Chapter 12: Muscle Physiology
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
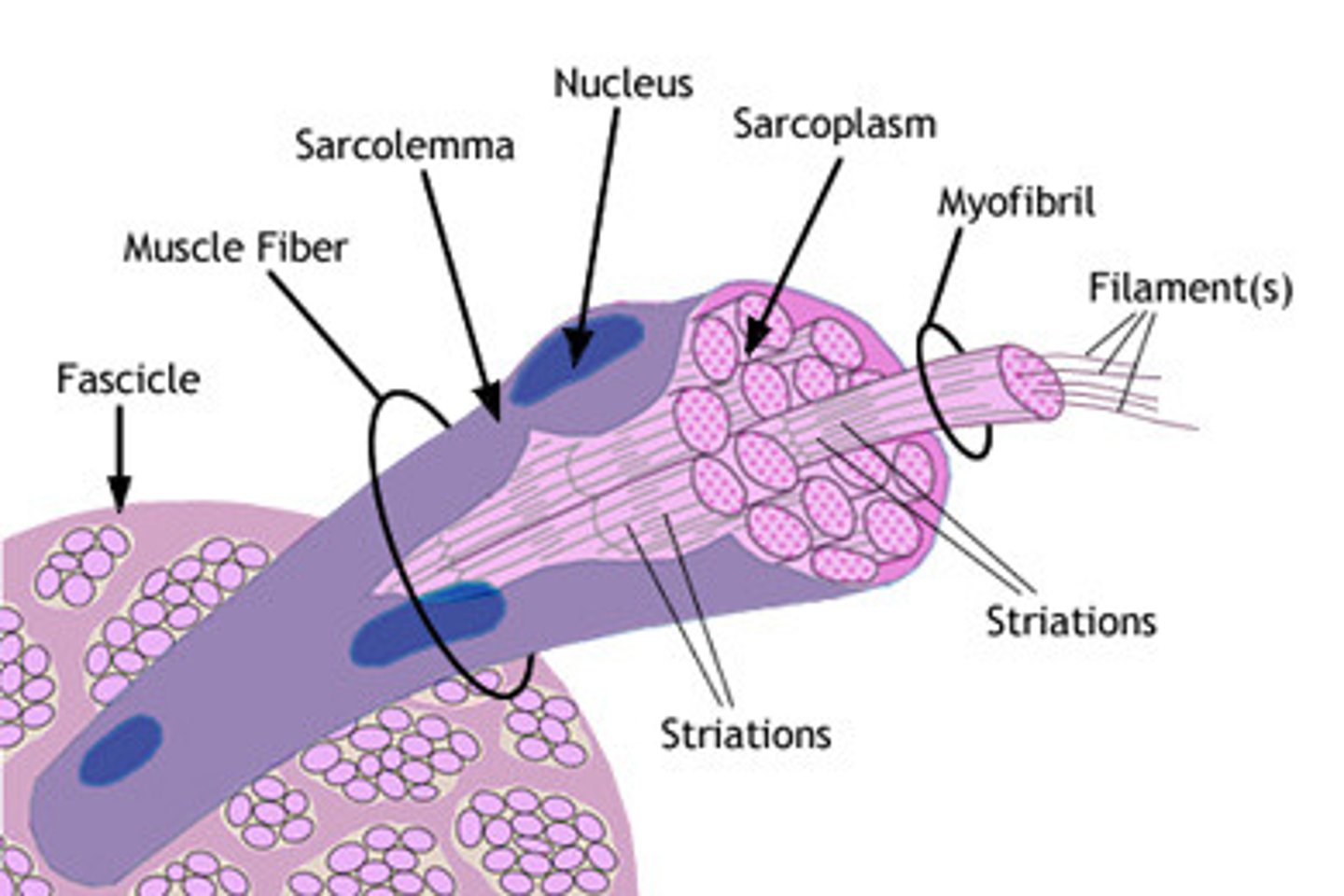
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
striated
marked with thin, narrow grooves or channels
cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart.
smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body
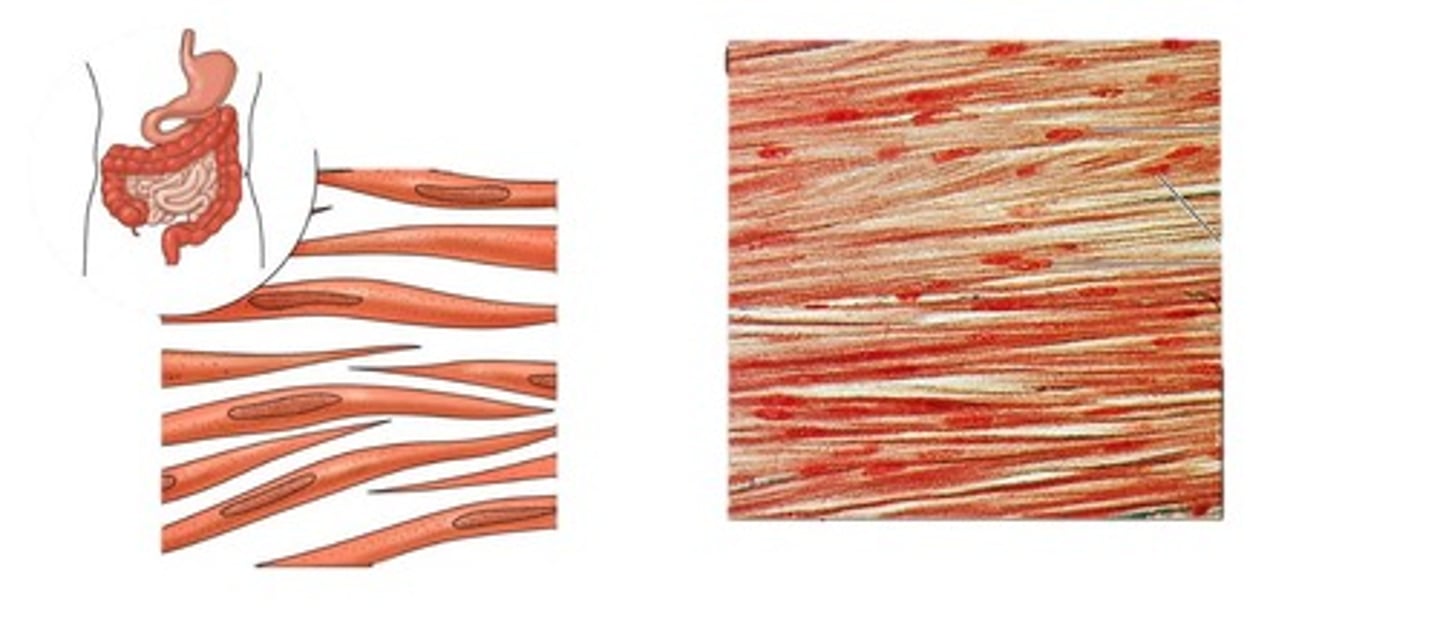
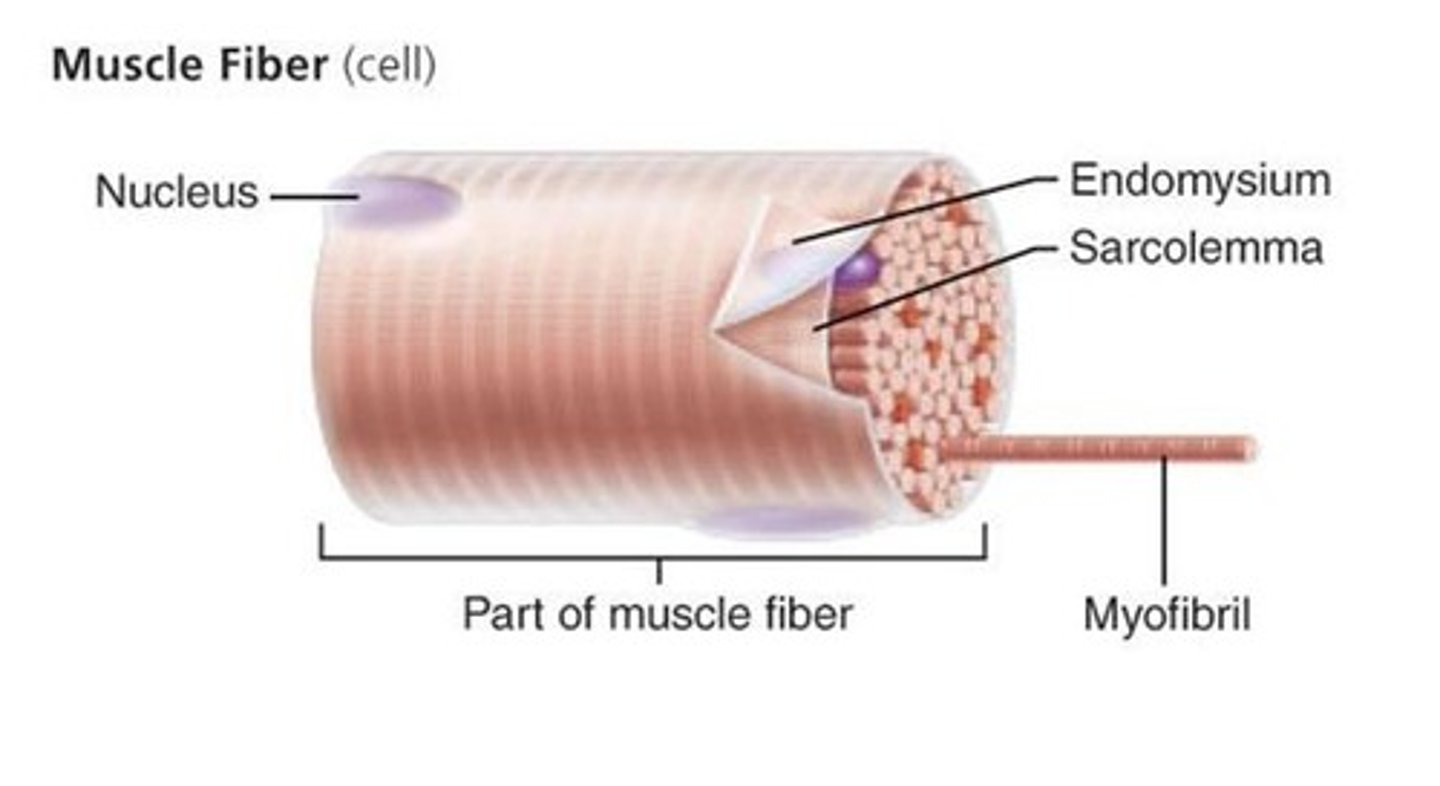
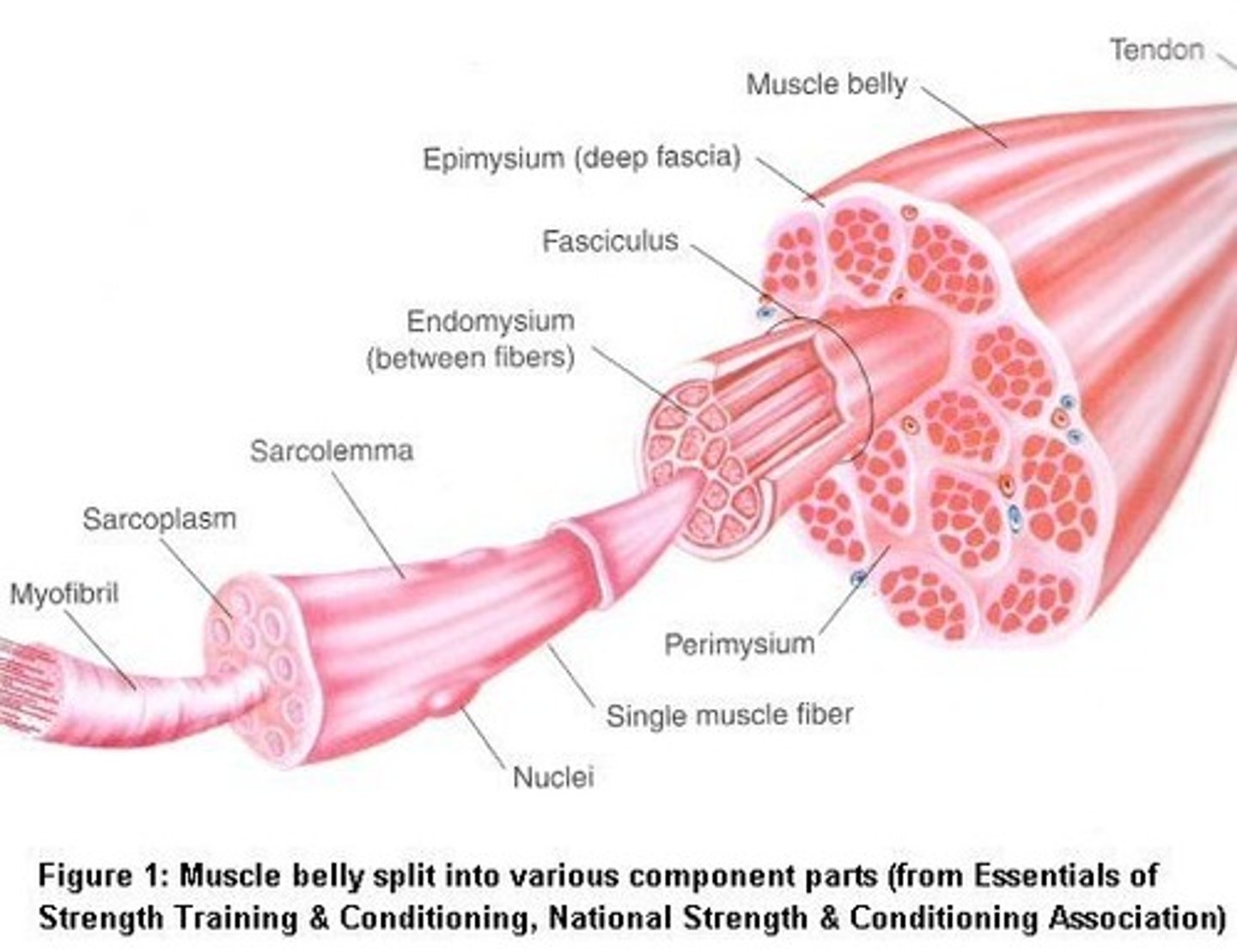
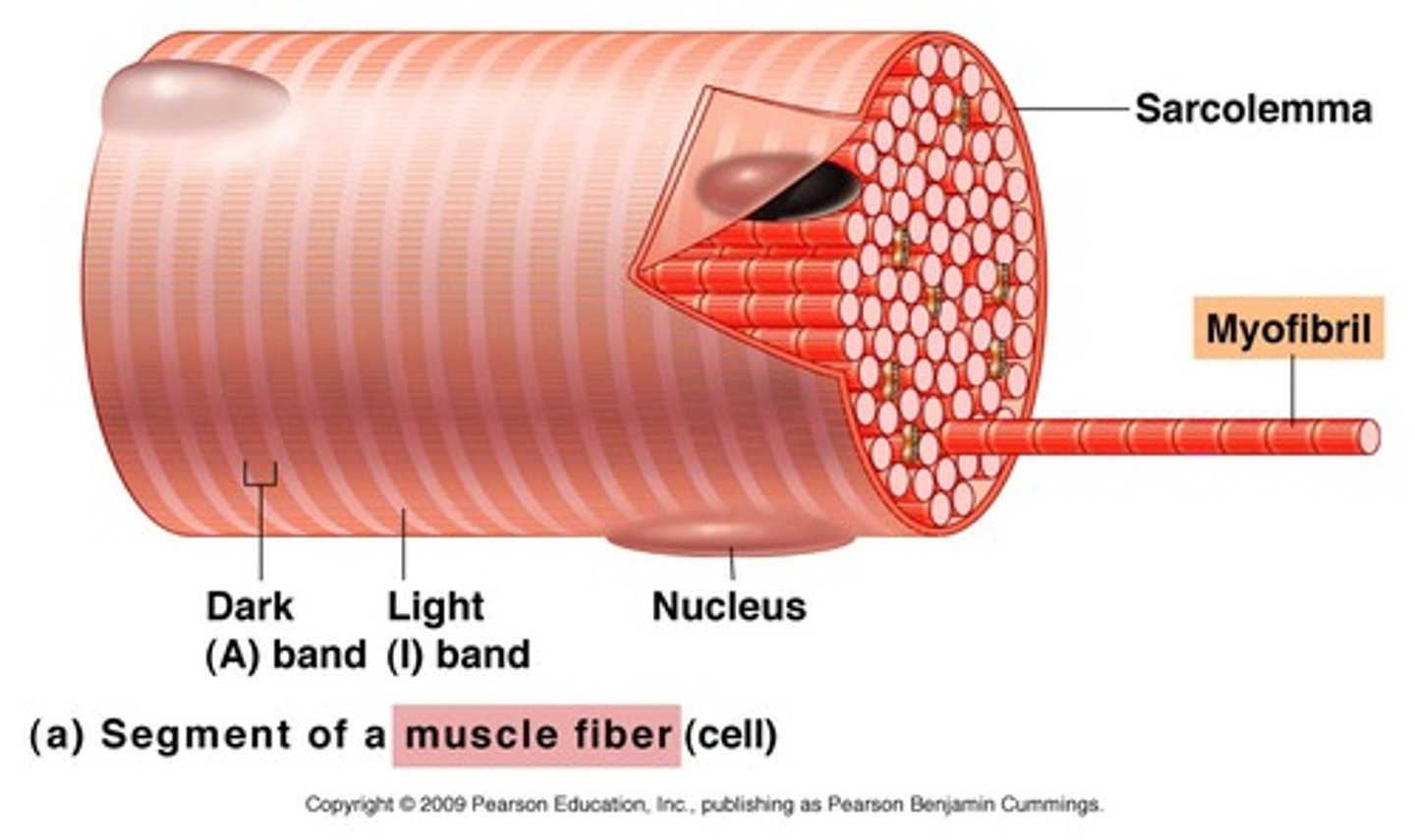
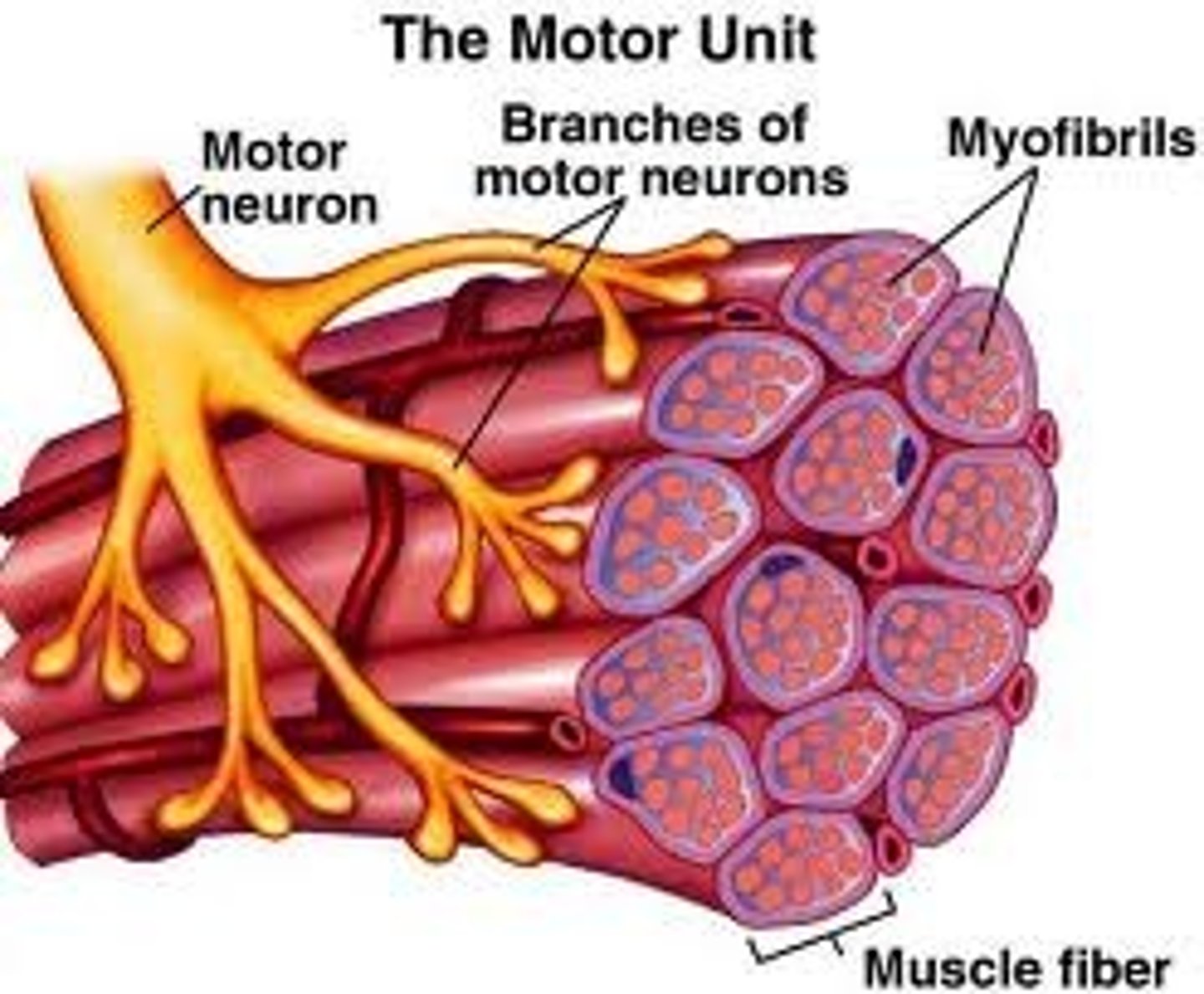
muscle fiber
long slender skeletal muscle cells
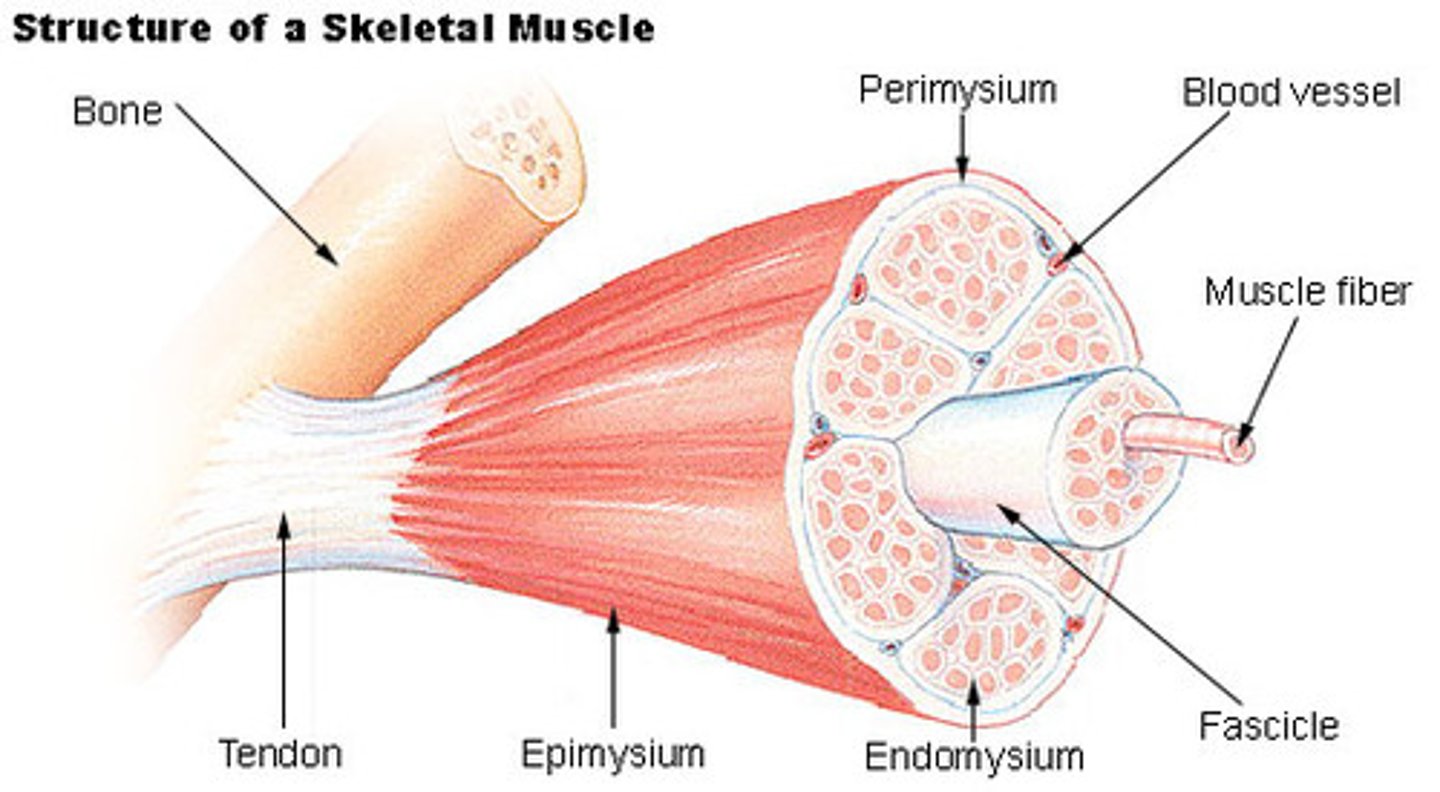
fascicles
Bundles of muscle fibers wrapped in perimysium
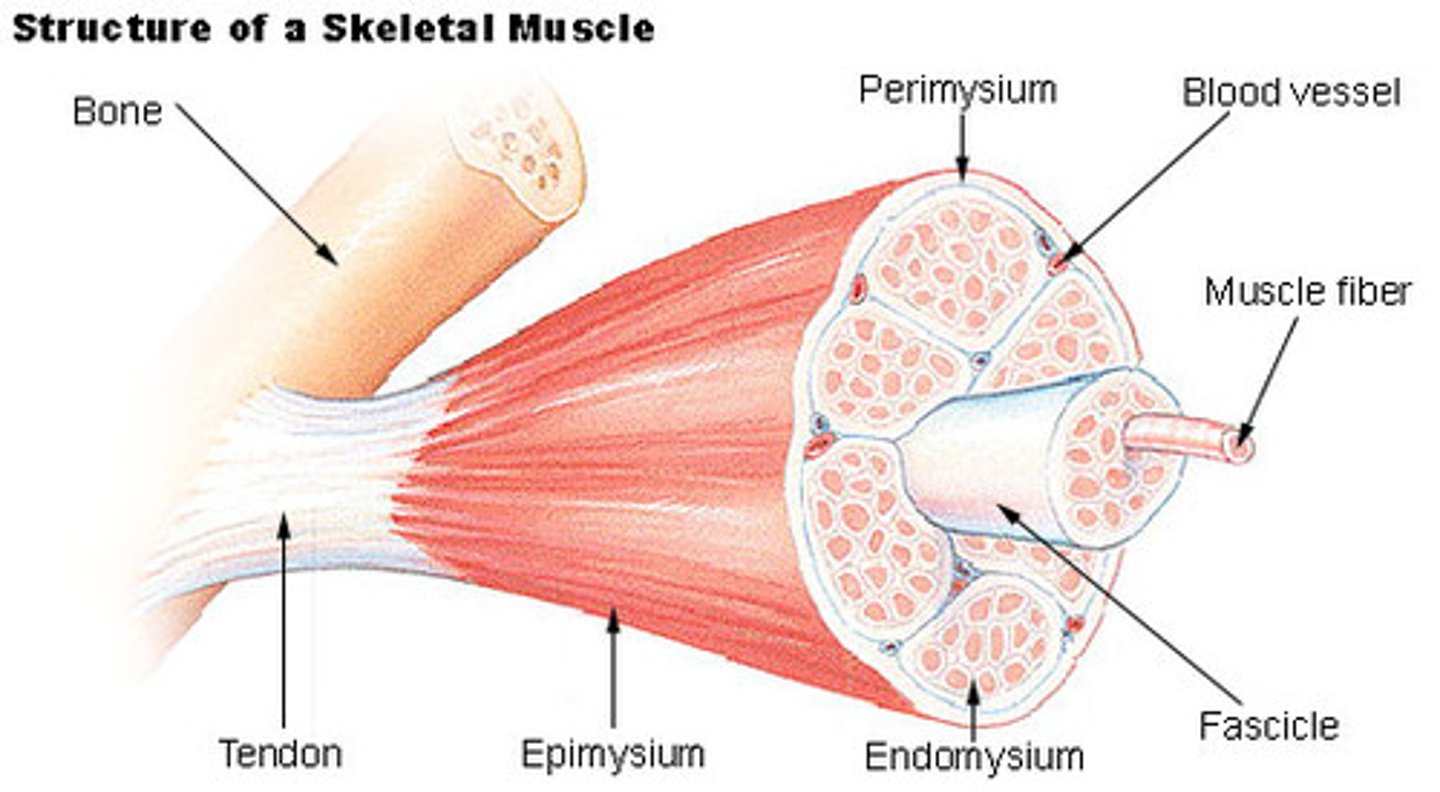
tendons
Connect muscle to bone
multinucleated
more than one nucleus per cell
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
transverse tubules
transmit muscle impulses into the cell interior.
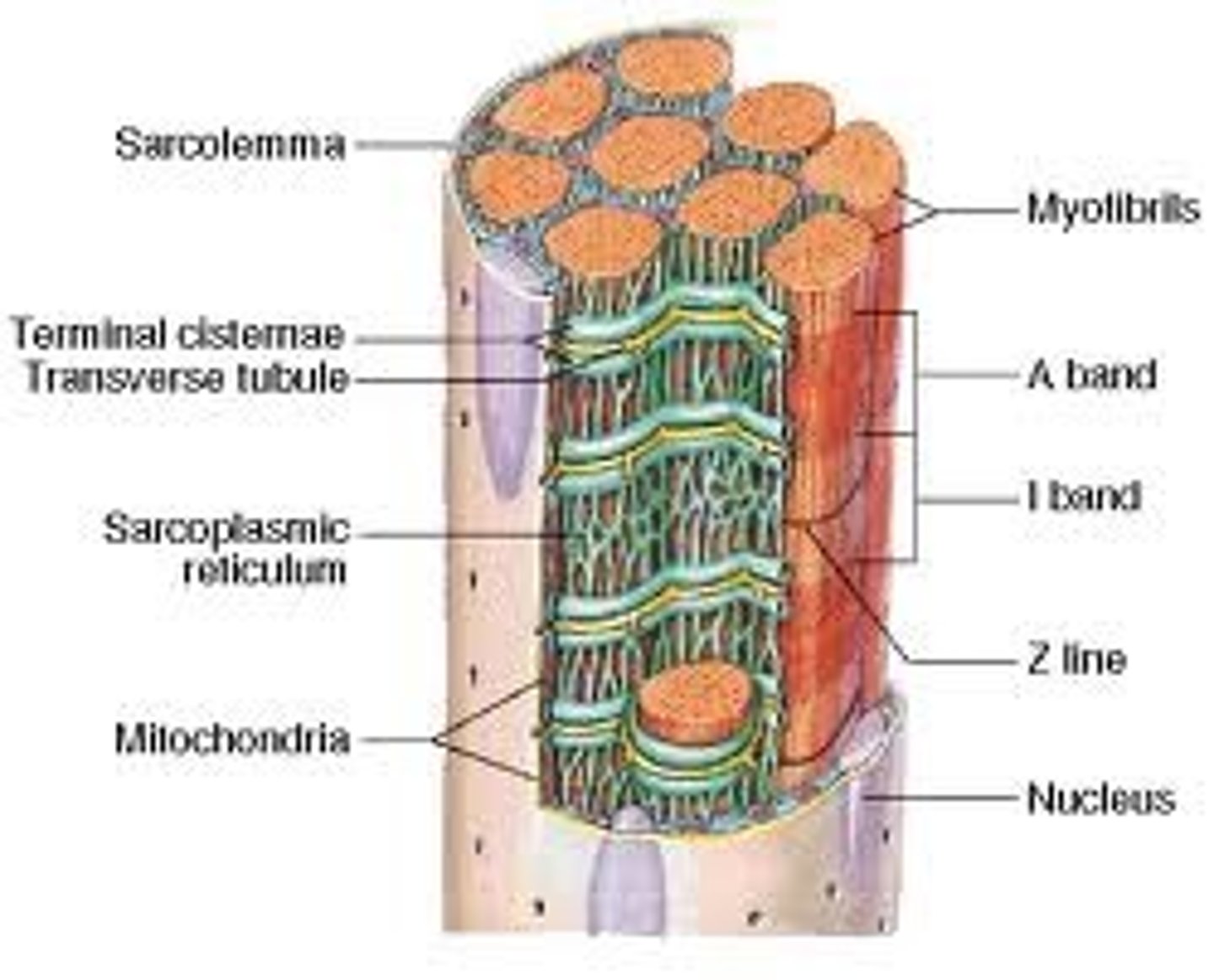
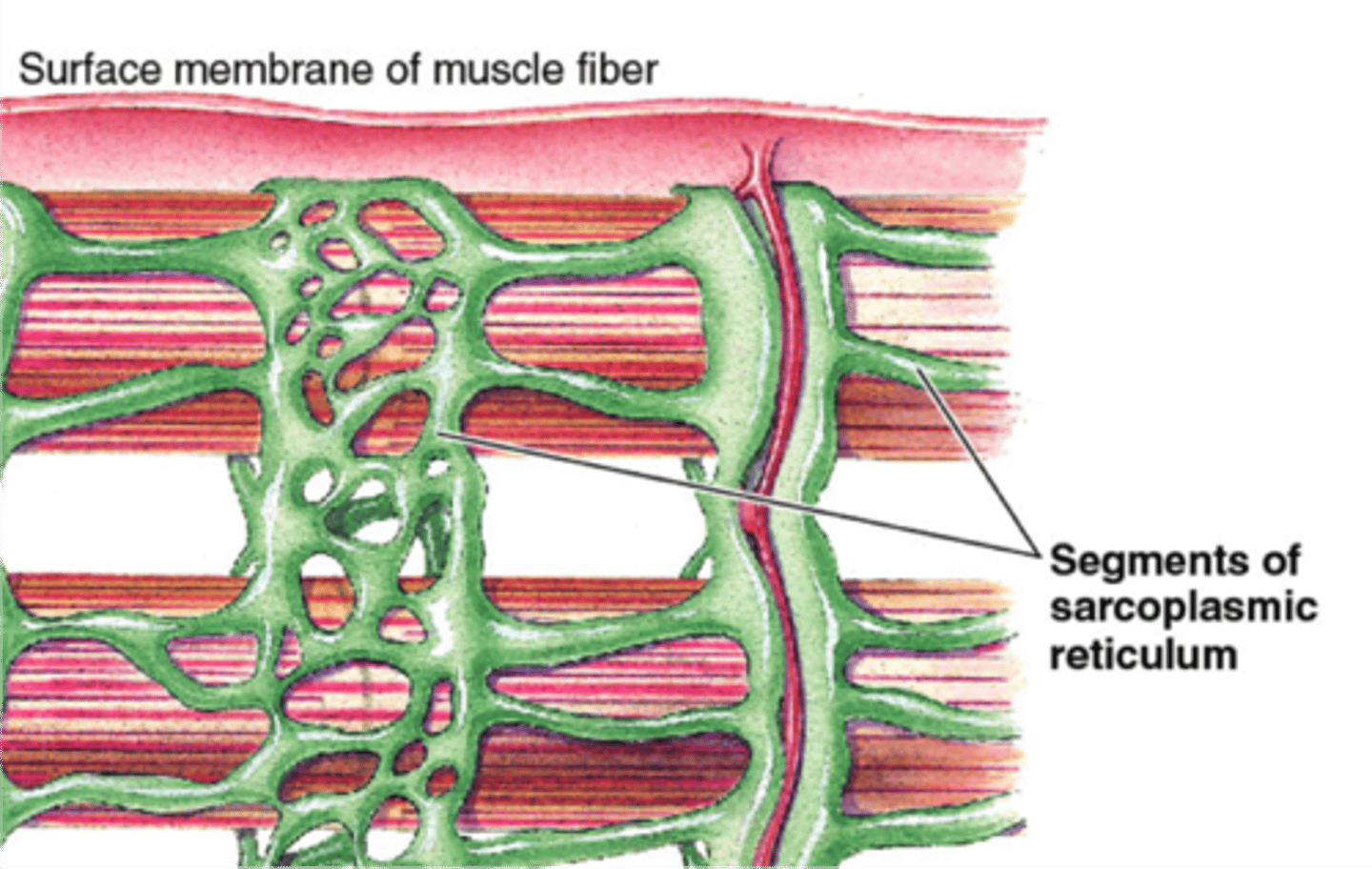
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium.
