Genetics Test 1
1/296
Earn XP
Description and Tags
f25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
297 Terms
What are the four levels of biological organization for the relationship between genes and traits?
Genes expressed at molecular level, proteins function at cellular level, traits observed at organism level, and genes/ traits in particular species can be studied at the population level
Traits are controlled by what?
The interaction between genes and the environment. One example being how a person’s diet has an effect on their height and weight
What is genetic variation?
The differences in inherited traits among individuals within a population.
How does genetic variation occur?
Due to various types of changes in the DNA at the molecular level; such as differences in gene sequences, number of chromosomes, and changes in chromosome structure
How can genetic variation be striking?
Some can be so striking that the same species could be mistaken for being two different species. A real-life example being a blue frog and yellow frog being the same species
What happens with genes during reproduction?
They’re passed from parent to offspring during reproduction
How can sexual reproduction enhance genetic variation?
It is able to result in a combination of traits that’s not found in either parent
What is biological evolution?
The genetic composition of species evolving over many generations. This leads to the genetic make-up of a population changing too
What is natural selection?
The process in which individuals with greater reproductive success are more likely to pass their genes onto future generations
What is biological fitness?
How many kids you have, the more the better
Why would researchers study model organisms?
So they can compare their research results
Why would an organism be considered a model organism?
Their reproduction rates and life rates are quick
What are the three genetic fields?
Transmission, molecular, and population genetics
Transmission Genetics
Explores inheritance patterns as traits are passed on (Mendels peas)
Molecular Genetics
Focuses on biochemical understanding of the hereditary material
Population Genetics
Concerned with genetic variation and its role in evolution but also how that variation relates to the environment
What are the scientific method steps?
Background info is provided, hypothesis to be tested is presented, experimental steps are fully explained, raw data is presented, and the data is analyzed
Define gender
Socially constructed characteristics of men and women
Define sex
Designation given at birth that is associated with reproduction and is also based on chromosome composition
What does “normal” mean?
Individuals displaying one or more characteristic that is commonly observed among members of its species
What is a wild type?
Any characteristic that is present in more than 1% of its members of a natural population
What is the four criteria genetic material must meet?
Information, transmission, replication, and variation
What is bacterial transformation?
When bacteria picks up DNA in its environment
Information
Must contain the information necessary to make an entire organism
Transmission
Genetic material must be passed from parents to offspring
Replication
Genetic material must be copied
What must happen for variation to occur?
Significant amount of phenotypic variation must occur
What is DNA and RNA also known as?
Nucleic acids
Why is DNA and RNA considered a nucleic acid?
Because they both release protons in water
What is the order for DNA structure?
Nucleotides, single strand, double helix, and the chromosome
What sugar is found in DNA?
Deoxyribose
What sugar is found in RNA?
Ribose
What are purine bases?
Adenine and guanine
What are the pyrimidine bases?
Thymine, cytosine, and uracil
How does synthesis occur for a DNA strand?
Only from a 5’ to a 3’ direction
What does a DNA structure have to consist of?
Two strands, ten nucleotides, and has to be helical
What forms the backbone of a DNA strand?
Deoxyribose and phosphates
What is the linkage in DNA/ RNA strands called?
Phosphodiester linkage
What are major and minor grooves?
Indentations in the outer surface of the DNA, major is wider than the minor
What makes Z DNA different from B DNA?
B DNA is right-handed with Z DNA is left-handed. Z DNA also tends to zigzag itself instead of being perpendicular
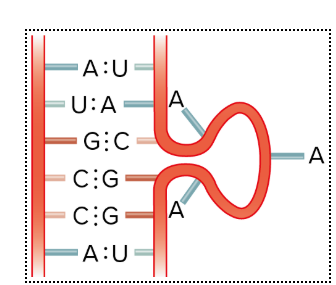
What is this?
RNA Bulge loop
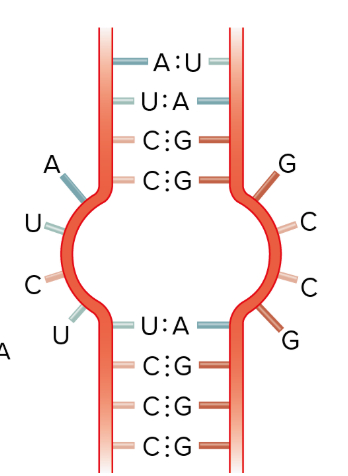
What is this?
