animal diversity pt 1 (consumers -> tissues)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
animals are what type of consumer?
heterotrophs + digest food inside the body
plants are what type of consumer?
autotrophs
fungi are what type of consumer?
heterotrophs + digest food outside the body using enzymes
→ are also specifically saprobes, parasites, and symbionts
animal cells lack a cell ___
wall
what is the most abundant protein in animals/animal cells?
collagen
what do animals use collagen for?
structural support in their cells because they lack a cell wall
what are the 3 junctions found between animal cells?
1) tight junction
2) desmosomes
3) gap junctions
what 2 specialized cells do animals have that plants and fungi do not?
1) nerve cells
2) muscle cells
tight junction
junction between animal cells that creates a barrier to prevent leakage of fluids between them
desmosome
junction that provides structural support by anchoring adjacent cells together, allowing them to withstand mechanical stress and move together
gap junction
open channels between animal cells to share material and communicate between one another
do most animal produce sexually or asexually?
sexually
what is the pathway for sexual reproduction in animals?
sperm + egg → zygote
zygote undergoes cleavage (cell divides) by mitosis → forms a morula (solid ball of cells)
morula becomes hollow → forms a blastula (hollow ball of cells)
blastula begins to form a germ layer (layers of embryonic tissue) in gastrulation → forms a gastrula (cell cluster)
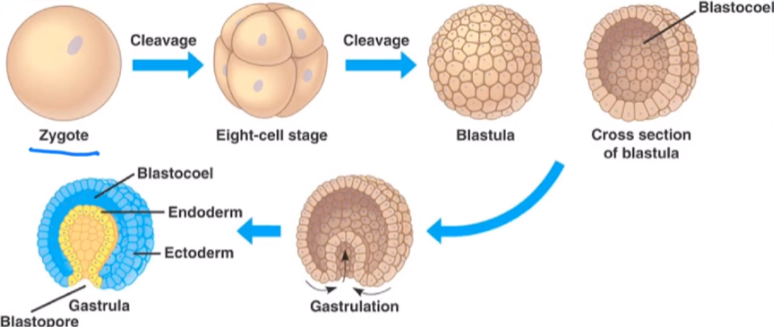
zygote
a fertilized egg
morula
solid ball of cells
blastula
hollow ball of cells
gastrula
germ layers formed through gastrulation
what 2 stages can animals go through in development?
A) “mini” adult stage
B) larval stage
“mini” adult stage
mature and immature form are very similar (i.e. babies and adults have similar parts, only one is more mature)
larval stage
sexually immature stage that looks very different from the adult, will have to go through a metamorphosis to develop into adult stage (i.e. frogs, butterflies)
animals share a family of genes called “hox genes.” what are they responsible for?
group of genes that ONLY evolved in animals
genes that can influence the outcome of other genes
→ will turn the expression of other genes on/off
neoproterozic era
record of the first early animals on earth
what did animals look like during the neoproterozic era?
simplistic in structure, not complex
→ corals, molluscs, segmented worms
paleozoic era
rapid diversification of animals (the cambrian explosion)
what caused the cambrian explosion?
1) new predator-prey relationships
→ animals being preyed upon were forced to evolve
→ predators losing their food source were being forced to evolve
2) more oxygen in the atmosphere
→ cells carry out higher metabolic function leading to more complexity
3) hox genes evolved
→ more changes in genes causing variations in gene expression
mesozoic era
dinosaurs emerged
small, rodent-like mammals appeared
large coral reefs began to form
cenozoic era - present day
mass extinction of terrestrial and marine animals
→ these newly opened niches gave rise to larger mammals
asymmetry
having no symmetry in body plan
radial symmetry
any cut through the central axis will provide a mirror image
bilateral symmetry
only one cut dividing the animal into left and right halves creates a mirror image
porifera have what kind of symmetry?
asymmetrical
sponges and cnidaria have what kind of symmetry?
radial symmetry
cephalization
development of the head + sensory equipment located on the anterior end along with a central nervous system
→ lobsters have this
tissues
groups of specialized cells that are isolated from other tissues because they are separated by membranous layers
porifera (sponges) have specialized cells, but they do not have true _____
tissue; they have only cellular level development because they do not have membranous layers separating a group of cells from another group of cells