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
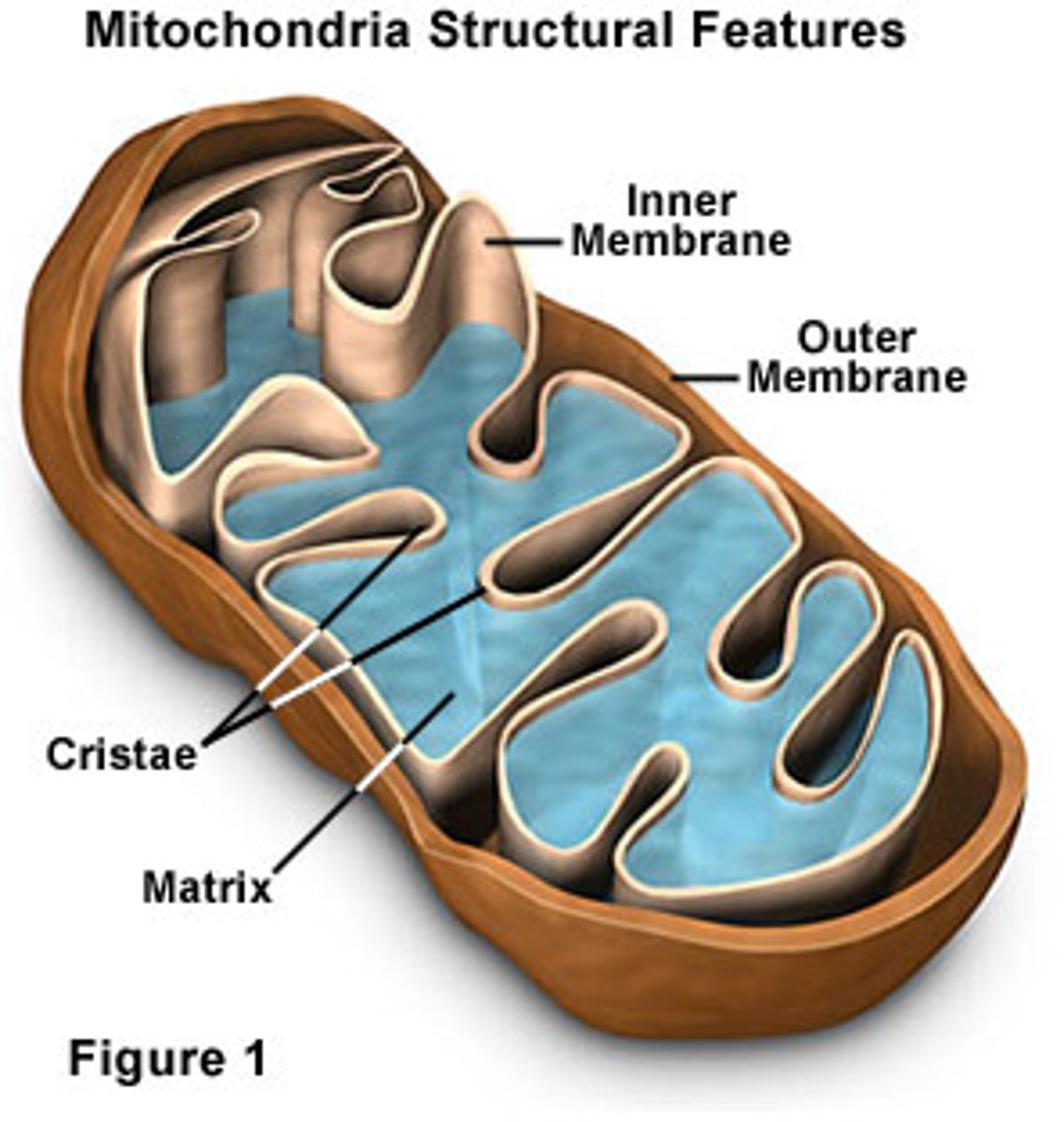
mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
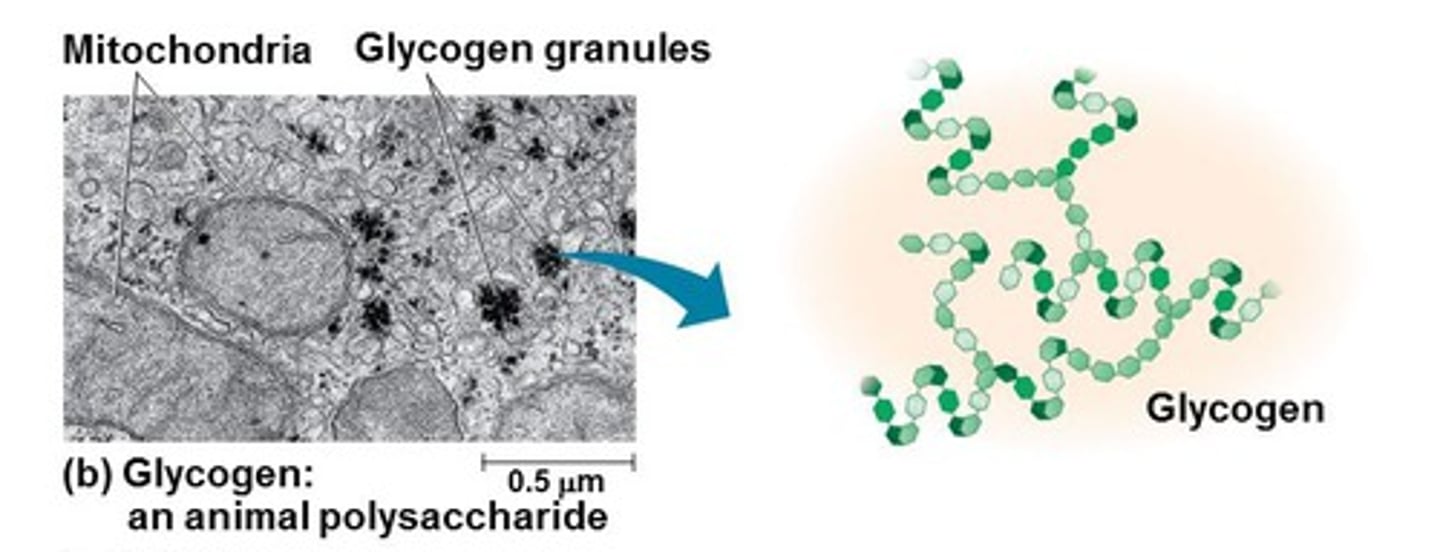
glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
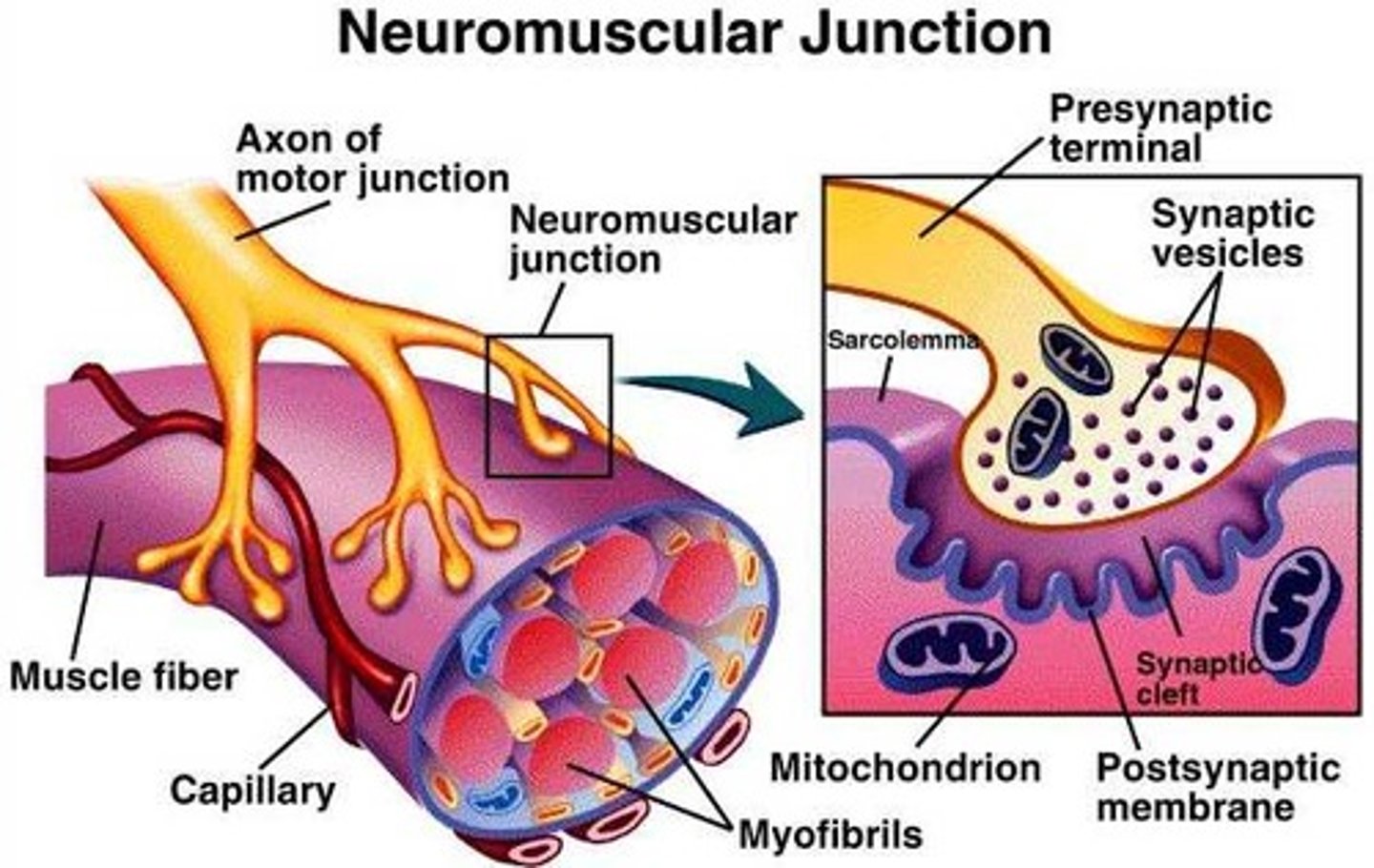
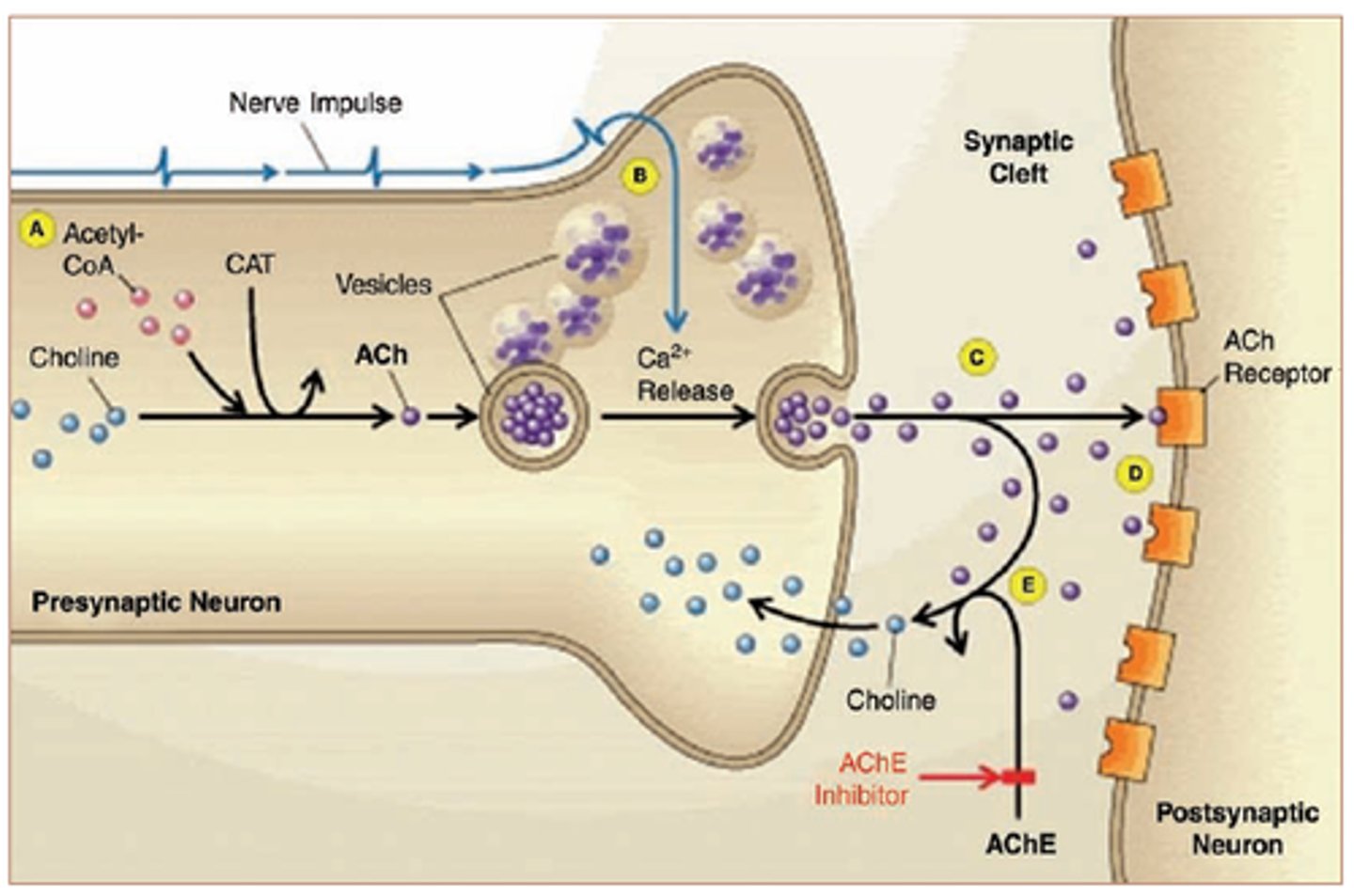
neuromuscular junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
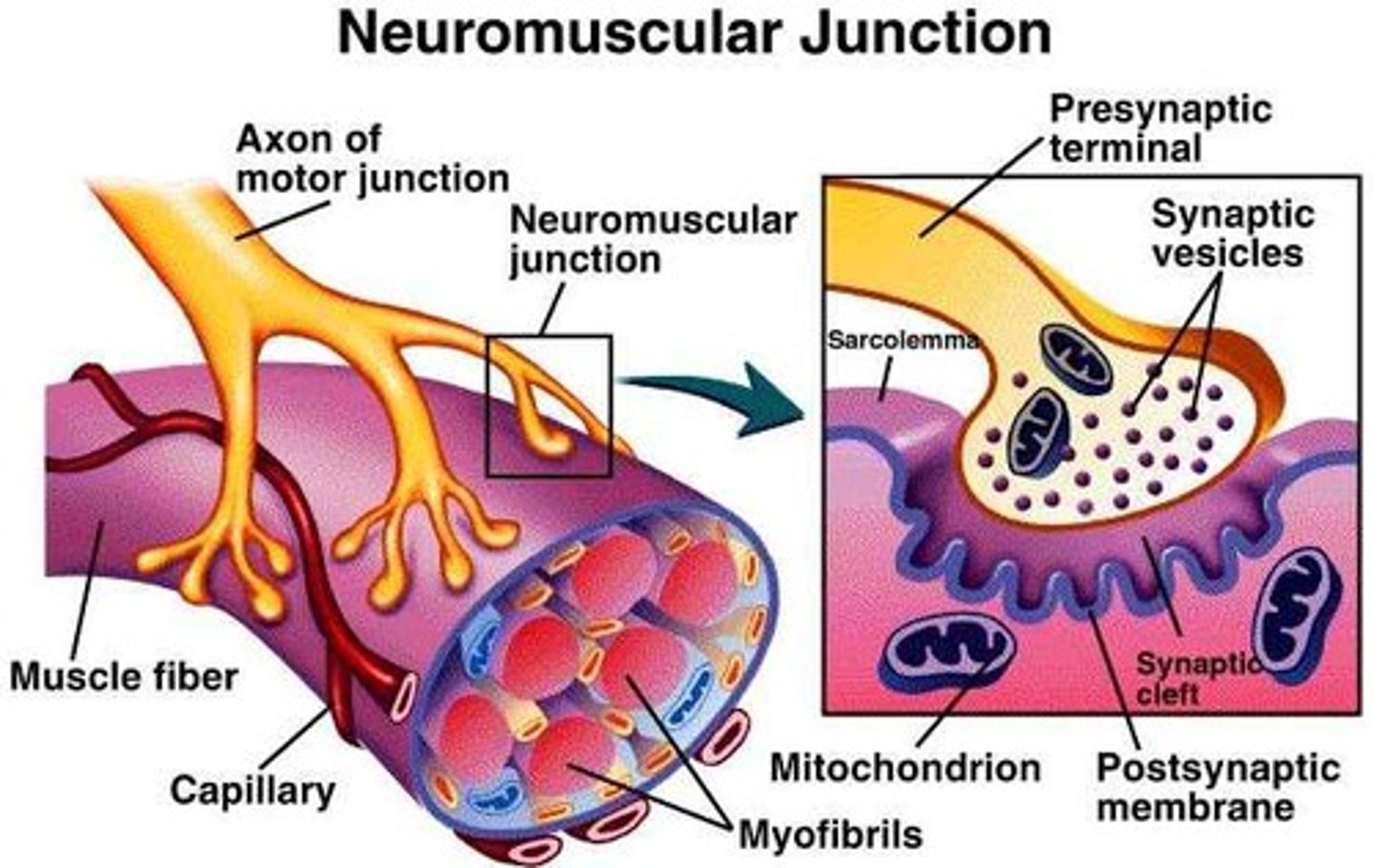
myofibrils
Microscopic protein filaments that make up muscle cells.
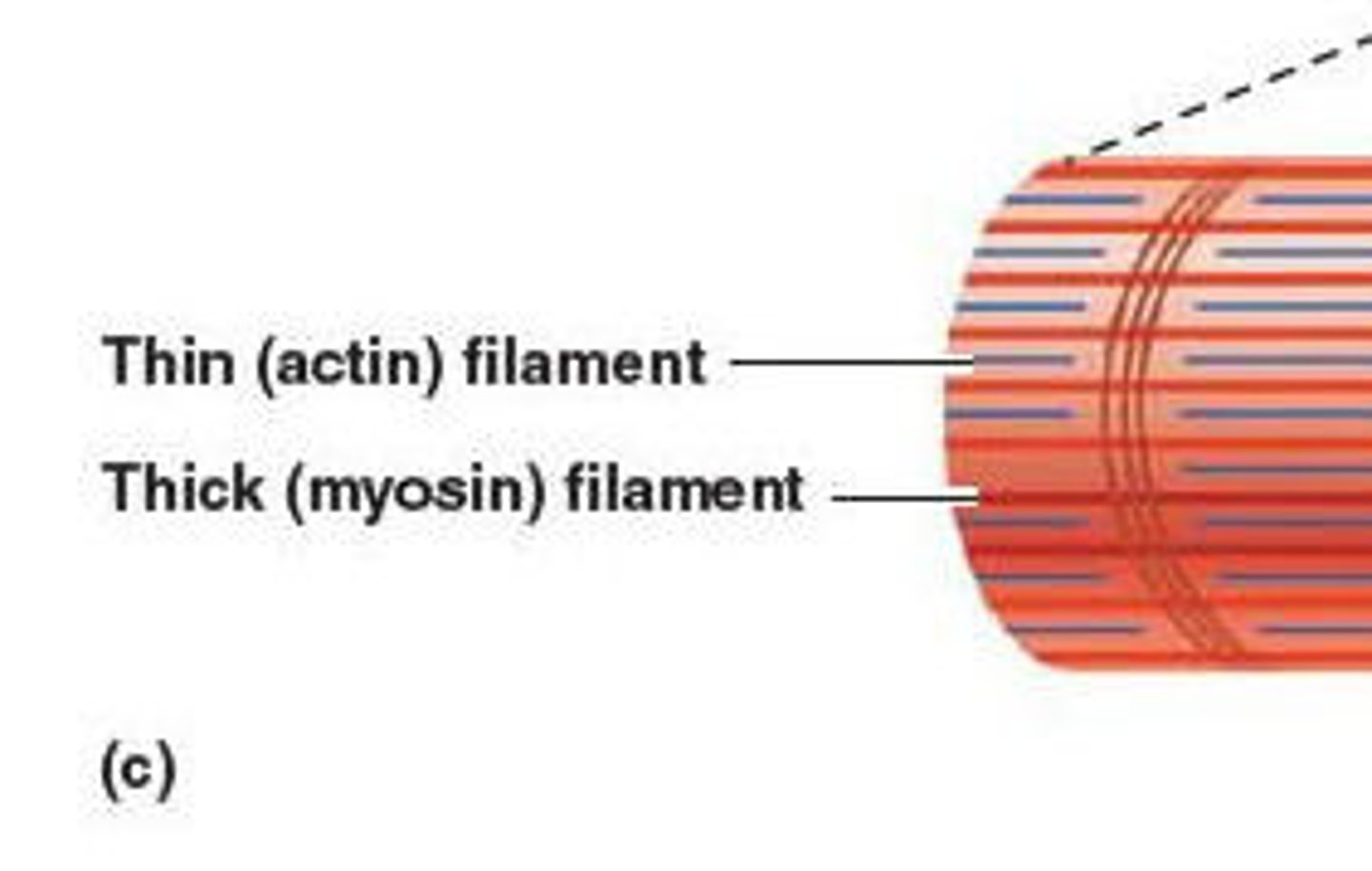
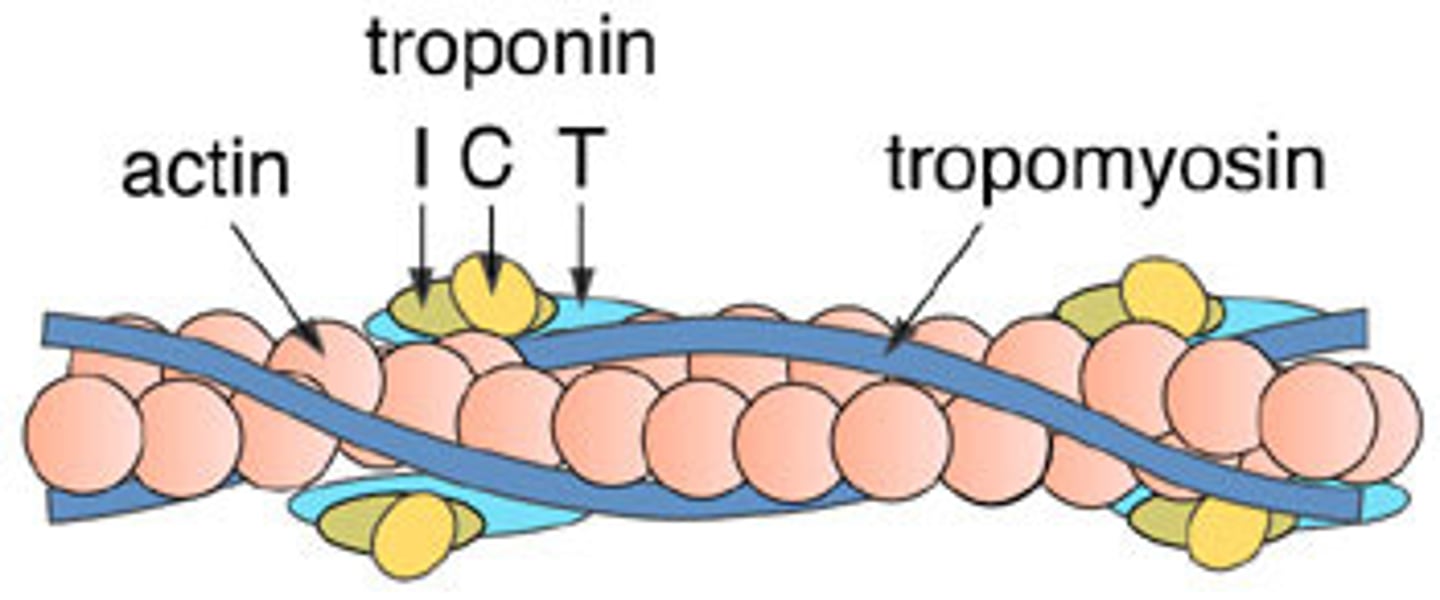
actin (thin filaments)
A globular protein that links into chains, two of which twist helically about each other, forming microfilaments in muscle and other contractile elements in cells.
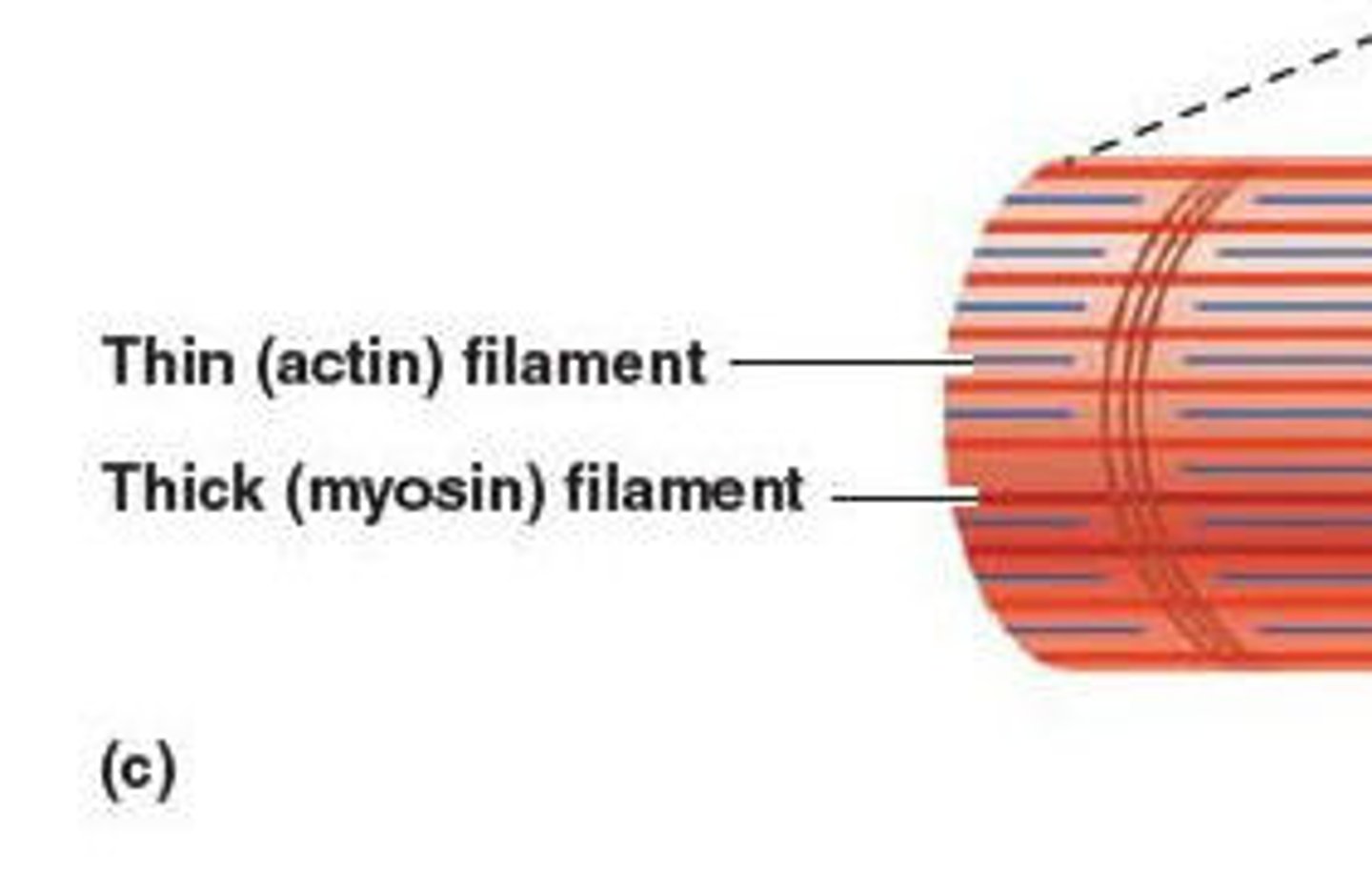
myosin (thick filaments)
a fibrous protein that forms (together with actin) the contractile filaments of muscle cells and is also involved in motion in other types of cells
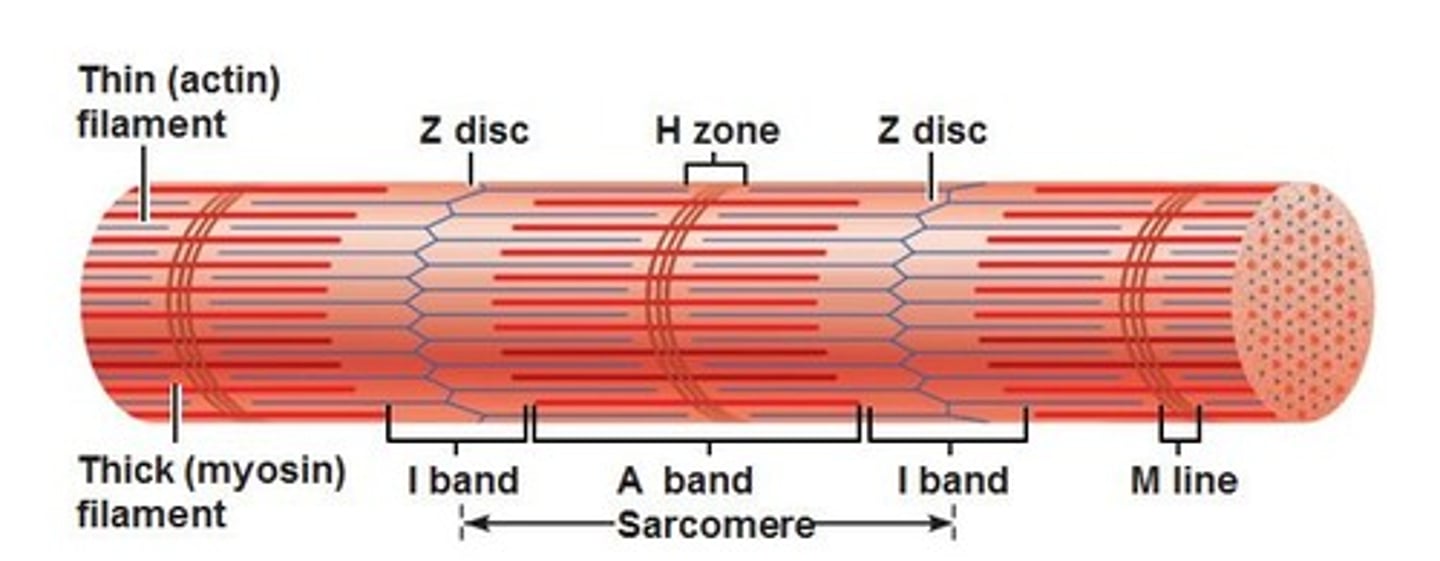
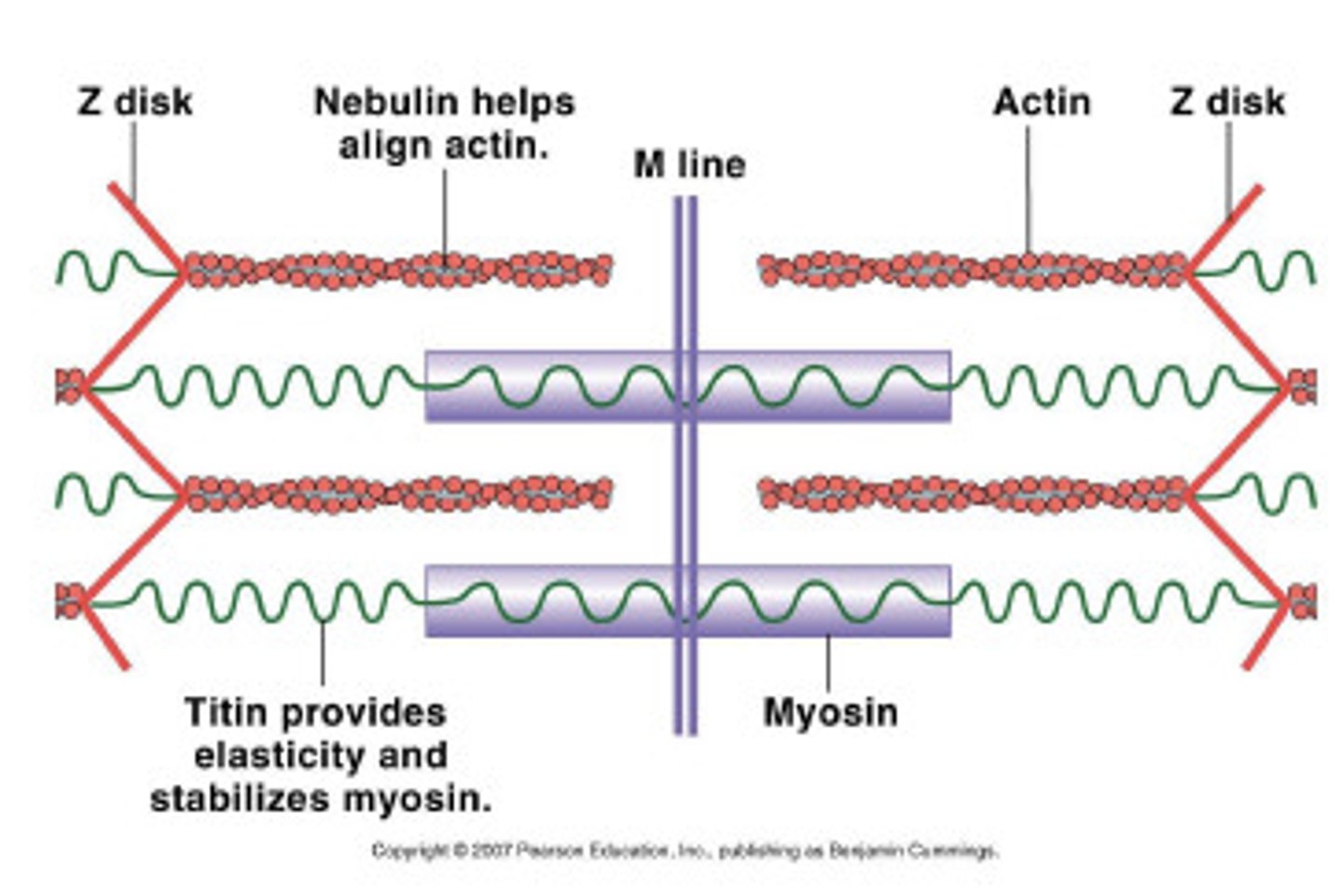
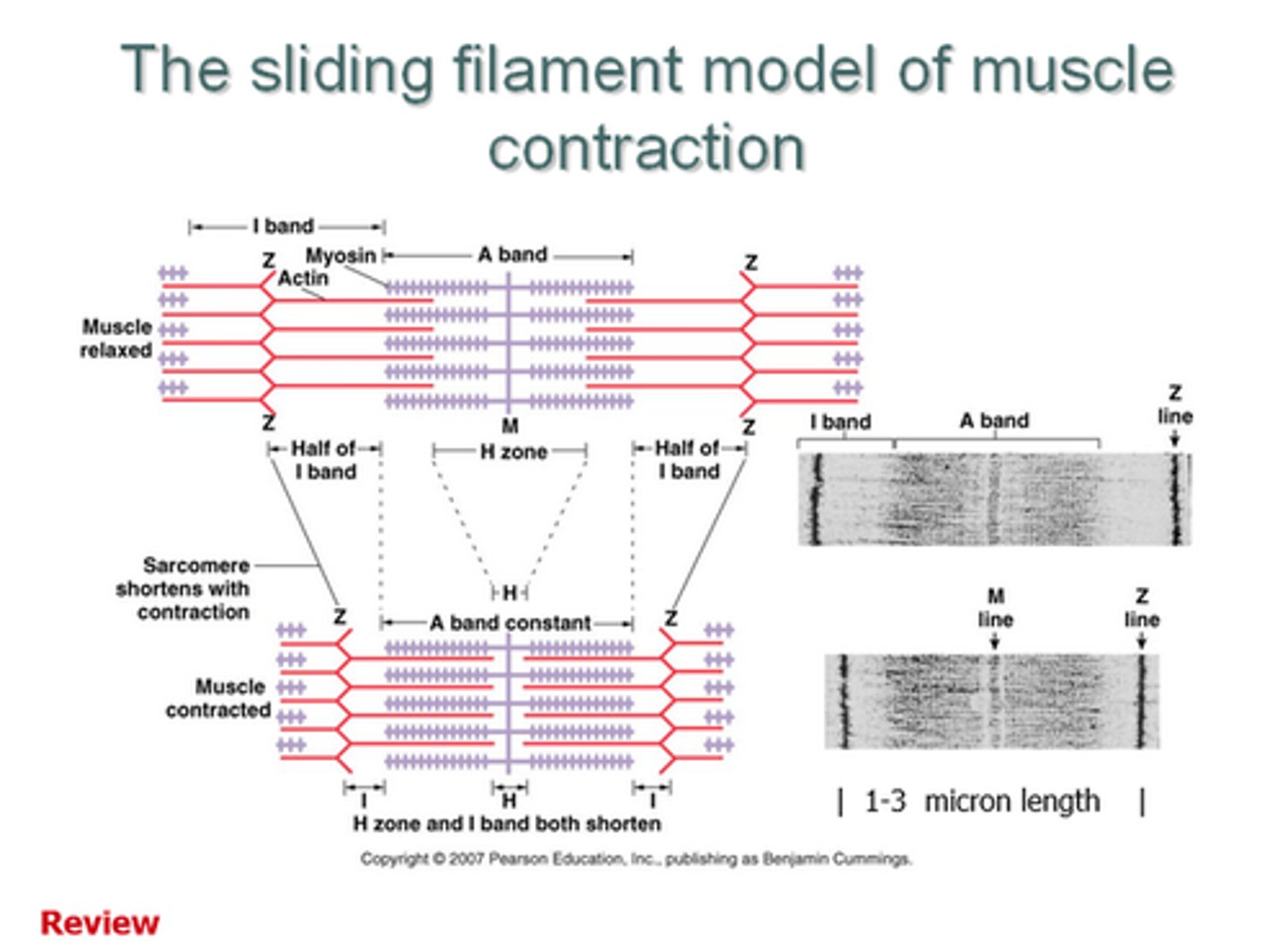
sarcomere
a structural unit of a myofibril in striated muscle, consisting of a dark band and the nearer half of each adjacent pale band.
