Epidemiology Week 2: 2. Measures of Disease Frequency
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what are the measures of disease frequency?
risk
incidence rate
prevalence
definition: measure of number of new cases of disease/health outcome of interest that develops in population at risk during a specified time period
incidence
definition: Measure of the number of new cases of a disease/health outcome of interest that develops in a population at risk during a specified time.
risk
what is this?
Measured in a closed population
The proportion of the population (BLANK) for the disease who becomes diseased within a given period of time
Also known as cumulative incident (BLANK) or incidents proportion
Must interpret only with specified time period
risk
which term?
Probability of those who will develop the disease
Does not include those who already have the disease or cannot get the disease
Example: someone with hysterectomy vs endometrial cancer
risk
which term?
numerator: # of new cases during time period of interest
risk
which term?
denominator: includes only people at risk
risk
solve for risk and cumulative incidence: 5000 residents w/o diabetes and at end of 5-yrs 100 new cases
risk: 100/5000 =0.02
cumulative incidence: 2/100 over five years (0.2×100=2)
how to calculate person-incidence rate and why would you need to?
number of new cases/person-time
cohort w unequal follow-ups, people enter and drop at various time points
what does person-time account for?
time at risk
persons at risk
what is person-time?
a measure that represents the total time that participants are at risk of developing a health outcome during a study. It is calculated by summing the time each individual contributed to the study while they were still eligible to experience the outcome
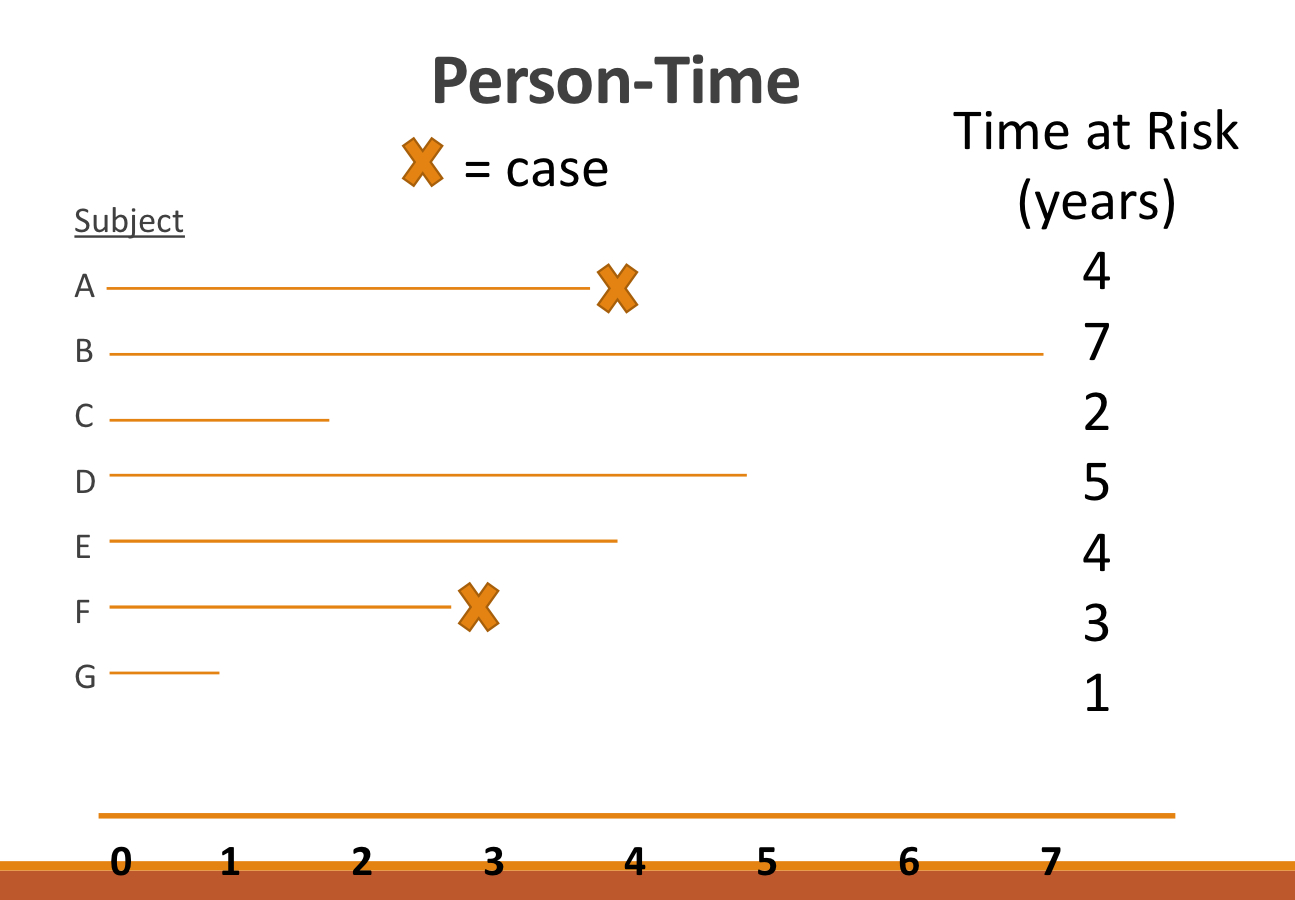
calcualte person-time
4+7+2+5+4+3+1= 26
2 cases
2/26=0.077 or 7.7 cases per 100 person-years
what are the three time units incidence rate can be interpreted by?
person-days
person-months
person-years
definition: proportion of a defined population that has disease at a specific point in time or during a specified time period
prevalence
which term
disease status rather than occurrence
reflects incidence and survival of the disease
prevalence
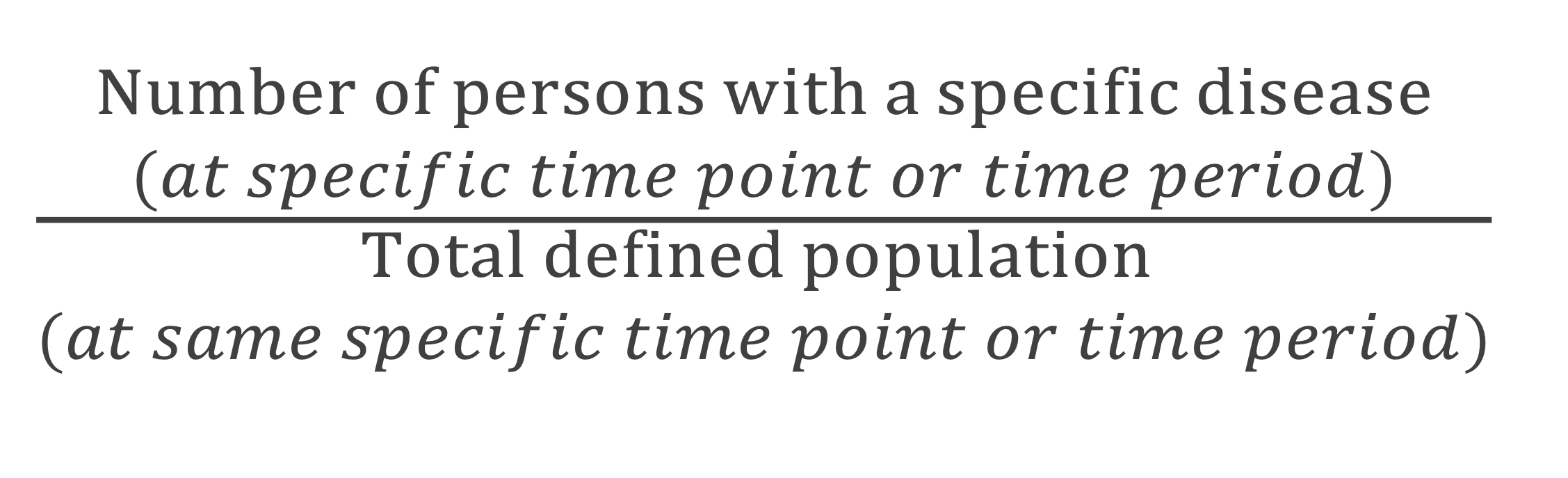
which term?
prevalence
calculate prevalence: 44,000 pts over five yra. 1100 had clicking or crepitus. what is the prevalence rate of clicking/crepitus in this group?