RNA Internal loop
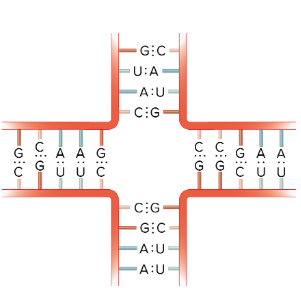
What is this?
RNA Multibranched junction loop
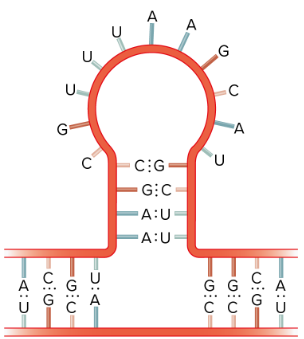
What is this?
RNA stem loop
What bases are found in DNA?
A-T, G-C
What bases are found in RNA?
A-U, G-C
What do cells always start with?
Replication
What are chromosomes?
Structures within living cells that contain genetic material
What are chromosomes biochemically composed of?
DNA and protein
What is chromatin?
The DNA-protein complex in eukaryotes
What two cells do animals have?
Somatic and germ cells
What are somatic cells?
Any cell that isn’t used for reproduction
What are germ cells?
Gametes AKA sperm and egg cells
What is cytogenetics?
The field of genetics that involves the microscopic examination of chromosomes
How many chromosome sets do diploid species have?
Two
Are all species diploid?
No, polyploidy is common in plants and animals
When you look at homologous pairs, where are the genes placed?
They are in the same spot
What are a couple of purposes of cell division?
To be able to do asexual reproduction and to achieve multicellularity; one real life example is humans starting out as a single fertilized egg and ending up as an adult with many trillion cells
What is DNA replication?
The process by which the genetic material is copied
What can original DNA strands be used for?
Templates for the synthesis of new strands
How do you READ DNA in replication?
From the 3’ to 5’ end
How do you SYNTHESIZE DNA in replication?
From the 5’ to 3’ end
Where does replication occur in bacteria?
Both ends of the chromosome no matter the shape since it’s bidirectional
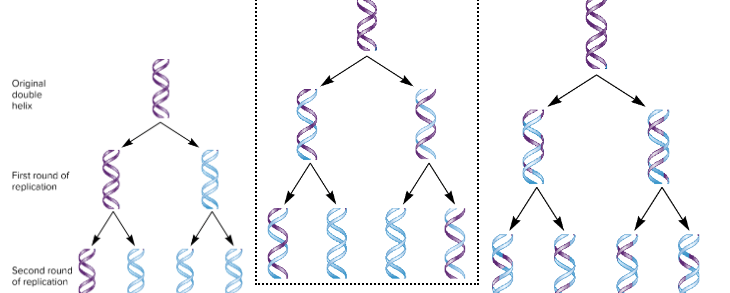
Which model of replication is correct? What is the name?
The middle one is the correct one. It’s the semiconservative model
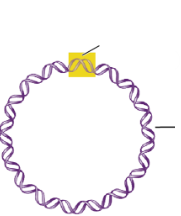
What is the yellow spot?
The origin of replication in a bacterial chromosome
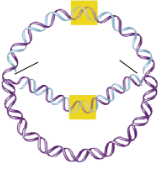
What are the black lines pointing to?
The replication forks in a bacterial chromosome
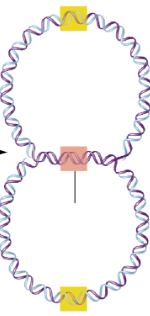
What’s the red box?
The site where replication ends in a bacterial chromosome
How is bacterial chromosome replication initiated?
The binding of DnaA proteins to the origin of replication
Where will DNA strands separate initially?
At the AT-rich region
What are DnaA boxes?