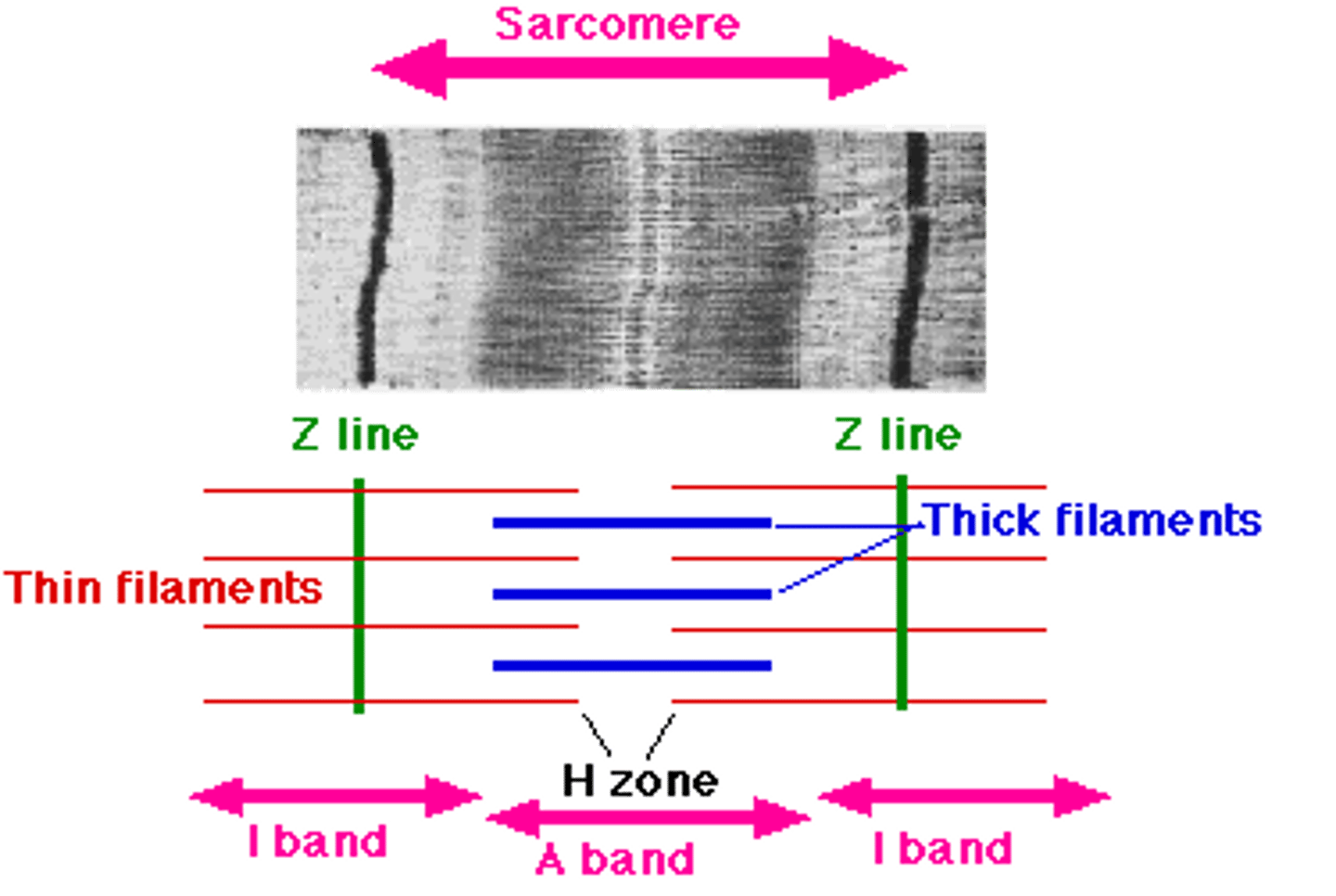
Z lines
define the boundaries of each sarcomere
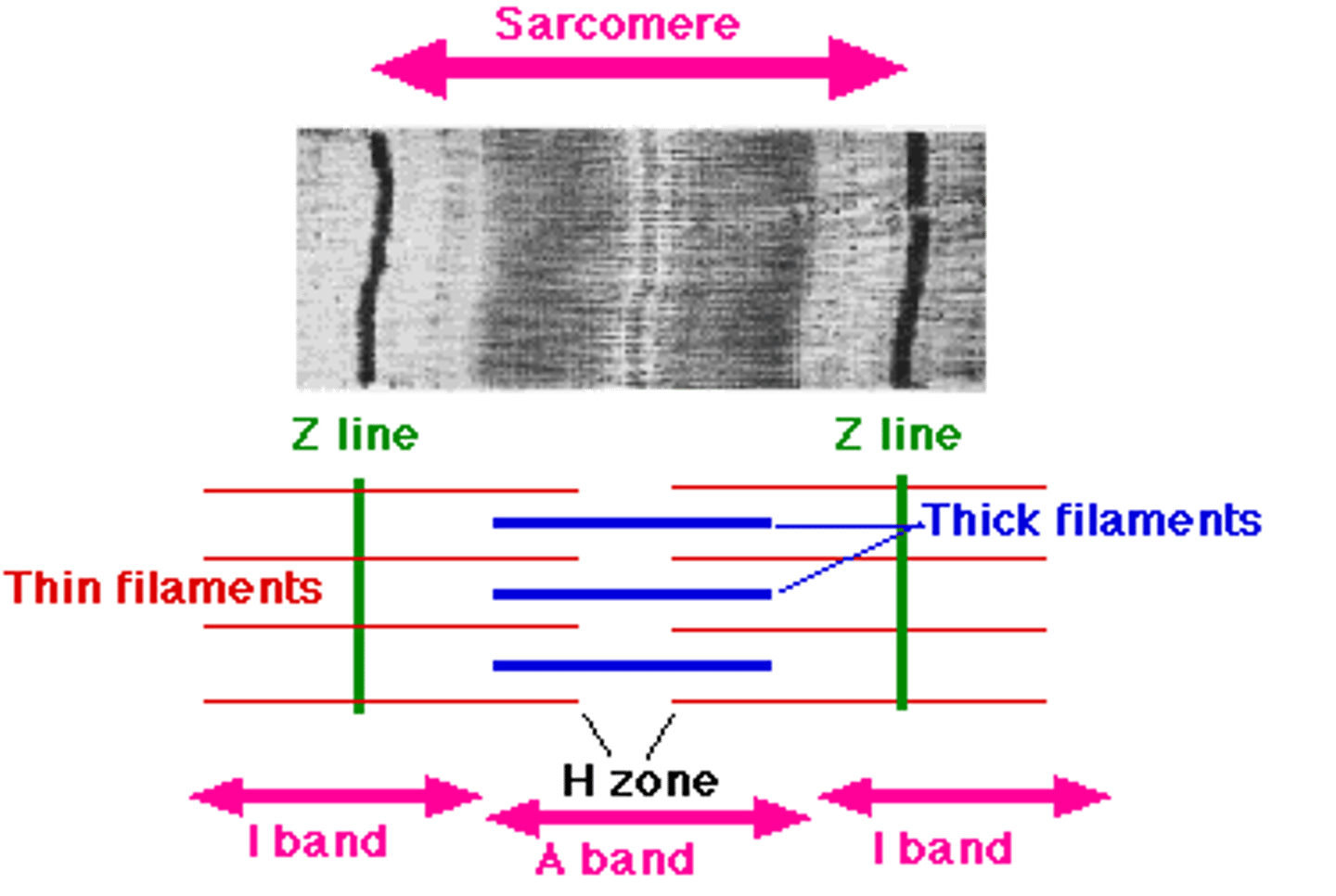
I band
thin filaments (actin) only
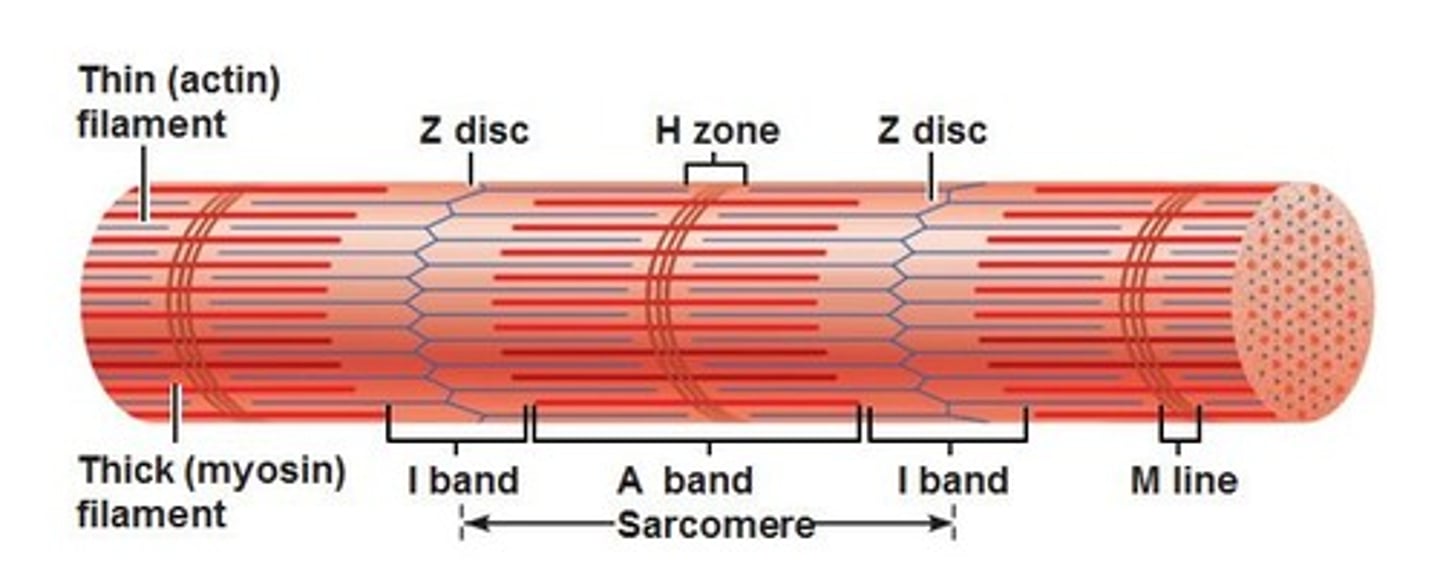
A band
dark area; extends length of the thick filaments
H zone
thick filaments only
M line
supporting proteins that hold the thick filaments together in the H zone
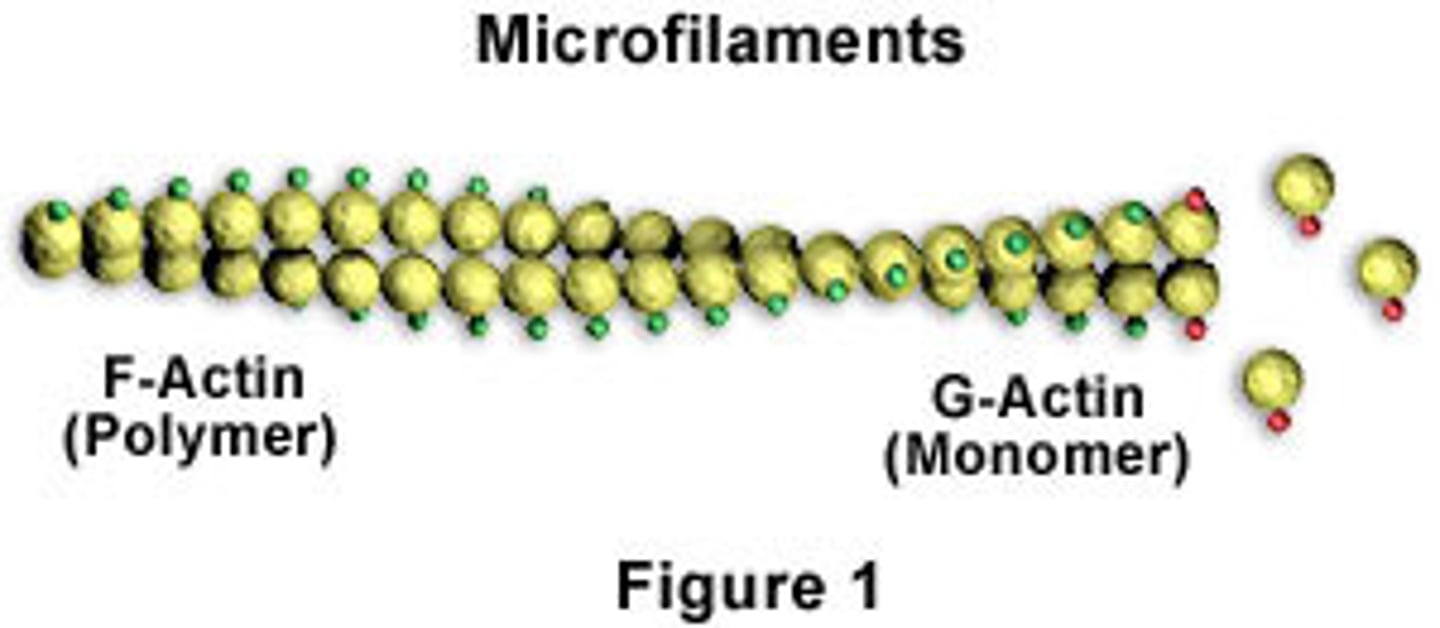
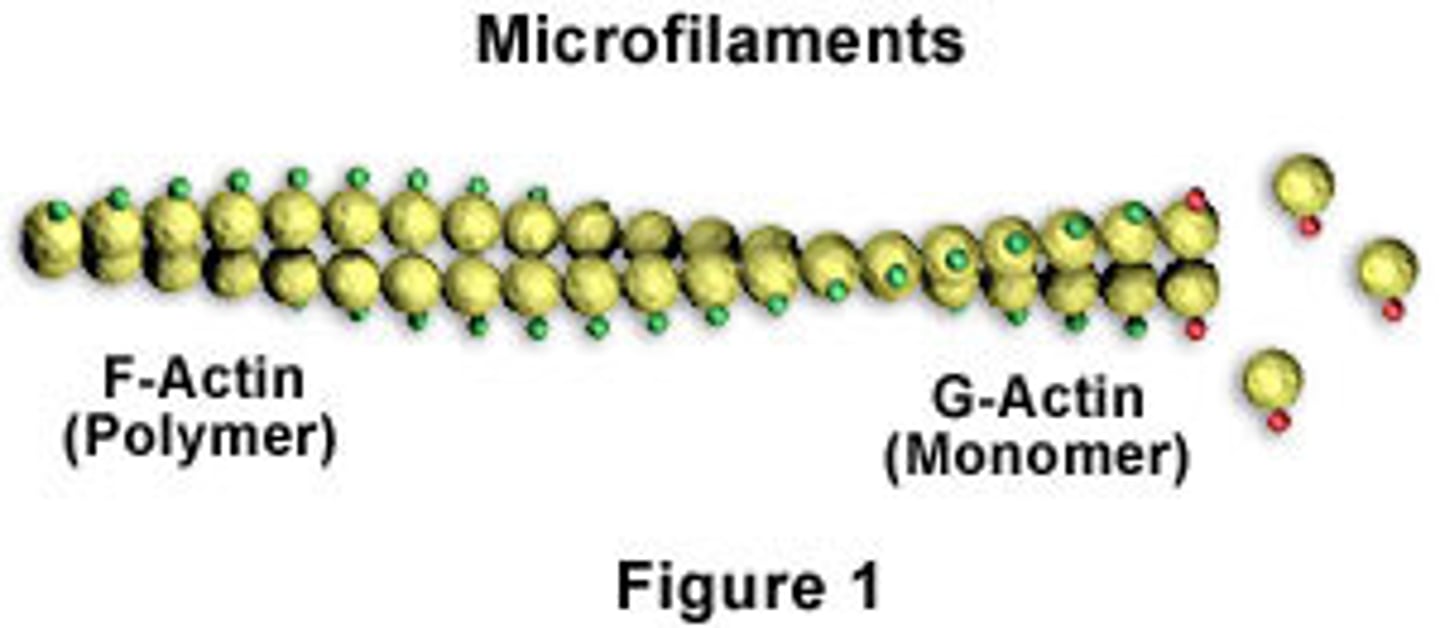
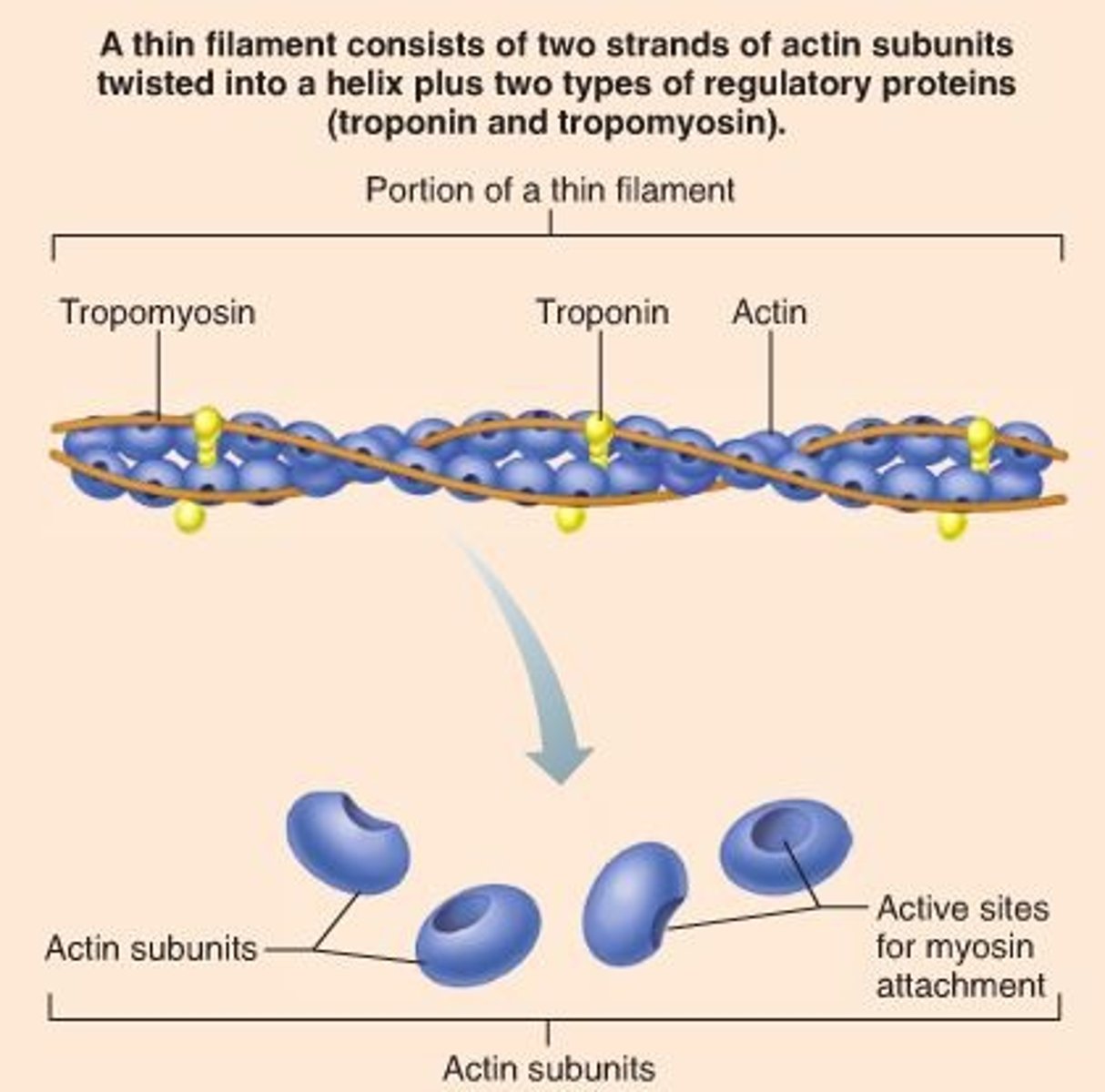
G actin
a globular subunit of F actin with an active site for binding a myosin head
myosin binding site
where myosin head attaches during contraction
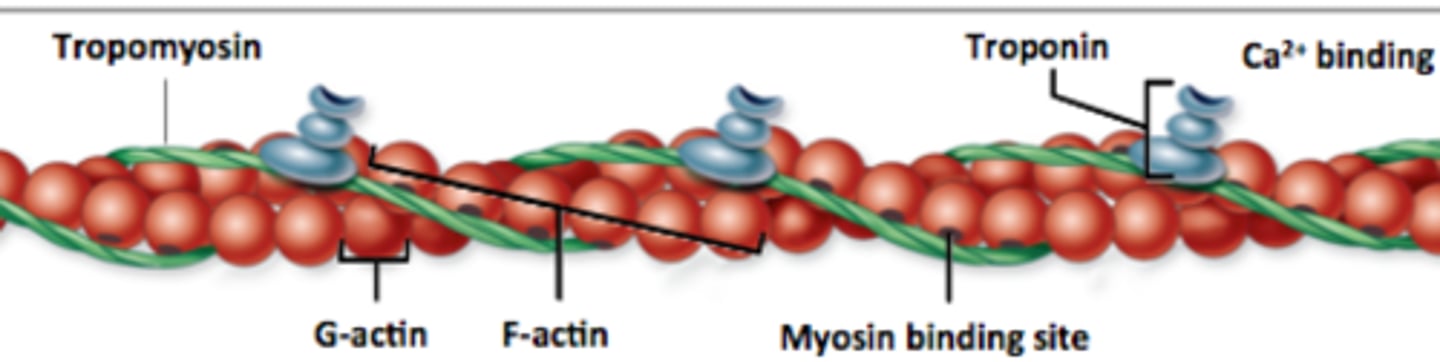
F actin
A fibrous protein made of a long chain of G actin molecules twisted into a helix; main protein of the thin myofilament
tropomyosin
A protein of muscle that forms a complex with troponin regulating the interaction of actin and myosin in muscular contraction
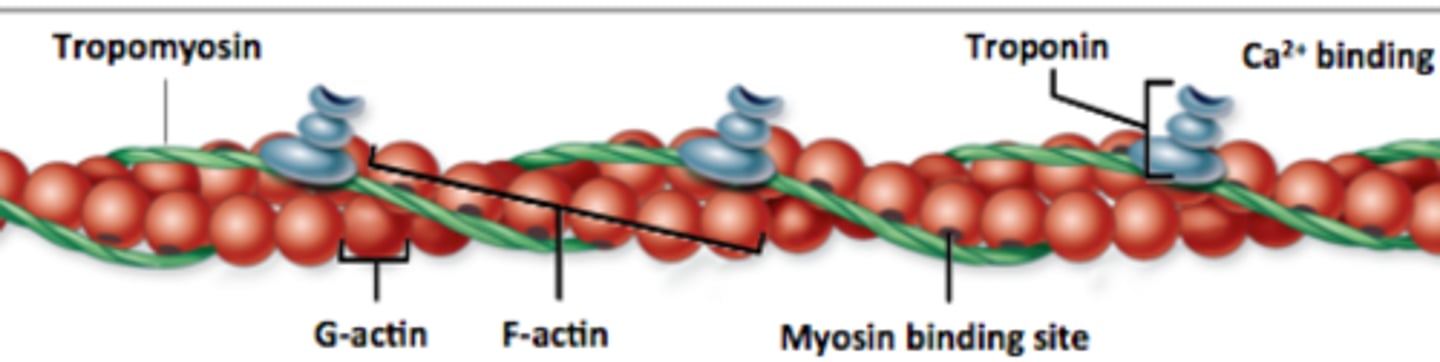
troponin
A protein of muscle that together with tropomyosin forms a regulatory protein complex controlling the interaction of actin and myosin and that when combined with calcium ions permits muscular contraction
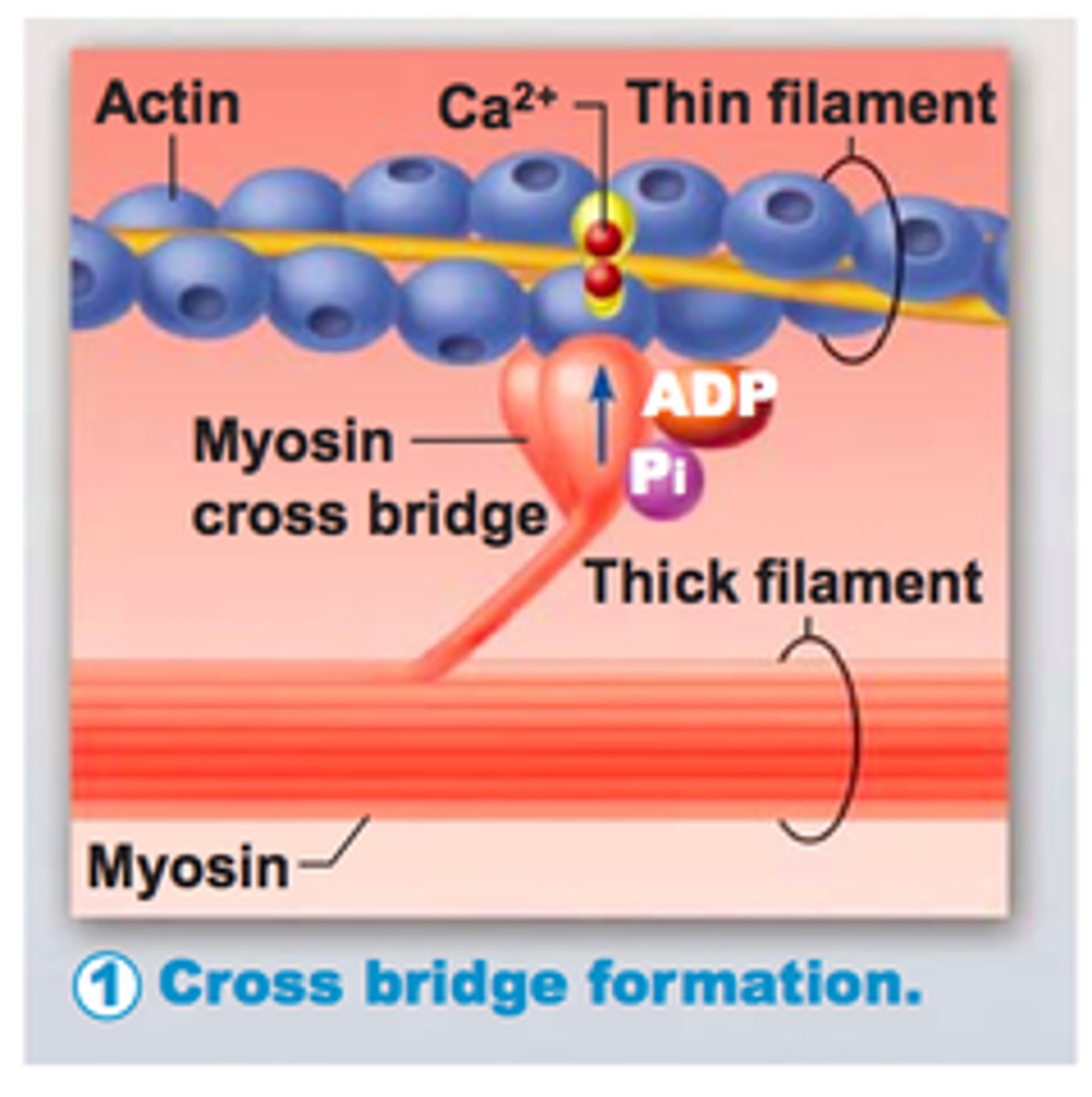
Ca2+
Calcium ion

crossbridges
when myosin heads attach to actin
actin-binding site
specialized region of the myosin head capable of binding to actin
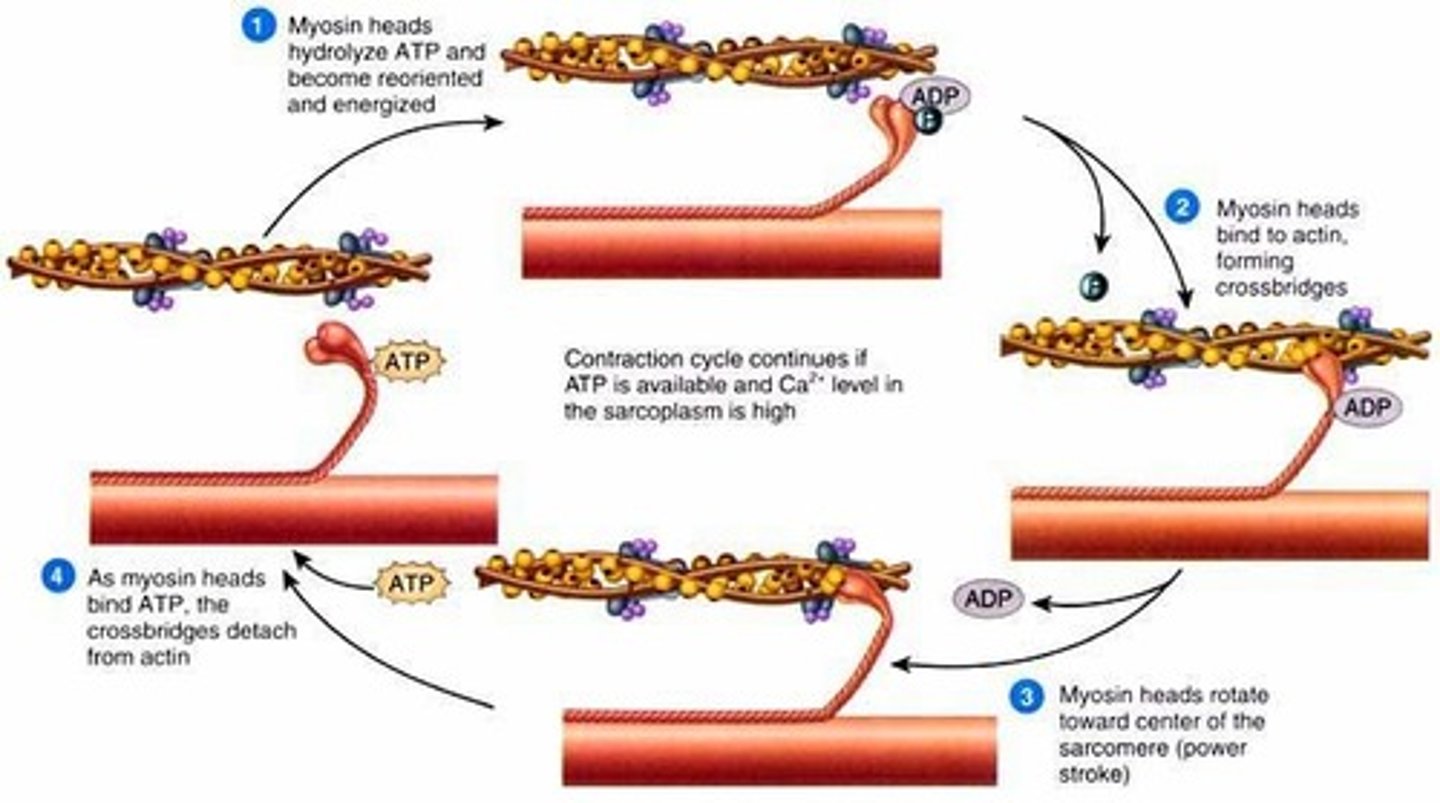
ATPase site
Located on heads of myosin molecules. Essential for producing contractile force
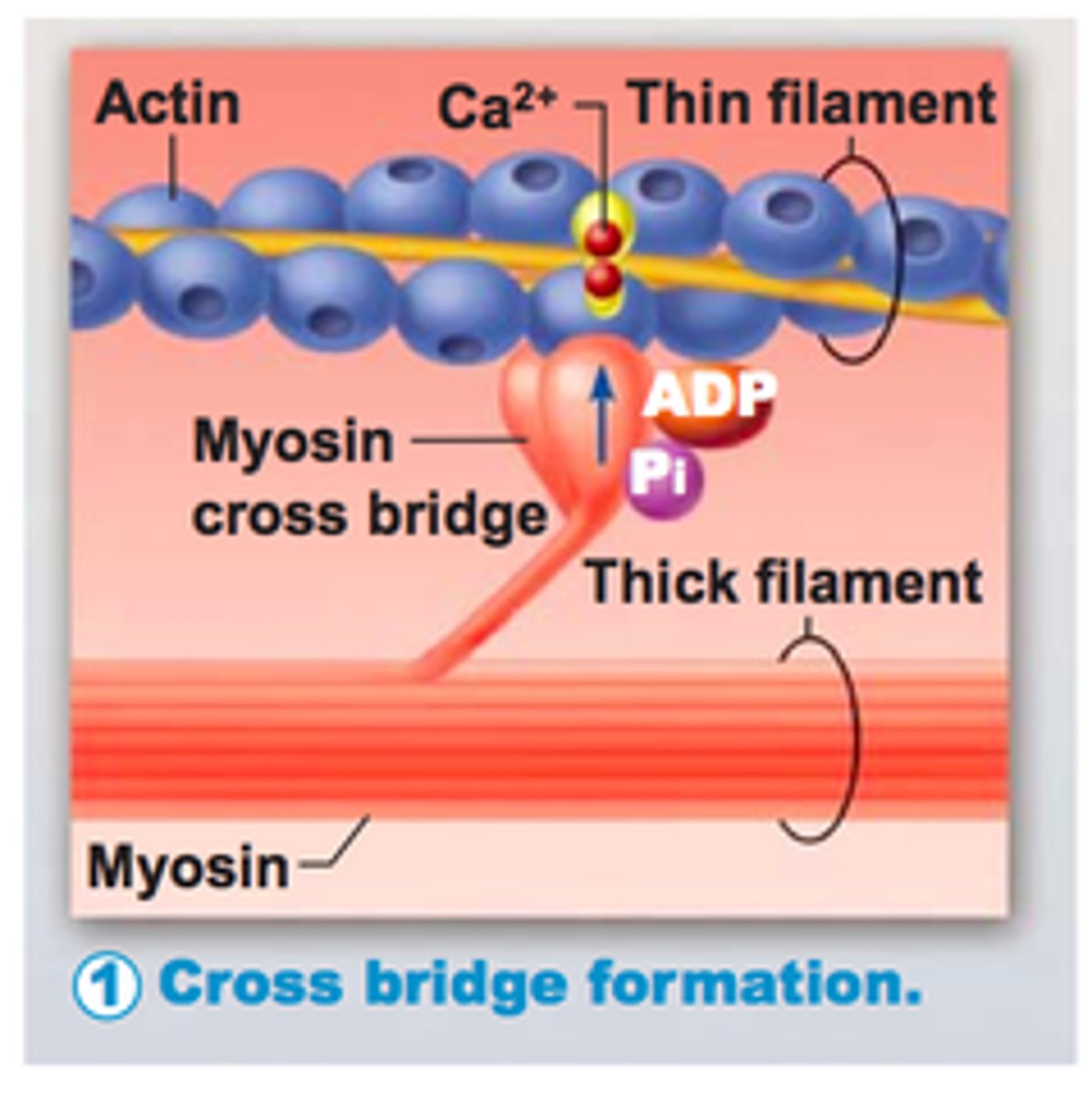
titin
a protein that positions the myosin filament to maintain equal spacing between actin filaments
sliding filament model
The theory explaining how muscle contracts, based on change within a sarcomere, the basic unit of muscle organization, stating that thin (actin) filaments slide across thick (myosin) filaments, shortening the sarcomere; the shortening of all sarcomeres in a myofibril shortens the entire myofibril
crossbridge cycle
the mechanism that drives muscle contraction
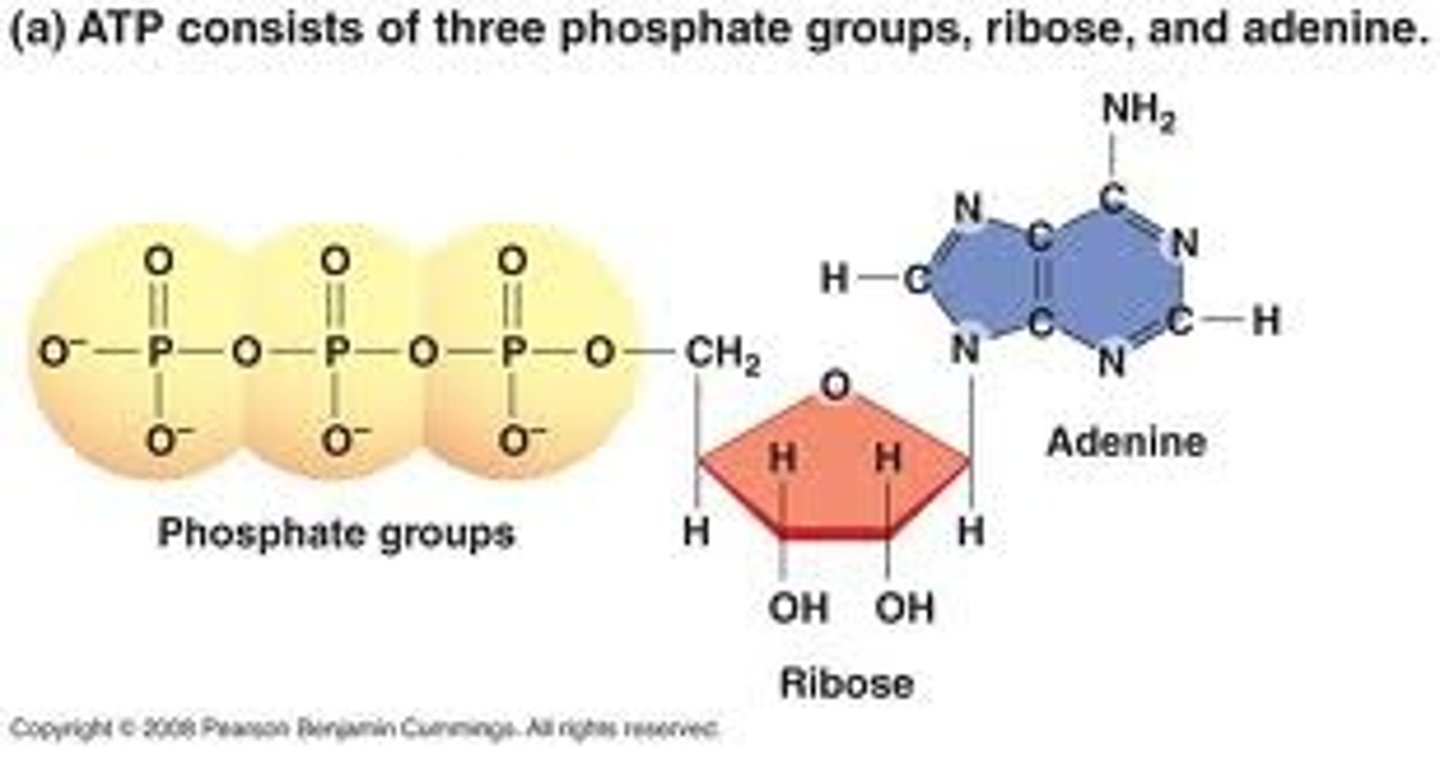
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Composed of a sugar ribose, nitrogenous base adenine, and a chain of three phosphate groups bonded to it.
