RSPT 2217 Specialties Final exam review
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
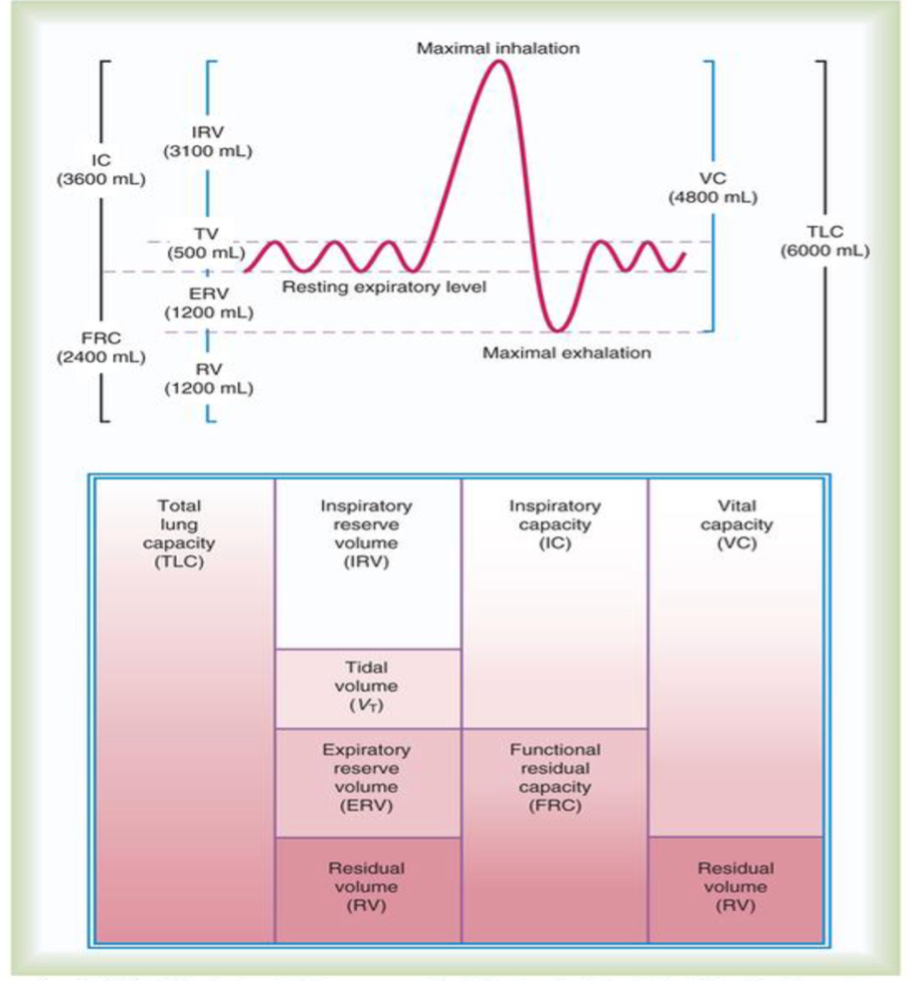
Lung volumes, know them all!
IRV = 3100
VT = 500
ERV = 1200
RV = 1200
IC = 3600
FRC = 2400
FVC = 4800
TLC = 6000
Define FVC
the maximum volume of gas that the subject can exhale as forcefully and as quickly as possible
An FEV1 percentage less than ______indicates obstructive disease.
70%
What are the indications for pulmonary function testing?
-to identify and quantify changes in pulmonary function
-to evaluate need and quantify therapeutic effectiveness
-to perform epidemiologic surveillance for pulmonary disease
-to assess patients for risk of postoperative complications (paralyzed diaphragm)
-to determine pulmonary disability
contraindications for pulmonary function testing?
-patients with acute, unstable cardiopulmonary problems
-patient who have nausea and who are vomiting
(aspiration)
-testing for patients who have had recent cataract removal surgery should be delayed
-patients with dementia or confusion may not achieve optimal or repeatable results
(cannot follow directions)
-in patients who are acutely ill or who have recently smoked a cigarette
Calculate FEV1/FVC%
dividing largest FEV1 by largest FVC
Calculate RV/TLC%
calculating by dividing the larger RV by TLC
Pulmonary Function Testing patient preparation importance
FVC is an effort-dependent maneuver requiring careful patient instruction and cooperation
-to ensure validity, each patient must perform at least 3 acceptable FVC maneuver
Pulmonary Function Testing patient preparation on how long to hold medications.