Sequences that provide binding sites for DnaA proteins
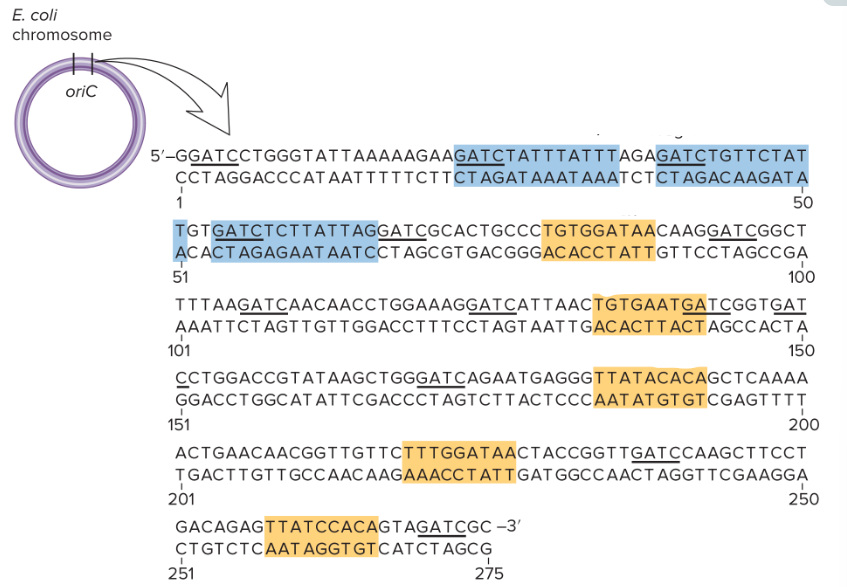
What are the blue boxes? What are the orange boxes?
The blue ones are AT-rich regions and the orange ones are DnaA boxes
Where does bacterial chromosome replication get the energy to replicate?
From ATP
What regulates replication in bacterial chromosome replication?
GATC methylation sites
What does DNA adenine methyltransferase do?
Methylates the A on both strands in bacterial chromosome replication
What do daughter strands do after bacterial chromosome replication?
Immediately adenine is incorporated into the daughter strands
What can DNA polymerase III NOT do?
Replicate on an empty strand
How does helicase coil? What fixes it?
Helicase coils positively so gyrase coils negatively
What does DNA polymerase III do?
Synthesizes a daughter strand of DNA
What does DNA polymerase I do?
Excises RNA primers and fills in the space with DNA
What does DNA ligase do?
Covalently links DNA backbones in the Okazaki fragments together
What other DNA polymerases can be found in Escherichia coli?
DNA polymerase I, II, III, VI, and V
What do single strand binding proteins allow?
They allow for nucleotides to come in
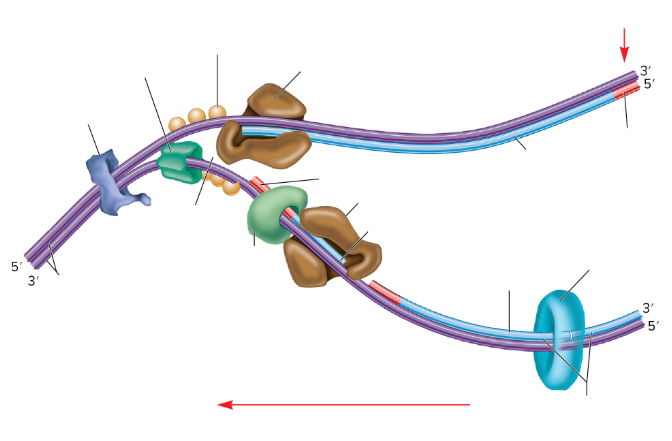
What is the lumpy dark blue thing?
DNA gyrase
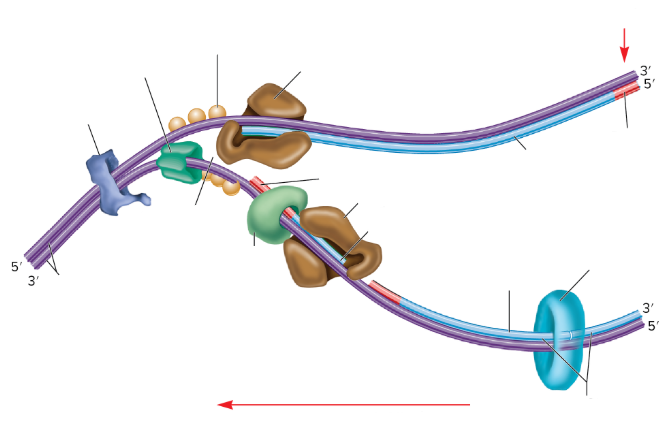
What is the dark green thing?