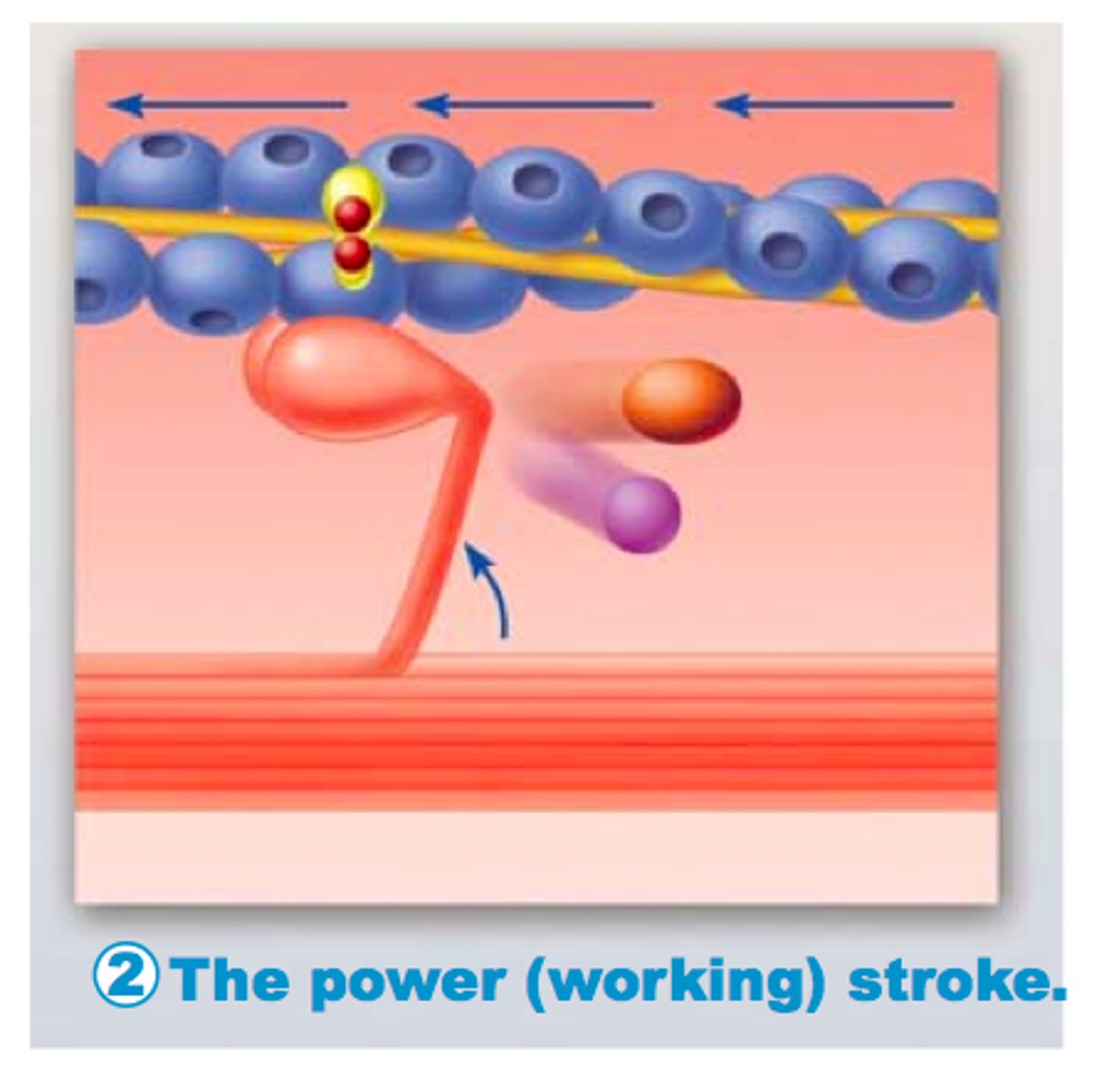
power stroke
action of myosin pulling actin inward (toward the M line)
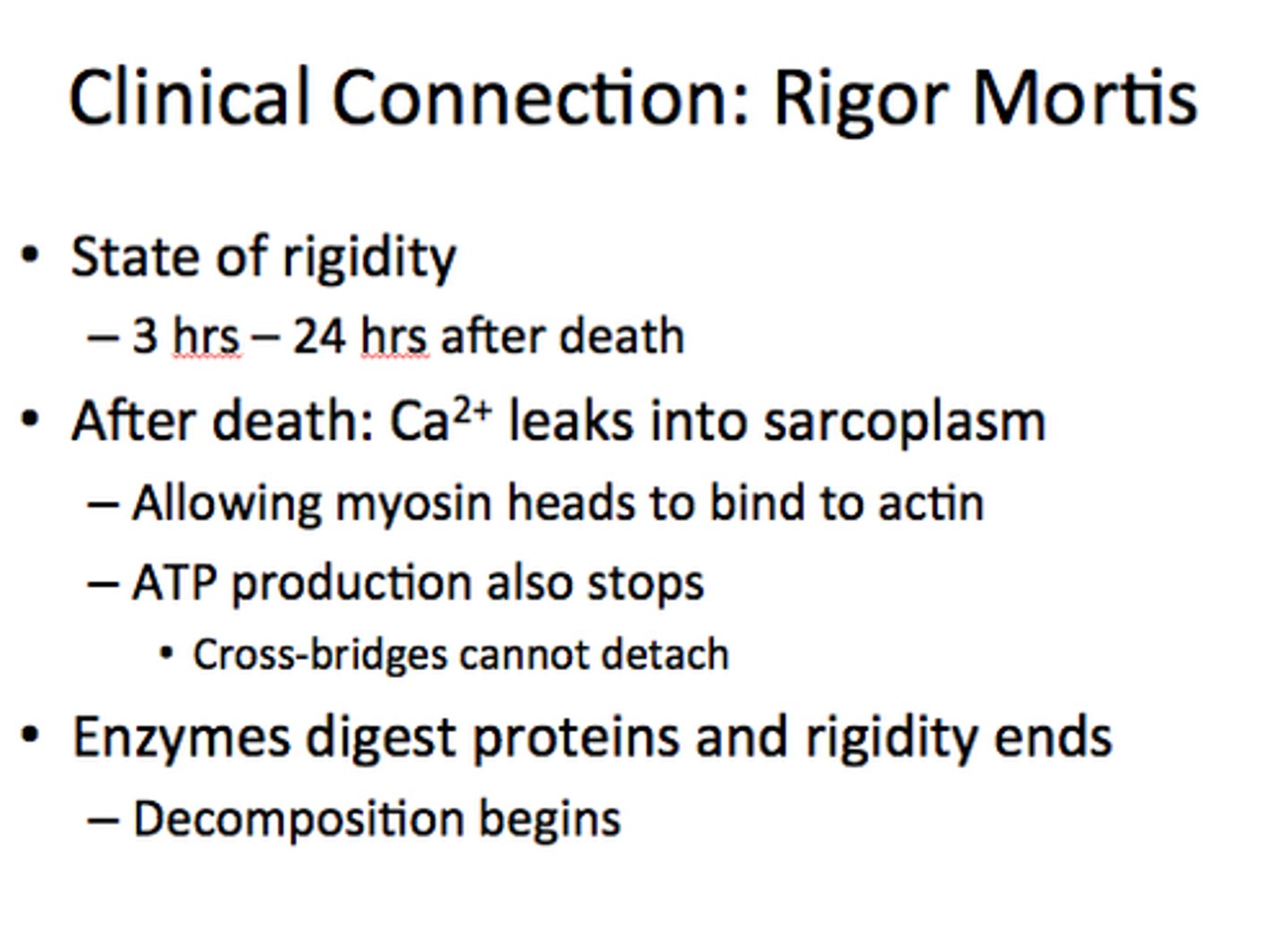
rigor
a state of rigidity in muscle tissues during which they are unable to respond to stimuli due to the coagulation of muscle protein
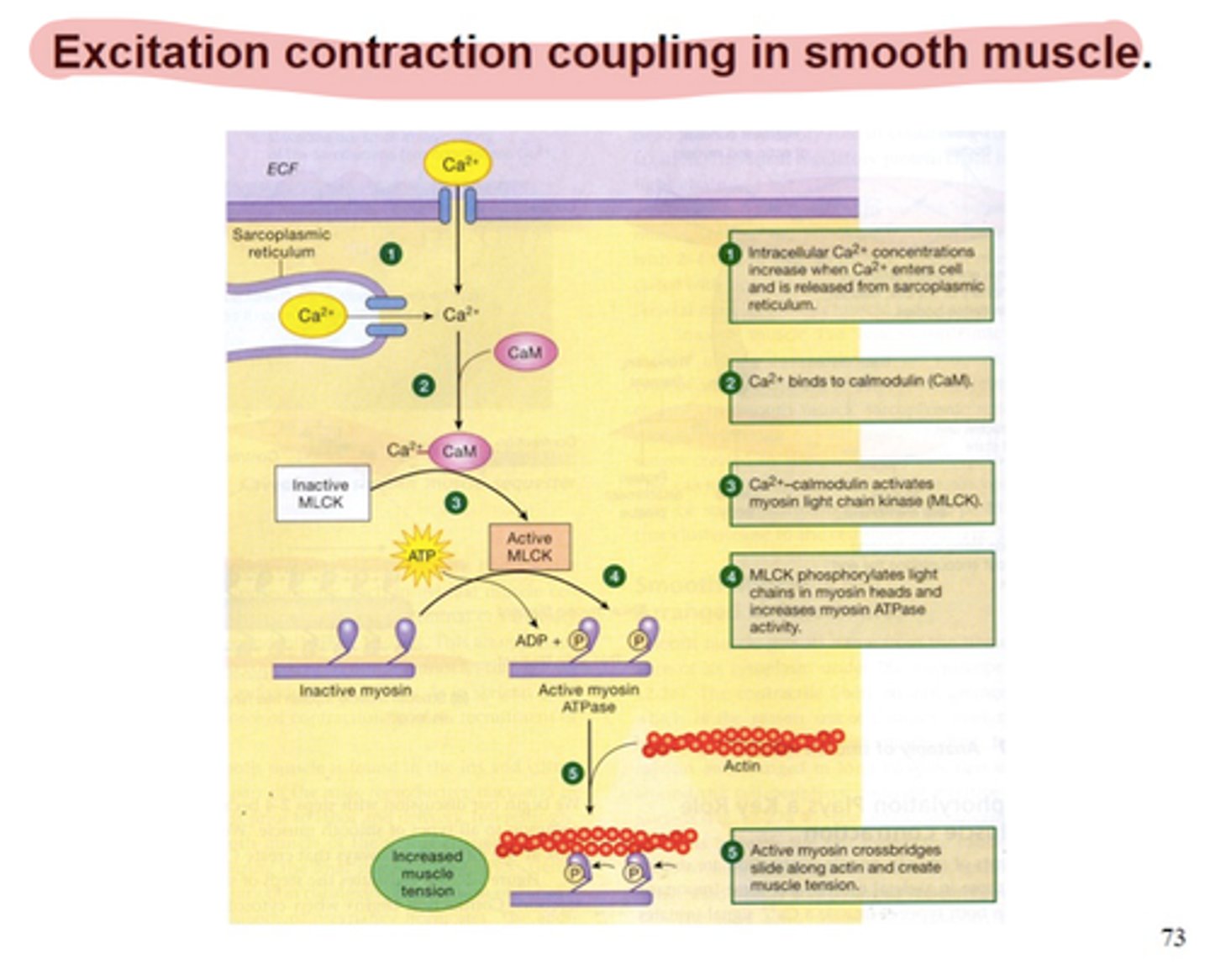
excitation-contraction coupling
sequence of events from motor neuron signaling to a skeletal muscle fiber to contraction of the fiber's sarcomeres
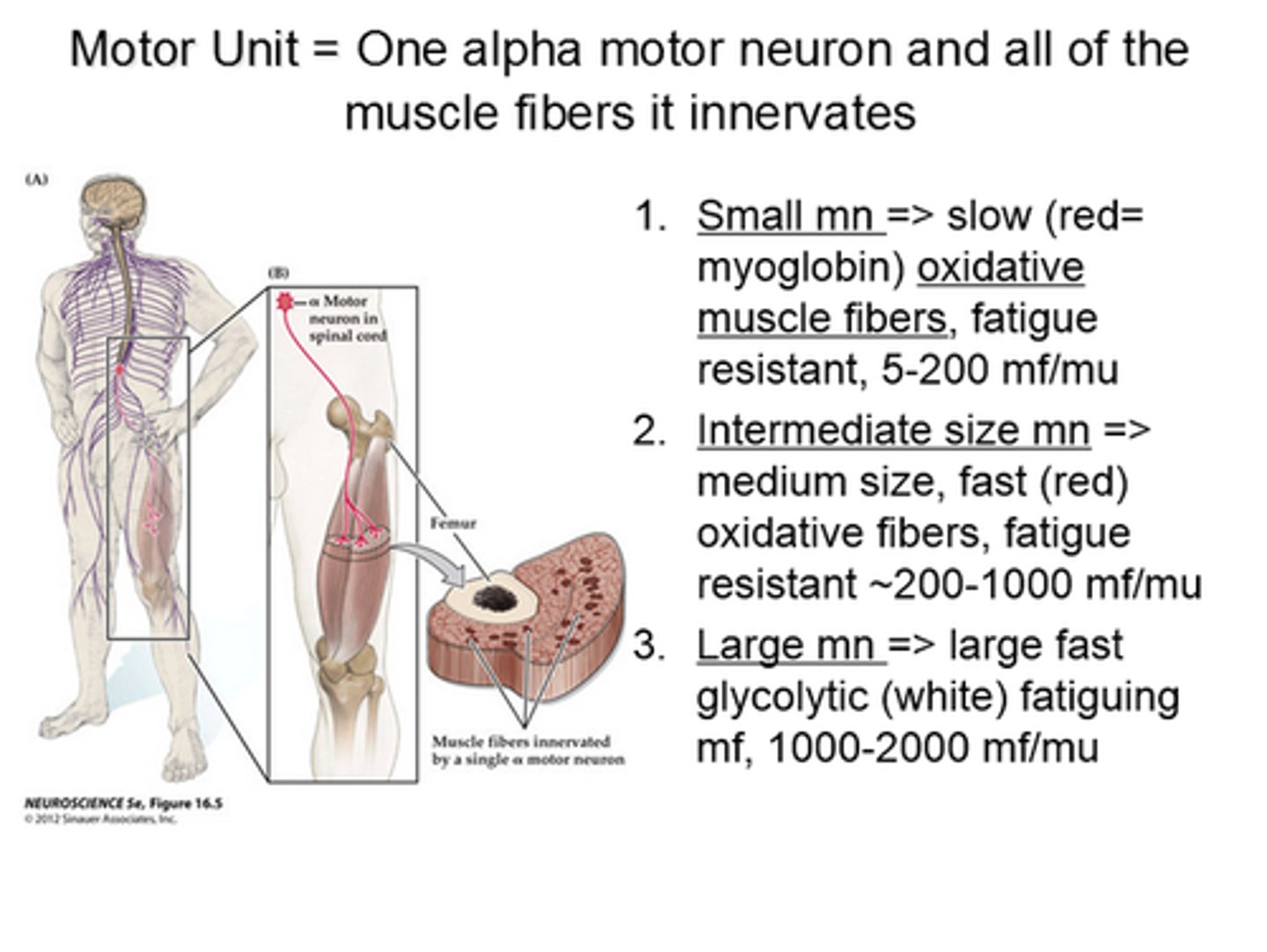
motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
neuromuscular junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
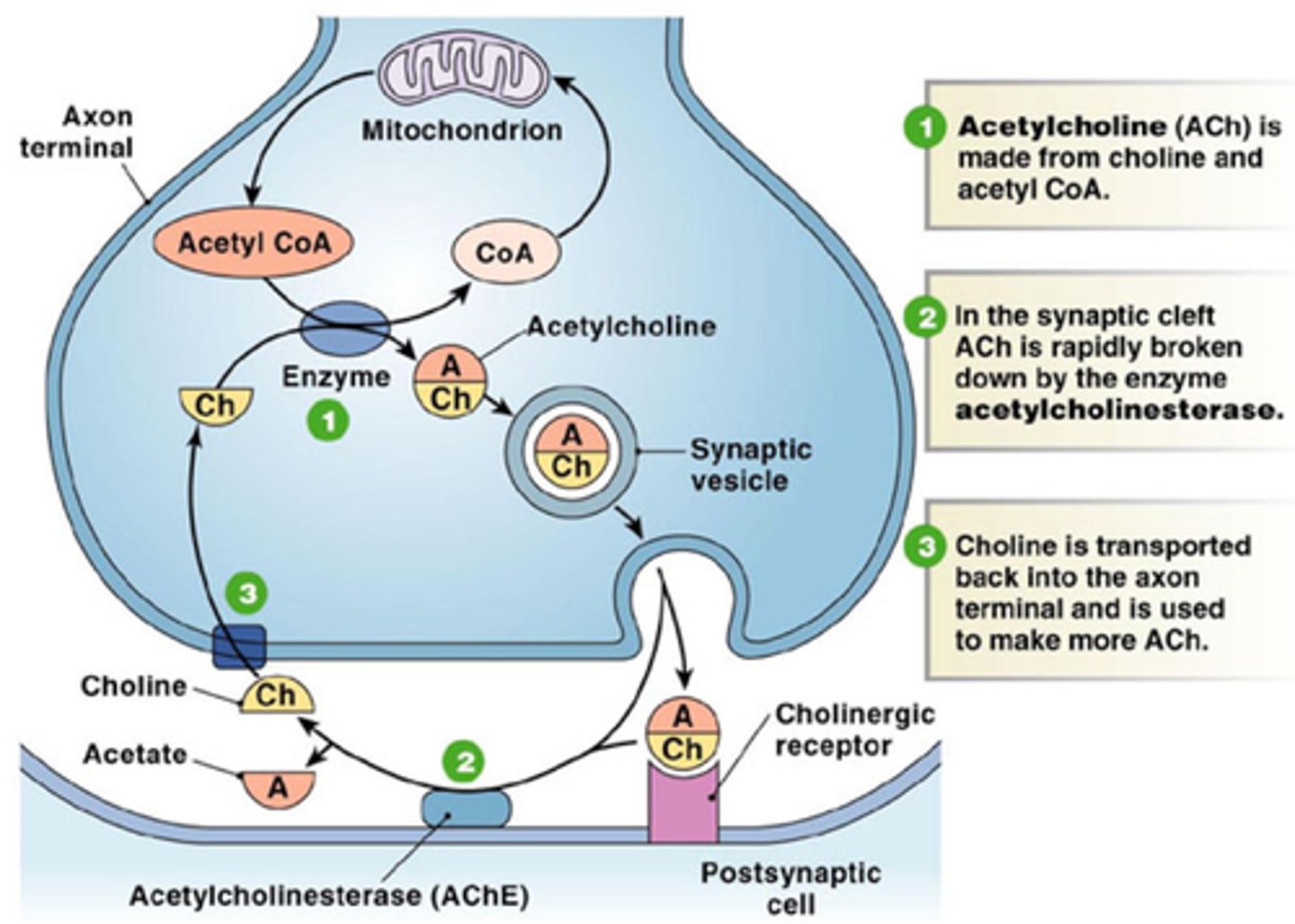
acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
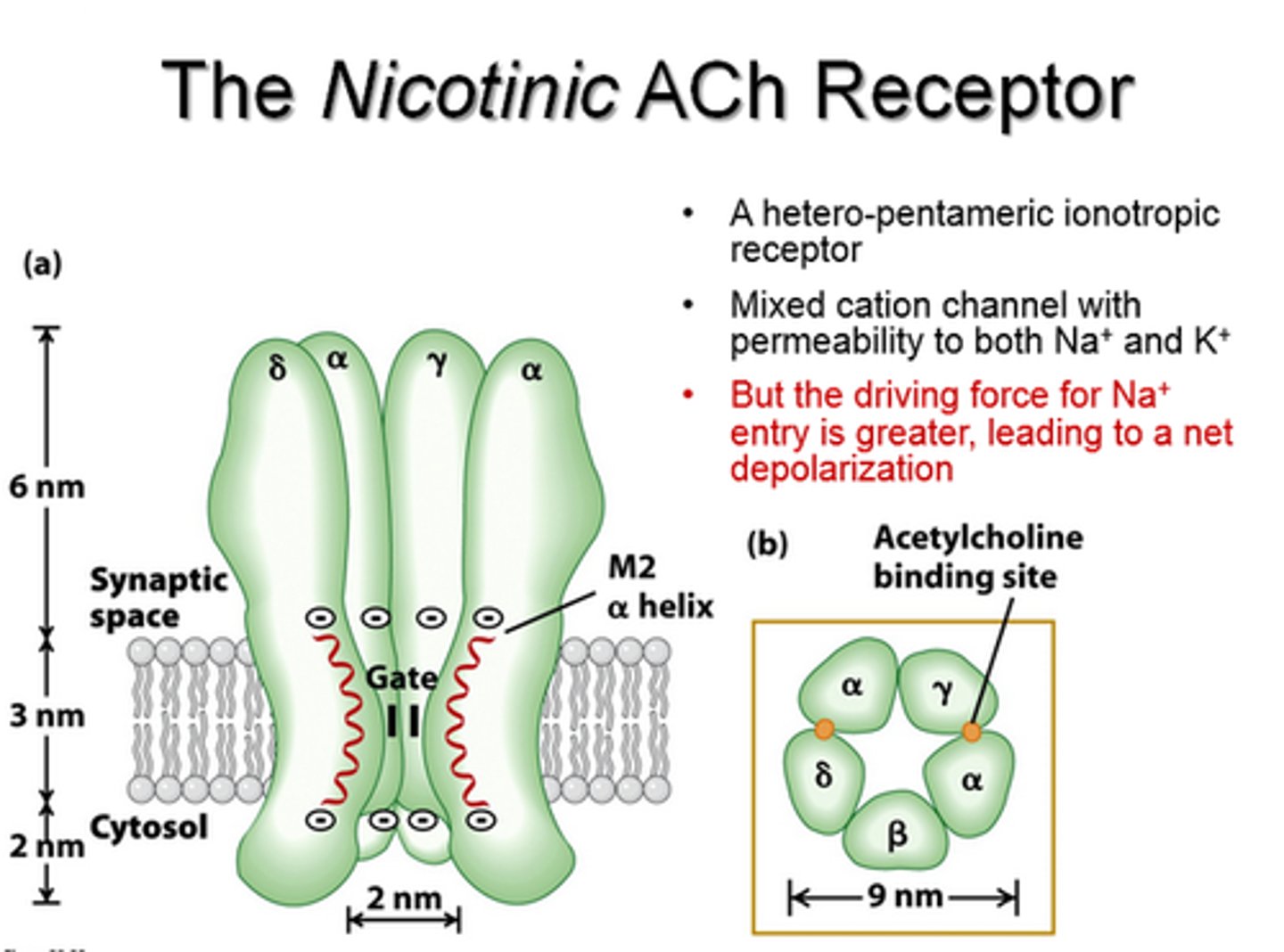
nicotinic cholinergic receptors
agonistic receptors found in skeletal muscle, in CNS, and autonomic division of the PNS
motor end plate
the flattened end of a motor neuron that transmits neural impulses to a muscle
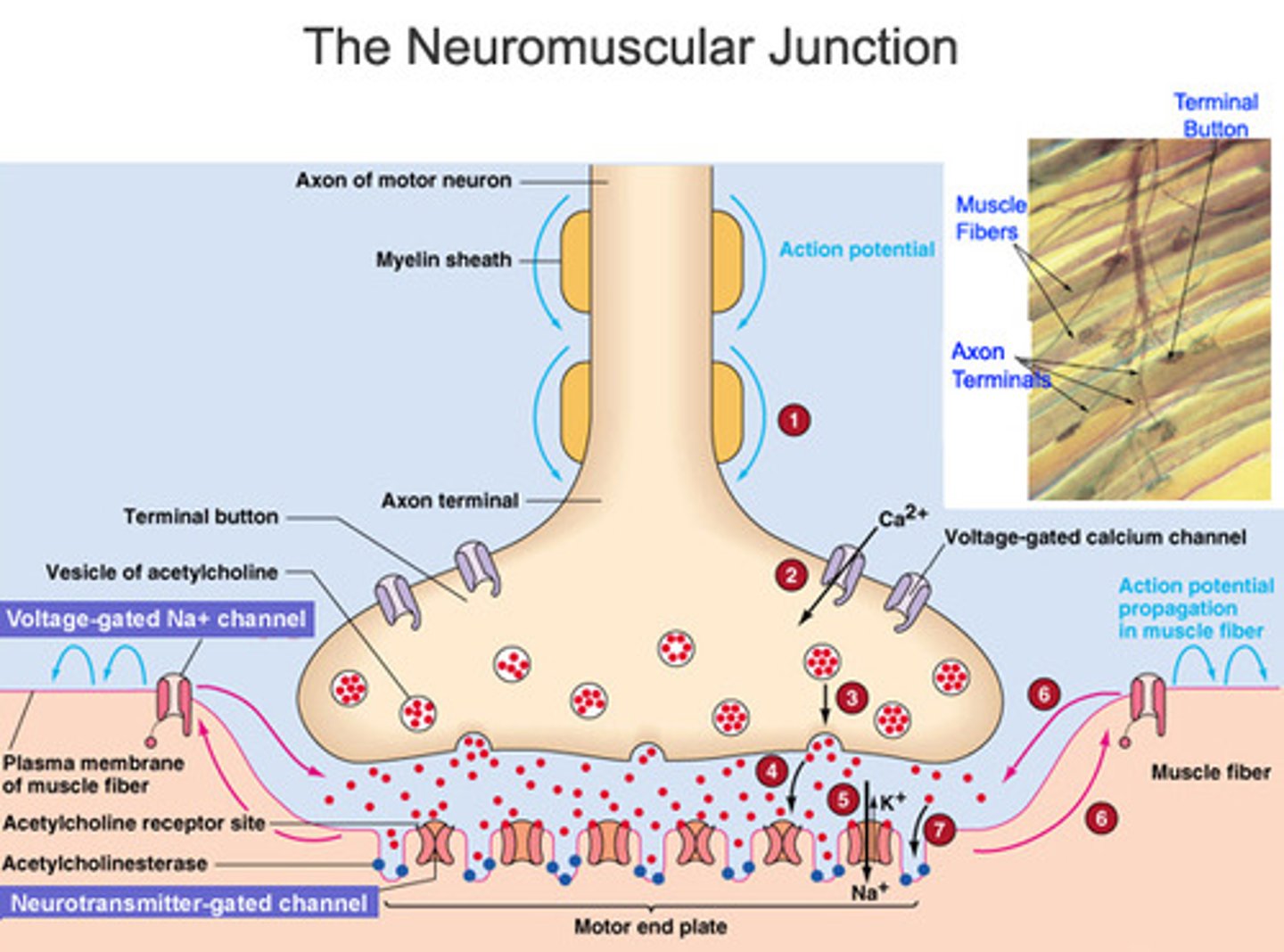
end-plate potential
The depolarization of the motor end plate on a muscle cell.
