PPT 15: INFANT INTUSSUSCEPTION, FAILURE TO THRIVE DEVELOPMENTAL MILESTONES, DOWN SYNDROME, CLEFT PALATE, IMPERFORATE ANUS,
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
INTUSSUSCEPTION
virus
a segment of intestine invaginates into the adjoining intestinal lumen, causing bowel obstruction.
a secondary to an imbalance in the longitudinal forces along the intestinal wall/disorganized pattern of peristalsis.
Cause: Most cases it is preceded by a __ that produces swelling
In this disorder, once there is a telescoping of the intestinal lumen, once this one’s will cut off the blood supply to the part of the intestine that is affected. In most cases, it is caused by a virus that produces swelling before the development of intussusception.
the lining of the intestine which then slips into the intestinal below will create a swelling and one’s there is swelling there is a development of INFECTION.
dance sign
vomiting
abdominal pain
passage of blood mucus per rectum
lethargy
palpable abdominal mass
S/Sx (INTUSSUSCEPTION):
__ (R hypochondrium sausage-shaped mass & emptiness in the R lower quadrant)
__ (bilious - there is a bile, greenish yellow ang color sa vomitus. Occurs when the bile merged along with the gastro contents producing a greenish to yellow discharge)
__ (colicky, severe, & intermittent)
__ (“currant jelly stool”) (early sign: diarrhea)
__ (sole presenting symptom which makes the dx challenging)
__ (palpated during quiet time)
Hydrostatic
Pneumatic; insufflation
Paraumbilical incision
Management & Treatment (INTUSSUSCEPTION):
Therapeutic Enemas:
with barium or water-soluble contrast
with air insufflation
__ is blowing of air into the body’s cavities specifically in the stomach to notice what area is affected
the intussuscepted part is delivered into the wound, & manually reduced
Also called periumbilical incision. Periumbilical is behind or around the belly button.
Adequate nutrition
Priority NCP for INTUSSUSCEPTION
radiology; 60%
UTZ
Contrast enema/ barium enema
air/contrast enema
DX TESTS FOR INTUSSUSCEPTION
__- plain abdominal x-ray reveals signs in only __ of cases
__- pseudo-kidney signs
__ - traditional & most reliable way to make the dx
Anal-ascending-transverse-descending- large intestine-small intestine para ma detect asa ang specific area nga naay intussusception
__ -diagnostic and therapeutic
shows a filling defect in the head of contrast where its advance is obstructed by the intussusceptum
“contrast material between the intussusceptum and the intussuscipiens is responsible for the coil spring appearance”
lethargy
currant jelly stool
mental alertness is depleted
sole presenting symptom which makes the dx challenging
a mixture of mucus, sloughed mucosa, and shed blood
borborygmi
contrast enema/ barium enema
5-30 times; (Gurgling or Borborygmi)
a rumbling or gurgling noise made by the movement of fluid and gas in the intestines
-procedure using an Xray. It is aided with a dye containing BARIUM or IODINE. -Shows the structure of the rectum, colon, and the large intestines.
NORMAL BOWEL SOUNDS: range:__; terms:__
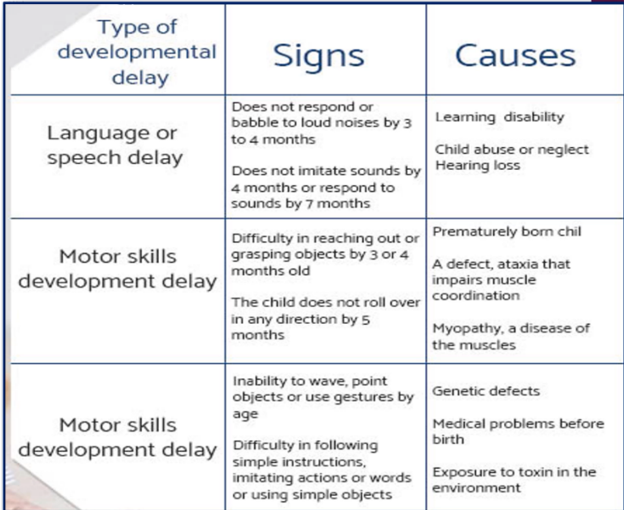
Failure To Thrive (FTT)
early childhood
a condition where a child is undernourished (failed to receive or can’t take in, keep, or use the calories that would help them grow & gain enough weight)
Age affected: __
S/Sx of FTT
lack of wt. gain
learning disabilities
developmental milestones delay
lack of emotions
delayed motor development
fatigue/ irritability/excessive sleepiness
lack of age-appropriate social response (i.e.,smile)
Use of Growth Charts
CBC
U/A; 1.005-1.030
Dx Tests for FTT:
(Babies who doesn’t gain weight for 3 months in a row – suspicious)
__ wt., length, head circumference
__ if high and WBC & RBC it indicates possible infection
__ (common is the specific gravity __) it will measure the ratio of the urine compared with the water density and the kidneys ability to constraint urine.