DNA helicase
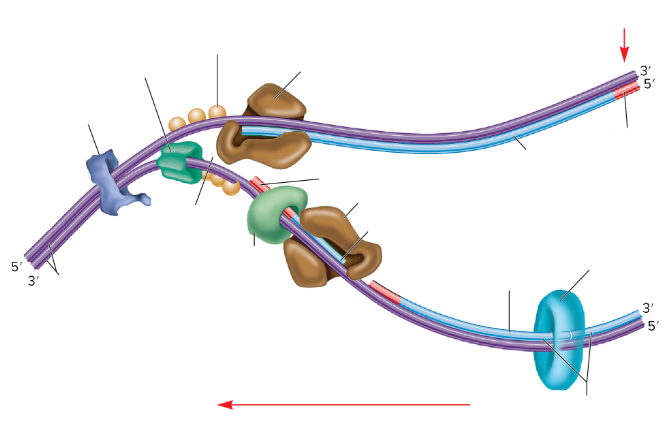
What is the lighter green thing?
Primase
What does primase do?
Synthesizes RNA primers
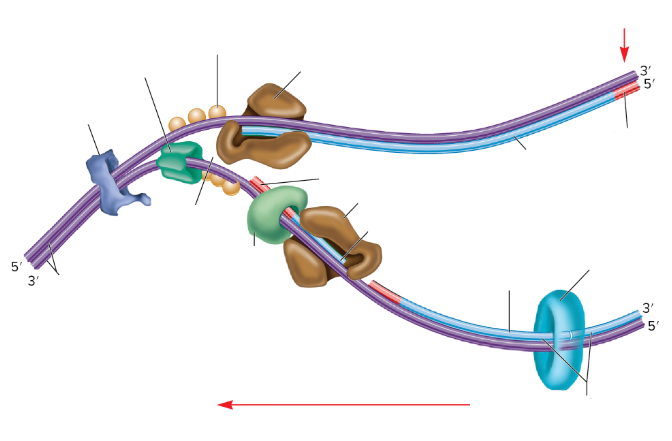
What is the empty space in the DNA called?
The replication fork
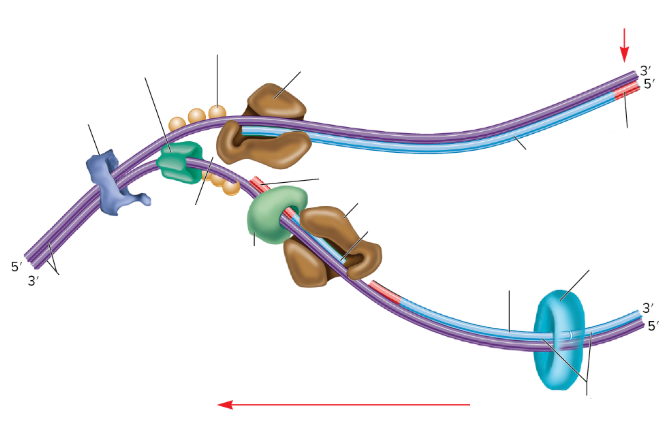
What are the two big brown things?
DNA polymerase III
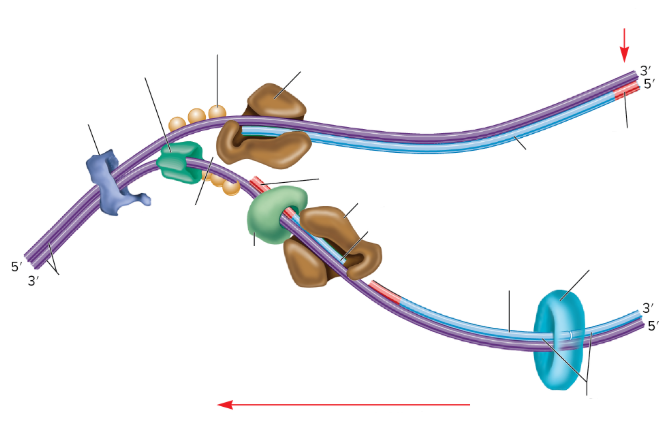
What is the red part on the strands supposed to be? (not the arrows)
RNA primer
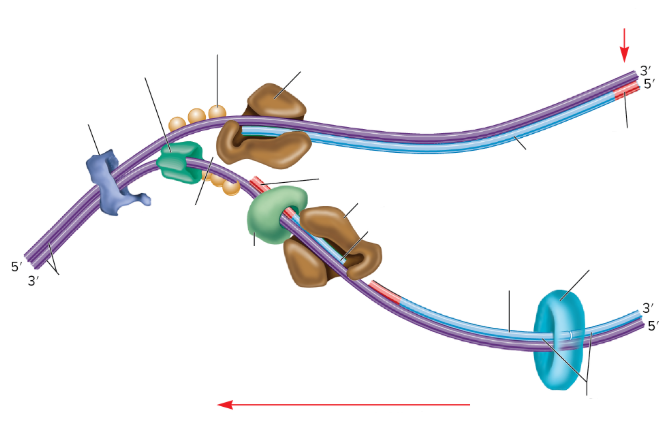
What are the three light orange balls?