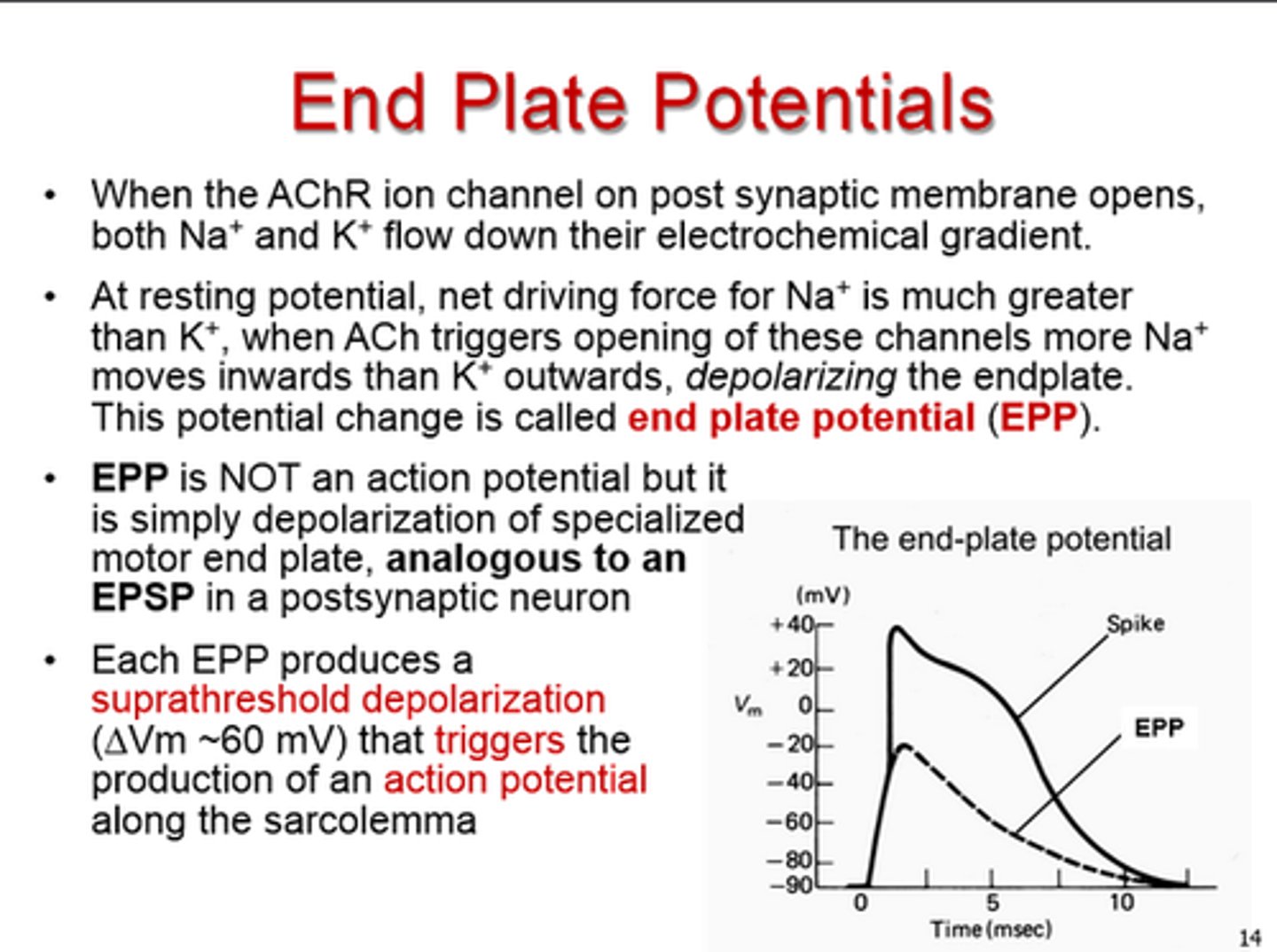
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
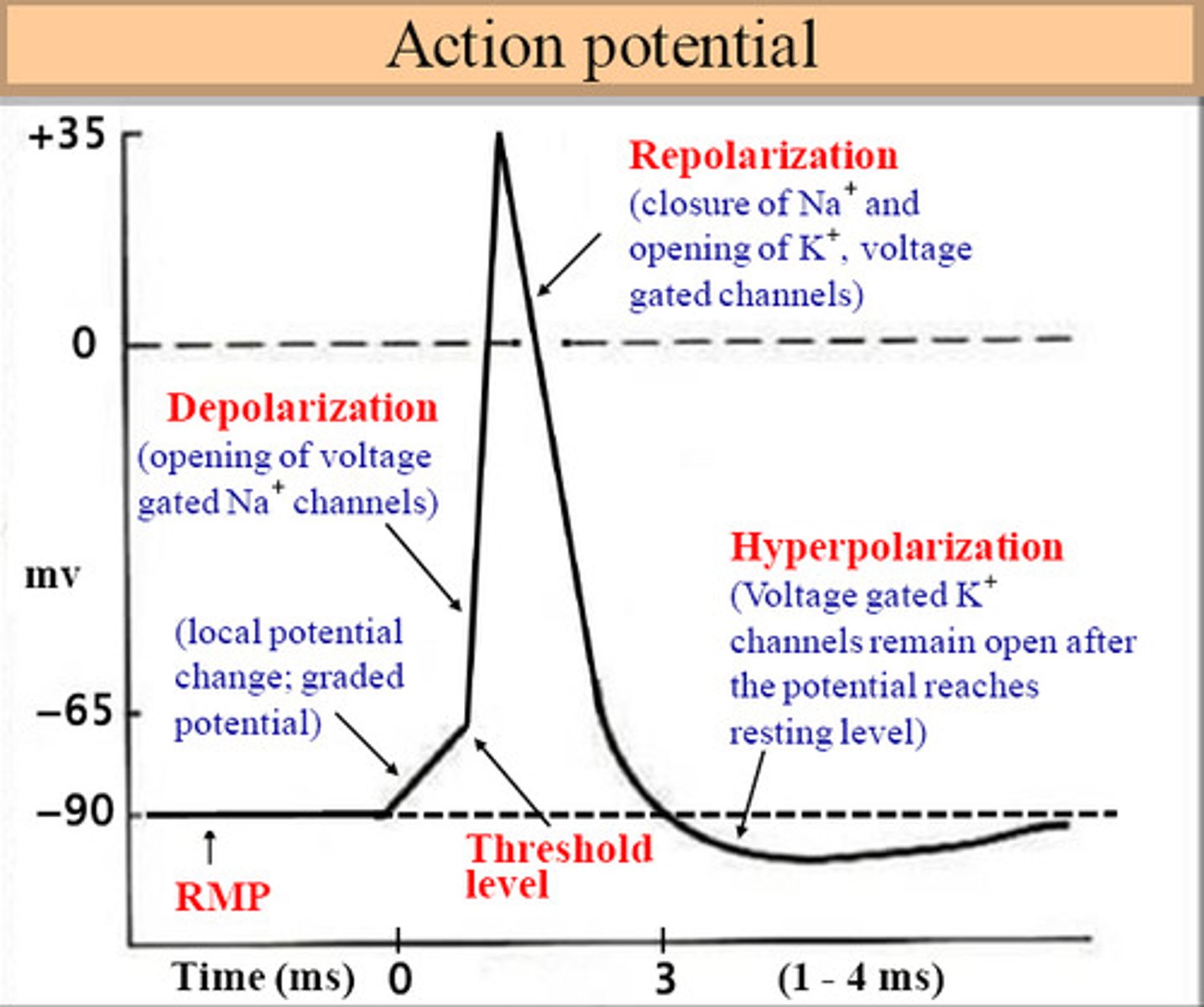
acetylcholinesterase
the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
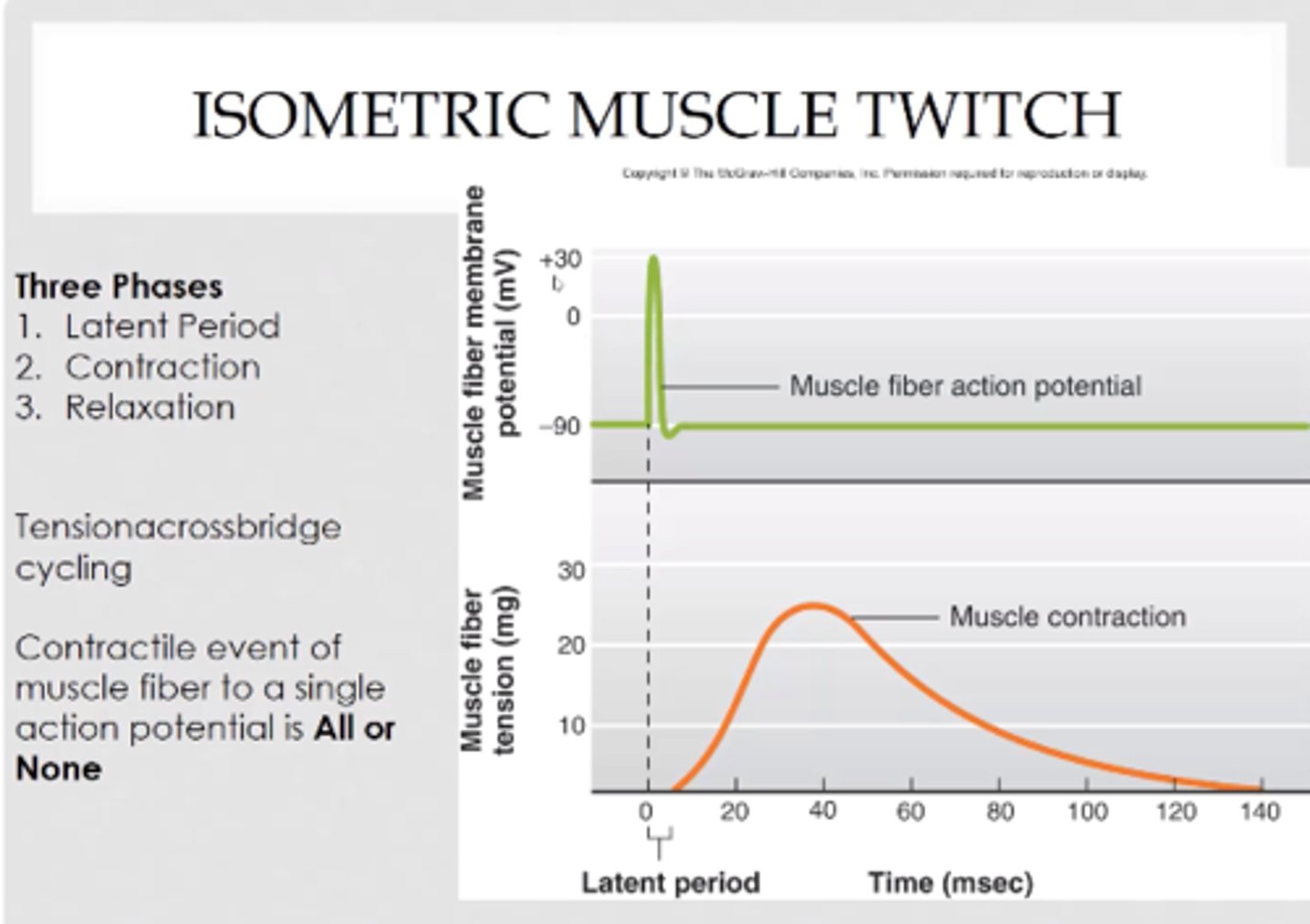
muscle twitch
the response of a muscle to a single brief threshold stimulus
isometric twitch
a twitch during which a muscle generates force but does not shorten
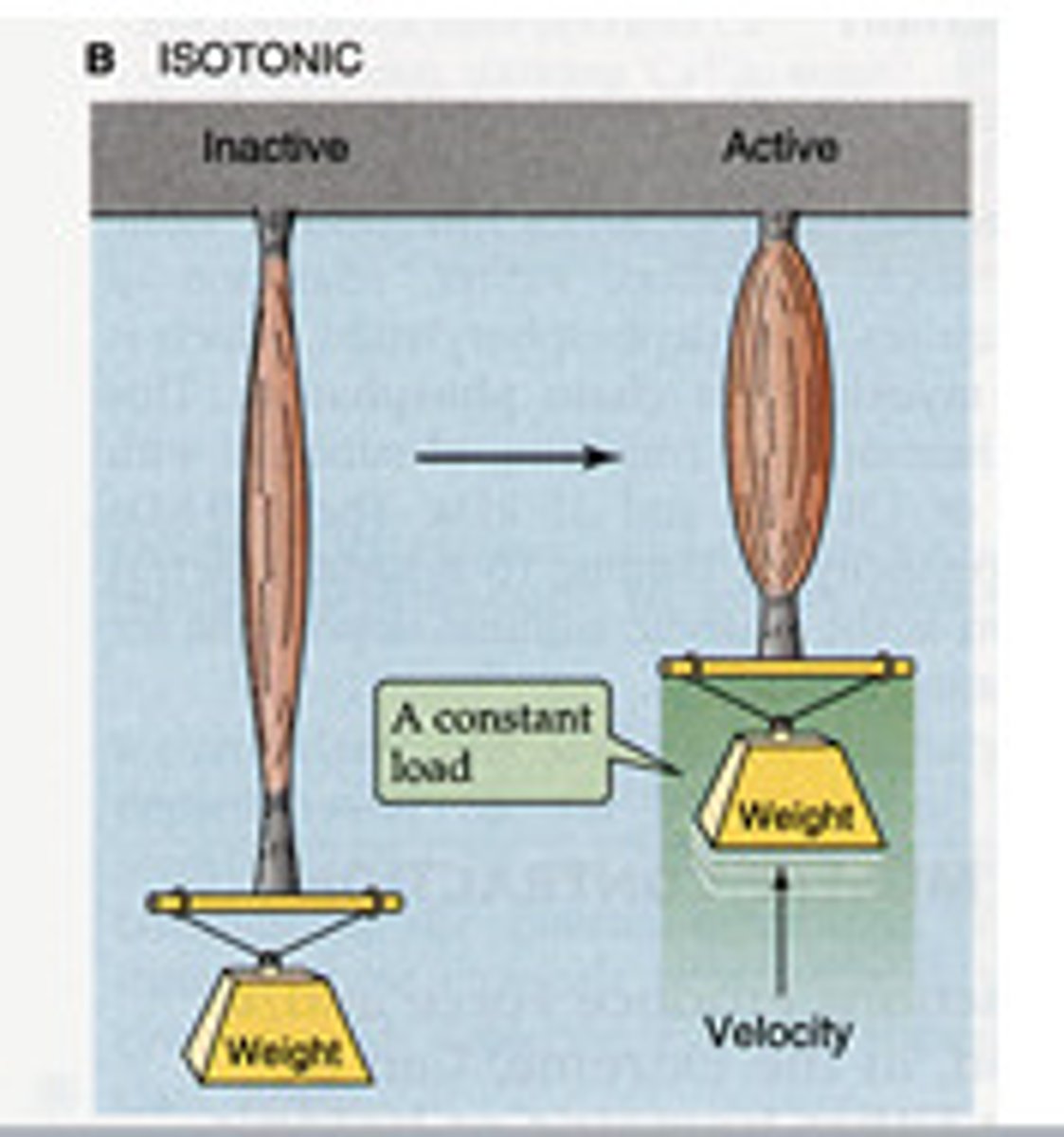
isotonic twitch
a twitch during which a muscle shortens and lifts a constant load
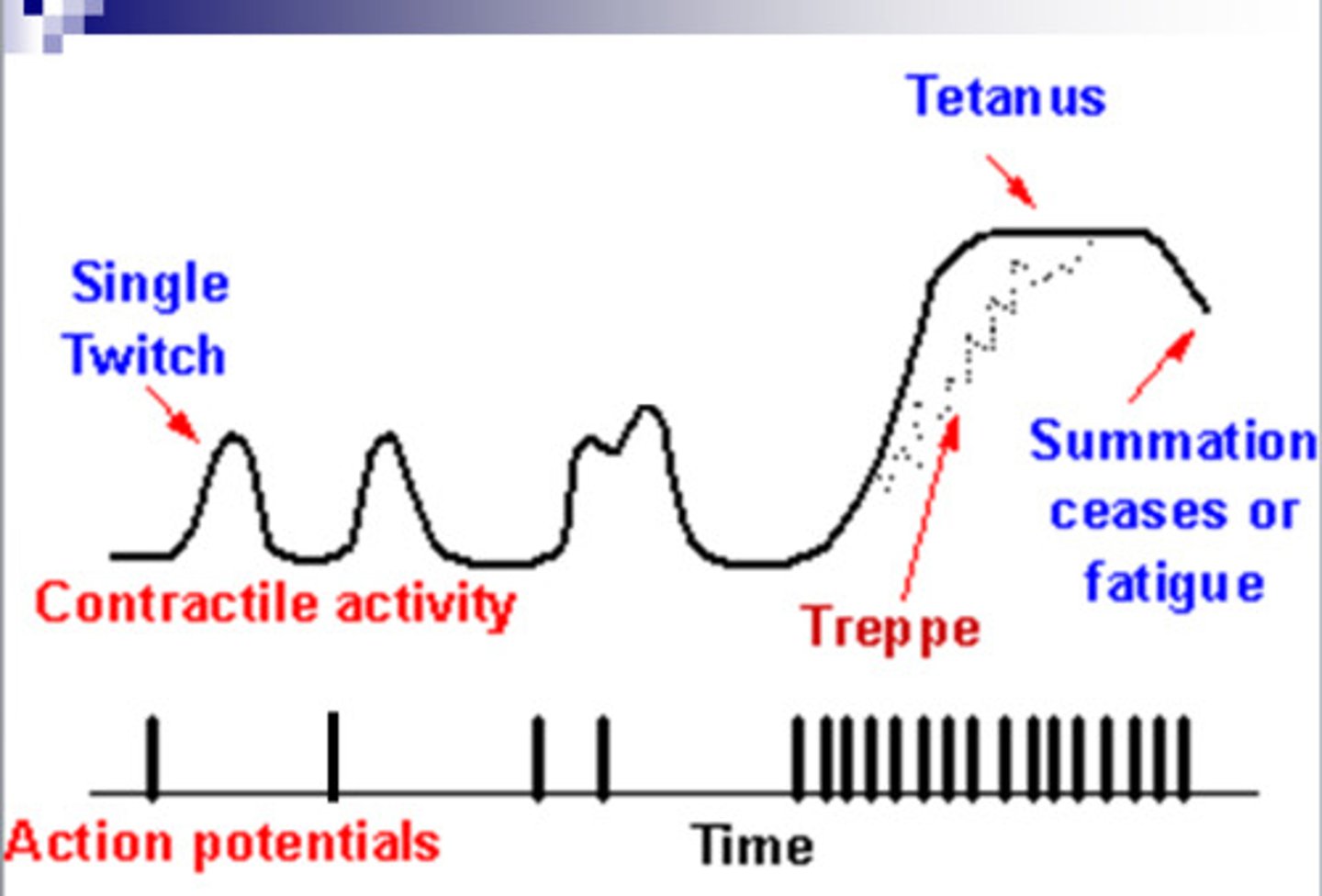
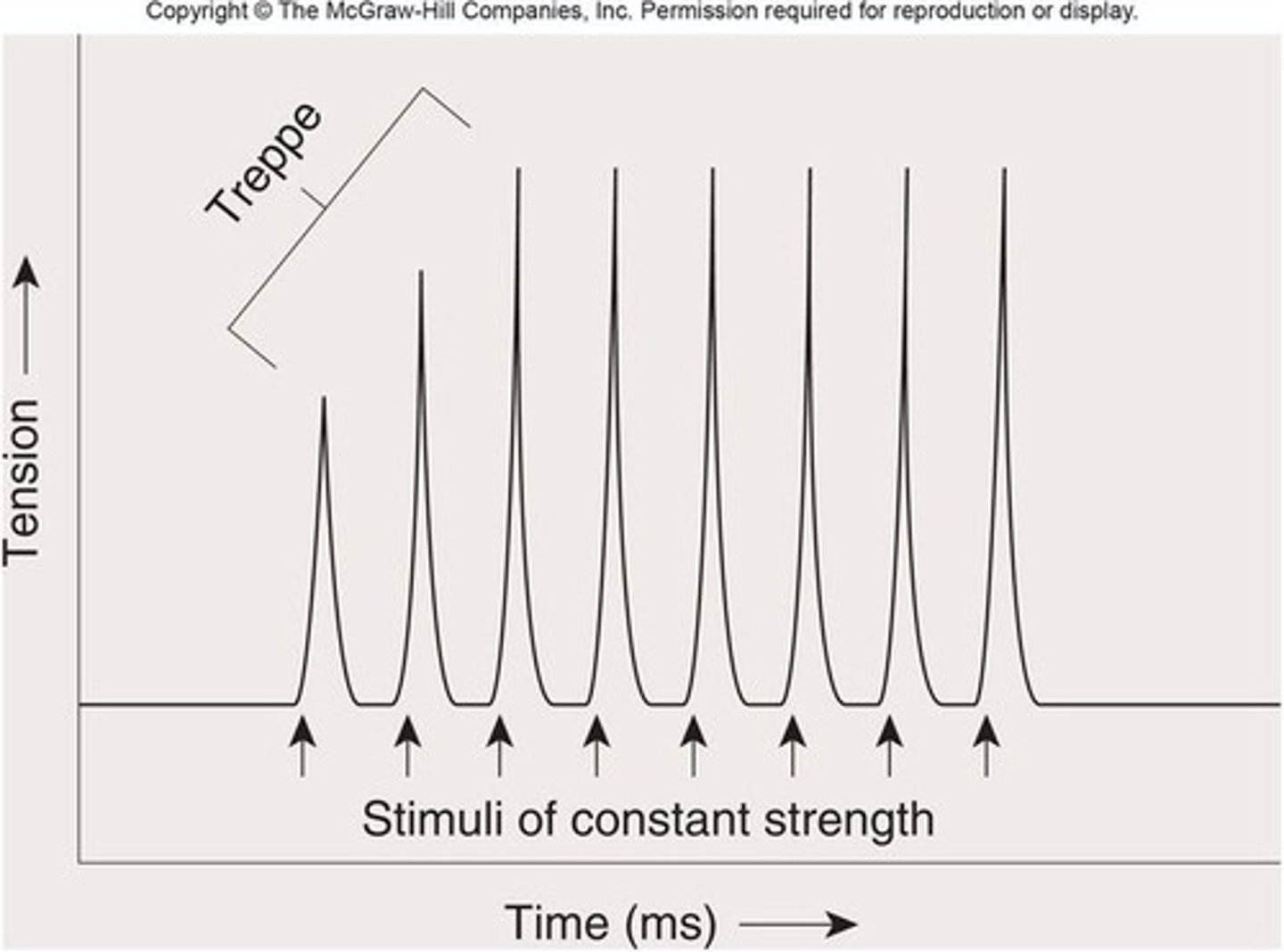
treppe
Phenomenon in which each successive twitch contracts more forcefully than the previous one
summation
increased force of contraction by a skeletal muscle fiber when a twitch occurs before the previous twitch relaxes
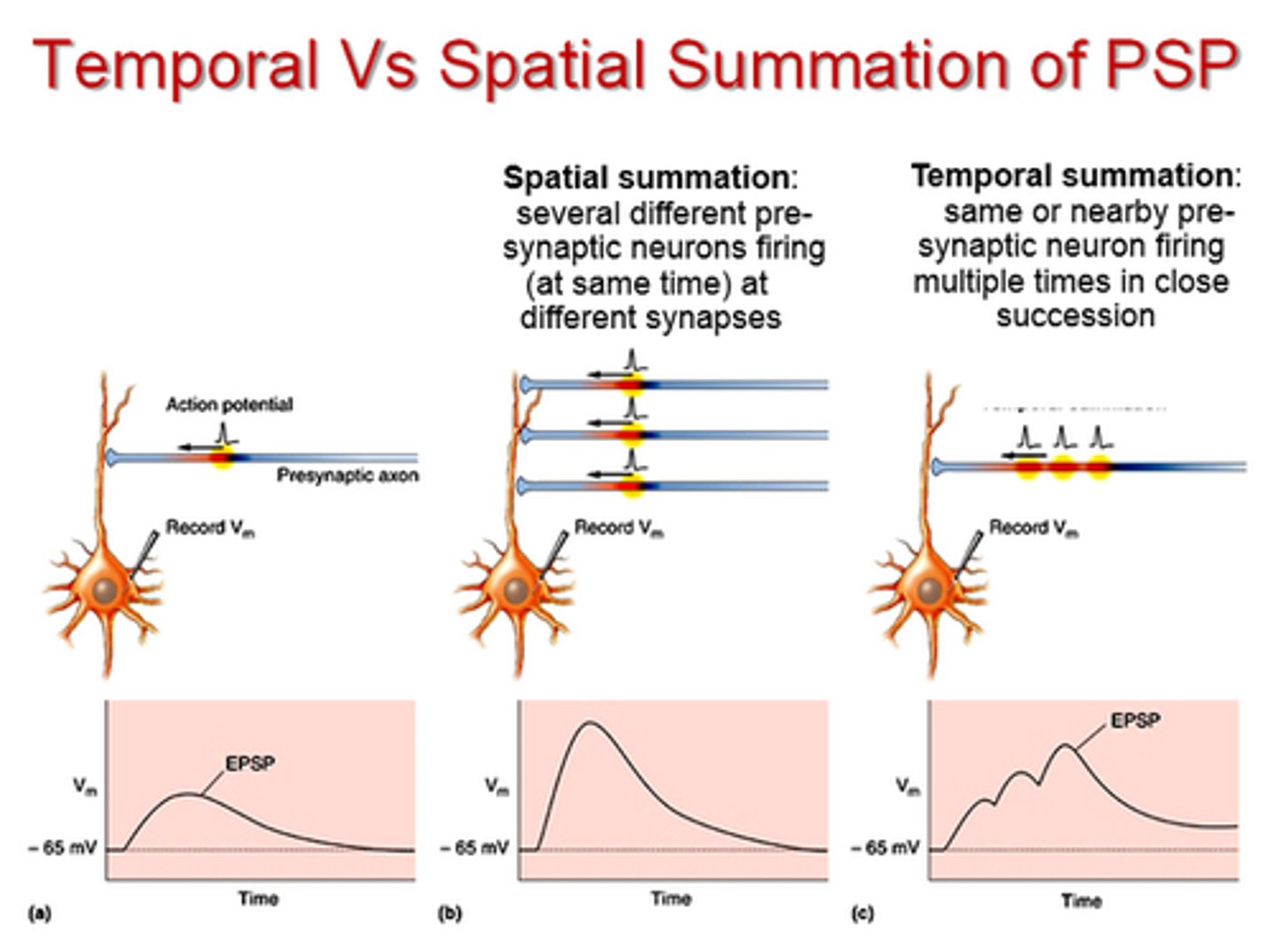
tetanus
a sustained muscular contraction resulting from a rapid series of nerve impulses
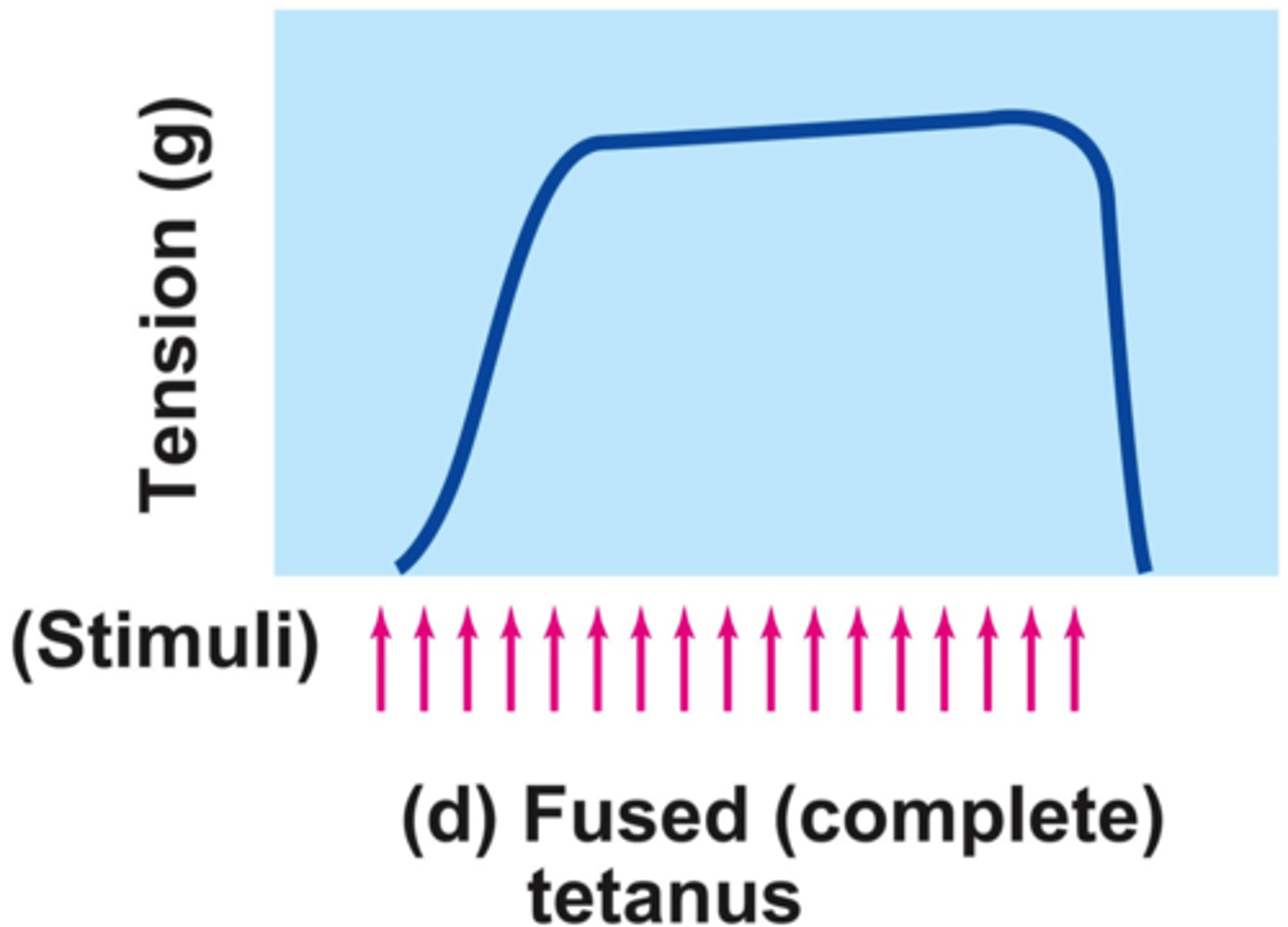
length-tension curve
the curve that accounts for the active and passive elements of muscle tension and dictates that optimal tension is developed at one point known as the resting length, the point in its range where peak torque is developed
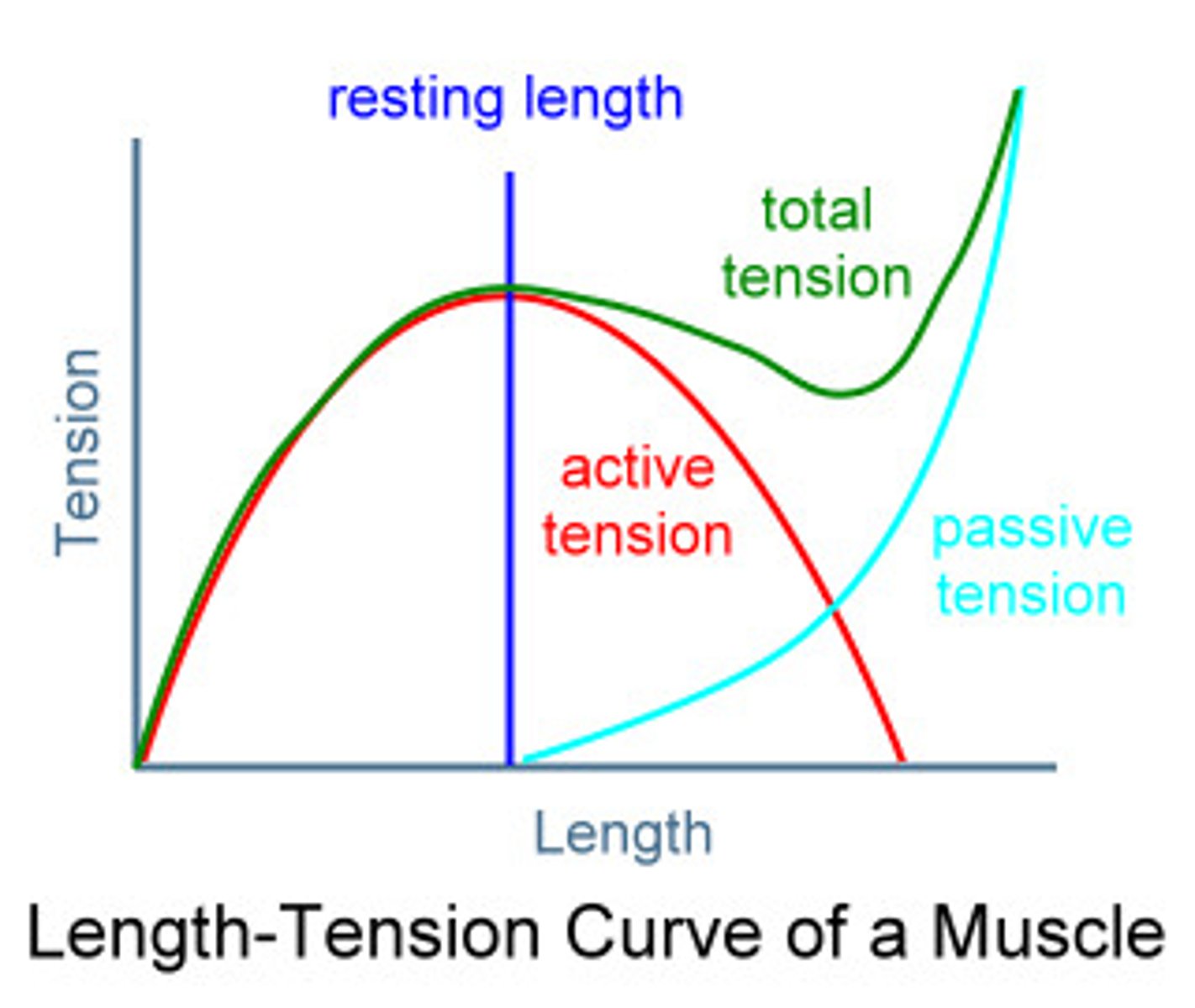
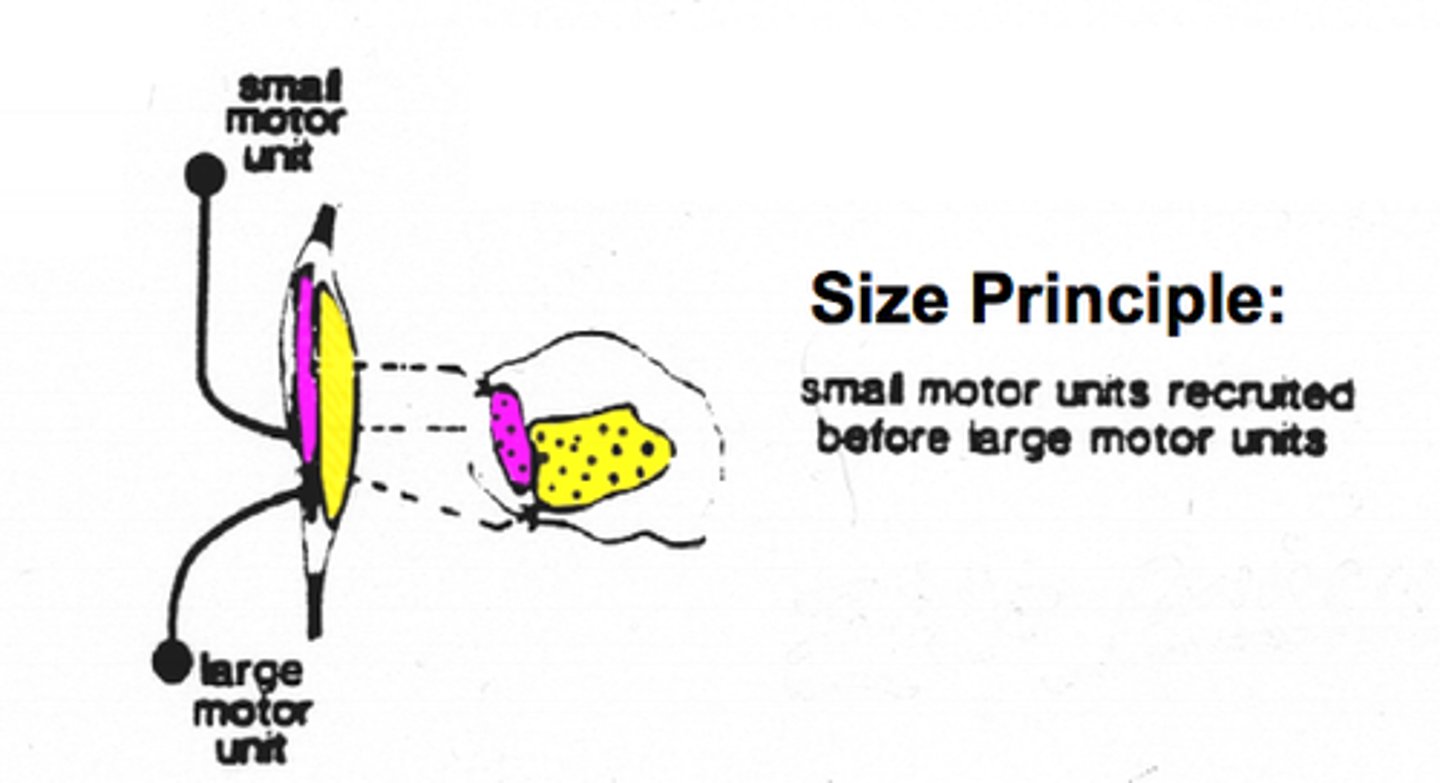
recruitment
an increase in the response to a stimulus owing to the activation of additional receptors, resulting from the continuous application of the stimulus with the same intensity
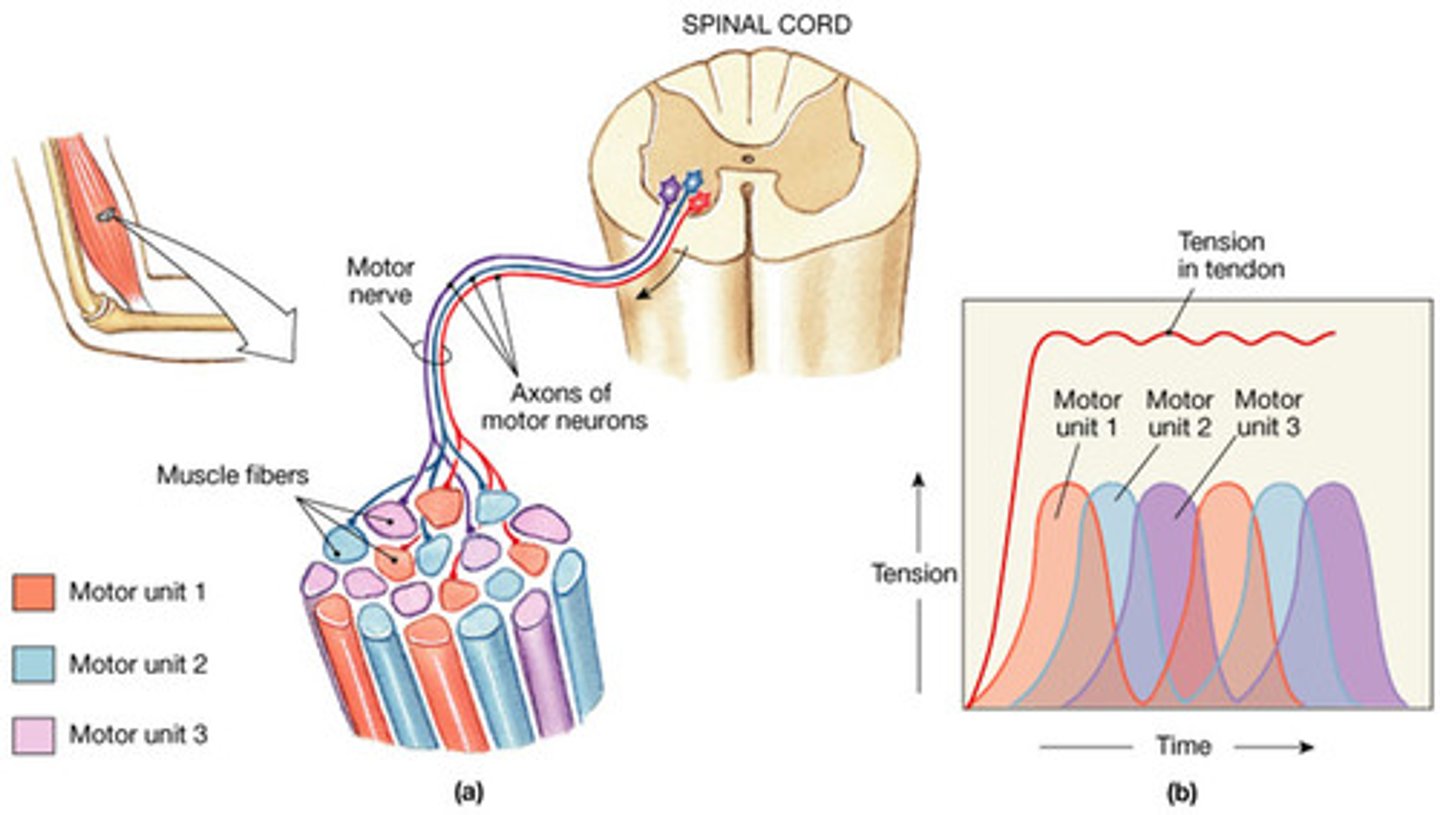
small motor units
fine degree of control
Three to six muscle fibers per neuron
Eye and hand muscles
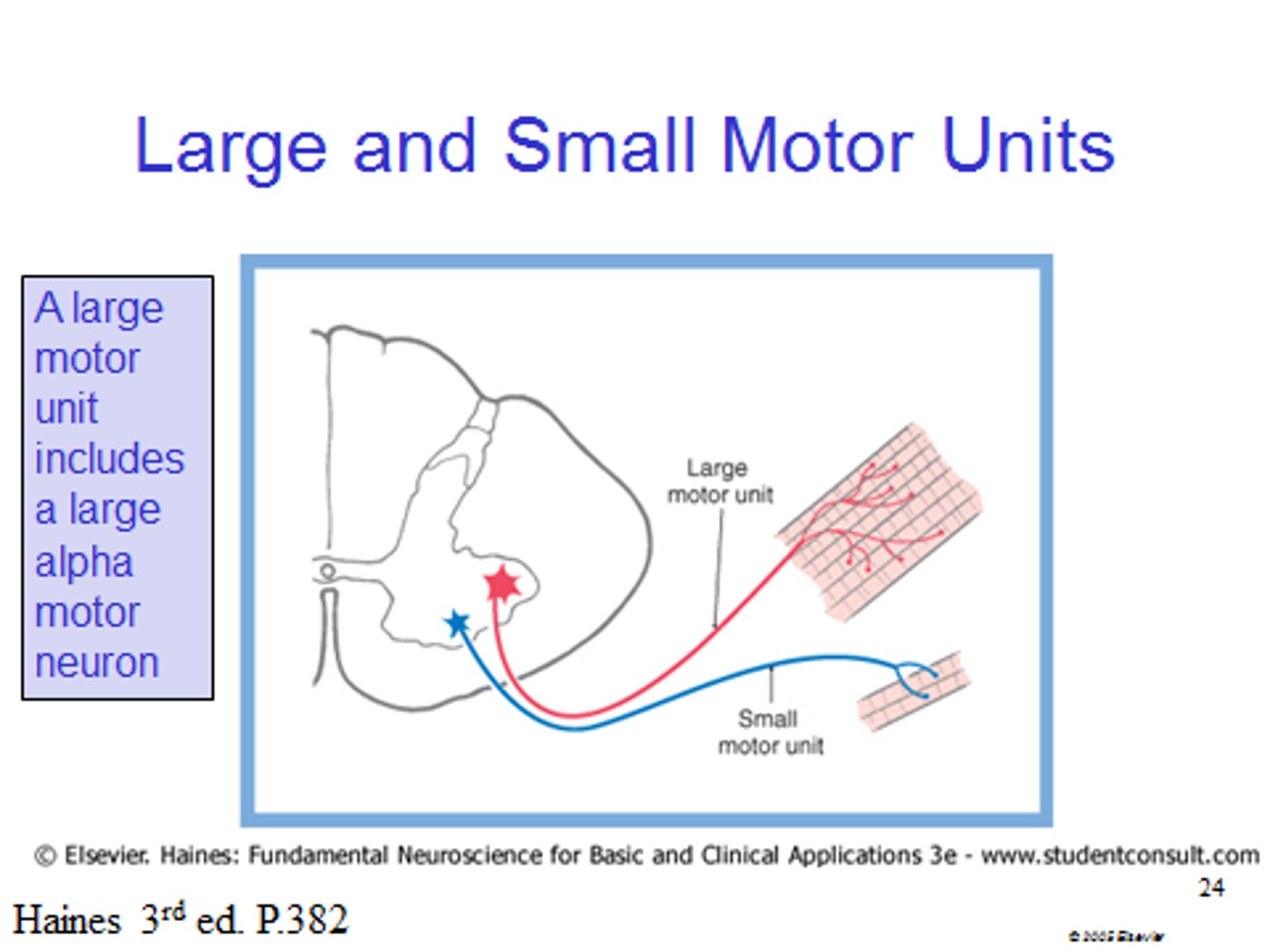
large motor units
more strength than control
Powerful contractions supplied by large motor units with hundreds of fibers
Gastrocnemius of calf has 1,000 muscle fibers per neuron
size principle
motor units with larger and larger fibers are recruited as stimulus intensity increases
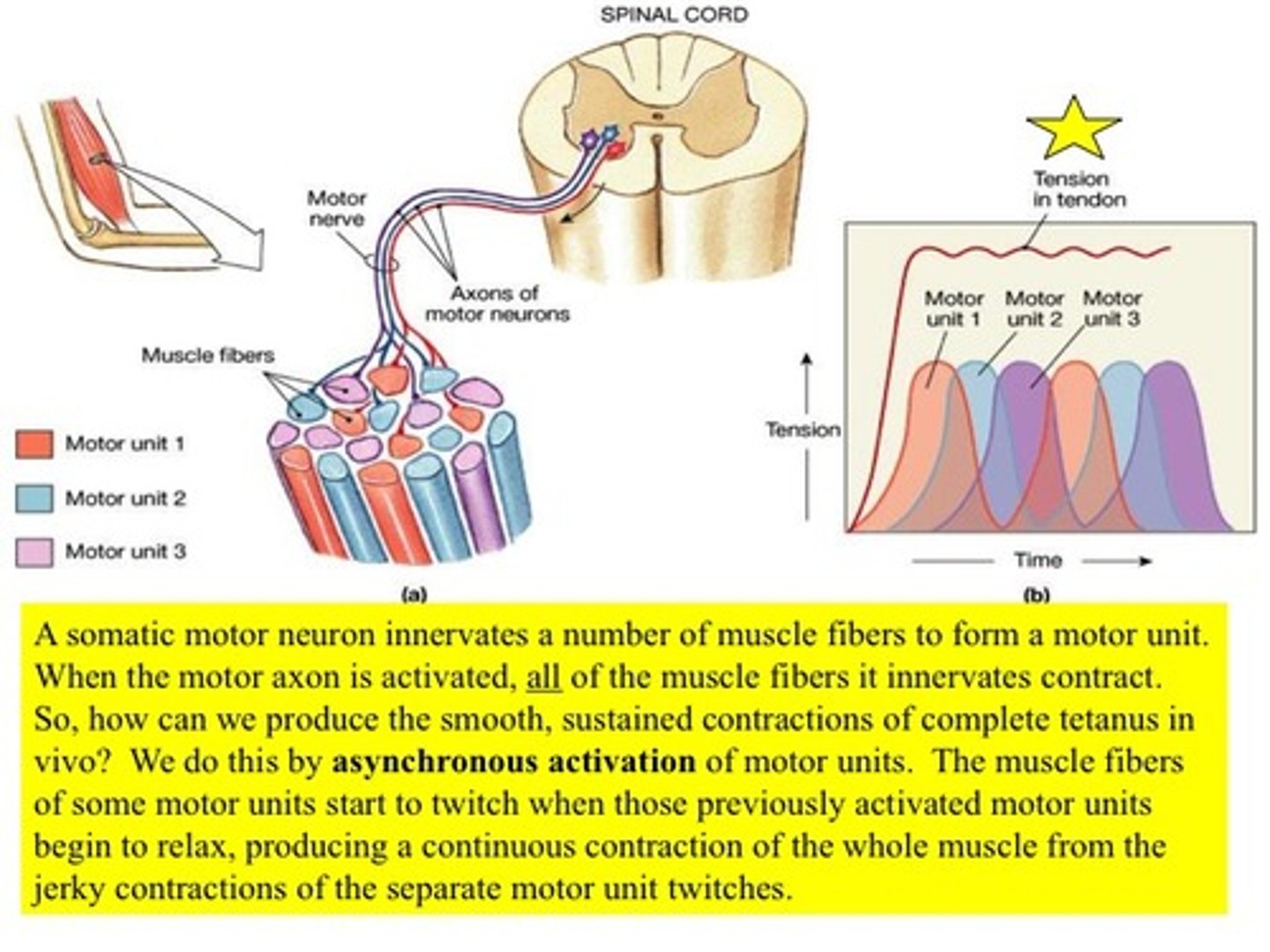
