Unit 12- Secretions and Sonographic Appearance (Elie)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are all of the steroids that the cortex secretes?
Mineralocorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Sex Hormones
What do the mineralocorticoids do?
Regulate electrolyte metabolism
What is the principal mineralocorticoid?
Aldosterone
Aldosterone plays a regulatory effect on what two things?
Mineral ions in body fluids
Water content of tissues
What does a low aldosterone result in?
Results in acidosis or lowered pH level
What role do glucocorticoids play in?
Plays a principal role in Carbohydrate Metabolism
What do Glucocorticoids do?
Promote deposition of glycogen
Inhibit use of glucose by cells
Result is increased blood sugar level
What are the two primary glucocorticoids and what do they do?
Cortisone
Hydrocortisone
Diminish allergic response
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatic fever
What are the male and female sex hormones?
Androgens- Males
Estrogens- Female
The adrenals secretes both sex hormones regardless _______
Gender
An over secretion has a marked effect and causes what other effect?
A masculinizing effect
In women - excess facial hair due to an increase in androgens
In men - accelerated puberty process
What is the adrenal cortex regulated by?
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone – (ACTH)
What can Hypersecretion of cortical hormones be caused by?
Pituitary tumor
Causing overproduction of ACTH
Tumor of adrenal cortex
Cushing’s syndrome
Conn’s syndrome
Adrenogenital syndrome
What is the medulla secretion epinephrine?
Is a heart rate accelerator and contractility
What is the medulla secretion norepinephrine?
Vasoconstrictor- constricts blood vessels
What do both epinephrine and norepinephrine do?
Both promote glycogenolysis
Increase in blood sugar levels
What are the factors that affect secretions?
Pain
Emotional stress
Hypoglycemia
Hypotension
Cold
Is the medulla essential for life?
No, is not essential and can be surgically removed
What can Pheochromocytoma cause?
An increased production of medulla hormones
What is the prep for scanning adrenal glands?
None specifically required
Fasting 6-8 hours may eliminate bowel gas
Normal adrenal ultrasounds can be difficult due to:
Small size
Medial Location
Surrounding perirenal fat
Adrenal visualization depends on:
Size of patient
Amount of surrounding perirenal fat
Amount and location of bowel gas
Mobility of patient to various positions
What type of adrenal is easier to identify and separate from the kidney?
Enlarged/ abnormal adrenals
What is the US appearance of the Right Adrenal Gland?
“Comma” appearance, or triangular shape
Should not appear rounded
What is the US appearance of the Left Adrenal Gland?
Flatter, longer appearance
More medial
Separate from crus & GE junction
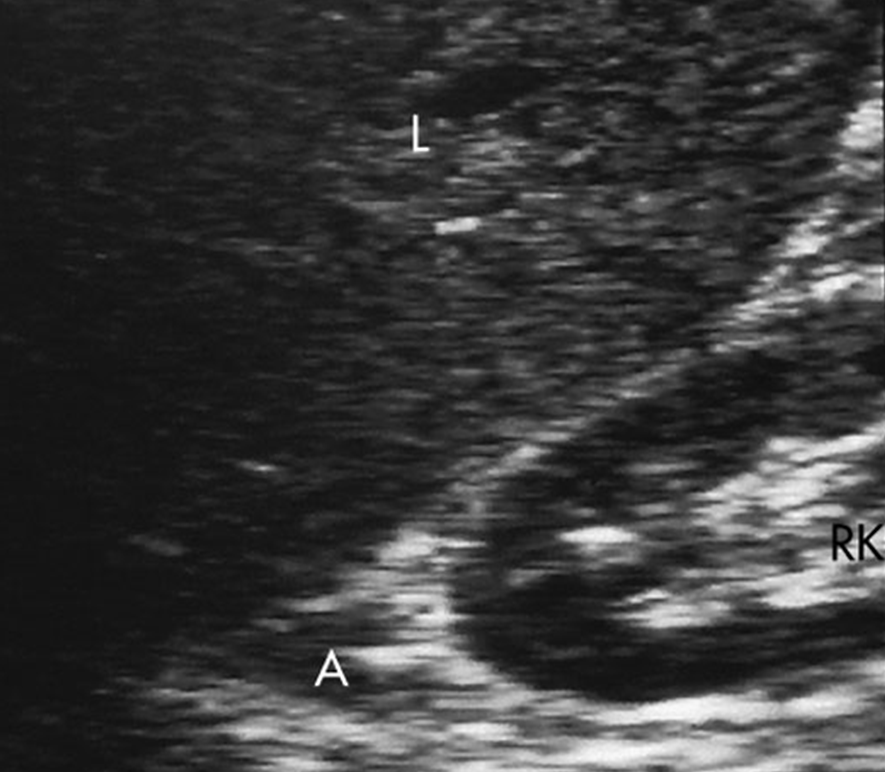
What is being labeled as A?
Right Adrenal Gland
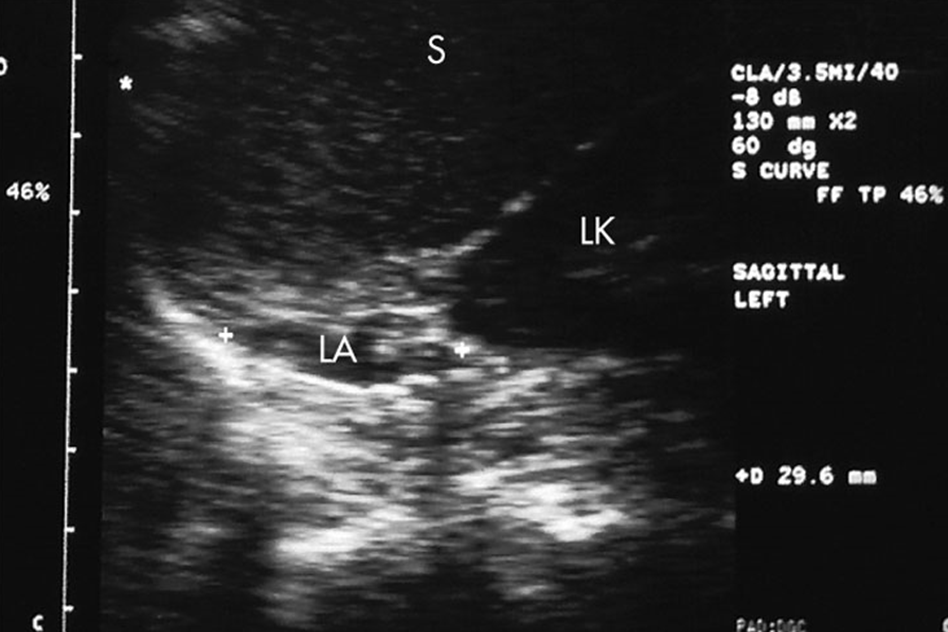
What is labeled as LA in the image above?
Left Adrenal Gland
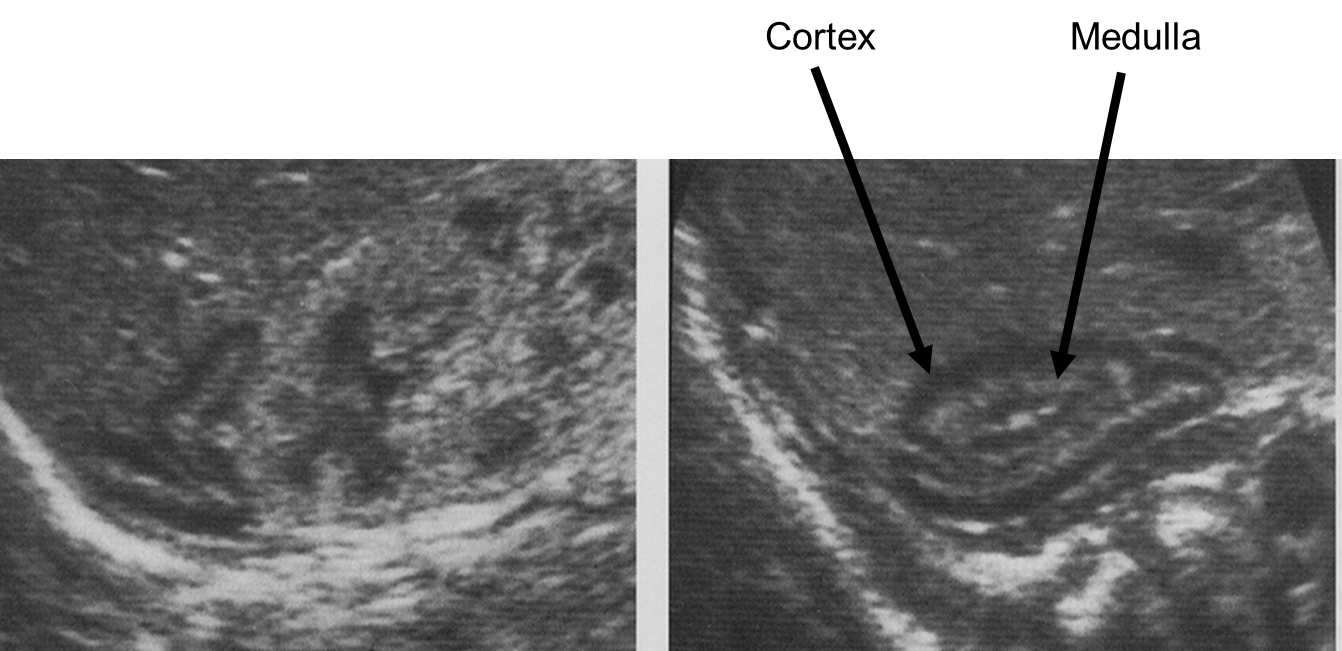
What is being shown in the image above?
Neonate adrenals- cortex and medulla
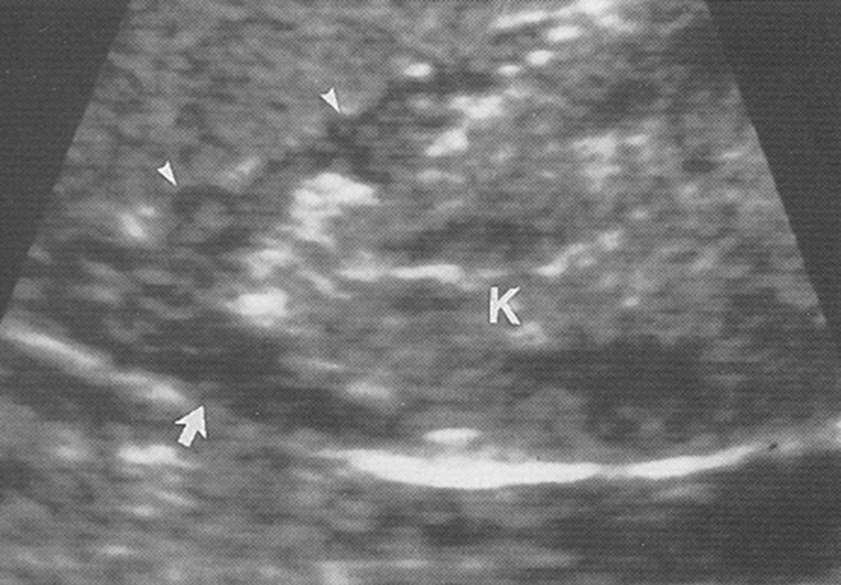
What is being shown in this image?
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
What are the sonographic pitfalls of the adrenals?
Rt. Crus of diaphragm
Duodenum
GE junction
Lobulations / Accessory spleen
Splenic vessels
Pancreatic body- tail / lesions
Retroperitoneal Lymphadenopathy