Single-strand binding proteins
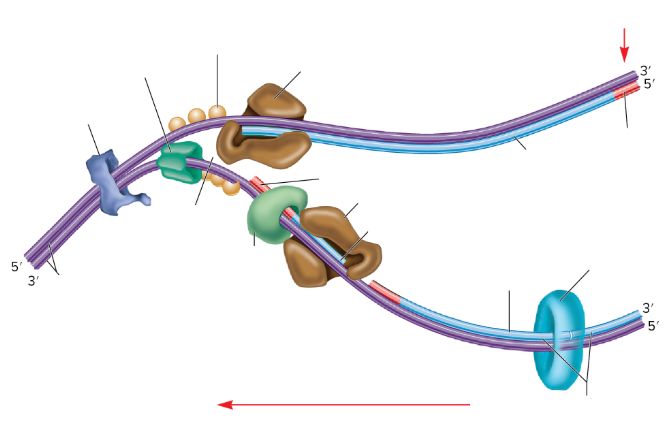
What is part of the DNA still connected together called?
Parental DNA
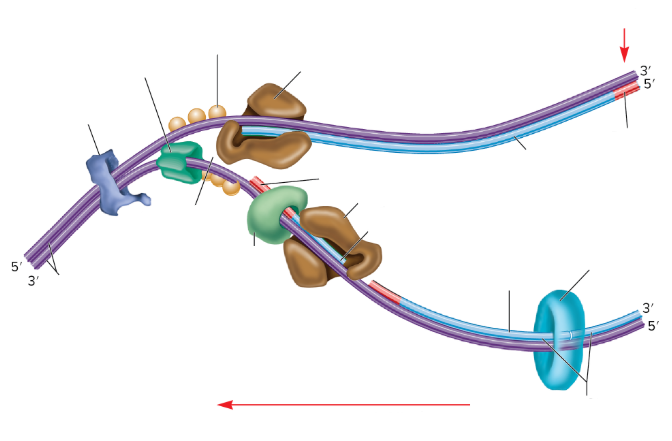
What is the light blue circle thing?
DNA Ligase
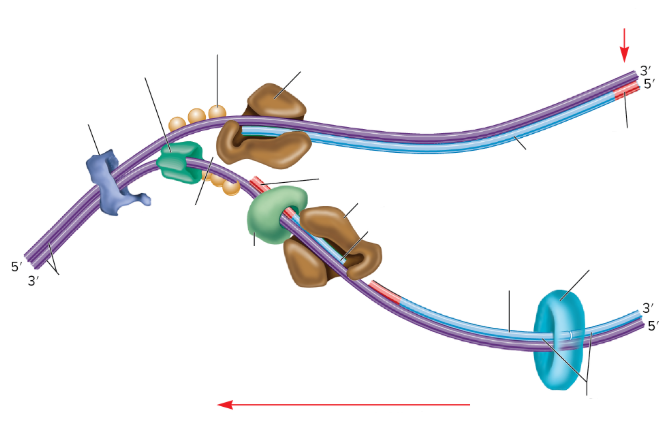
Which one is the leading strand? Why?
