Signaling at the cell surface and secondary messenger cascades
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
🔹 Modes of Cell Signaling
Q: What is endocrine signaling?
A: Signal (e.g., hormone) is released into the bloodstream and acts on distant target cells (e.g., insulin).
🔹 Modes of Cell Signaling
Q: What is paracrine signaling?
A: Signal acts on nearby cells within the same tissue (e.g., neurotransmitters).
🔹 Modes of Cell Signaling
Q: What is autocrine signaling?
A: Cell releases a signal that acts on itself (common in immune response and cancer).
🔹 Modes of Cell Signaling
Q: What is contact-mediated signaling?
A: Signal requires direct physical contact between cells (e.g., Notch-Delta pathway).
🔹 Hormone Receptor Occupancy
Q: Why does the hormone's effect exceed the receptor occupancy?
Why does the functional effect of hormone binding consistently exceed the bound fraction (occupancy) of the receptor by its cognate hormone?
A: Signal transduction includes amplification steps: binding of a few receptors activates many intracellular molecules (e.g., via second messengers like cAMP or IP₃).
🔹 GPCRs (G Protein-Coupled Receptors)
Q: What was the first structurally characterized GPCR?
A: Rhodopsin, from rod photoreceptor cells.
🔹 GPCRs (G Protein-Coupled Receptors)
Q: Name two important GPCRs in mammals.
A:
β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR) – regulates heart rate and airway relaxation
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor – modulates neural and cardiac function
🔹 GPCRs (G Protein-Coupled Receptors)
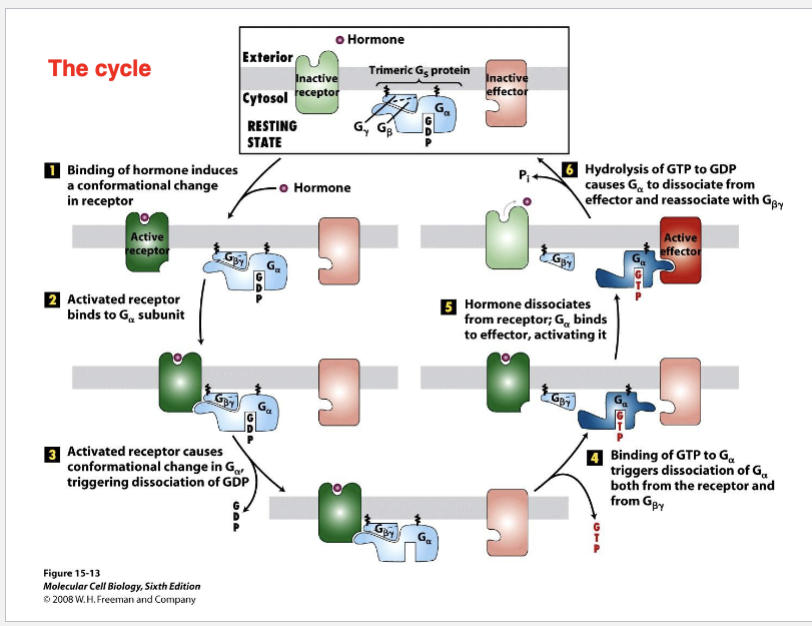
Q: What is the functional cycle of a GPCR?
A:
Ligand binds to GPCR
GPCR undergoes conformational change
Gα exchanges GDP for GTP
Gα and Gβγ dissociate and activate effectors (e.g., adenylyl cyclase)
GTP is hydrolyzed → Gα reassociates with Gβγ → cycle resets
🔹 Gα Subunit Functions
Q: What is the function of GTP and the GTPase activity in Gα subunit?
A:
GTP activates Gα
GTPase activity hydrolyzes GTP to GDP → inactivates Gα
Acts as a built-in timer to limit signaling duration
🔹 Gα Subunit Functions
Q: What is the role of a GEF (Guanine Exchange Factor) in G-protein signaling?
A: GEF (often the GPCR itself) promotes GDP-GTP exchange, activating Gα.
🔹 Gα Subunit Functions
Q: What is the scale of β2AR's conformational change during activation?
A: ~14 Å movement of transmembrane helices rearranges the intracellular face to allow G protein binding.
🔹 Gα Subunit Functions
Q: What role does β2AR play in Gs activation?
A: β2AR activates Gs, a stimulatory G protein that activates adenylyl cyclase, increasing cAMP production.
🔹 Phototransduction
Q: What is the origin of the disc-filled outer segment in rod cells?
A: Derived from specialized plasma membrane infoldings, packed with rhodopsin for light detection.
🔹 Phototransduction
Q: What pigment does rhodopsin contain and how does it respond to light?
A: 11-cis-retinal, which undergoes photo-isomerization to all-trans-retinal, triggering rhodopsin activation.
🔹 Phototransduction
Q: What is the key ion channel in the visual cascade and how is it regulated?
A: Cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channel, regulated by cGMP levels. Light → ↓cGMP → channel closes → hyperpolarization.
🔹 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
Q: What activates RTKs?
A: Ligand binding induces dimerization, activating kinase domains for autophosphorylation.
🔹 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
Q: Name two RTK examples.
A:
EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor)
Insulin receptor
🔹 Notch Signaling
Q: How does the Notch receptor work?
A: Contact-mediated signaling: ligand (Delta) binding triggers proteolytic cleavage of Notch → intracellular domain enters nucleus → regulates gene expression.
🔹 JAK-STAT Pathway
Q: What does the STAT complex do in EPO signaling?
A: Erythropoietin (EPO) binds its receptor → activates JAK kinase → phosphorylates STAT, which dimerizes and enters the nucleus to activate genes for red blood cell production.
🔹 Transcription & Chromatin
Q: What does it mean that a transcription factor “opens” chromatin?
A: It recruits chromatin remodeling complexes or histone acetyltransferases (HATs) to make DNA more accessible for transcription by loosening nucleosomes.