-refrain from smoking and exercising 6 hours before
-no supplemental O2 for 10min before testing
-avoid alcohol and caffeine 4 hours before
-refrain from SABA and cromolyn sodium for 8 hours
-should hole ipratropium medication and leukotriene modifiers for 24 hours
-LABA and nedocromil medications 48 hours before
-Hydroxyzine medications should be held 3 days/72 hours
What should the PFT Technician do if the test preparation instructions are not followed?
Do not perform the test
How do you ensure test validity?
Make sure we measure what is intended to be measured
To ensure validity, each patient must perform
at least three acceptable FVC maneuvers
Identify normal and abnormal values on Spirometry and
Forced vital capacity (FVC)
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)
Other forced expiratory flow measurements
Maximum voluntary ventilation
what the results of Spirometry indicate.
These measurements assess ability of lungs to move large volumes of air quickly through airways
When is a methacholine challenge test considered positive?
if the patient's lung function, specifically the forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), decreases by 20% or more from their baseline measurement after inhaling methacholine.
AND 10% with diluent, then it is a positive test as well
What FEV1% is considered a significant response to bronchodilators?
Significant bronchodilator response is generally defined as an increase of/ or equal to 12% and more than 200mL in either FEV1 or FVC compared with baseline
What are helium dilution used to determine/measure?
Helium dilution is used to measure lung volumes, particularly functional residual capacity (FRC), in patients with respiratory disorders.
What is nitrogen washout used to determine/measure?
It is used to measure functional residual capacity (FRC) and assess for lung volume abnormalities.