pediatrician
dietician
social worker
Txt for FTT:
recommends food to take (High caloric food/formula)
will work together with pediatrician
integrate nutritional history (base)
formulate feeding pattern
compute recommended diet prescribed by the pediatrician.
Advocates for the unprivileged people. Specifically in referrals e.g. PHILHEALTH or DSWD
occupational therapists
speech therapists
psychologists/ mental health professional
specialists
Txt for FTT:
to help caregivers & child develop successful feeding behaviors
provides patient needs in the course of the treatment (physically, psychologically, environmental)
give advice to the parents/caregivers. Arrange support for the family members
to address sucking or swallowing prob.
develop individual treatment plan along with the family members and healthcare providers.
make specific treatment plan
language therapists
Develop treatment plan and also administer psychological tests and determining result
like cardiologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist
psychologists
not medical doctors but can focus on psychotherapy (Talk therapy).
psychiatrists
licensed doctors (can prescribe medications and diagnosed illness).
energy rich foods
10-14 days or months
round the clock
high caloric food/formula
monitoring: RTC for __
it means daily
whole milk
banana
eggs
chickens
vegetables
high caloric foods:
(WBECV)
4 months
1y/o
young age
Normal Growth:
Birth weight double by __
Birth wt. triples by __
Maximum brain development at __
Causes of FTT
not enough food offered
child eats too little
metabolic disorder/ ongoing illness common metabolic disorder is Gastroesophageal reflux, diarrhea or s liver disease. Also problems with swallowing, left pallet, autism, cerebral palsy
food intolerance ( body is sensitive to certain foods) lactose intolerance
CNS prob./anemia/GIT problems.
6 months
(dev’tal milestones)
copies sounds
begins to sit without support
likes to play with others (esp parents)
responds to own name
strings vowels together when babbling ("ah, "eh, "oh)
12 months
(dev’tal milestones)
uses simple gestures such as shaking head for "no" or waving "bye bye"
copies gestures
responds to simple spoken requests -say "mama" and "dada" -pulls up to stand
18 months (1 and a half years)
(dev’tal milestones)
play simple pretend (feeding a doll)
points to show others something interesting
knows what ordinary things are for (telephone, brush, spoon)
says several single words -walks alone
2 years
(dev’tal milestones)
-say sentences with 2-4 words
gets excited when with other children
follows simple instructions
kicks a ball
points to things or pictures when they're named
3 years
(dev’tal milestones)
copies adults and friends (running when other kids run)
carries a conversation using 2-3 sentences
climbs well
plays make-believe with dolls, animals and people
shows affection for friends without prompting
4 years
(dev’tal milestones)
hops and stands on one foot for up to 2 seconds
would rather play with other children than alone
tells stories
draws a person with 2 to 4 body parts
plays cooperatively
DOWN SYNDROME/ Trisomy 21
older mother
a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21.
