Reactivity Series
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
acid with dilute sulfuric or hydrochloric acids
metal + acid = salt + hydrogen
metal displacement reactions?
reacting with a metal oxide by heating
reacting with a metal with an aqueous solution of a metal compound
reactivity series?
Potassium
Sodium
Lithium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminum
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Hydrogen
Copper
Silver
Gold
factors for iron to rust?
oxygen and water
Barrier methods to prevent iron from rusting
paint
oil
grease
electroplating
Sacrificial Protection?
more reactive metal can be attached to a less reactive metal
more reactive metal will corrode first, protecting less reactive metal from corrosion
Zinc is more reactive than iron. E.g. zinc bars on the side of ships
Galvanising
process where the iron to be protected is coated with a layer of zinc
can be done by electroplating or dipping into molten zinc
Oxidation?
a substance gains oxygen
a substance loses electrons
Reduction?
a substance loses oxygen
a substance gains electrons
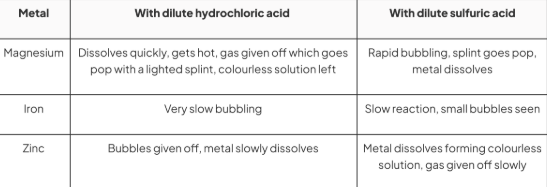
method to investigate metals reacting with acids
. Wear some safety glasses before handling acids
. Using a small measuring cylinder, add 5 cm of dilute hydrochloric acid to each of the three test tubes
. Add about 1 cm length of magnesium ribbon to the first tube, observe and note down what you see
. Use a lighted splint to test any gases given off
. To the second test tube add a few pieces of iron filings and to the third some zinc turnings
. Observe what happens, test for any gases and note down your observations
. Repeat the experiment with dilute sulfuric acid
results for metals with acids