What is Plethysmography used to determine/measure?
Plethysmography is used to measure the total lung capacity (TLC) and residual volume (RV) by assessing changes in pressure and volume within the thoracic cavity during breathing.
What is DLCO?
aka diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide
What does DLCO measure?
Diffusion capacity
How does DLCO work?
a pulmonary function test measurement to assess the lungs ability to transfer gas or diffuse from inspired air to the bloodstream. A very small concentration of CO is used because of its high affinity for hemoglobin
Factors decreasing DLCO
Anemia,
Carboxyhemoglobin,
Pulmonary Embolism,
Diffused pulmonary fibrosis,
Pulmonary emphysema.
Factors increasing DLCO
Polycythemia,
Exercise,
Congestive heart failure.
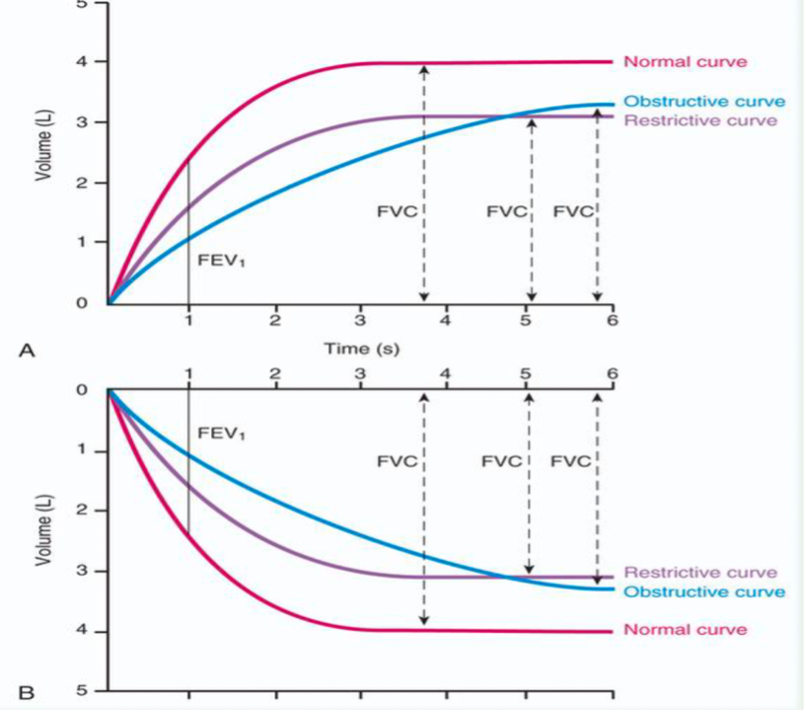
When given a flow volume loop determine what the shape of the loop indicates - restrictive disease
show reduced lung volumes. shorter exhalation time. narrower loop
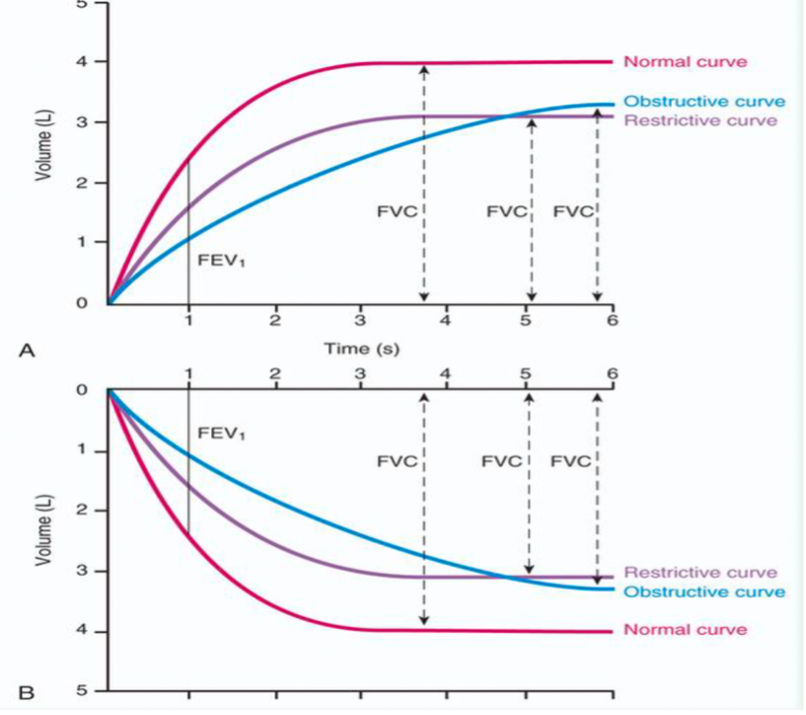
When given a flow volume loop determine what the shape of the loop indicates - Obstructive
causes a concave shape in loop
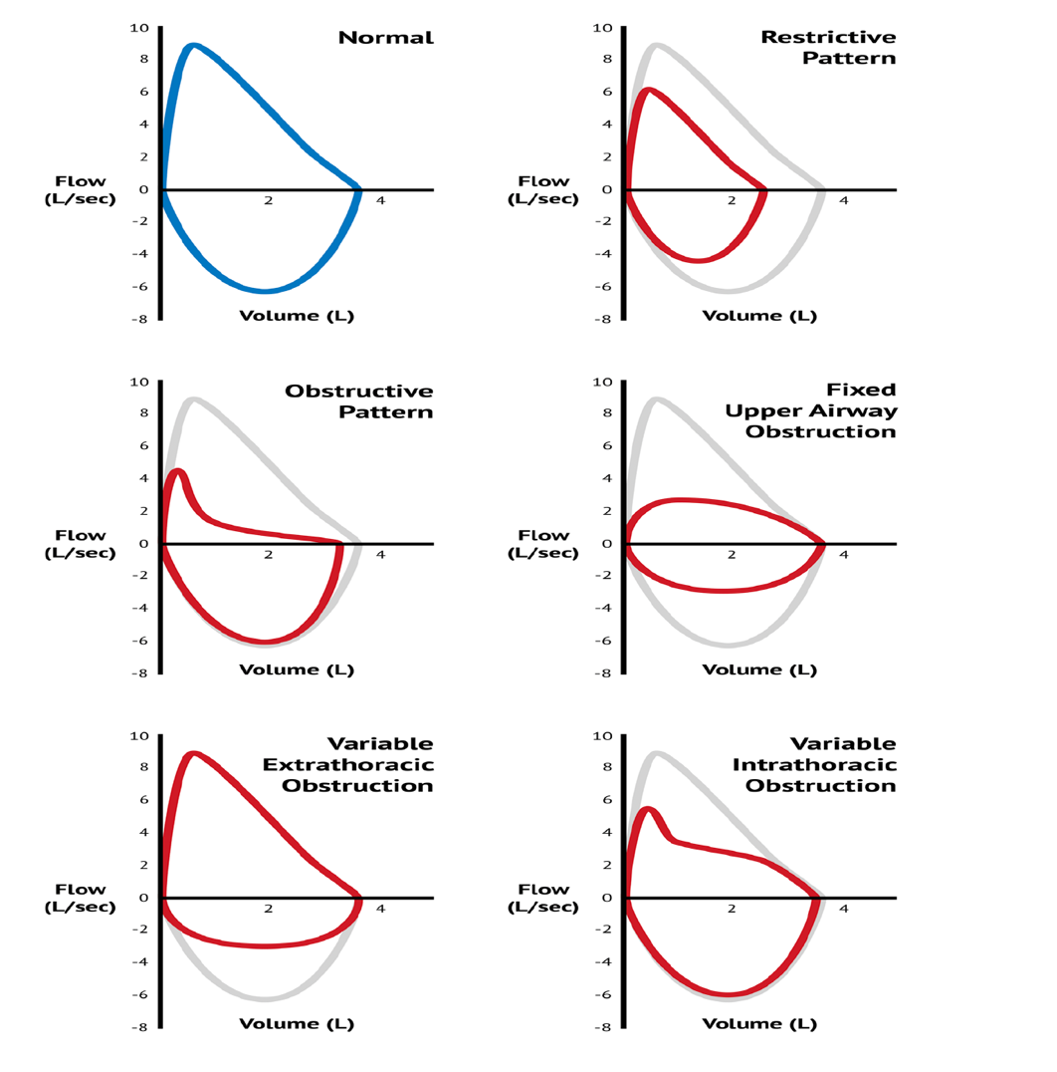
Know the loops
Normal, Restrictive, Obstructive, Fixed, Variable
Flow-Volume Loop Values
PEF, FEF25%, FEF50%, FEF75%, FVC, and PIF; points on the expiratory limb of the loop indicate flow rate at 25%, 50% and 70% of the exhaled FVC.
What must be included in a pulmonary rehab referral?
May take referrals from PA,NP, or MD
But MUST have physician signed orders
Diagnosis/Patient demographics/insurance
Most recent history and physical
Any prior diagnostic testing
**Less than 5% of Medicare patients with COPD have actually been enrolled
What is the criteria for patients to qualify for pulmonary rehab?
COPD
FEV1 less than 80%
FEV1/FVC% less than 70%
Covid-19
No PFT required
Restrictive Lung Disease/other
No PFT required
Common pulmonary rehab obstructive diseases
COPD (including alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency),
persistent asthma,
diffuse bronchiectasis,
and cystic fibrosis.
CBABE
Cystic Fibrosis,
Bronchiectasis,
Asthma,
Bronchitis (chronic),
Emphysema – major obstructive diseases.
Common restrictive disorders in Pulmonary rehab
Interstitial lung diseases,
pulmonary fibrosis,
occupational/environmental lung disease,
sarcoidosis,
connective tissue diseases,
hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
ARDS survivors,
kyphoscoliosis.
An exercise prescription for pulmonary rehab should include?
Mode
Exercise Frequency
Exercise Duration
Exercise Intensity (Note: Intensity targets must be within AACVPR and ACSM published guidelines)
Oxygen saturation and titration
Strength Training
Progression
What is the difference between OSA and CSA?
Effort detected but no airflow, with or without desaturation, defines OSA
Effort detected with minimal airflow, with or without desaturations, defines hypopnea
No effort and no airflow, with or without desaturations, defines CSA
What are the symptoms of OSA?
Snoring,
witnessed apneas,
gasping/choking,
excessive daytime sleepiness,
morning headaches,
nocturnal GERD,
nocturia,
cognitive decline,
erectile dysfunction.
When should the PFT technician discontinue testing?
Patients with:
acute, unstable cardiopulmonary problems
Patients who have nausea and who are vomiting
Testing for patients who have had recent cataract removal surgery should be delayed
Patients with dementia or confusion may not achieve optimal or repeatable results In patients who are acutely ill or who have recently smoked a cigarette, the test validity of measuring the forced vital capacity (FVC) may be hindered
What physiologic variables are measured during polysomnography?
EEG, EOG, chin EMG, ECG,
airflow (nose/mouth),
Ventilatory effort by inductive plethysmography
Oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry (SpO2)
When might the RT recommend PSG for OSA or CSA?
During sleep, upper airway dilator muscles relax, allowing narrowing or closure in one-to-many sites
Waxing and waning of respiratory drive • Noted by increase then decrease in f and VT • Cheyne-Stokes respiration Often occur in CHF or stroke Severe type of periodic breathing Pattern of crescendo-decrescendo with hyperpnea alternating with apnea
Stop Bang Questionnaire will help to determine if the patient needs a study
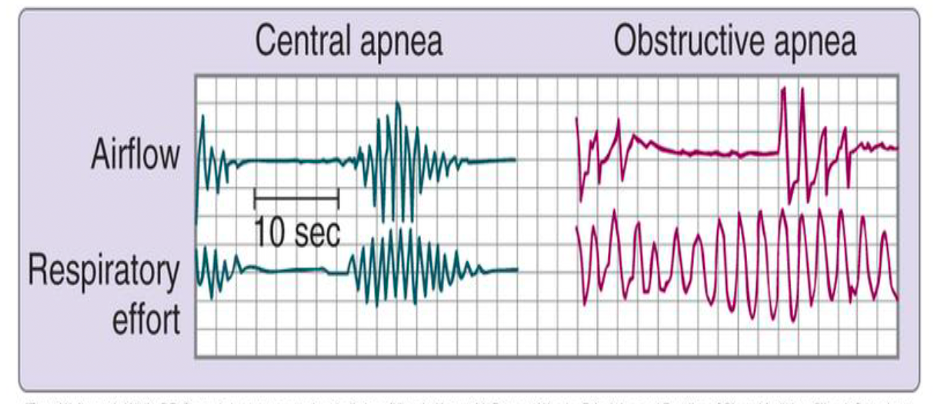
Interpret PSG graph.
OSA on a polysom - effort detected but no airflow, with or without desaturation
CSA on polysom - no effort and no airflow, with or without desaturation
What test uses the principle of Boyles Law to measure TGV?
-plethysmography: most accurate
-volume of pressure increases, and gas will decrease
What PFT results would you expect to see on a patient with COPD?
FEV1 less than 80%
FEV1/FVC less than 70%
FEV1is reduced with both obstructive and restrictive lung disease.
FEV1/FVC - Reduced with obstructive disease
Other measures of expiratory flow are also reduced when obstructive disease is present
What PFT results would you expect to see on a patient with restrictive lung disease?
TLC less than LLN of predicted normal and FEV1/FVC is normal—restrictive disease is present
FEV1/FVC
Normal with restrictive disease
TLC, FRC, and RV decrease with restrictive impairment
TLC is always reduced in restrictive lung diseases because of a loss of lung volume; RV
What disease processes would you see with PFT results for restrictive diseases?
Interstitial lung diseases › Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis › Occupational or environmental lung disease(asbestosis) › Sarcoidosis › Connective tissue diseases (scleroderma, RA, lupus, Sjorgen) › Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (black mold) › ARDS survivors › Kyphoscoliosis
What patients will benefit from apnea monitoring?
OSA, CSA
CPAP titration goal
Eliminate all apneas and minimize hypopneas during PSG.
BiPAP titration guidelines
Recommended minimum of IPAP-EPAP differential = 4 cmH2O
Recommended maximum IPAP-EPAP differential = 10cmH2O
Recommended maximum IPAP = 30cmH2O
Raise IPAP to abolish hypopneas and snoring
Raise EPAP to abolish obstructive events
What is the role/responsibilities of the RCP during transport?
Respiratory Therapists must change their focus to monitoring the status of patients and performing procedures while operating in a changing and often hostile environment
Moving ambulance or aircraft
Utilization of transport equipment
Stabilization and optimization of care in outlying facility
What members make up a transport team?
A registered nurse
A respiratory therapist
An emergency medical technician
A neonatal nurse practitioner and/or
A staff physician, resident, or fellow (if needed)
-- Most pediatric transport teams in the US are led by a nurse and accompanied by an RT
How is the transport team scheduled and staffed?
2 types of teams:
Unit based transport team
Dedicated transport team
Describe Unit based transport team
Staffed and scheduled within ICU’s and are given a patient assignment but “pulled” from that assignment when a transport is called for (most cost-effective)
Describe Dedicated transport teams
Scheduled and staffed separately from the ICU personnel
They generally “float” around the hospital without a patient assignment and are able to leave immediately for a transport (large volume of transports is necessary to justify= Cook Children’s Teddy Bear Transport)
What qualities of a transport team should be exemplified?
Qualities of the team members are as important as the team composition
Exemplary clinical skills
Leadership and decision-making abilities
Flexibility
Compassion and assertiveness
All while working in a HIGH STRESS transport service
What components are needed to safely transport a mechanically ventilated patient?
Mechanical ventilator
Manual resuscitator (Capable of 100% , PEEP valve)
Resuscitation masks
Video guided laryngoscope
Tank key
Pliers
Screwdriver
Airway Pressure manometer
HME,
Intubation equipment
Stethoscope
Suction/catheters
LMA’s
Miscellaneous:
Adhesive tape
Scissors
Replacement batteries
Assorted syringes
What are the 3 modes of transportation for a transport team?
Ground transport
Air transport
Fixed-winged aircraft
Determine the best way to transport a premature baby when given report. What equipment is needed.
Transport Incubator (isollette)
Ability to transport an infant with a body weight of 5 kg or less in a neutro-thermal environment
Manual resuscitator (Capable of 100% , PEEP valve)
Resuscitation masks
Video guided laryngoscope
replacement batteries
Tank key
Pliers
Screwdriver
Airway Pressure manometer
HME,
Intubation equipment
Stethoscope
Suction/catheters
You are called for an Emergent NICU transport on a premature infant requiring surfactant and mechanical ventilation. What information should be provided to the referring facility during report prior to the transport team departing.
-Name
-Weight
-General description of the patient’s condition
-Relevant past medical history
-Current vital signs including oxygen saturation
-Major clinical problems currently presenting
Referring hospital also should be given the following information:
• Recommendations for changes in the medical management
• Estimated arrival time of the transport team
• Phone numbers to call in case of changes in patient conditions or questions prior to the arrival of the team
How does increased altitude affect tidal volumes and oxygen diffusion?
- Increased altitude, increases tidal volume during ventilation. Because the atmospheric pressure decreases,
- barometric pressure decreases – less partial pressure of oxygen is available in the alveoli
There will be less diffusion of oxygen and more of an opportunity for hypoxemia
What risks are associated with flexible bronchoscopy?
Arrhythmias
Fluctuations in blood pressure related to the procedure
coughing
vomiting,
bleeding,
laryngospasm
bronchospasm
Refractory hypoxemia
What should be continuously monitored during a bronchoscopy?
Cardiac monitoring (heart rate)
Blood pressure
Oximetry
Keep track of the patients responses to verbal command or spontaneous movements
Chest movement may continue despite near total obstruction of the airway
Capnography is highly recommended
Indications for self-expanding metallic stent placement.
Extrinsic compression of central airways
Stabilizing airway patency after endoscopic removal of an intrinsic tumor
Sealing fistula between the lung and the gastrointestinal tract
What causes hypoxemia during a flexible bronchoscopy?
Airway manipulation
The volume of fluid administered the number of segments lavaged, duration of the procedure
Indications for oxygen outside the acute care hospital.
Patients on room air while at rest and awake when tested
Arterial oxygen saturation at or below 88%
or
Arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) at or below 55 mm Hg
Patients on room air at rest while awake when tested but who have a confirmed diagnosis of congestive HF, pulmonary hypertension, or erythrocythemia with a hematocrit greater than 56%
Arterial oxygen saturation of 89% (or less) at rest (awake)
or
Arterial PO2 of 56 to 59 mm Hg or less
What are the benefits of respiratory home care?
- Supporting and maintaining life
- Improving patients’ physical, emotional, and social well-being
- Promoting the self-sufficiency of both patient and family
- Ensuring cost-effective delivery of care
- Maximizing patient comfort near the end of life
Recommend appropriate portable system depending on patient need.
- Nasal cannula is most common O2 delivery system for long-term care
- Transtracheal O2 therapy used in selected patients; it conserves the use of O2 and has cosmetic advantages
- Demand-flow O2 systems