Evolution
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Geographic Isolation
When a population is physically separated; causes new subspecies to be created because new gene pools are created
2
New cards
Speciation
When new species are created from a pre-existing species because of geographic isolation
3
New cards
Animals produce more offspring than can survive and many that survive may not produce offspring; all species have genetic variation; there is competition (Exists within and among species); survival of the fittest; decent with modification
What are the 5 parts of The Theory of Natural Selection
4
New cards
Food, water, shelter, space (FWSS)
What do animals among species(Not of the same species) compete for?
5
New cards
Food, water, shelter, space, mates (FWSSM)
What do animals within species compete for?
6
New cards
Survival of the fittest
Some organisms are more suited to their environment as a result of variations in the species
7
New cards
Fitness
The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment
8
New cards
Decent with modification?
the idea that all animals physical characteristics have been modified from their ancestors
9
New cards
adaptation
an inherited characteristic that increases an organisms chance for survival
10
New cards
Biodiversity
the variation of animals within a species
11
New cards
Evolution
A genetic change in a population over time
12
New cards
Fossil
Remains or traces of an animal that lived long ago
13
New cards
Fossil Remain
A physical part of an organism that lived long ago
14
New cards
Fossil Traces
An imprint left by an organism that lived long ago
15
New cards
Homologous Structure
physical parts of an organism that is similar to other organisms but serves a different function
16
New cards
Vestigial Structures
physical parts of an organism that no longer serve a purpose
17
New cards
If the animal has the same structure as another animal with a similar still functioning structure, then they are related; an organisms evolutionary past
What do vestigial structures show?
18
New cards
A common ancestor
What do similar looking embryos of different species show?
19
New cards
animals are somewhat related; may share a common ancestor
What do similarities in amino acids show?
20
New cards
evolutionary relationships
What does a cladogram show?
21
New cards
Biogeography
geographic distribution of similar living species
22
New cards
Geographically separated species may have a common ancestor
What does biogeography show?
23
New cards
Population
Number of individuals of the same species that live together in one area
24
New cards
Biotic Potential
The size of a population if nothing stopped it
25
New cards
Limiting factors (FWSS)
What controls population growth?
26
New cards
Carrying capacity
The maximum number of organisms that an environment can support
27
New cards
Natural disasters, climate, food, water, shelter, space, population size
What can change carrying capacity?
28
New cards
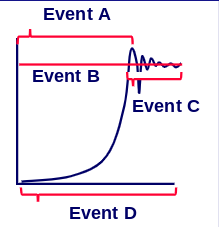
Stage D; there is always genetic variability in a species
In what stage is genetic variation shown on this graph?
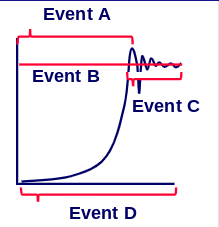
29
New cards
Stage A; potential to increase is at its maximum before carrying capacity is reached
In what stage is the ability to increase the greatest?
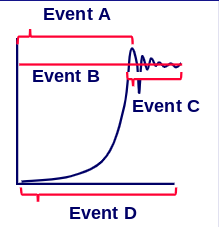
30
New cards
Stage C: Competition is at its height after carrying capacity is reached
In what stage is competition at its greatest?
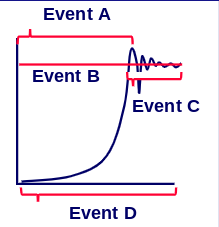
31
New cards
Stage C: When carrying capacity is reached, only the organisms with the best variations survive
In what stage is survival of the fittest at its greatest?
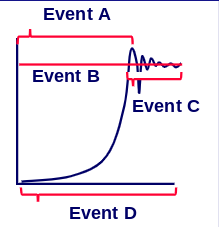
32
New cards
Stage C: The organisms with the best traits survive and reproduce, then pass down their traits to their offspring
In what stage is descent with modification at its greatest?
33
New cards
Variation
What must be present in a population for evolution to occur?
34
New cards
Crossing over and gene mutations
Where does variation come from?
35
New cards
Divergent evolution
One ancestral species causes multiple descendant species to be born
36
New cards
When evolution occurs
When genetic equilibrium is disrupted?
37
New cards
Natural Selection, Migration, Genetic Drift, Isolation, Mutation, and sexual selection
What are the 6 causes of genetic equilibrium being disrupted?
38
New cards
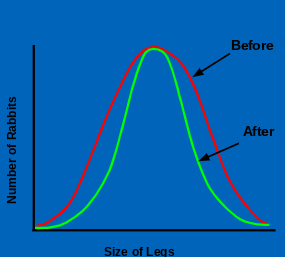
Stabilizing; eliminates extremes of a trait, causing a reduction of variation in a species
What kind of natural selection is this?
39
New cards
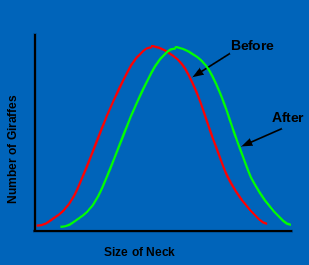
Directional; moves the average of a trait to the left or right
What kind of natural selection is this?
40
New cards
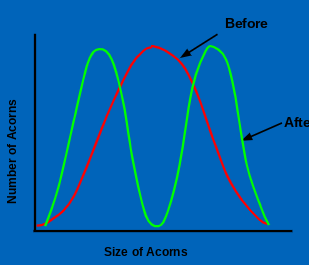
Disruptive; selects against the average and favors the extremes
What kind of natural selection is this?
41
New cards
Gene flow
The movement of alleles from one population to another changes allele frequencies in each area; is caused by immigration and emigration
42
New cards
Isolation
A type of divergent evolution; can be geographic or behavorial; can lead to speciation
43
New cards
Genetic Drift
A chance occurrence that changes allele frequency (Hurricanes and tornadoes)
44
New cards
Sexual Selection
Certain physical traits attract mates, allowing the traits to be passed on
45
New cards
Allele
A sequence of nucleotides; determines physical traits (Ex: AGG)