it is associated with physical growth delays, characteristic facial features & mild to moderate delay in Cognitive Ability (Mental Retardation or MR)
Risk Factor: __
S/Sx of DNS
abnormal teeth
slanted eyes/ flat nasal bridge
shortened hands/ poor muscle tone (Hypotonia)
short neck/ small chin
narrow roof of mouth
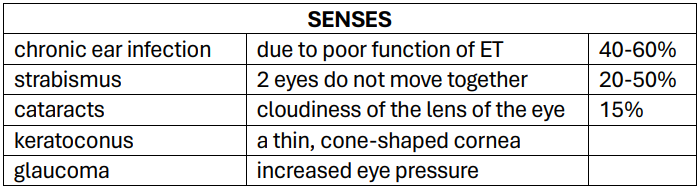
obstructive sleep apnea
bent fifth finger tip
large protruding tongue (due to small mouth)
brushfield spots in the iris
abnormal outer ear
single transverse palmar crease
separation of 1st & 2nd toes (Sandal gap)
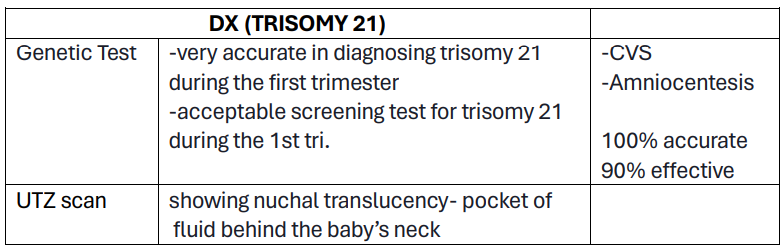
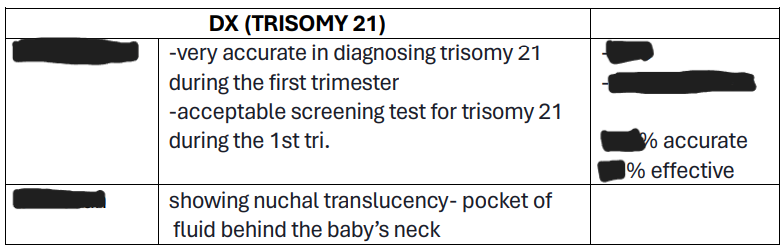
Dx:
Prenatal screening
Genetic Test; 10-13 wks AOG or 1st tri.
UTZ scan
Priority NCP: Safety
Dx for DNS:
P__
__ nearly 100% accurate, One is the chorionic villi sampling or amniocentesis, and should be performed between __ or __.
showing nuchal translucency – pocket of fluid behind the baby’s neck
Priority NCP: __
educational support
sheltered work environment
TXT (TRISOMY 21):
Individualized educational program, it addresses the child's unique needs (home school or school with same cases of classmates)
They have short attention span and short-term auditory memory. Constant guidance shall be provided.
A conducive family environment
Vocational training
Plastic surgery
Cognitive development
Motor development (music therapy)
Management for DNS:
There should be quiet and organized home environment
Child must feel supported, welcomed, and respected.
improve overall development
Supervise (e.g. buttoning and unbuttoning of clothes, self-feeding.)
to reduce facial features
communication skills
language or speech therapists
music therapy
to stimulate people with DS
50 average IQ (young adults)
NEUROLOGIC (DS IQ)
equivalent to the mental ability of an 8 or 9 year old child
Cerebrum
Why there is developmental delay for the DS?
Because of the of the __ — process memory. Brain maturation is affected and once it’s affected, pathophysiologic also affected
50-69 mild disability
NEUROLOGIC (DS IQ)
can be trained and can be independent
a child may encounter difficulty in school, at home, or communities.
if trained, there is a special schooling and eventually they can progress and functional members of the society
35-50 moderate disability
NEUROLOGIC (DS IQ)
also need specialty classes, they can be trained but eventually they cannot progress to become independent
20-35 severe disability
NEUROLOGIC (DS IQ)
dependent but they need support in their entire life
10% -45% stutter or rapid & irregular speech
NEUROLOGIC (DS IQ)
dependent and has an irregular speech, and need guidance 24/7
Short stature
154 cm (5’1”)
142 cm (4’8”)
PHYSICAL APPEARANCE (DNS):
Adults - __
Average height (Men) - __
Average height (Women) - __
5-10%
early adulthood
BEHAVIORAL
Autism - __%
Depression, Anxiety - __
nuchal translucency; 11-13+6 wks of pregnancy
obstructive sleep apnea
Brushfield spots
is the term used to describe sonographic appearance of a collection of fluid under the skin behind the fetal neck at __ weeks of pregnancy
The upper airways are larger, and it happens because of hypotonia and abnormal facial structure.
are small, white, or grayish/brown spots on the periphery of the iris in the eye due to aggregation of connective tissues, a normal constituent of the iris stroma
are a characteristic feature of the chromosomal disorder called trisomy 21
23 pairs (46 in total)
60 yrs old
10-13 wks AOG
chromosome 21; 200-300 genes
eustachian tube
how many chromosomes
average lifespan for DS
CVS & AMNIOCENTESIS PERFORMED in what week
it will be multiplied by three times in DS
it contains __ genes that will provide instructions in making proteins in our body.
they equalizes pressure going into the eardrum.
an opening that connects the middle ear with the nasal-sinus cavity
it helps balance the pressure in the middle ear
cleft lip
contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose (1 side, both sides or in the middle)
cleft palate
the roof of the mouth (hard palate) are not completely joined/opening in the nose
Orofacial Cleft
CLP
other terms for cleft lip & cleft palate
Risk Factors for CLP
smoking during pregnancy
DM
obesity
older mother
UTZ during pregnancy
Dx for CLP
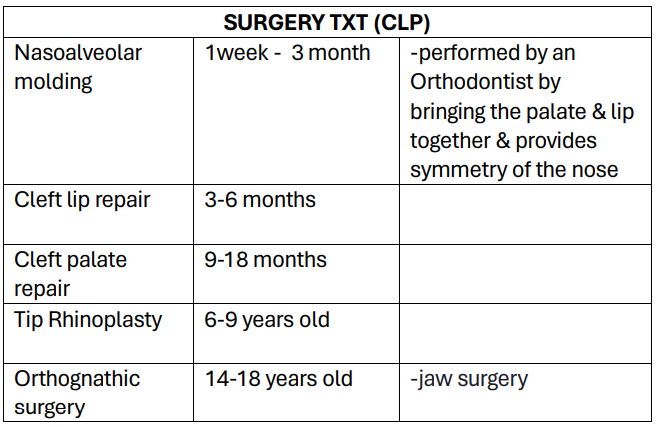
Surgery
Nasoalveolar molding
Cleft lip repair
Cleft palate repair
Tip rhinoplasty
Orthognathic surgery(jaw surgery)
Speech therapy
Dental care
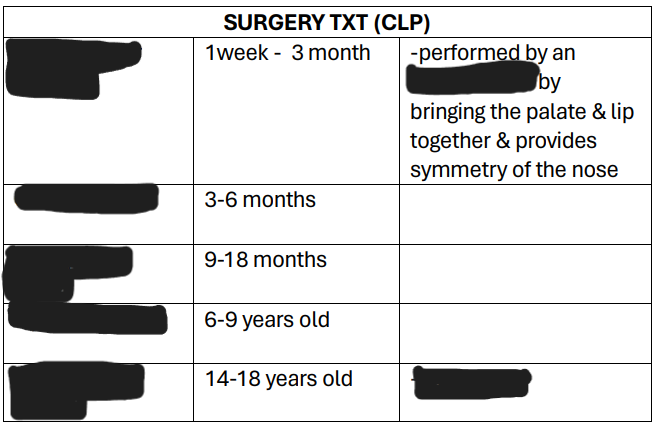
TREATMENT (CLP):
S__
__ (1wk. to 3months of age). Performed by an orthodontist by bringing the palate & lip together & provides symmetry of the nose.* (orthodontist correct the malposition of teeth and jaws and also modifying the facial growth) dentofacial orthopedic is performed if the outer part of the face is affected *
__ (3-6 months of age) regular bootle feeding but make sure the position is upright and burp after
__ (9-18months of age) (upright position, bottle should be tilted, and it should be point down away from the cleft lip or the affected part to prevent nasal regurgitation(natuk an))
__ (6-9y/o) ( correct the lower 1/3 of the nose)
__ (14-18 y/o)
S__
D__
Considerations (cleft palate)
head (well-supported)
upright position (upright)
tilted (bottle)
point down bottle away from the cleft to prevent liquid going into the baby's nose.
Considerations (cleft lip)
upright position (bottle feeding position)
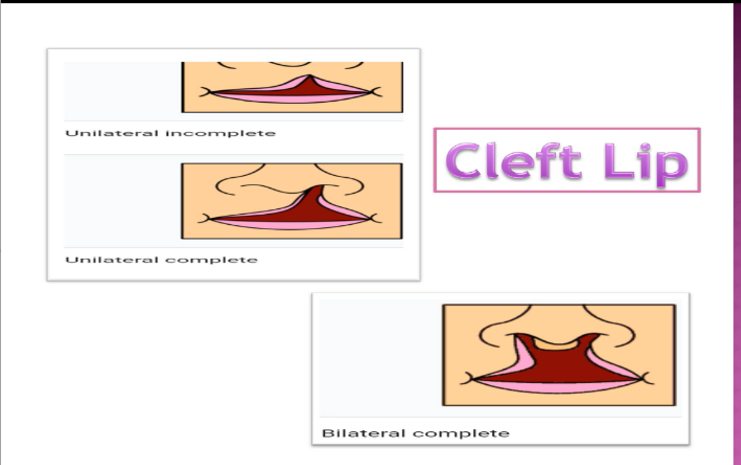
Unilateral incomplete
Unilateral complete
Bilateral complete
types of left clip:
(UUB)
Incomplete cleft palate
Unilateral complete lip and palate
Bilateral complete lip and palate
Types of Cleft Palate:
(IUB)
orthodontist
dentofacial orthopedic
nasal regurgitation
specialized dentist that corrects malposition teeth and jaws; Modifying facial growth
it includes the teeth and facial area.
is when swallowed food or fluid backtracks and enters the nose.
Imperforate Anus/ Anorectal Malformations (ARMS)
1:5000 births
1. Low lesion
2. High lesion
a genetic defect where the muscle of the anus lacks a normal opening or absence of an opening from the rectum
some babies have anus, but it is too narrow to let the feces out
Affected: __:__ births
Classification: __; __
S/Sx of Imperforate Anus
▪ absence of opening in the anus
▪ no passage of fecal material
▪ passing of fecal material in other opening
▪ swollen belly
x-ray
UTZ (Spinal UTZ)
2D echo
MRI
DX TESTS (ARMS)
__detect if there is a bone abnormality
__ detect if there is an abnormality in the vertebral body or the bone of the spine
__to detect if there are cardiac anomalies
__detect evidence of esophageal defects
formation of fistula in cardiac area or respiratory, there are fistula in the trachea or windpipe
rectal thermometer
passage of fecal material
Boys: urethra, Girls: vagina
are used not only to check body temperature but also to check the anal opening.
within a day or two (24-48 hours)
no passage of fecal material within this timeframe, suspected for imperforate anus
Passage of fecal material (other opening): boys: __, girls: __
low lesion
the colon remains close to the skin
presence of Stenosis (narrowing) of the anus or the anus may be missing altogether with the rectum ending in a blind pouch
high lesion
colon is higher up the pelvis
there is a fistula connecting the rectum & the bladder, urethra or the vagina
nasogastric tube
perineal anoplasty
colostomy
posterior sagittal approach (PSARP)
TXT (ARMS)
(First is insert __ to open the drain coming from the __ to decompress the stomach from the retain fecal material)
__ surgical procedure wherein any fistula are closed. Rectum will no longer be connected to the urethra or vagina.
__ within the first 24 hours of birth
temporary just to evacuate fecal material. Performed to create two openings (stoma)
first is to insert Nasogastric Tube to decompress the stomach and retain fecal material.
__most popular
involves dissection of the perineum without entry into the abdomen & 90% of defects in boys can be repaired this way
it enables to construct an anal canal and suture the bowel wall to the striated musculature and the mucosa going to the skin to reduce or avoid complications of STENOSIS so that there is no prolapse happening
stenosis
fistula
stoma
Nutrition and safety
means narrowing
an abnormal connection between two body parts, such as an organ or blood vessel and another structure.
is a small opening in the abdomen that is used to remove body waste (feces and urine) into a collection bag.
Priority NCP for Imperforate Anus