asynchronous activation of motor units
When the nervous system modulates the firing rates of the motor so that different motor units take turns maintaining muscle tension
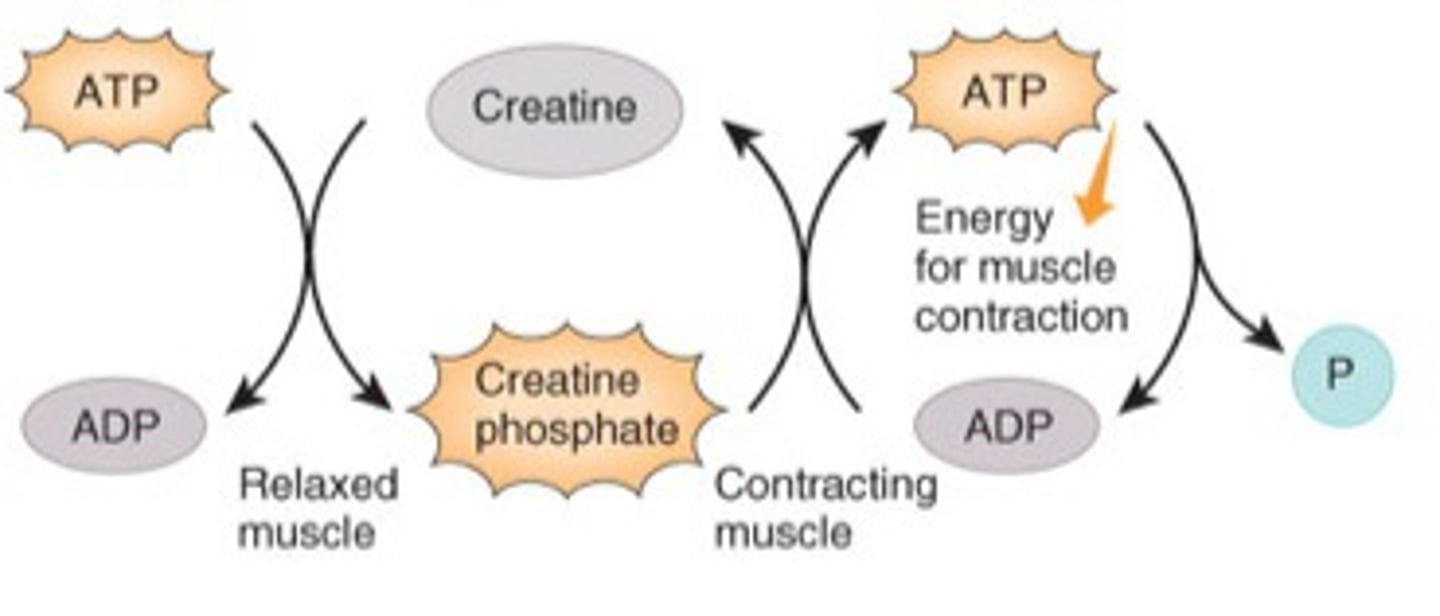
creatine phosphate
An energy storage molecule used by muscle tissue. The phosphate from creatine phosphate can be removed and attached to an ADP to generate ATP quickly.
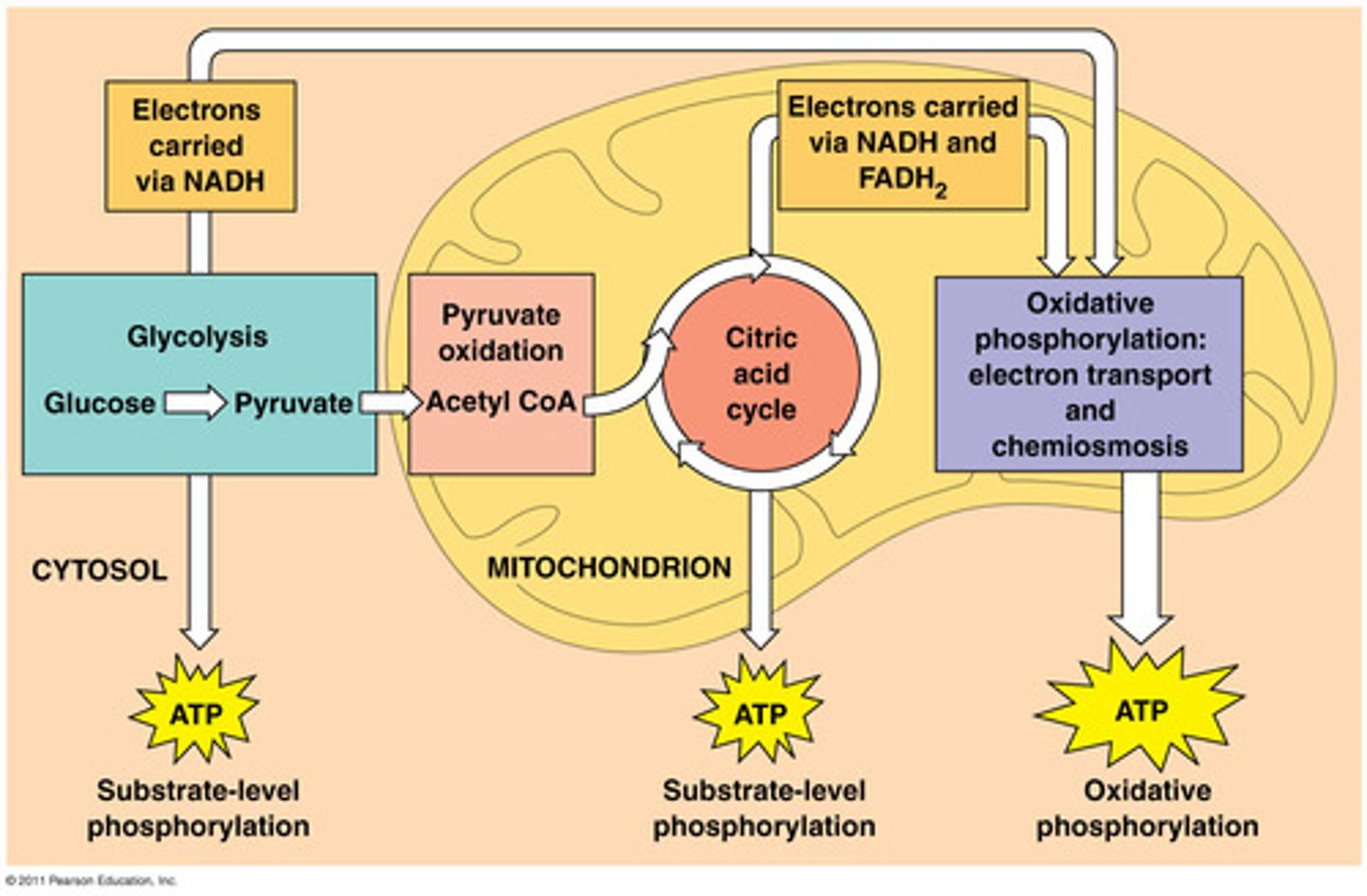
oxidative phosphorylation
When energy is released at each step of the chain is stored in a form the mitochondrion can use to make ATP.
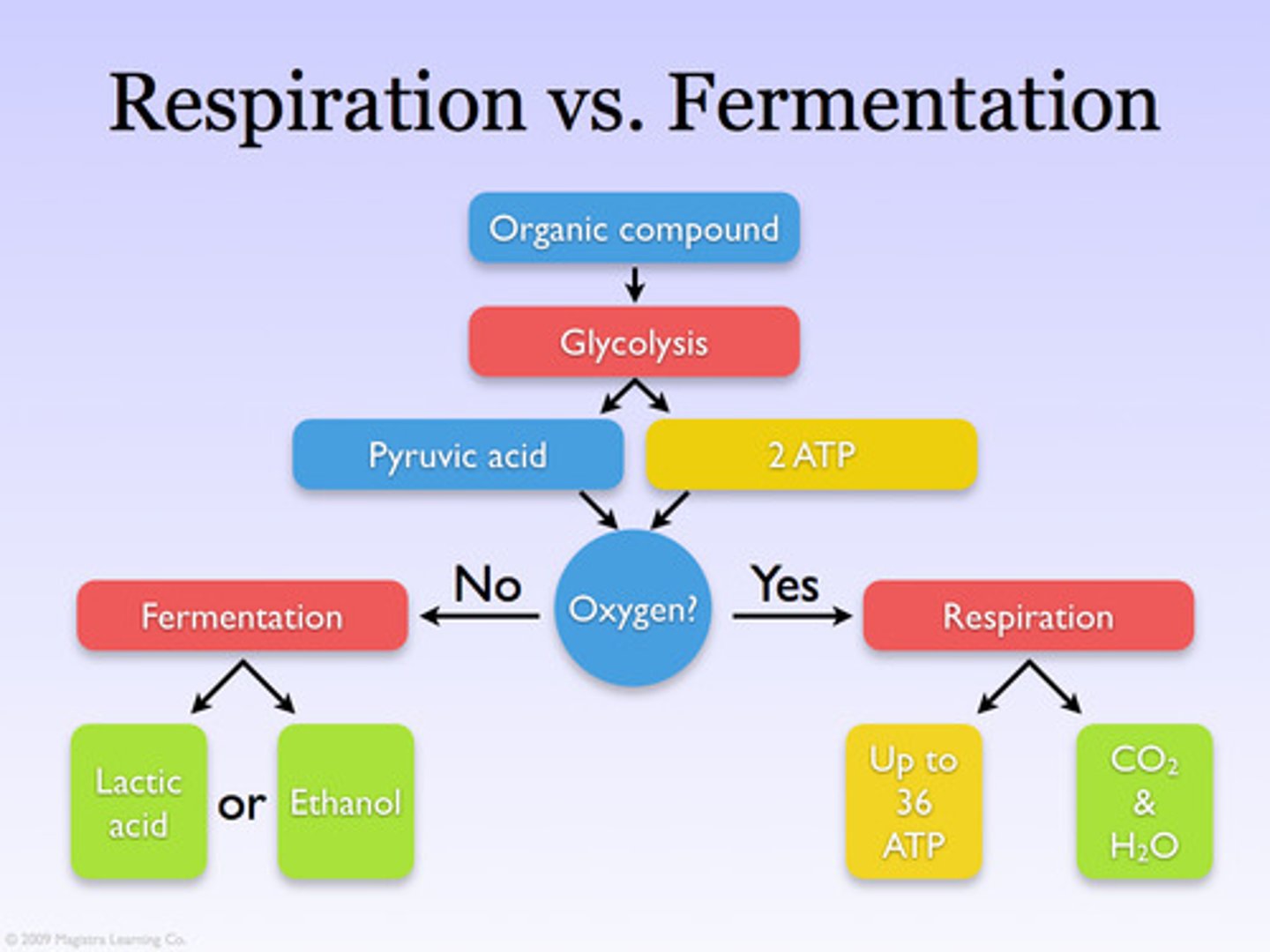
fermentation (anaerobic respiration)
Process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen
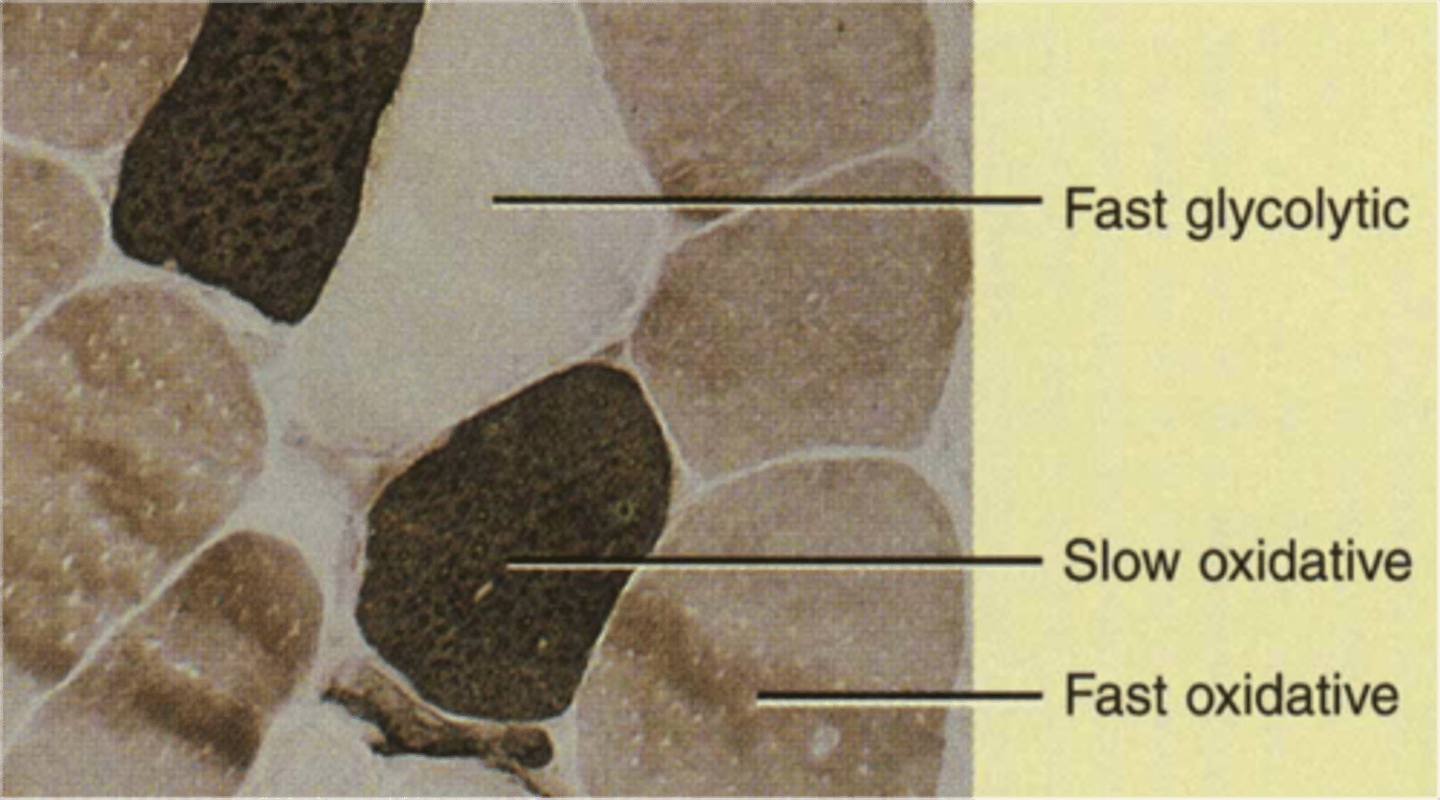
fast twitch fibers
muscle fibers that contract rapidly and forcefully but fatigue quickly

fast glycolytic fibers
contract quickly, have fast myosin ATPase, and are easily fatigued
muscle fatigue
inability of muscle to maintain force of contraction after prolonged activity
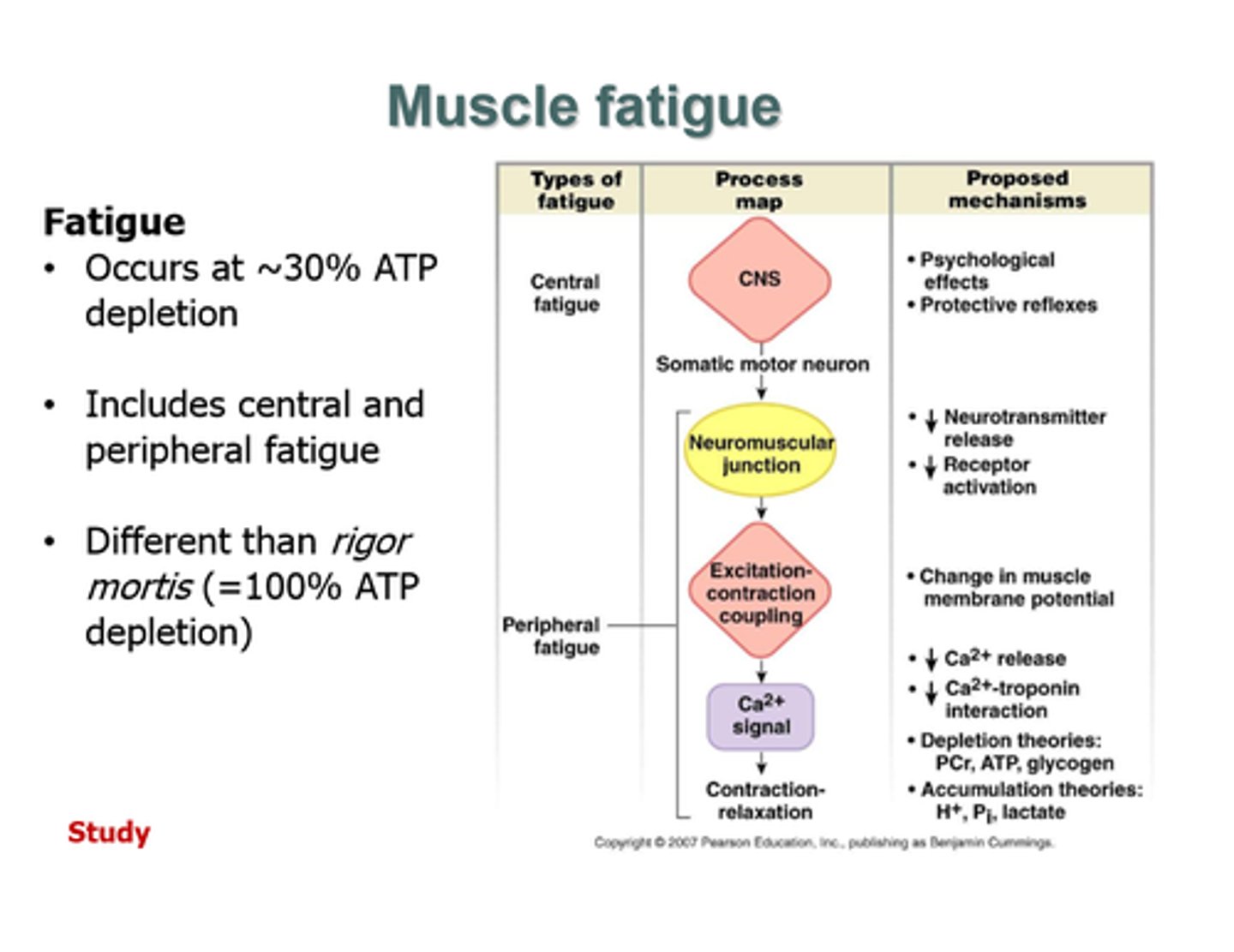
muscle atrophy
loss of muscle bulk due to muscle disease, nervous system disease, or lack of use; commonly called muscle wasting
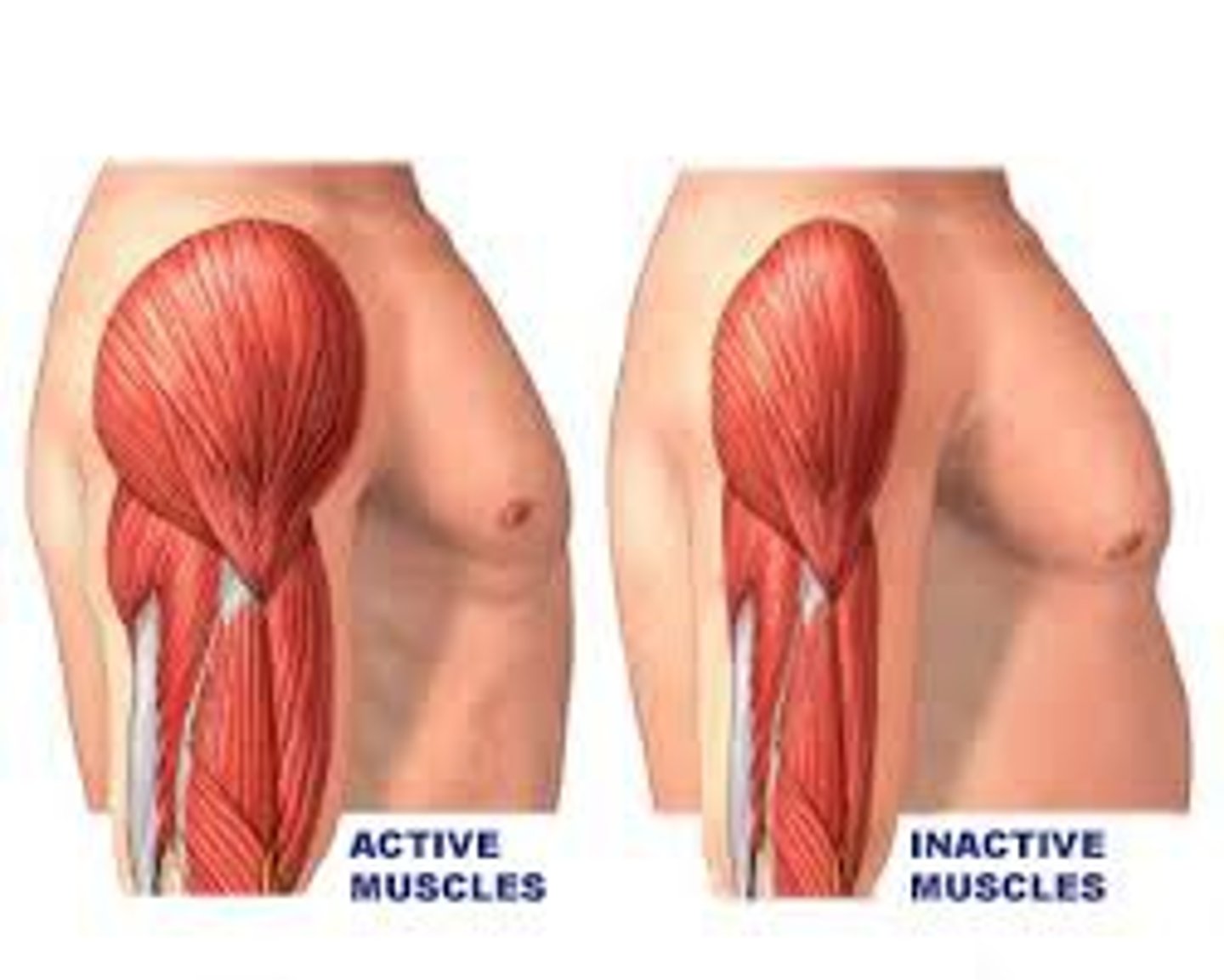
muscle hypertrophy
muscle enlargement from overuse
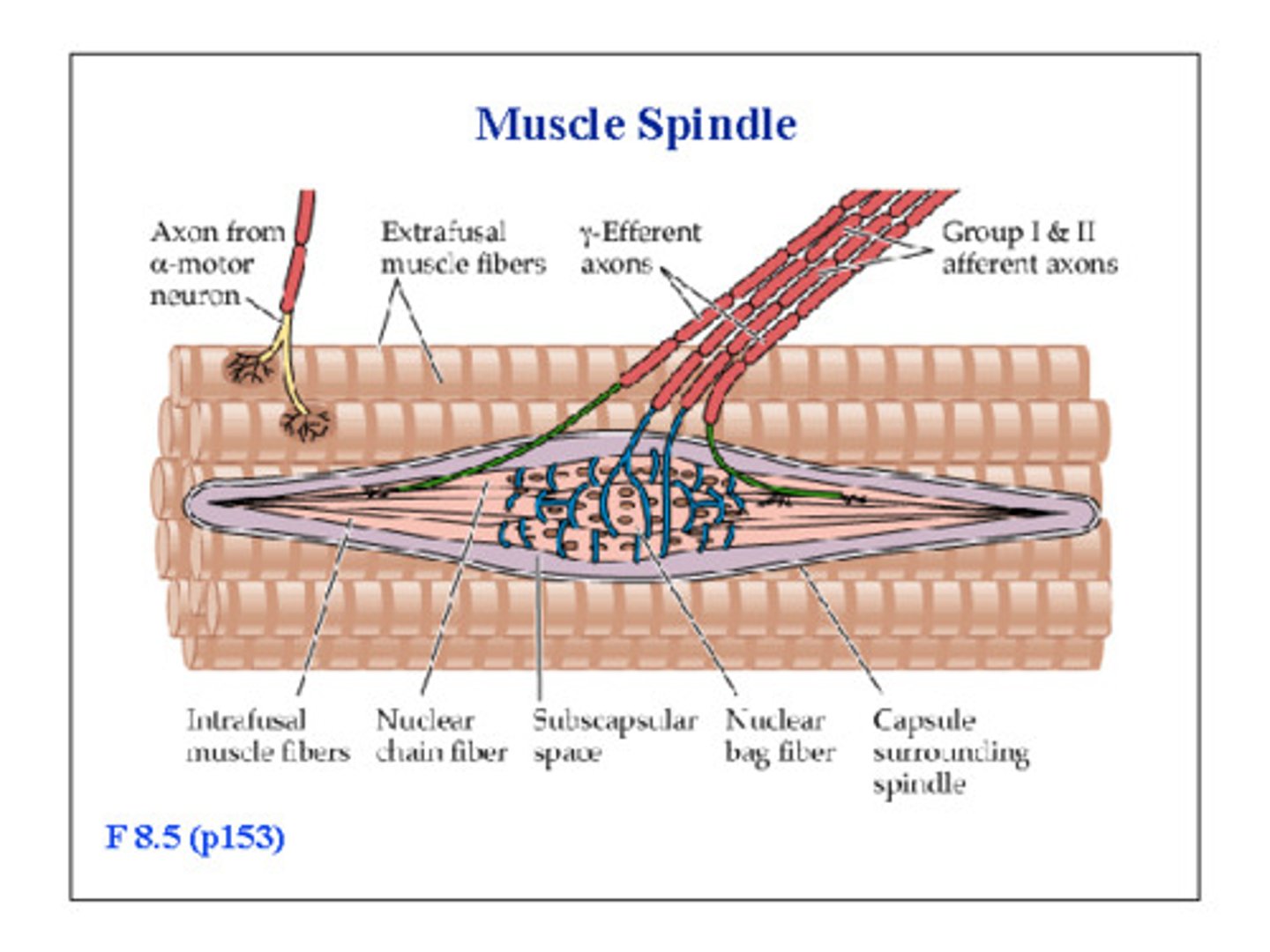
muscle spindle
a sensory receptor located in a muscle that senses its tension
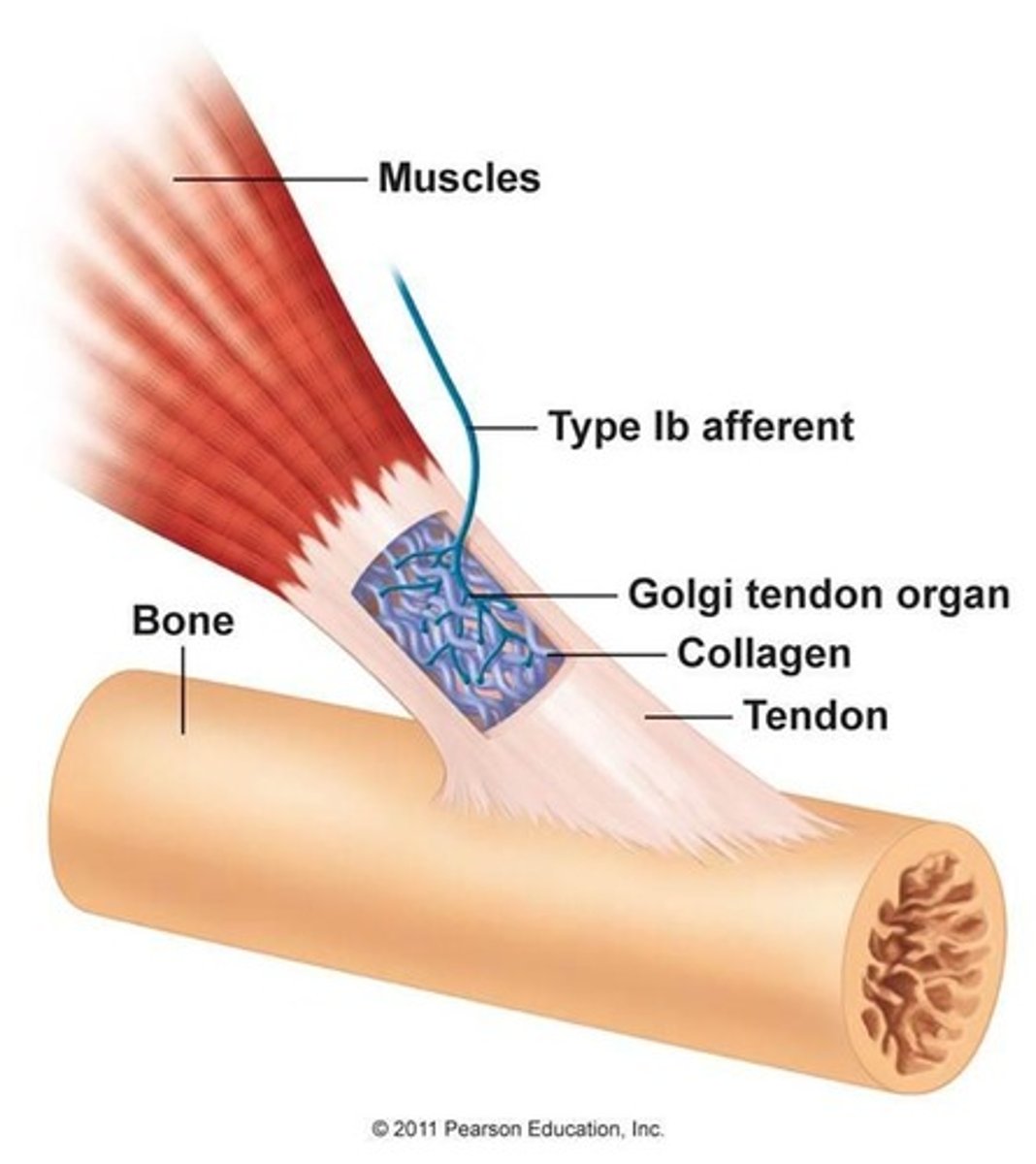
Golgi tendon organ
the receptor organ at the junction of the tendon and muscle that is sensitive to stretch
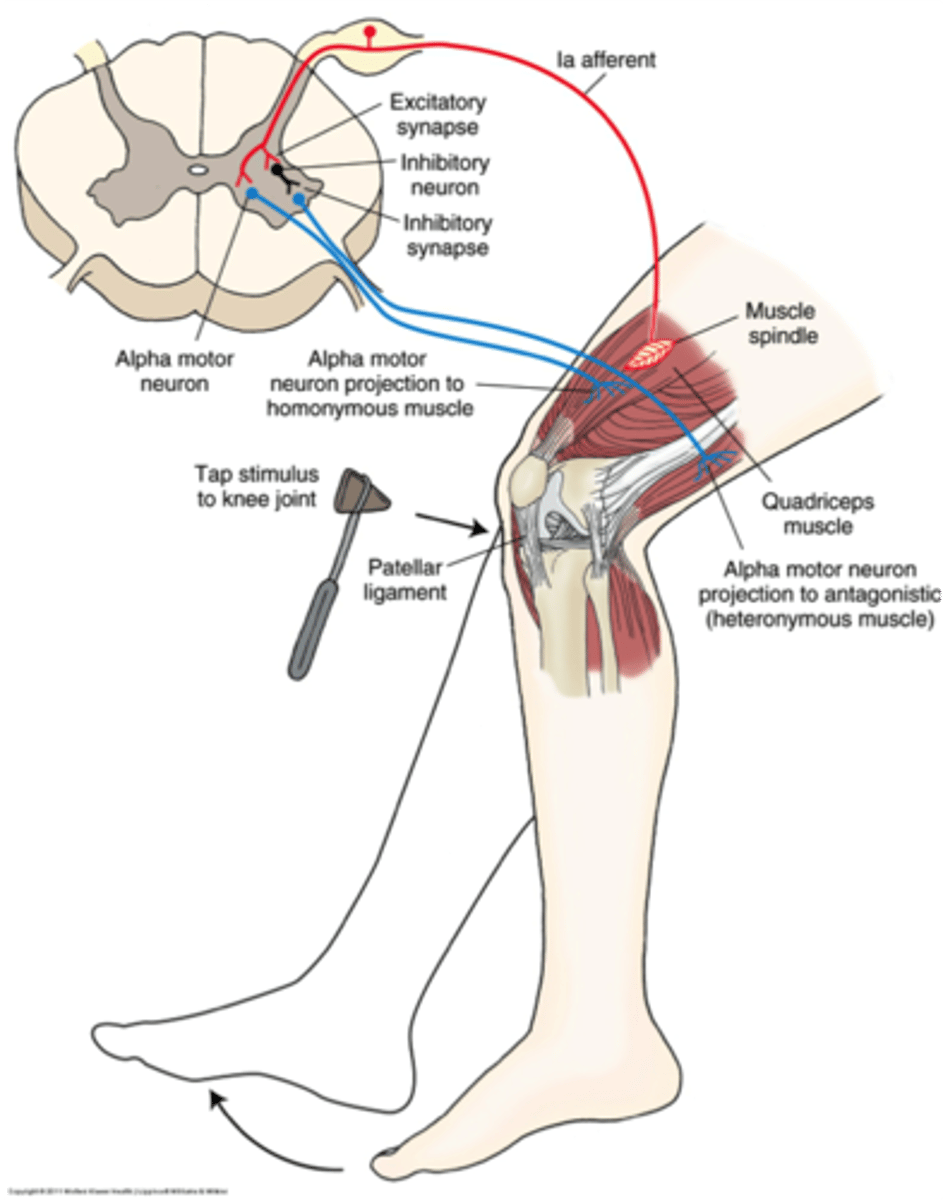
muscle spindle stretch reflex
spinal reflex, is the only known monosynaptic reflex in the human body
For example, in the knee jerk reflex, tapping the patellar tendon stretches the quadriceps muscle, which excites muscle spindles in that muscle and triggers APs that travel to the spinal cord. Efferent neurons in the muscle stimulate the quadriceps to contract an the leg to "kick" forward, or extend.
