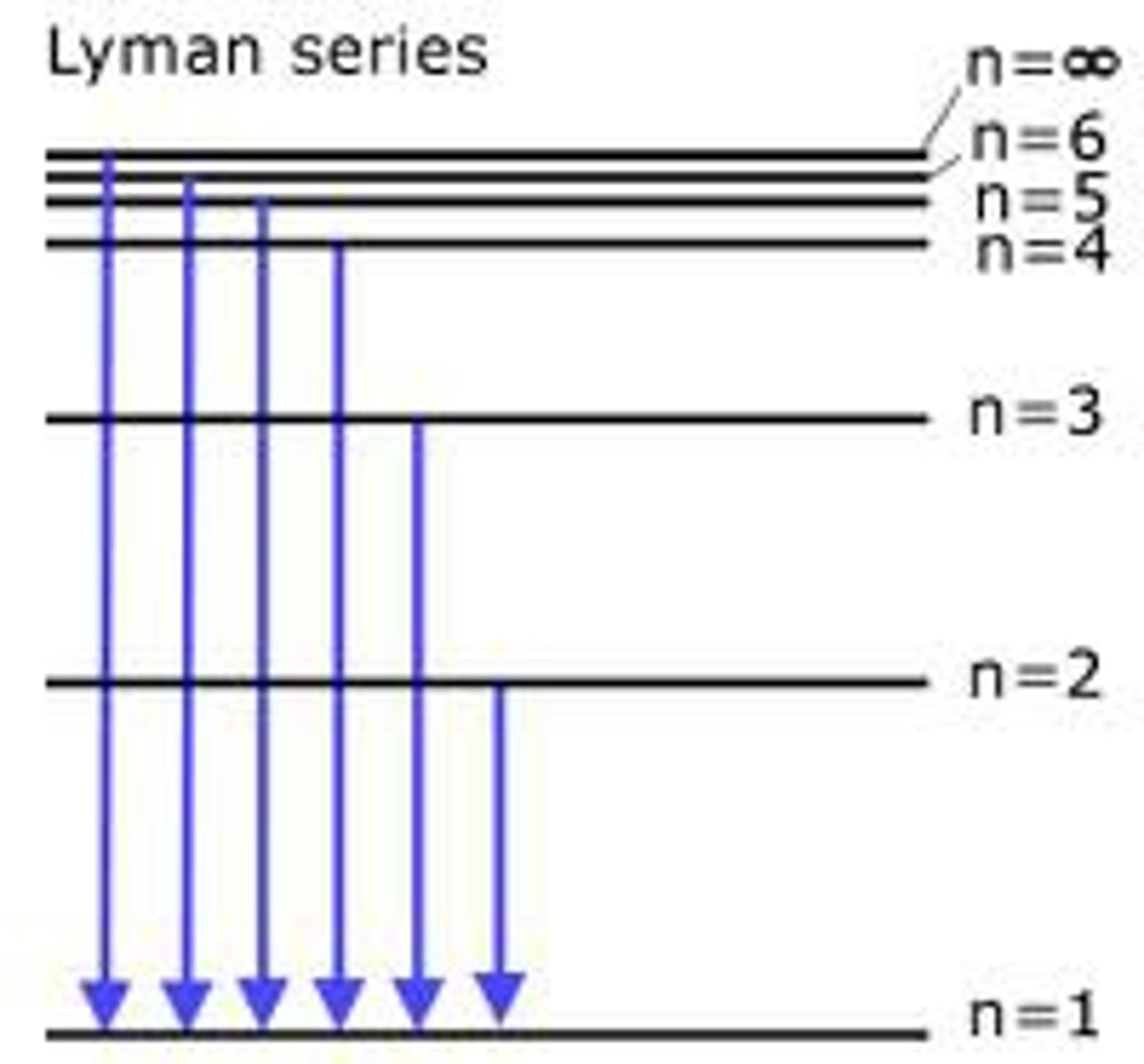
Lyman emission spectrum:
- not visible: in the Ultra-violent (UV) region
- ends on n=1
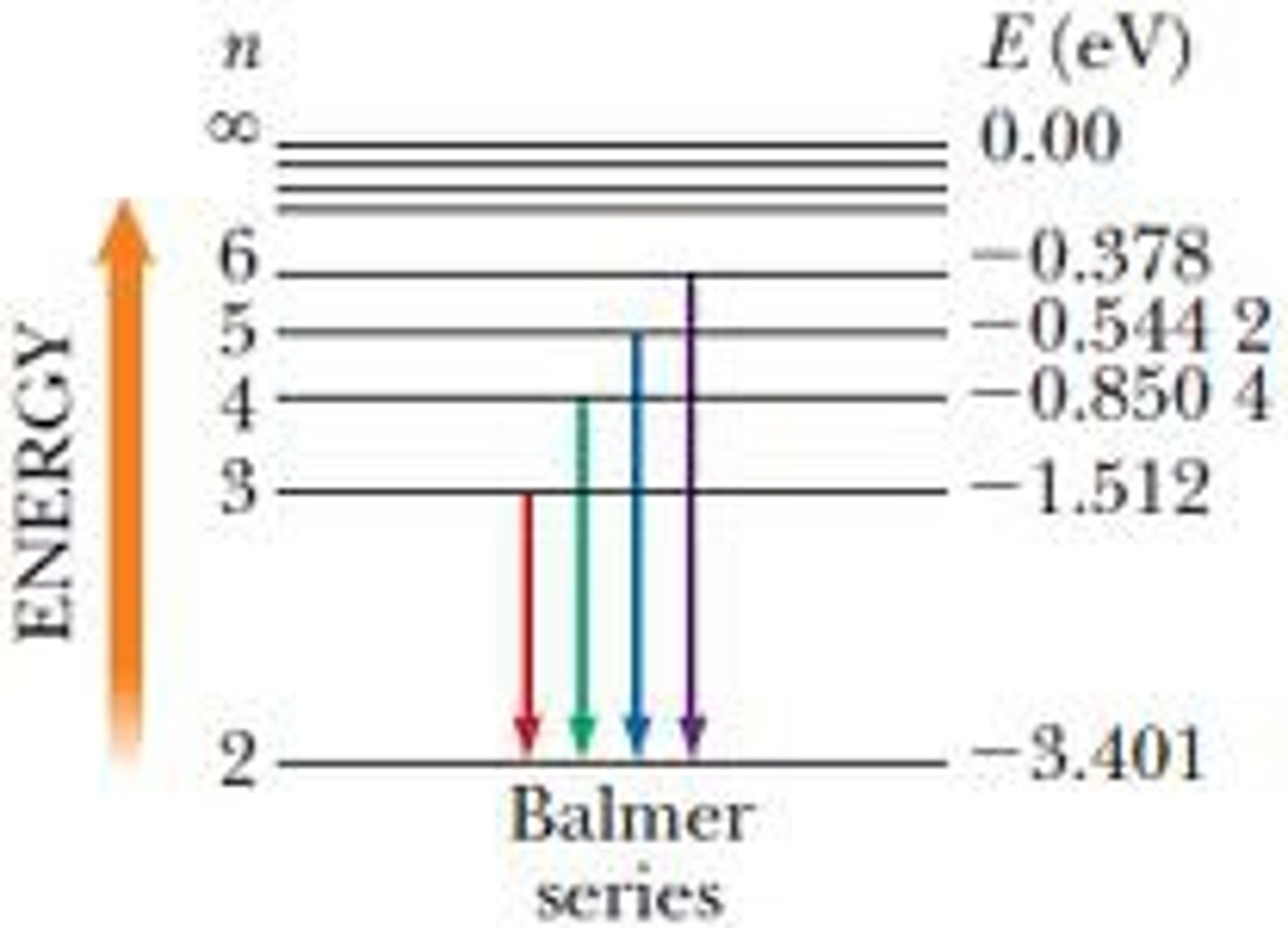
Balmer emision series:
- visible
- ends on n=2
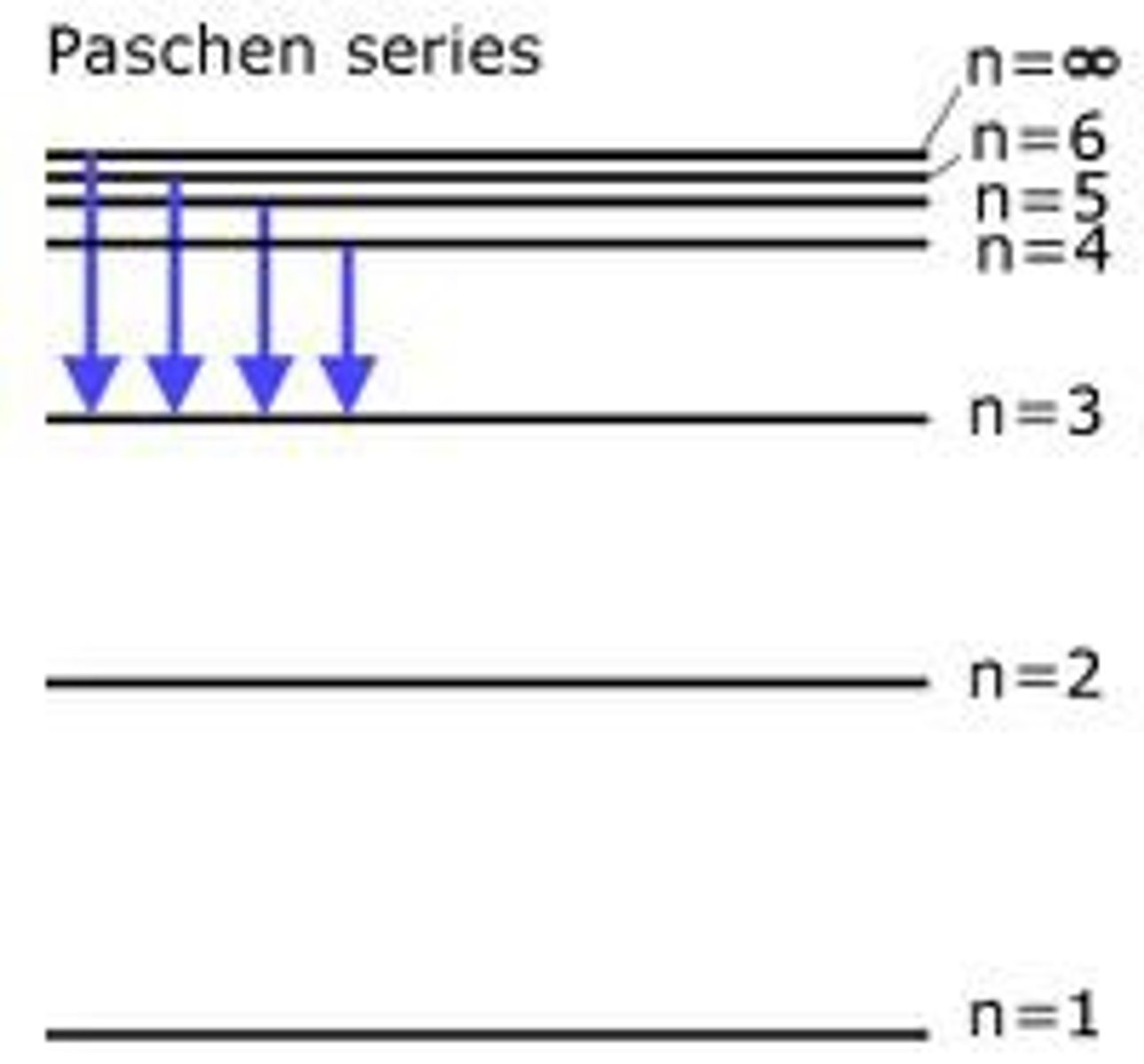
Paschen emission series:
- infrared region
ends on n=3
Blackett emission series:
- infrared region
- ends on n=4
Characteristics of the emission spectrum:
- arrows in diagram point downwards
- electrons going from high to low energy
- series are arranged and named according to where the transition ends
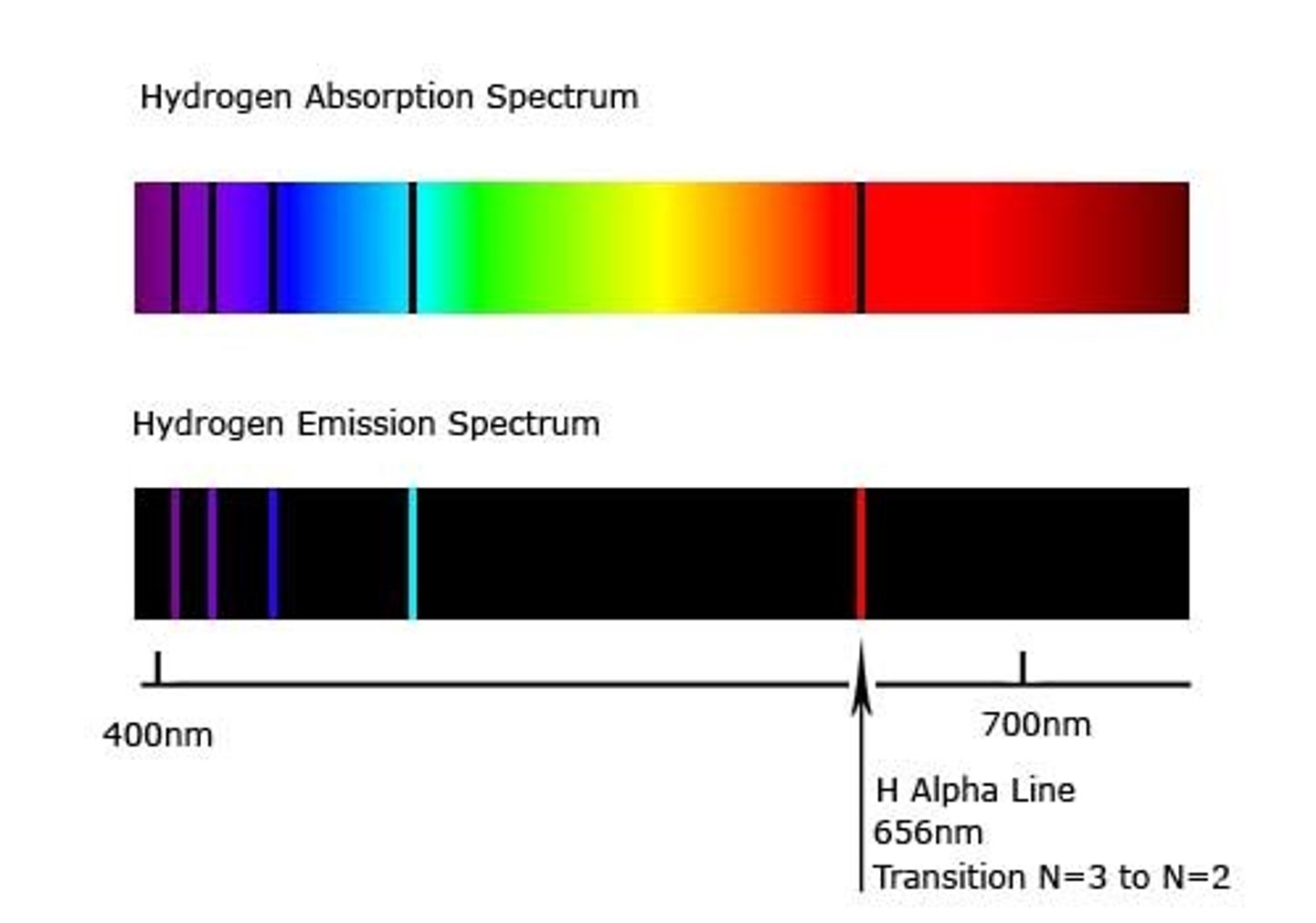
What happens to the emission spectrum w/ increasing frquency?
the lines become closer together as the frequency increases until it converges to forms a continuous spectrum
What is the convergence limit?
The point where the lines of the spectrum eventually come together
What does the convergence limit represent?
an electron falling from the highest possible energy level
What happens when an electron has more energy than the convergence limit?
it becomes free from the pull of the nucleus of the atom, i.e. the atom is converted to an ion.