(1100/44000) = 0.025 ×100 = 2.5 cases per 100
what are the two options for resolution?
recovery or death
what is the relationship btwn prevalence and incidence of chronic diseases?
low incidence and long duration
high prevalence
ex: diabetes, HIV, Crohn’s
what is the relationship btwn prevalence and incidence of acute diseases?
high incidence, short duration
low prevalence
ex: common cold
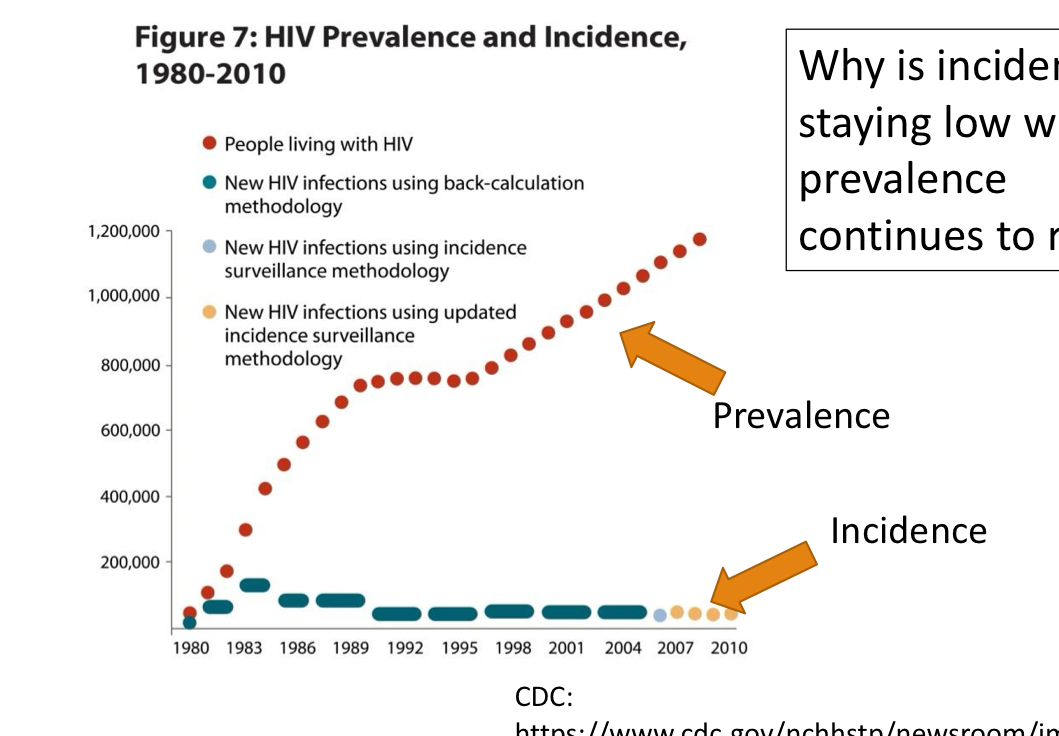
why would incidence stay low but prevalence continues to rise for a chronic disease like HIV?
new drugs (1996)
better prognosis
life expectancy increased significantly
general things to report w frequency measure:
who
what
where
when
who: describe your population
what: condition of interest
where (location)
when (time frame)
definition: an exposure that is statistically related in someway to an outcome
risk factor
Definition: an environmental, behavioral, or biological factor confirmed by temporal sequence usually in a longitudinal studies which if present directly increases the probability of a disease occurring and if absent or remove reduces the probability
risk factor
T or F: risk factors are part of the causal chain or expose host to causal chain
true
T or F: once disease occurs removal of a risk factor results in a cure
false
which type of studies are necessary to demonstarte risk factors?
prospective
definition: an exposure which is associated with an outcome only in cross-sectional data
risk indicator
can a risk indicator be a probable risk factor?
yes but caution is needed bc cross-sectional relationships can be deceptive
risk factor implies…
causality, so apply only when time sequence s established by prospective studies
when to use risk indicator?
wen you need to impute risk from cross-sectional data