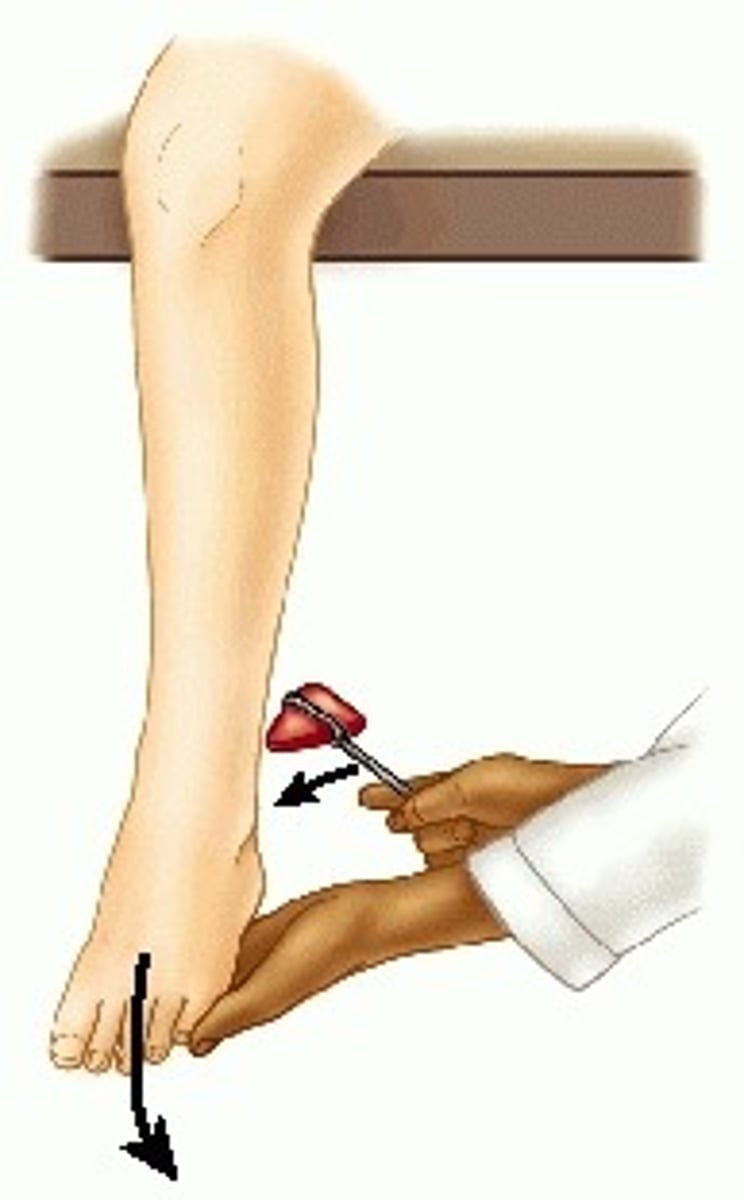
tendon reflex
reflexive contraction of a muscle when its tendon is tapped
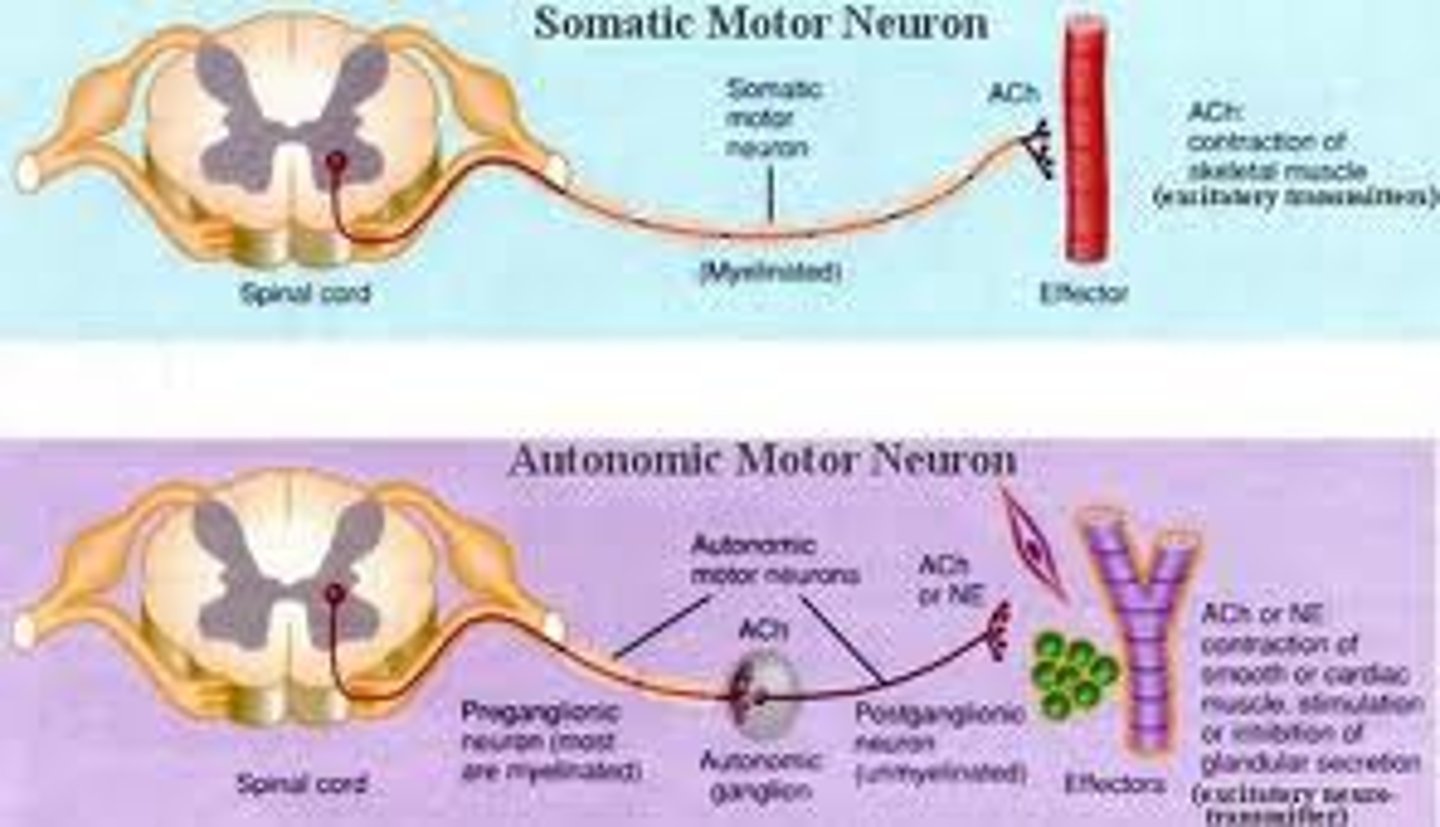
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
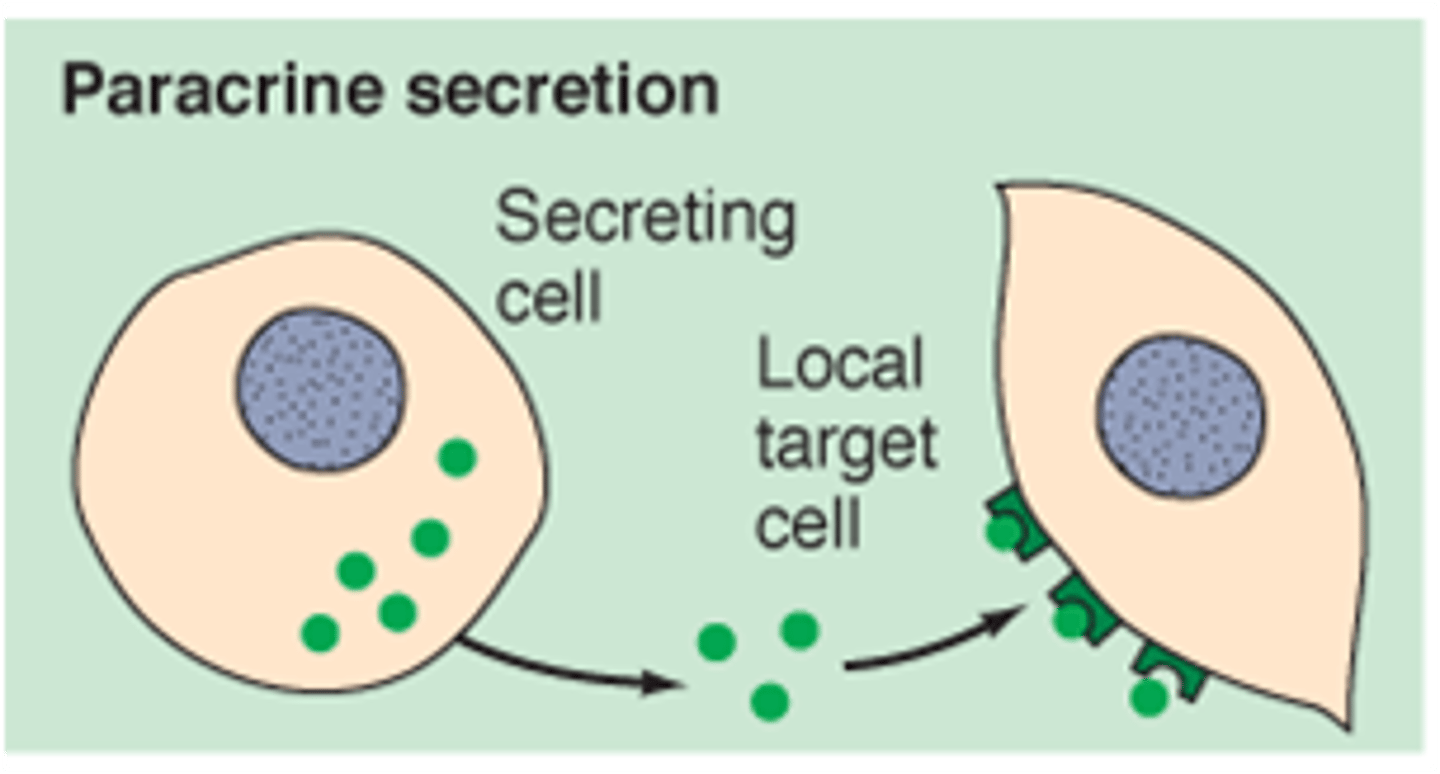
paracrines
locally acting chemicals that affect cells other than those that secrete them
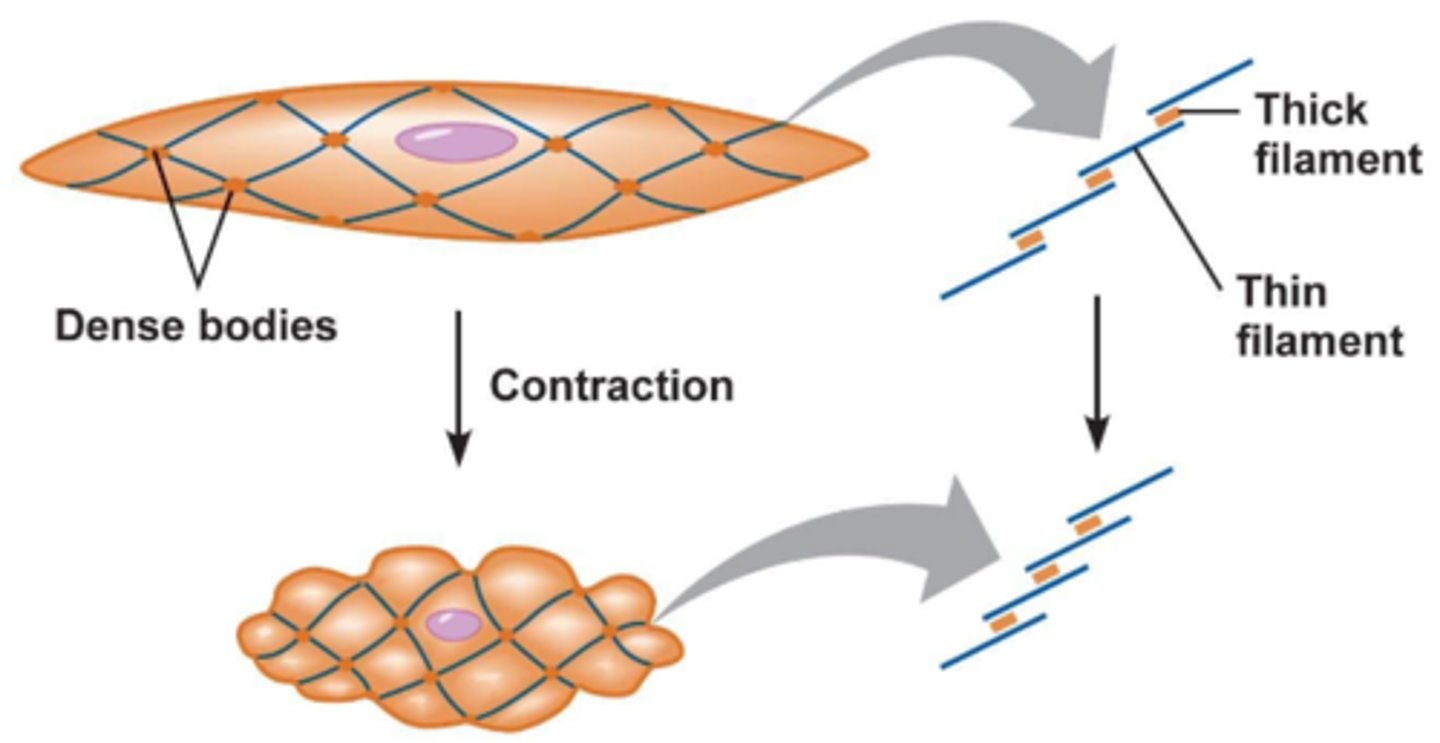
dense bodies
cytoplasmic structure to which thin filaments of a smooth muscle fiber are anchored
calmodulin
calcium binding protein
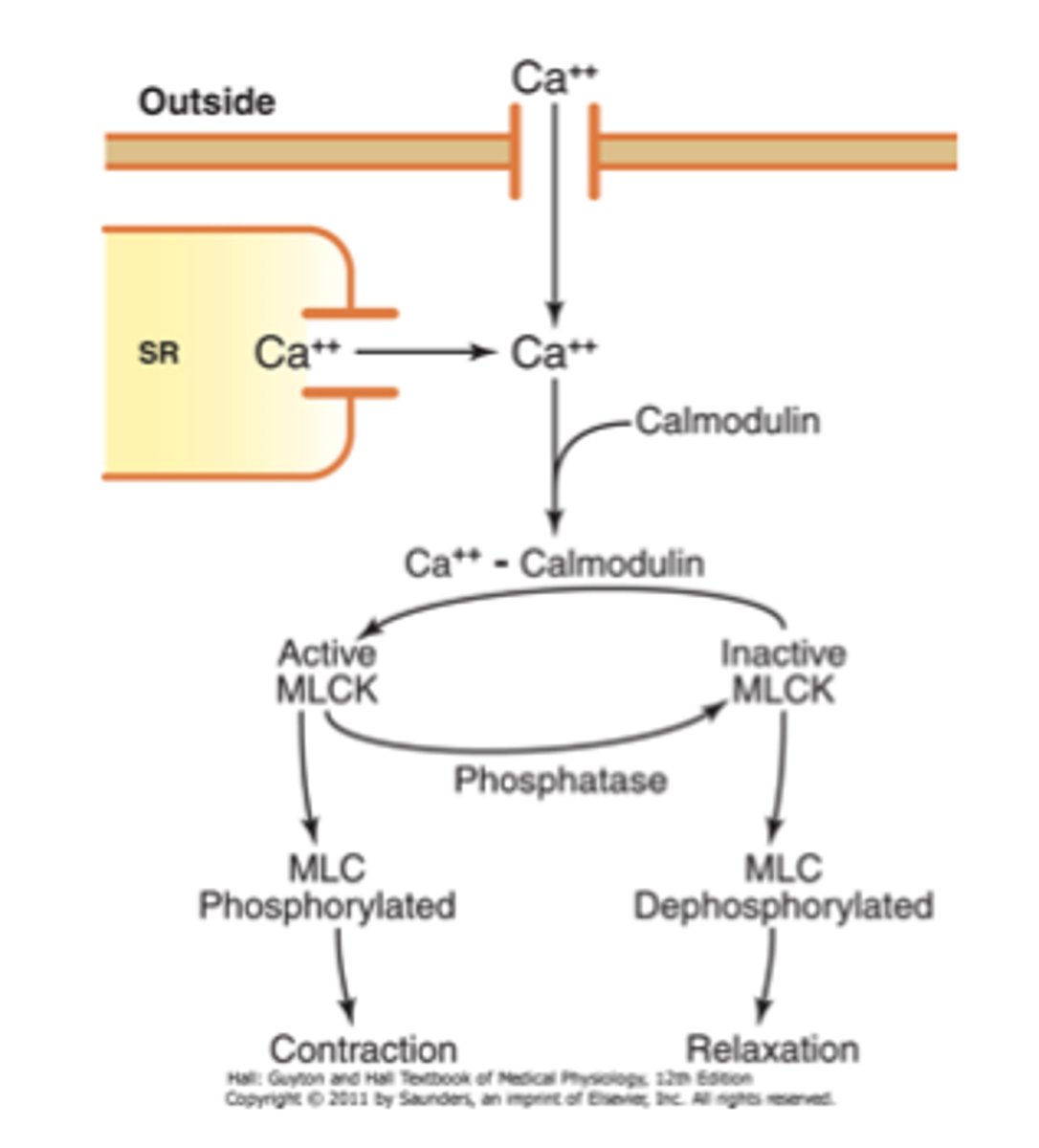
myosin light-chain kinase (MLCK)
A kinase in smooth muscle cells activated by calmodulin the presence of Ca2+. As its name implies, this kinase phosphorylates myosin, activating it so that muscle contraction can occur.
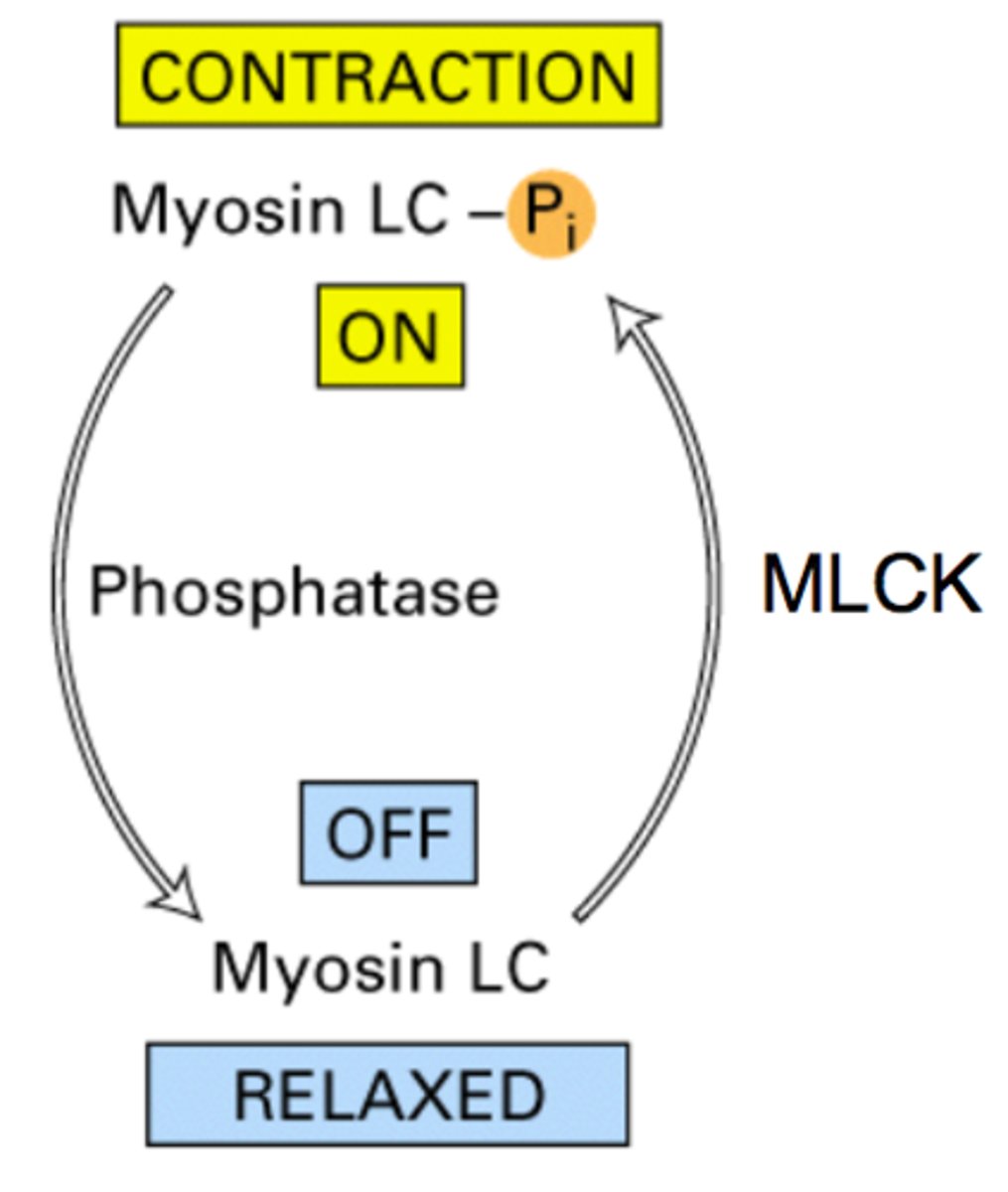
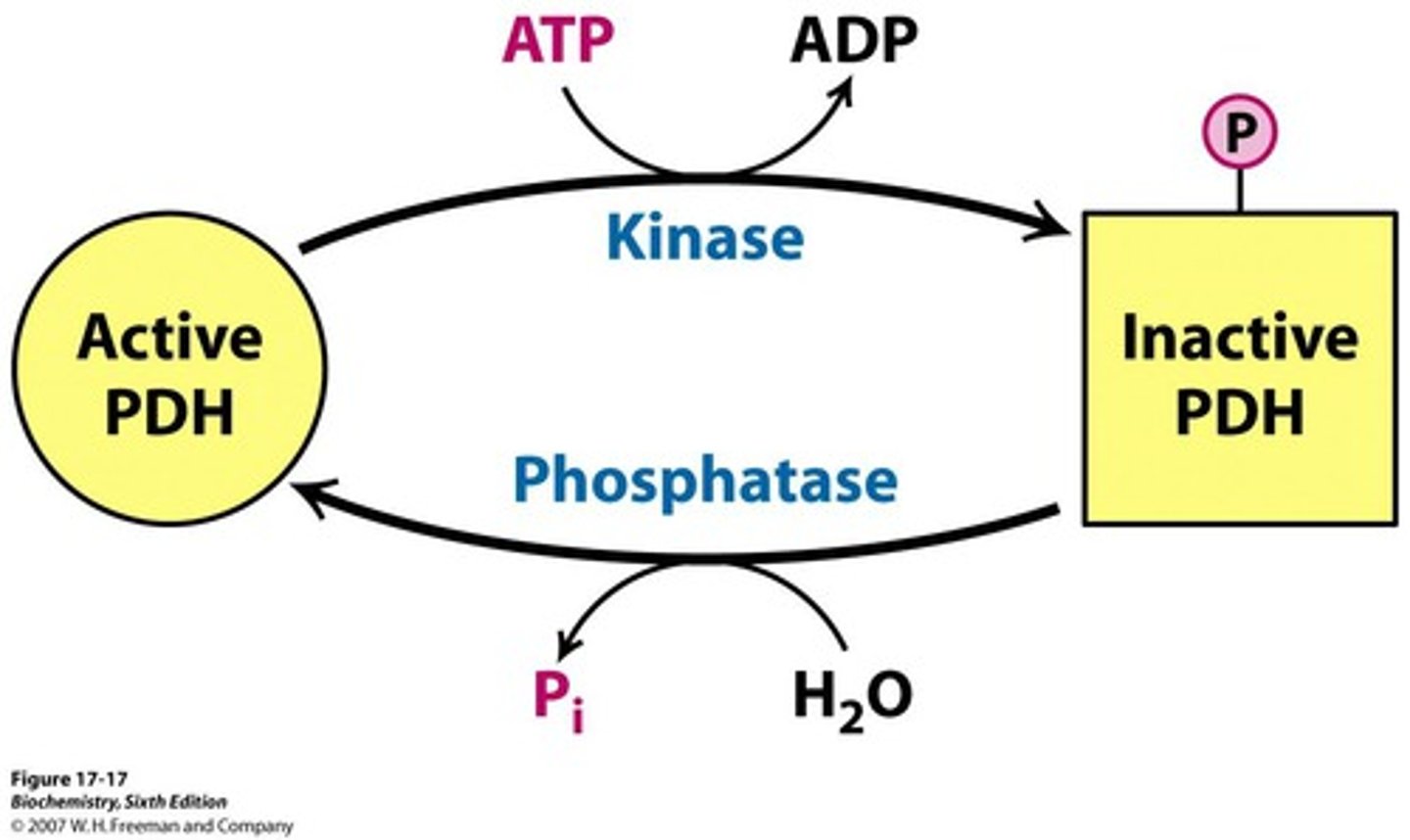
phosphatase
removes a phosphate group from a molecule
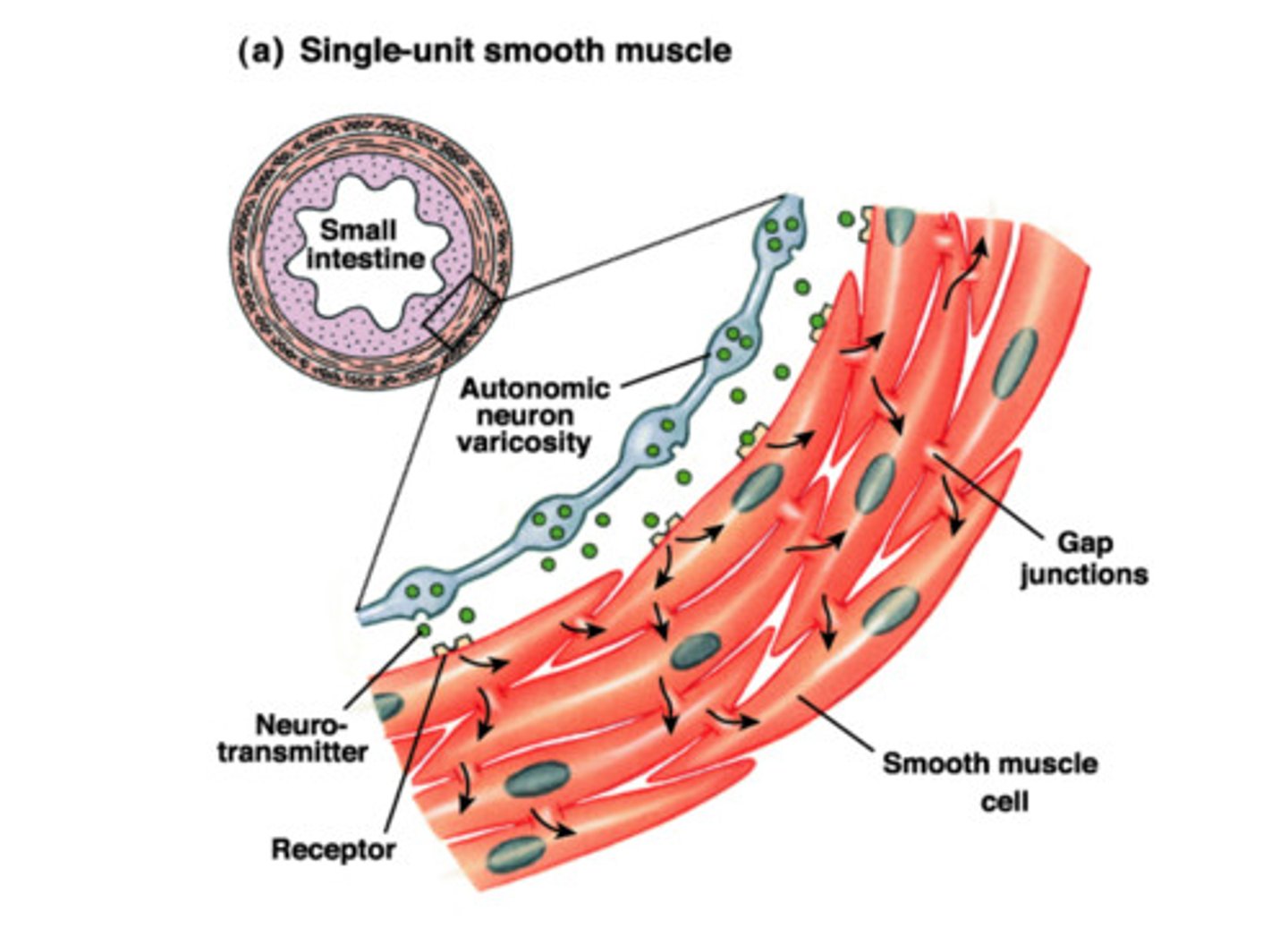
single unit smooth muscle
Smooth muscle with gap junctions linking the cells together so they function as a unit
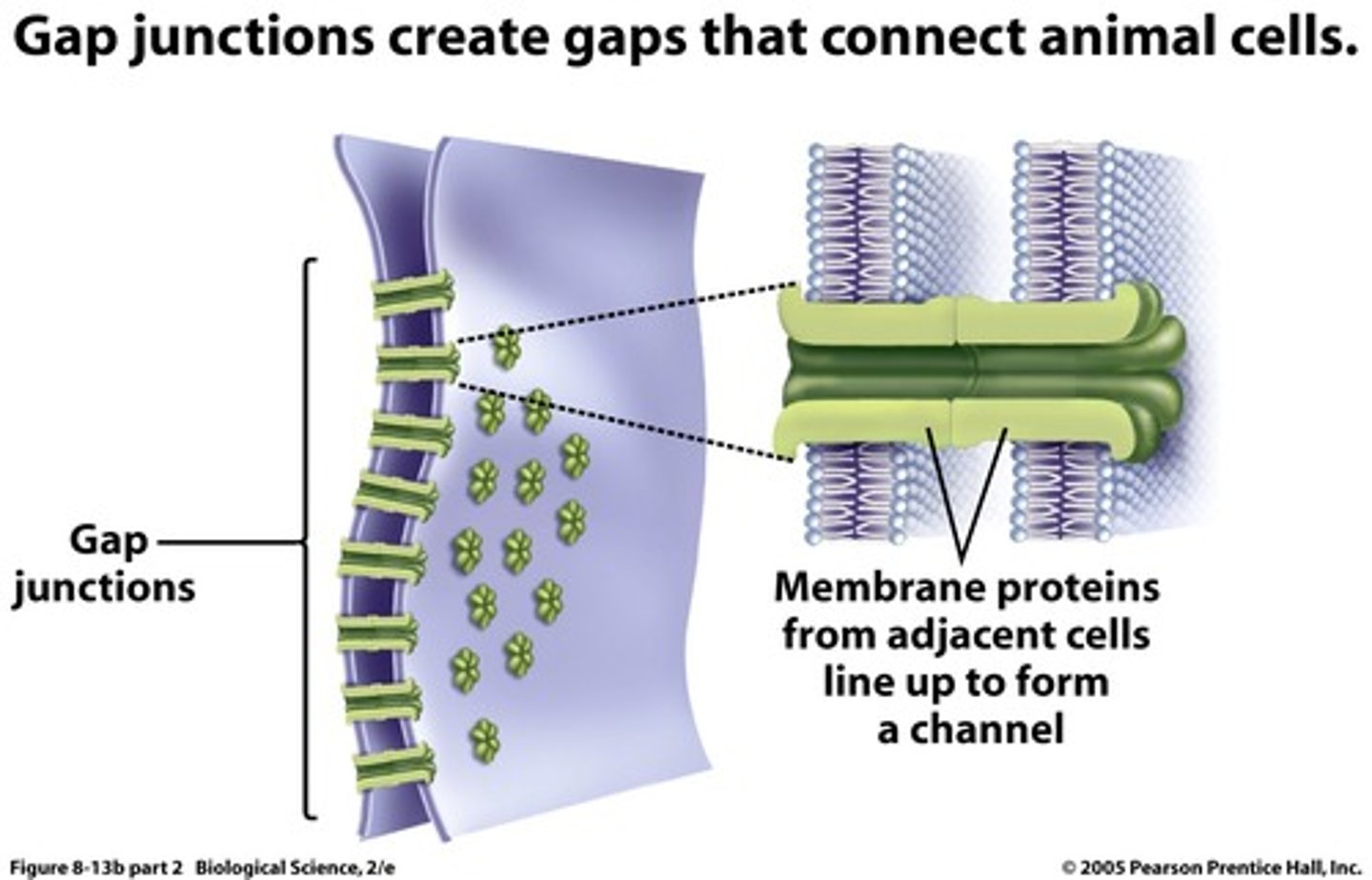
gap junctions
Points that provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to another with special membrane proteins. Also called communicating junctions.
