L63b: disfunction of the salivary gland
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
MCQ: what is the medical terminology for protrusion of the eyeball?
proptosis
exophathalmos
buphthalmos
ptyalism
excessive secretion of saliva
what is another name for ptyalism?
hypersialosis
what are the causes of ptyalism?
stomatitis
encephalitis
heavy metal poisoining
what nerves are overstimulated during encephalitis leading to hypersialosis?
CN 7 and CN9
what are the portals of entry/pathways of spread for disorders of the salivary gland?
hematogenous
direct penetration from foreign objects
obstruction of excretory ducts
bite wounds
what is in saliva that acts as a defense mechanism?
iodine
mucus
antibacterial compounds (secretory IgA)
EGF (epidermal growth factors)
antimicrobial enzymes (lysozyme)
what are the categories that common disorders related to the salivary glands fall under?
inflammatory
degenerative
obstructive
neoplastic
MCQ: what characterizes a ranula?
lined by epithelium
what can attempted incomplete regeneration of the gland from ductal epithelium be mistaken for?
neoplasia
what species do we see salivary gland infarction in?
dogs and cats
salivary gland infarction
necrosis due to ischemia from blocked blood vessels
what is the etiology of neoplasia of salivary glands?
idiopathic
what is the gross appearance of neoplasia of salivary glands?
firmness and swelling
what is the microscopic appearance of neoplasia of the salivary glands?
discrete foci of parenchymal necrosis with peripheral hemorrhage and inflammatory cells
what is neoplasia of the salivary glands composed of?
glandular or ductular elements
combination of epithelial and mesenchymal components
sialoliths
sloughed cells or inflammatory exudate forms a nidus for mineralization; degenerative/obstructive disorder
what are sialoliths are secondary to?
sialoadenitis
what is the sequelae of sialoliths?
ranula formation
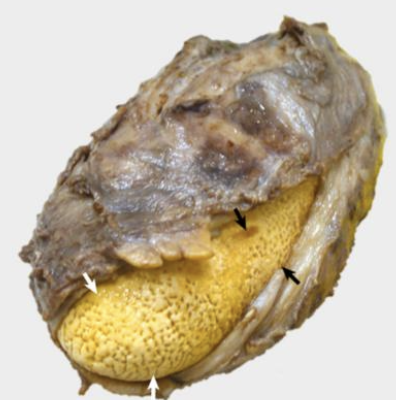
what is the image showing?
sialoliths
salivary mucocele
degenerative/obstructive disorder in which pseudocysts are not lined by epithelium but filled with saliva
what are the causes of salivary mucocele?
idiopathic
traumatic rupture of the duct of a sublingual salivary gland
what happens when there is traumatic rupture of the duct of a sublingual salivary gland?
leakage and filling of saliva by reactive connective tissue leading to salivary mucocele

what is this image showing?
raunula
ranula
Cystic saliva-filled distention of the duct
of the sublingual or submaxillary salivary
gland
what is the cause of ranulas?
idiopathic
sialoliths
MCQ: What gross lesion is associated with inflammatory disorders of salivary glands?
swelling and edema
what will be seen with inflammatory disorders of the salivary glands?
swelling and edema
pain of palpitation
abcesses
what happens if there is an abscess in the retrotubular zygomatic gland?
proptosis due to increased pressure from abcess
what are abscesses secondary to in inflammatory disorders of the salivary glands?
migration of foreign bodies
what are the inflammatory disorders of the salivary glands?
sialodenitis
sialodacryodenitis
suppurative parotid sialodenitis
which species do we see suppurative parotid sialodenitis?
pigs
what bacteria causes suppurative parotid sialodenitis?
salmonella typhisuis
how is saliva spread to cause sialodentitis?
spread by bite wounds
while rare in vet med, when do we see sialoadentis?
rabies
canine distemper
what features will be seen in sialoadenitis?
focal necrosis
mononuclear cell inflammation
negri bodies in nuclei of ganglion cells
negri bodies (ICIB)
inclusion bodies (viral products) that will appear on the cytoplasm
what are some of the results from dysfunctional response to injury in salivary glands?
incomplete regeneration (from ductular epithelium)
atrophy
fibrosis
squamous metaplasia of secretory epithelium
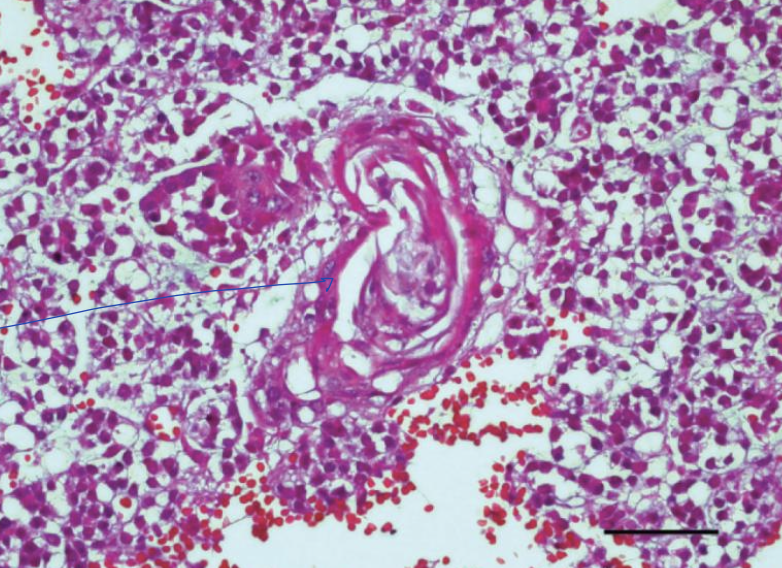
what is the image showing?
squamous metaplasia
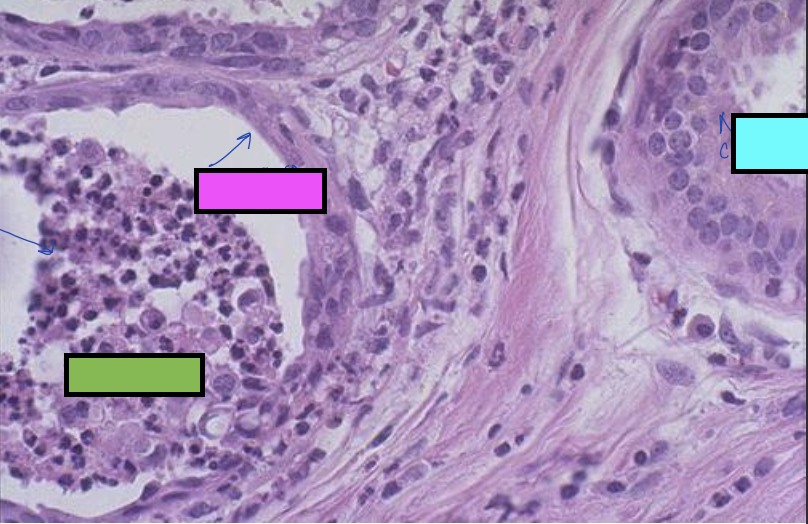
what is the blue box cell showing?
normal cuboidal cell of salivary glands
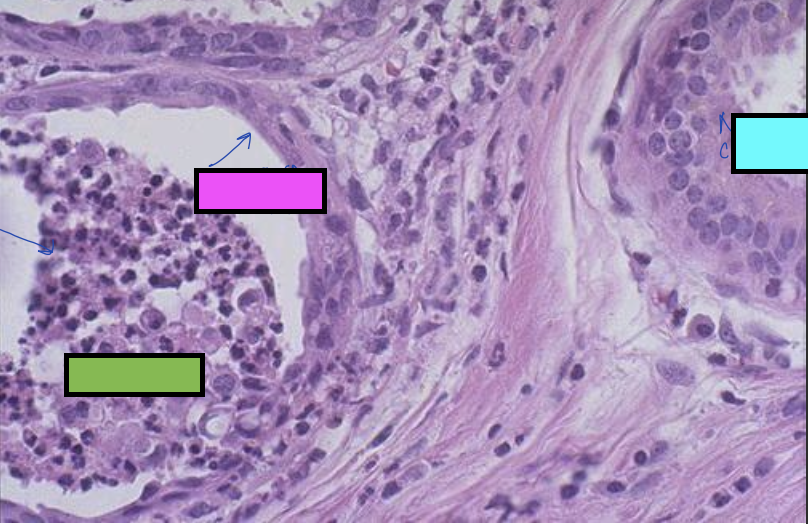
what is the pink box cell showing?
flattened squamous cell from squamous metaplasia
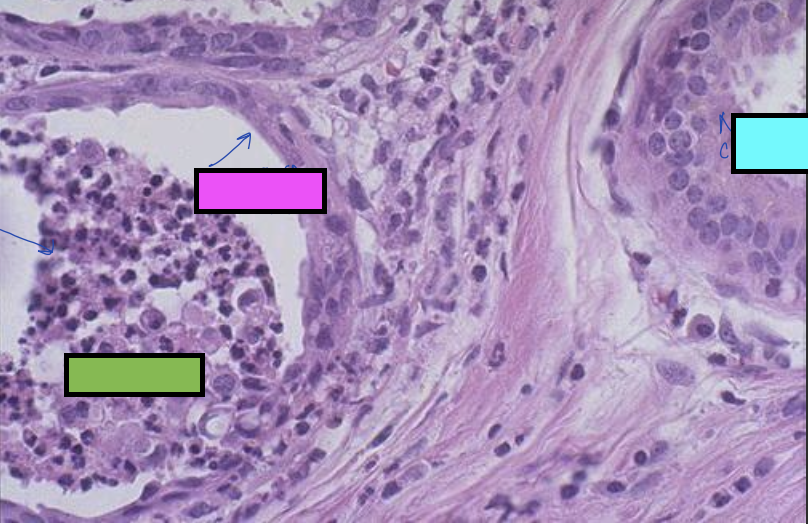
what is the green box cell showing?
blockage of salivary duct
how will atrophy of the salivary glands be seen histologically?
acinar cells collapse and smaller in size
what will squamous metaplasia of secretory epithelium lead to?
blockage of duct = development of saliva-filled cysts