The top one is the leading strand because it’s going from the 5’ to 3’
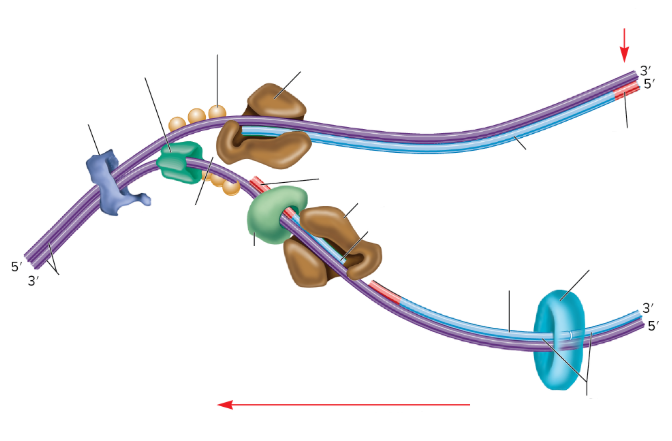
Which one is the lagging strand? Why?
The bottom strand because it’s going from 3’ to 5’
What does Tus in E. coli DNA replication do?
Binds to ter sequences and prevents the advancement of the replication fork
What do Tus proteins do?
Help separate chromosomes
What does TER 1 and TER 2 do?
End replication— when they’re still together the bacteria is called catenanes
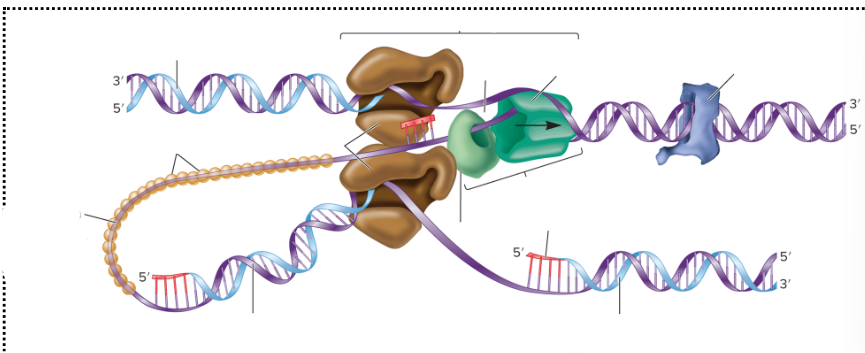
What is this?
A three dimensional view of DNA replication
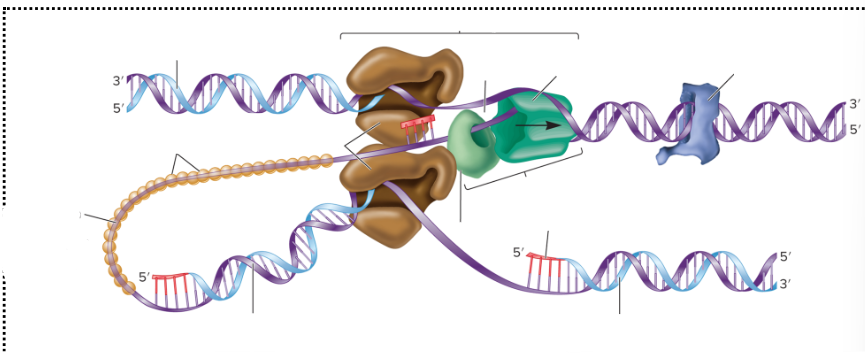
What is the brown, dark green, light green thing together called?
It is a replisome
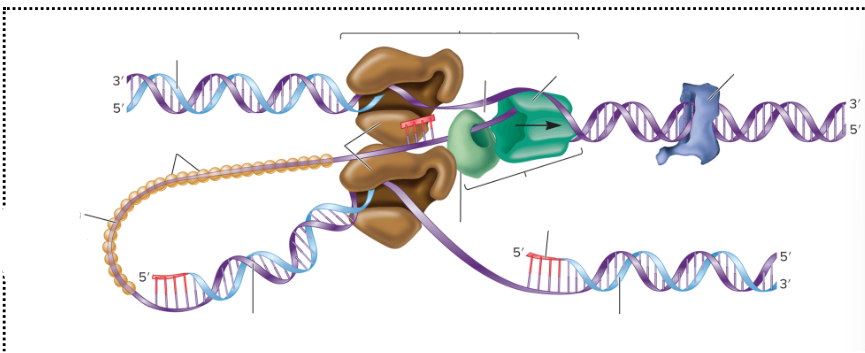
What is the dark green and light green thing called?
It’s the primosome