Post Harvest 1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Development of plant
Initiation - Growth - Maturation - Ripening - Senescence - Death
Maturation
A stage in plant development that leads to physiological maturity
Physical Maturation
A stage in plant development of fully mature that continues to develop even it is harvest
Ripening
Process occurring after growth to early stage of senescence resulting in creation of specific characteristics
Senescence
Process after physical maturation leading to death of plant
Plant Growth Stages
Sprout - Seedling - Vegetative - Budding - Flowering - Ripening
Pre harvest
Crucial in agriculture and involve a range of practices and strategies to optimize crop production
Key preharvest activities
Crop selection and planning
Soil preparation
Fertilization
Pest and Disease control
Weed control
Post harvest
Focuses on the handling, storage, processing and transportation of agriculture produce from the time of harvest until it reaches the consumer
Application of scientific and engineering
Importance of post harvest
Preserve qualities
Extension of shelf life
Market access and value addition
Reducing post harvest losses
Food security
Economic benefits
Environmental impact
Post harvest lost
Biggest problem affecting economic growth globally
FAO estimated 1/3rd of loss in the food products occur every year
Factors of post harvest lost
Intrinsic factors
Transpiration
Respiration
Ethylene production
Change of chemical composition
Ripening / senescence
Extrinsic factors
Temp
Humidity
Gases
Light and gravity
Diseases and insect
Supply chain
Sorting - Packaging - Storage - Transport - Marketing - Consumers
Causes of post harvest losses in sorting phase
Bruising
Decay, insects and disorders
Inefficiency
Causes of post harvest losses in packaging phase
Contamination
Leakage
Bruising
Environmental impact
Causes of post harvest losses in storage phase
Heat, extreme cold
Disorders
Off flowers
Overripening
Causes of post harvest losses in transport phase
Overripening
Bruising
Breakage
Causes of post harvest losses in marketing phase
Quality losses
Improper retail conditions
Consumers dissatisfaction
Contamination
Transpiration / water loss
Evaporation of water from plants
Disadvantages of transpiration
Weight loss
Wilting or shriveling - loss appearance
Decline in textural quality
Loss of nutritive value
Stomata
In the underside of the leaf
Convert CO2 to O2
Responsible for transpiration
Lenticel
Pores in the produce responsible for transpiration
Cuticle
Cover the epidermis layers of fruits
Prevent water passing in/out of the crop
Bruises
Bruises caused from physical abuse
Rubbing
Dropping / Falling
Bruises cause a breakdown of tissues around bruised areas
Microorganisms can attack easier
Scars
Plant skin scarred leads to water loss and microorganism can enter
Benefits of transpiration
Some fruits benefit from water loss such mangosteen
Its rough skin leads to several lenticels
Rough skin have higher transpiration rate than smooth skin
Water loss make the sugar and acid more concentrated making it more tasty
Respiration
Aerobic respiration (with O2)
Biochemical process in living cells to convert nutrients to energy
Fruit ripening process in climacteric fruits
High respiration rate
Ripen after harvest
Fruit ripening process in non-climacteric fruits
Stable low respiration rate
Will not ripen after harvest
Climacteric fruits
Ethylene production skyrockets during ripening process
Respiration process slowly goes down during development stage but goes up a bit during ripening
Non-climacteric fruits
Constant ethylene production
Respiration process go down overtime during development, ripening and senescence
Fruit growth
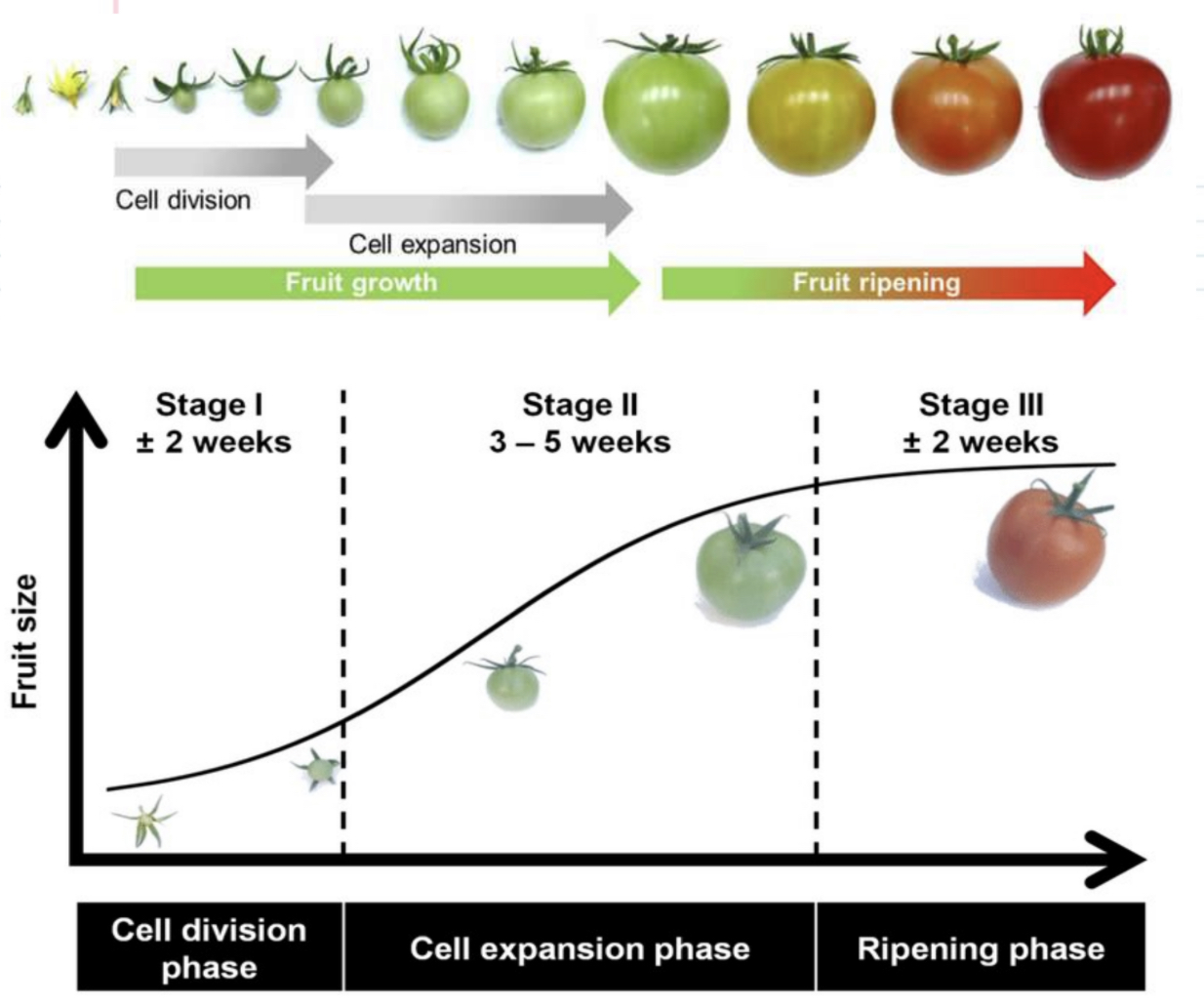
Changes from green to yellow banana
Probiotics
Resistant starch / sugar
Phenolic compounds
Acidity
Taste
Color
Texture
Odor / volatile compounds