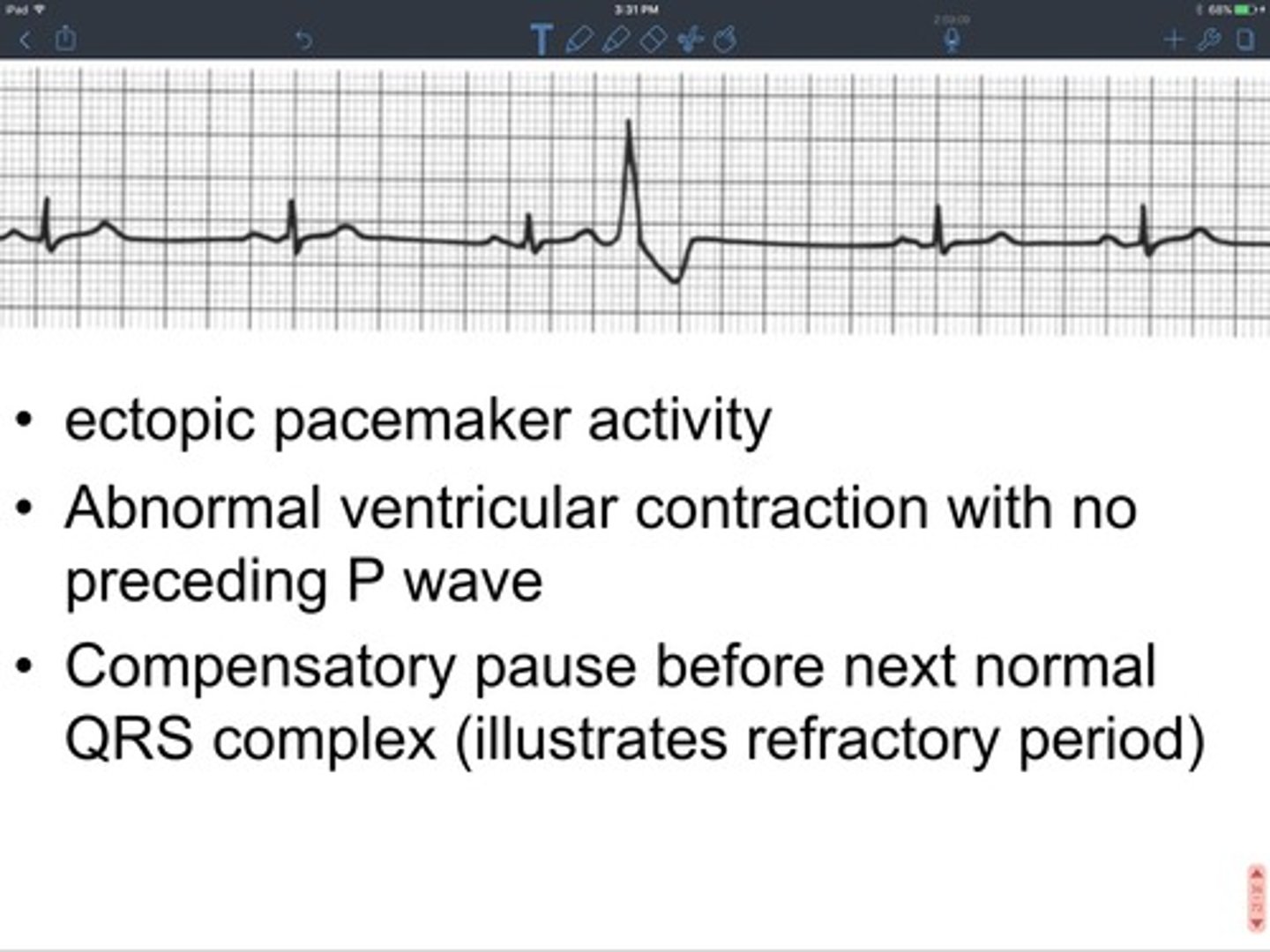
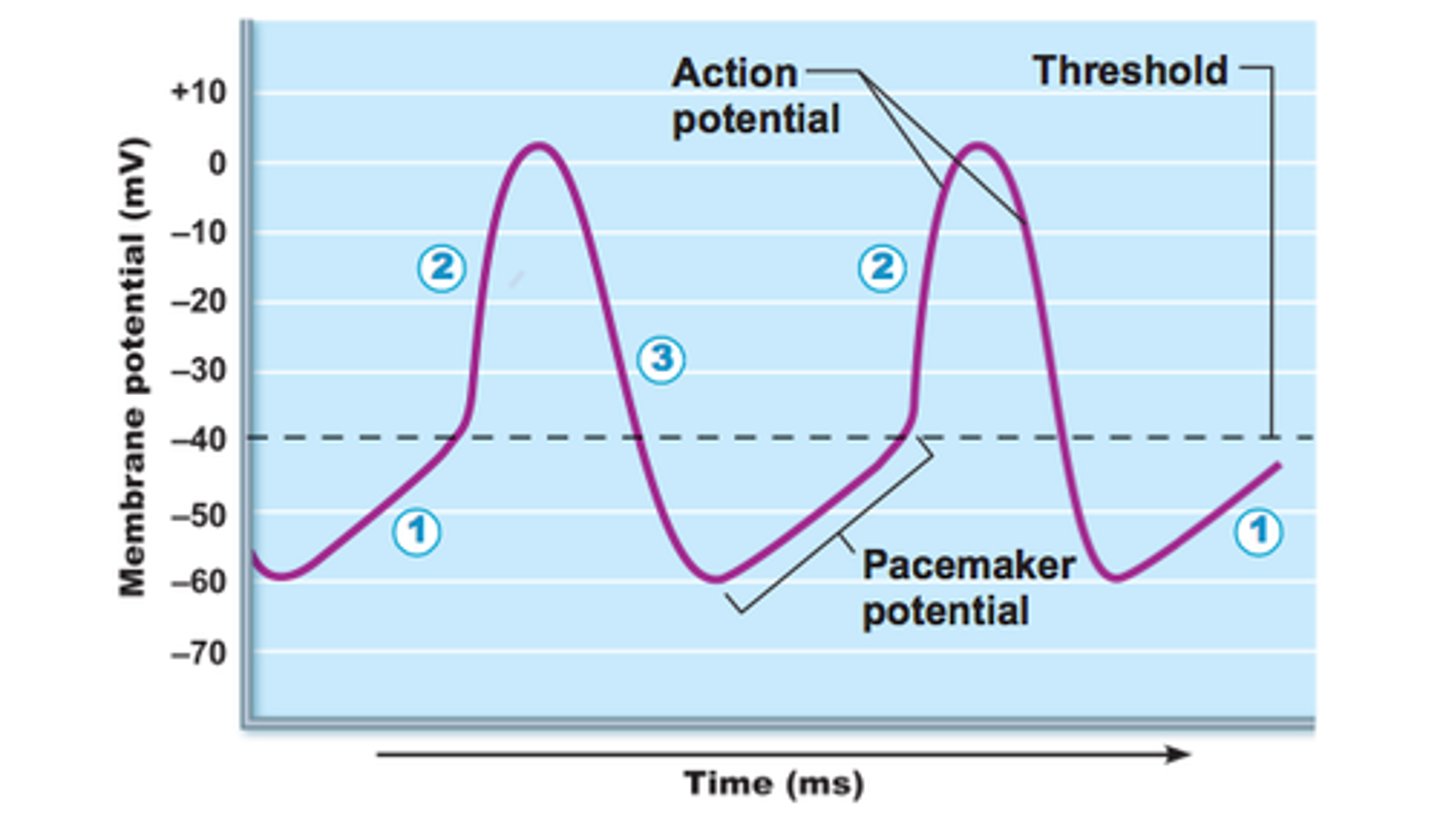
pacemaker activity
some cells contain special ionic channels which open or close spontaneously and rhythmically without external stimulation which results in a threshold depolarization at the initial segment
pacemaker potentials
initiate the action potentials that spread out through the heart to trigger its rhythmic contractions
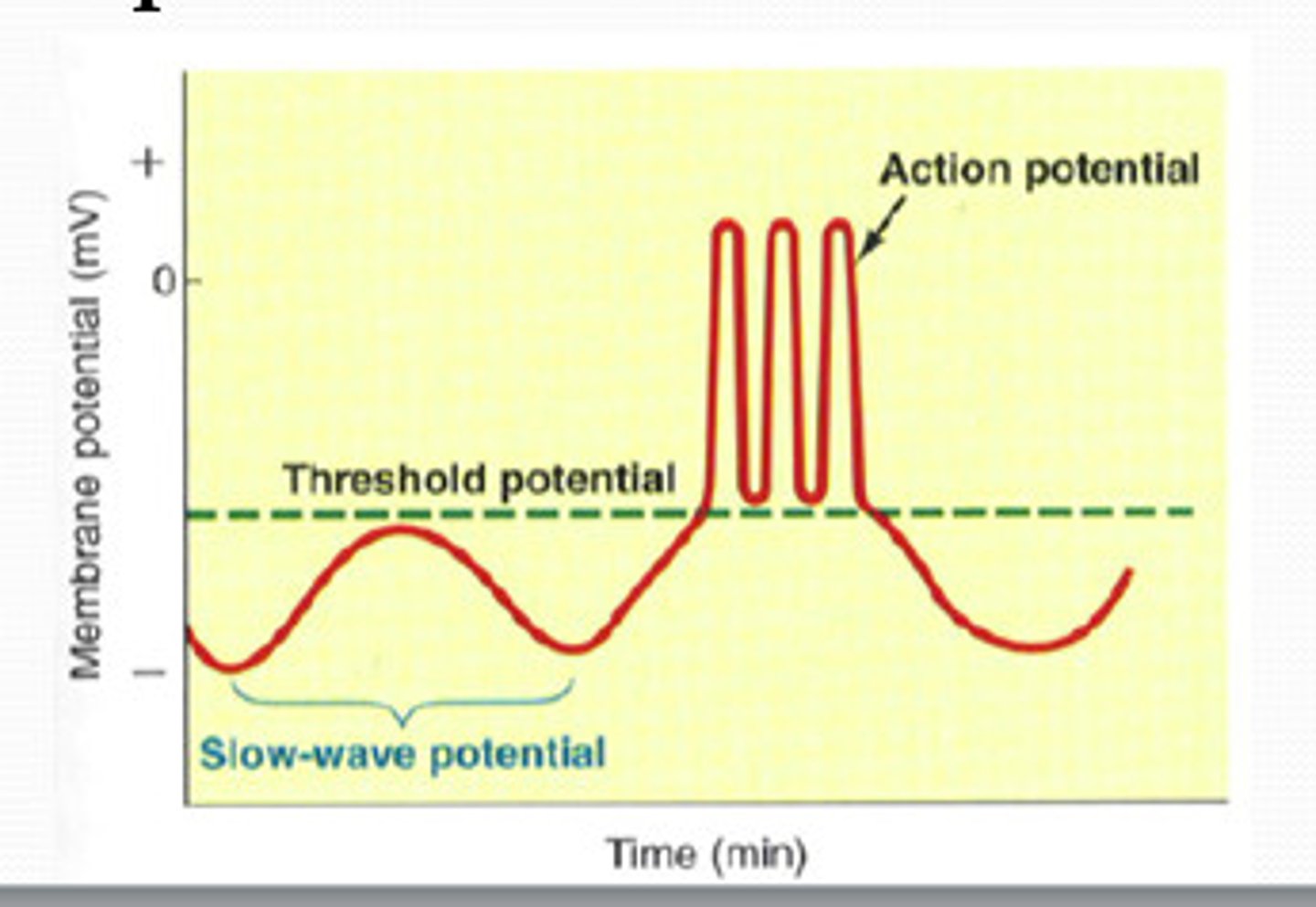
slow wave potentials
basic electrical rhythm of GI tract, spontaneous, rhythmic cycles of depolarization and repolarization
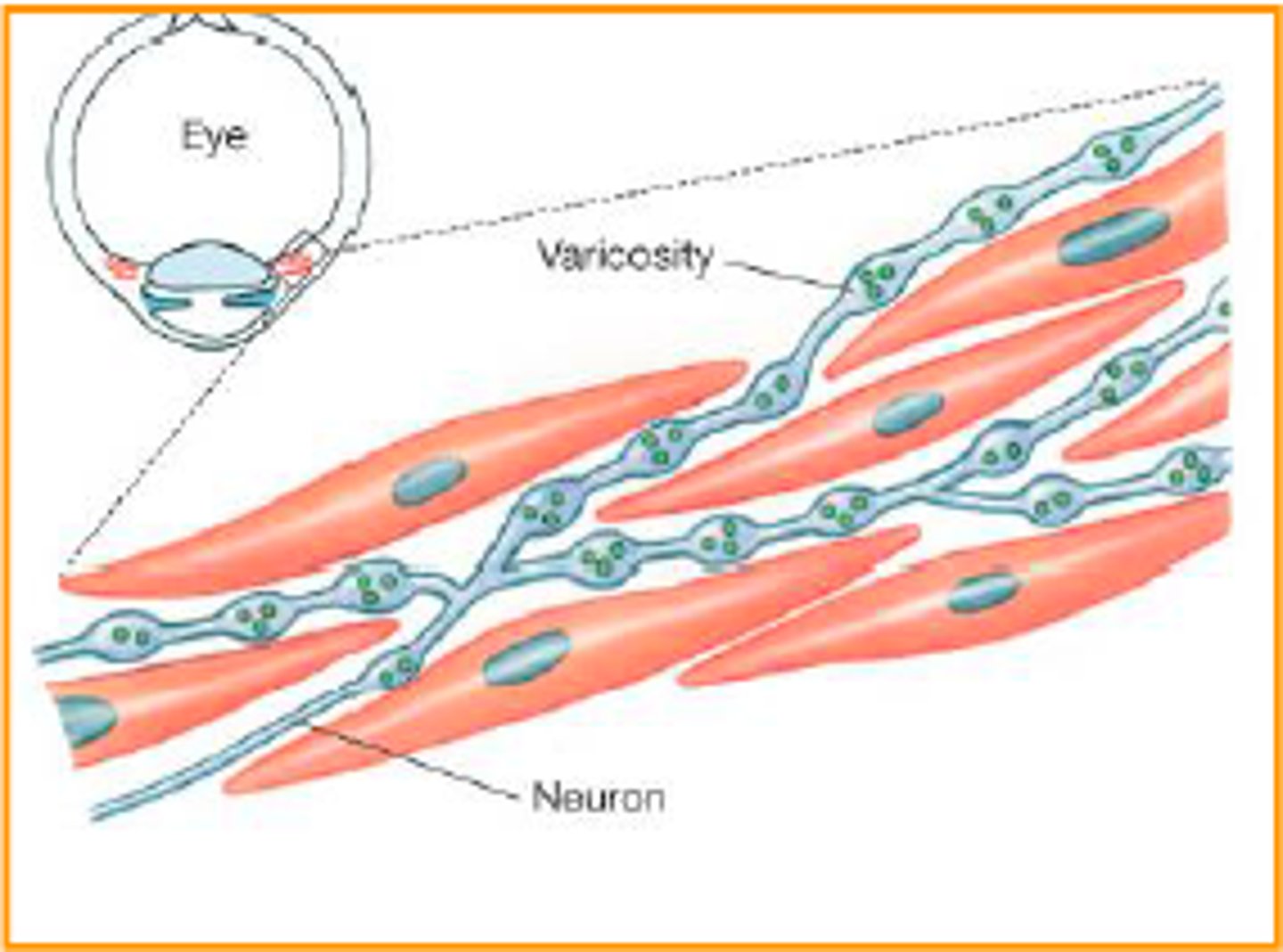
multi-unit smooth muscle
a type of smooth muscle found in the iris of the eye and in the walls of blood vessels
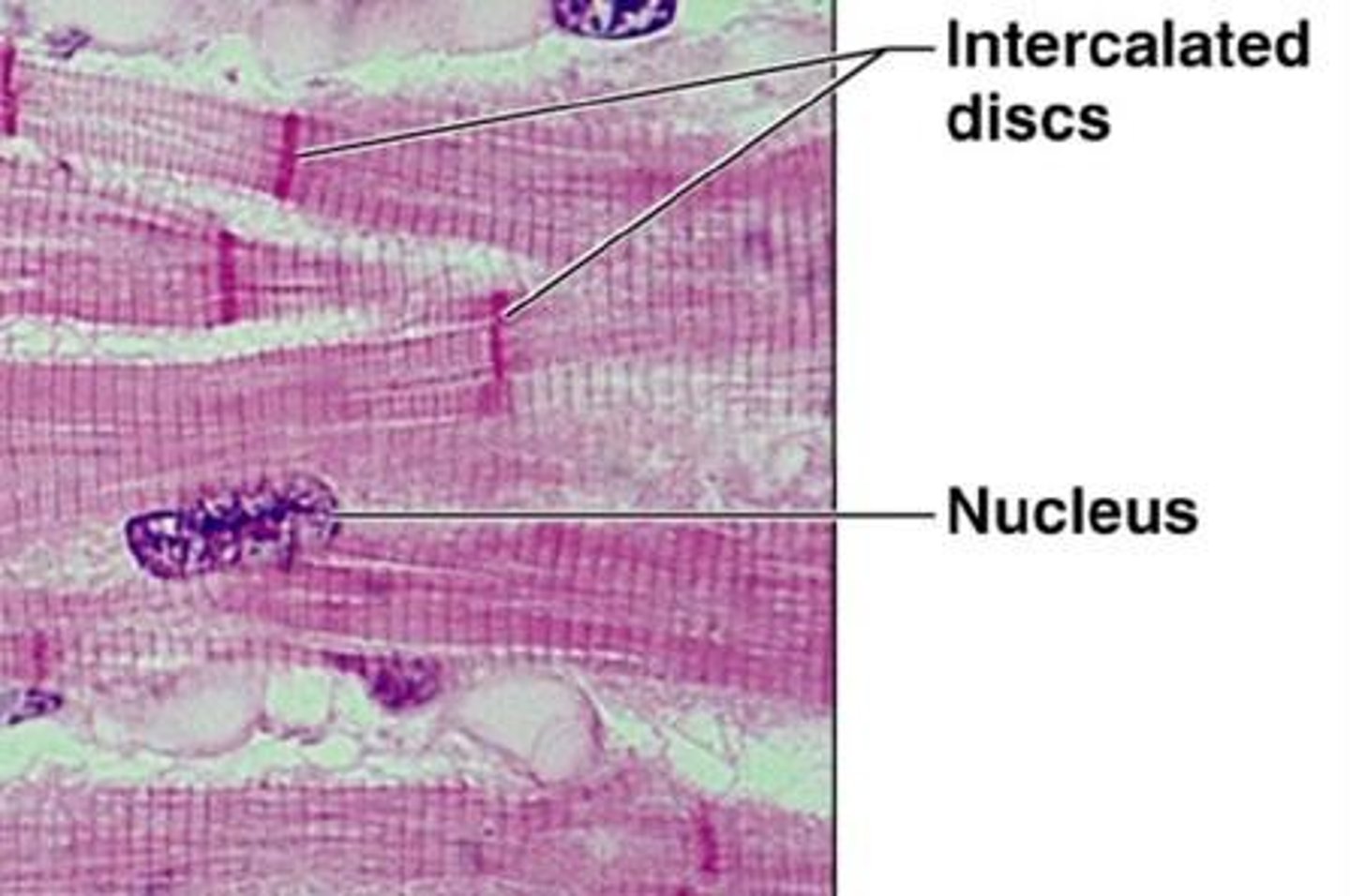
intercalated disks
These structures branch and connect cardiac cells. They contain specialized gap junctions and coordinate muscle contractions.
pacemaker cells
heart cells that regularly produce spontaneous electrical impulses
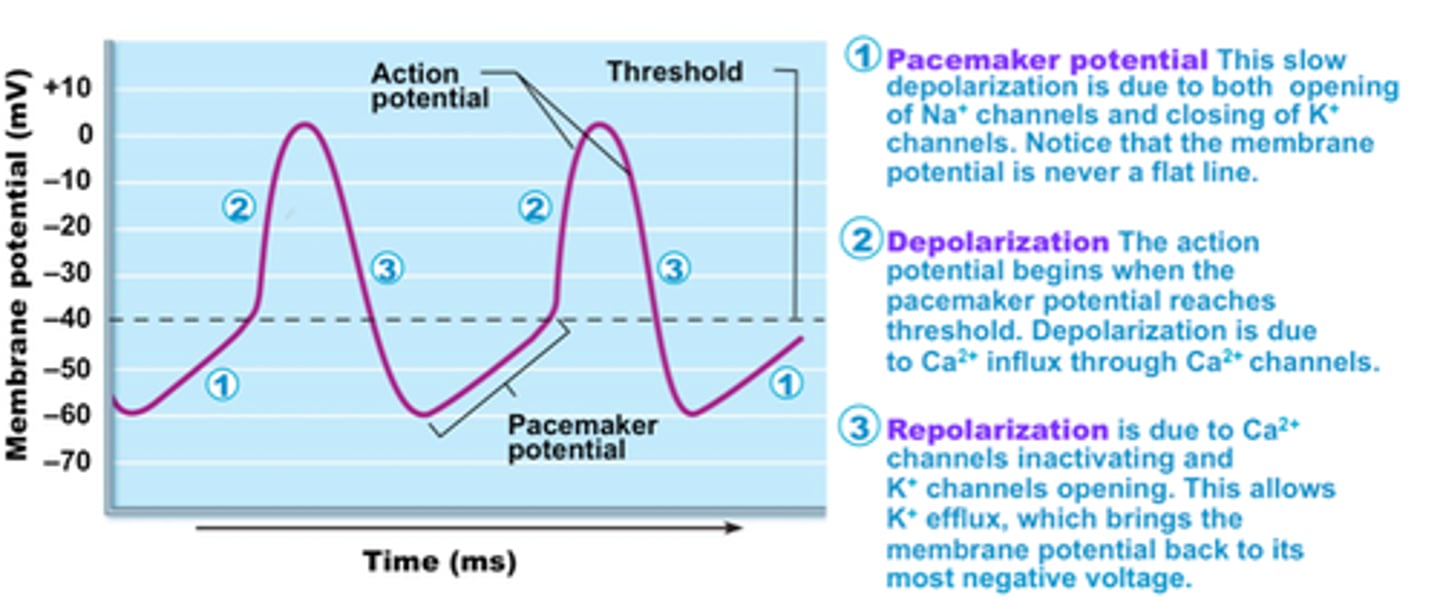
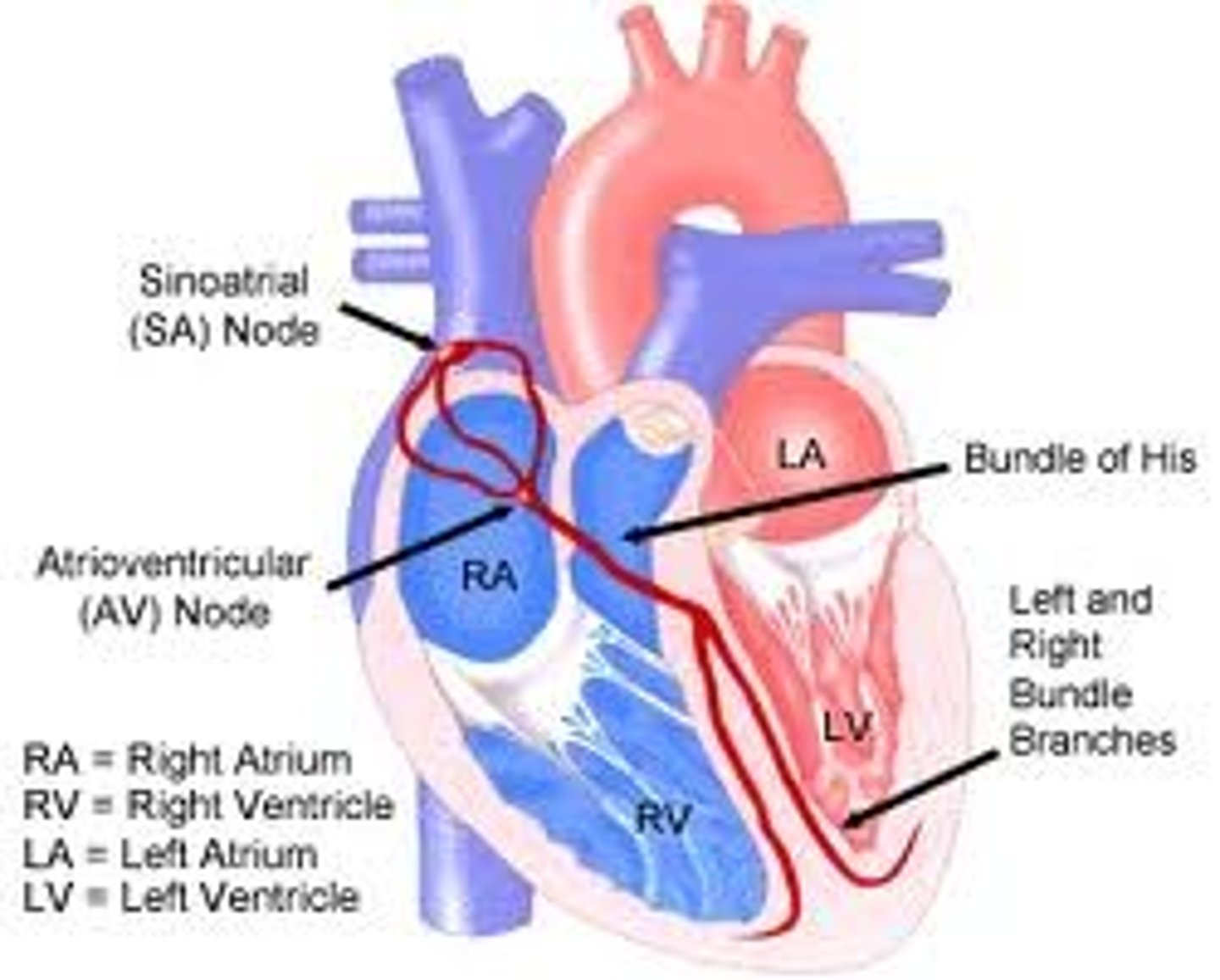
sinoatrial node
A small mass of tissue that is made up of Purkinje fibers, ganglion cells, and nerve fibers, that is embedded in the musculature of the right atrium, and that originates the impulses stimulating the heartbeat -- called also S-A node, sinus node.
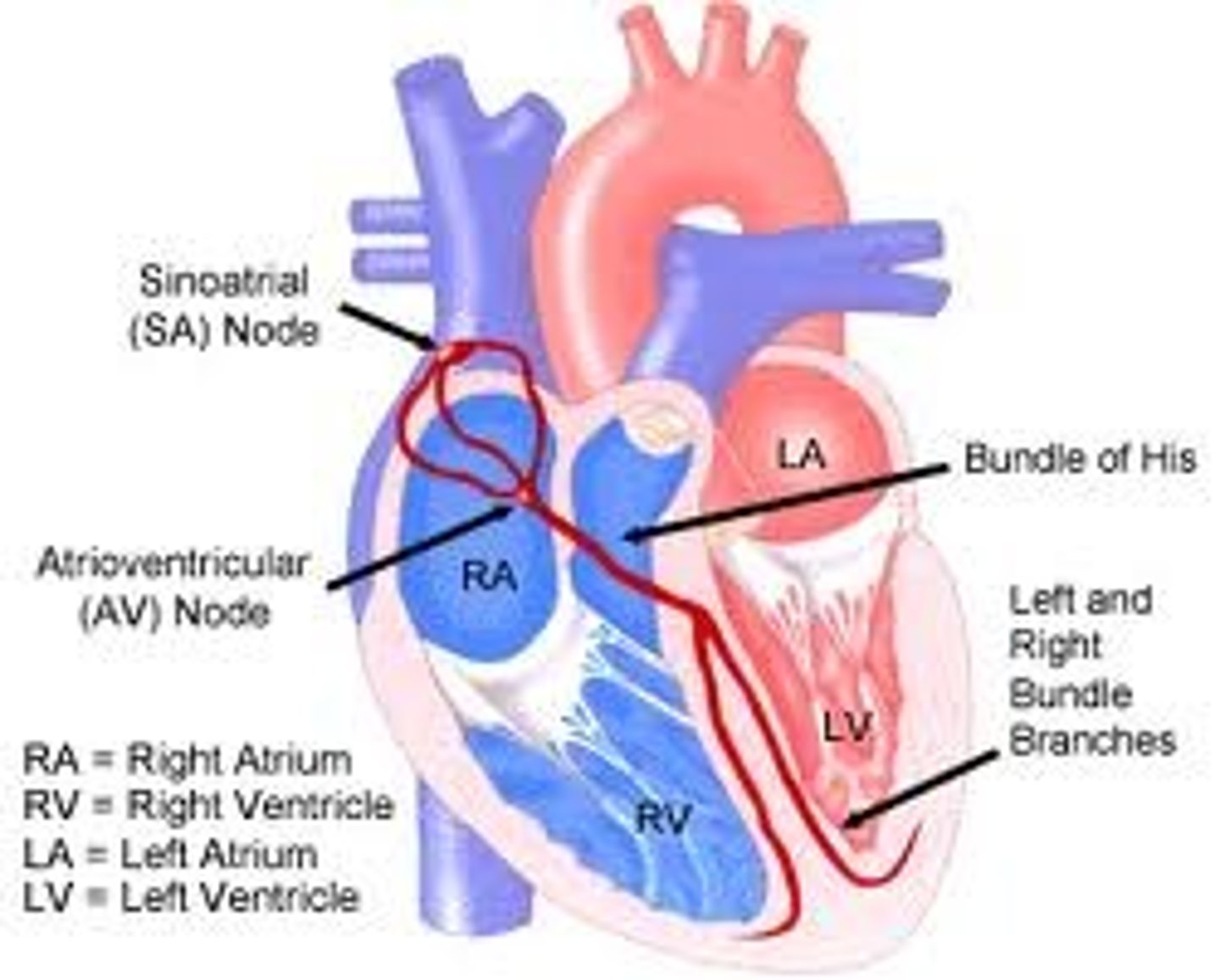
atrioventricular (AV) node
neurological tissue in the center of the heart that receives and amplifies the conduction of impulses from the SA node to the bundle of His
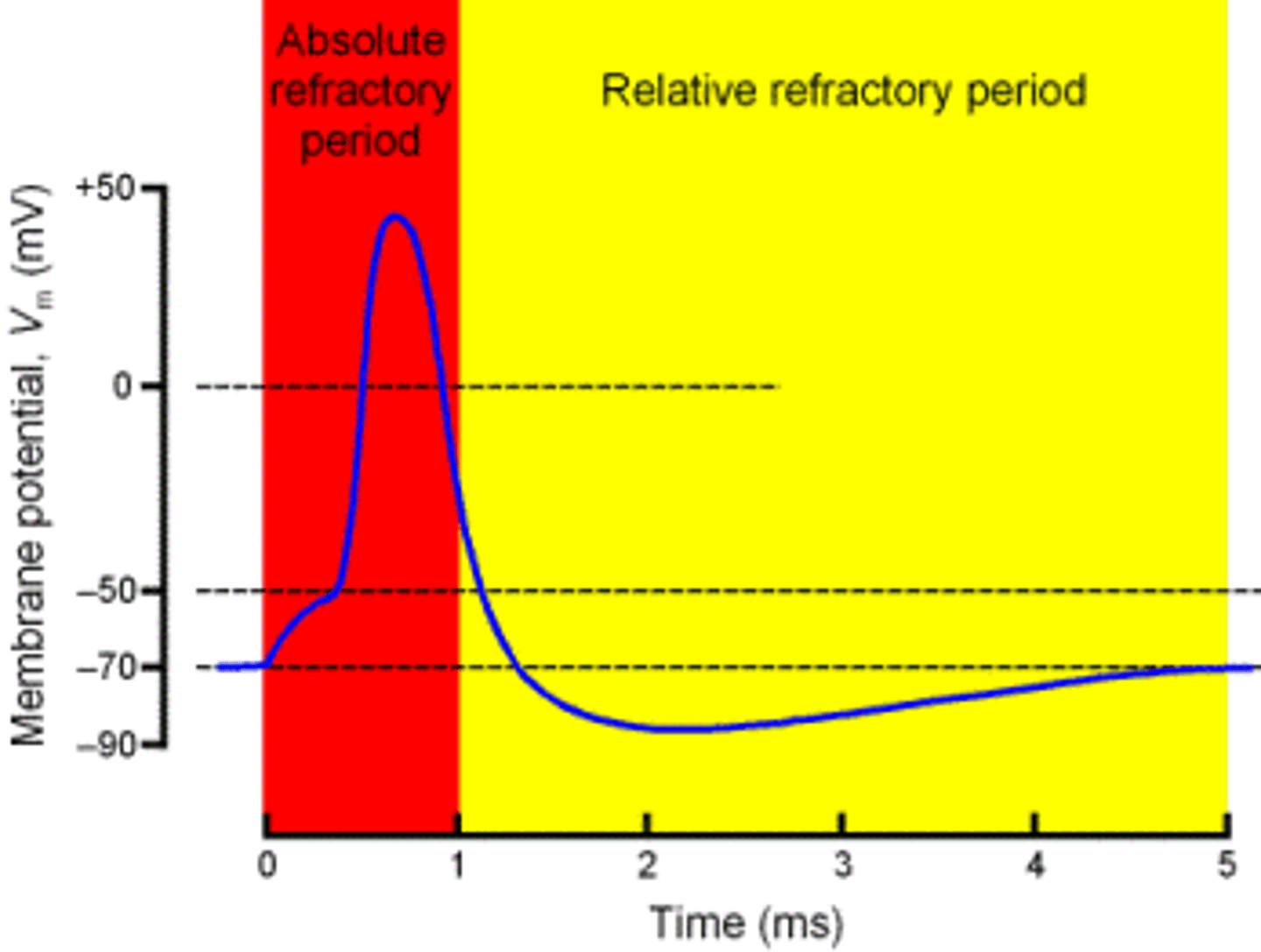
refractory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired